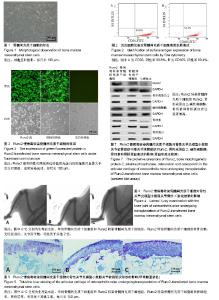
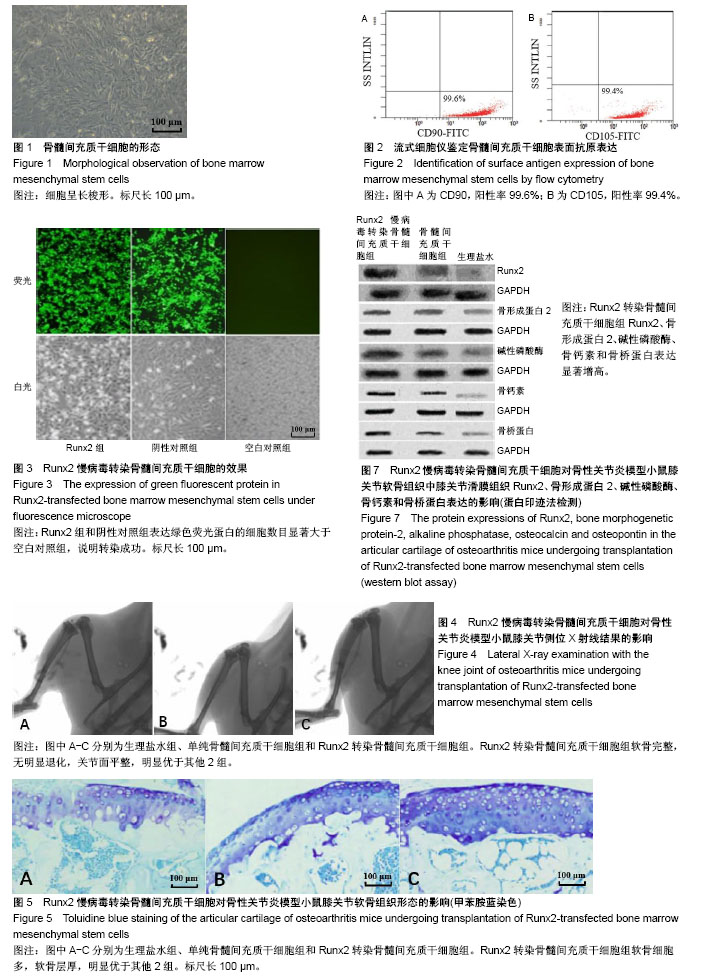
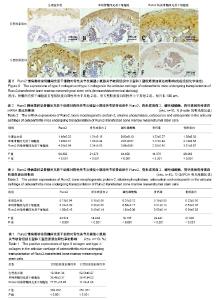
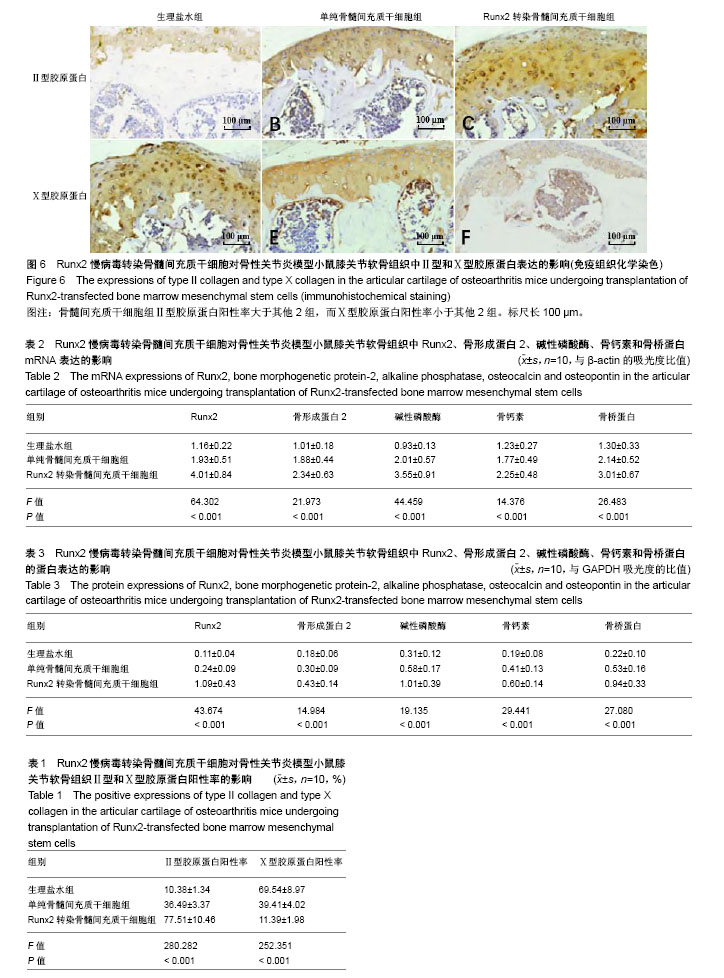
| [1] Allen KD, Golightly YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: state of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(3):276-283. [2] Michael JW, Schlüter-Brust KU, Eysel P. The epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010;107(9):152-162. [3] Lee AS, Ellman MB, Yan D, et al. A current review of molecular mechanisms regarding osteoarthritis and pain. Gene. 2013;527(2):440-447. [4] 赵昌盛,钟群杰,林剑浩.中国膝关节骨关节炎流行病学调查现状[J].广东医学,2016,37(13):2050-2052.[5] 韩祥祯,何惠宇,胡杨,等.人骨形态发生蛋白-2重组慢病毒载体转染羊骨髓间充质干细胞及其成骨调节作用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2014,27(6):540-542.[6] 邬波,马旭,朱大木,等.胰岛素样生长因子1对骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化及基质金属蛋白酶表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(19):3421-3429.[7] 鲁先闯,张志峰,黄健.骨髓间充质干细胞修复软骨缺损的应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(19):3083-3088.[8] 韩操,马宁,李忠义,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞载体复合物修复骨缺损的组织学观察[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(6):891-897.[9] Lee KS, Kim HJ, Li QL, et al. Runx2 is a common target of transforming growth factor beta1 and bone morphogenetic protein 2, and cooperation between Runx2 and Smad5 induces osteoblast-specific gene expression in the pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12. Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 20(23):8783-8792.[10] Vimalraj S, Arumugam B, Miranda PJ, et al. Runx2: Structure, function, and phosphorylation in osteoblast differentiation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;78:202-208. [11] Heijink A, Gomoll AH, Madry H, et al. Biomechanical considerations in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(3): 423-435. [12] 叶铄,甄平,贾小云.膝骨性关节炎临床治疗进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(2):76-80.[13] 赫淑倩,王海斌,孙青,等.兔前交叉韧带切断骨关节炎模型软骨MMP-1 MMP-3及诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达的研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2007,11(5):284-287.[14] 刘强,洪加源,胡维界.膝骨性关节炎治疗进展[J].医学综述, 2015, 21(3):474-476.[15] Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387. [16] 付志杰,张巨峰,王大平,等.