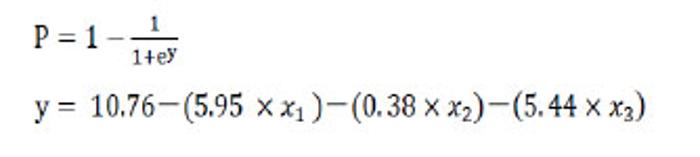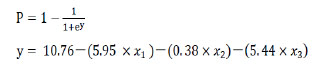Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 3005-3013.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0318
Previous Articles Next Articles
Accuracy of three kinds of pattern recognition models in the diagnosis of nerve root compression in lumbar disc herniation
Li Xiang-rong1, Cheng Lin2, Xi Jia-ning3, Li Wei3
- 1Peking University Hospital, Beijing 100871, China; 2Out-Patient Department of Asian Games Village, Equipment Development Department of Central Military Commission, Beijing 100101, China; 3Beijing Rehabilitation Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing 100144, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Li Wei, M.D., Attending physician, Beijing Rehabilitation Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing 100144, China -
About author:Li Xiang-rong, Associate chief physician, Peking University Hospital, Beijing 100871, China -
Supported by:the Capital Clinical Application Research and Achievement Promotion Project, No. Z161100000516127
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Xiang-rong, Cheng Lin, Xi Jia-ning, Li Wei. Accuracy of three kinds of pattern recognition models in the diagnosis of nerve root compression in lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 3005-3013.
share this article
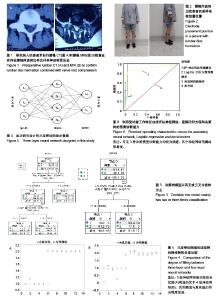
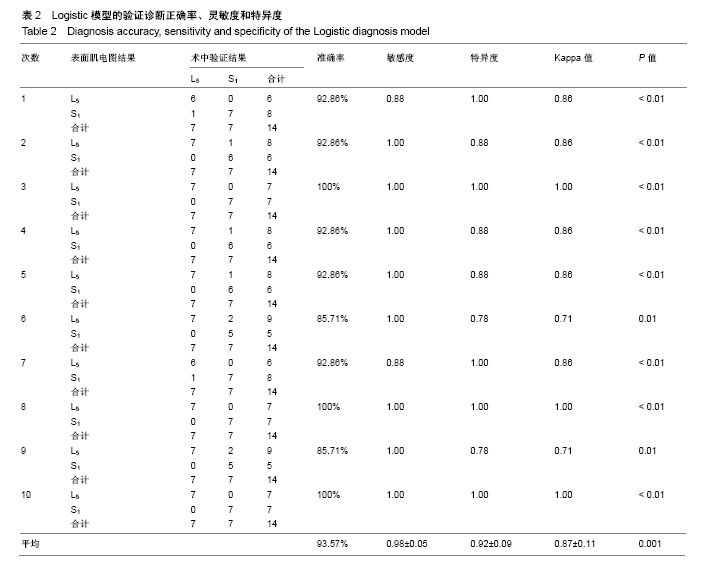
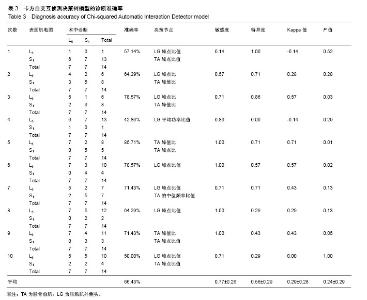
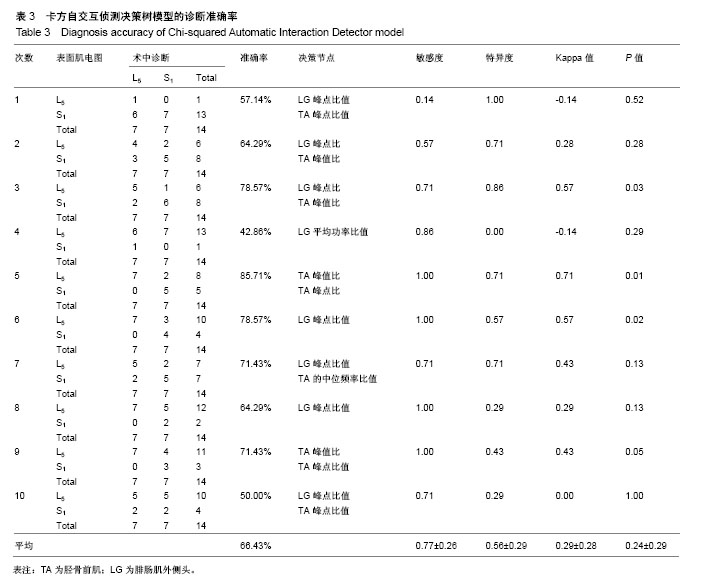
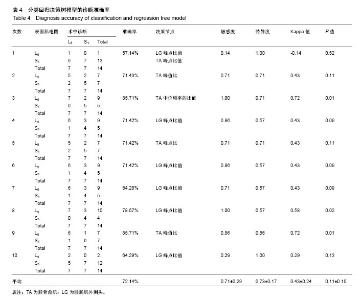
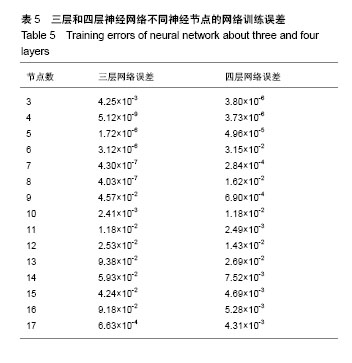