携带低氧诱导因子1α慢病毒感染小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞后成骨基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(28):4455-4462.[17] 宋晋刚,许建中,周强,等.不同频率脉冲电磁场诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2005, 27(3):134-137.[18] 廖庆辉,黄震,蔡德鸿.抗坏血酸、β-甘油磷酸钠和地塞米松联合诱导小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(1):88-91.[19] Li YJ, Zhao BL, Lv HZ,et al.Acellular allogeneic nerve grafting combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the repair of long-segment sciatic nerve defects: biomechanics and validation of mathematical models. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(8):1322-1326.[20] Deng P, Torrest A, Pollock K,et al.Clinical trial perspective for adult and juvenile Huntington's disease using genetically-engineered mesenchymal stem cells.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(5):702-705.[21] 张建萍.不同浓度地塞米松在体外定向诱导分化兔骨髓间充质干细胞为成骨细胞的实验研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2012, 21(24):2642-2645.[22] 范金柱,杨柳,罗卓荆,等.雌激素对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2013,6(3):232-239.[23] Hosseini SM, Farahmandnia M, Razi Z,et al.12 hours after cerebral ischemia is the optimal time for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(6):904-908.[24] Zhou YJ,Liu JM,Wei SM,et al.Propofol promotes spinal cord injury repair by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(8):1305-1311.[25] Ducy P, Schinke T, Karsenty G. The osteoblast: a sophisticated fibroblast under central surveillance. Science. 2000;289(5484):1501-1504.[26] Komori T. Runx2, a multifunctional transcription factor in skeletal development. J Cell Biochem. 2002;87(1):1-8.[27] Enomoto H, Furuichi T, Zanma A, et al. Runx2 deficiency in chondrocytes causes adipogenic changes in vitro. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 3):417-425.[28] 韩艳,崔建军,李秀花,等.CD45和CD90鉴定小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞[J].中国药物与临床,2014,14(12):1646-1647.[29] 刘斌钰,李宁毅,樊功为,等.全骨髓贴壁培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外成骨的定向诱导及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(50):10181-10184.[30] 徐晓明,杨慧,王晓萍.慢病毒载体的构建及优化[J].中国临床康复, 2006,10(9):147-149.[31] 褚波,黄雪峰,唐云明.慢病毒载体及其应用进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2008,25(1):224-226. |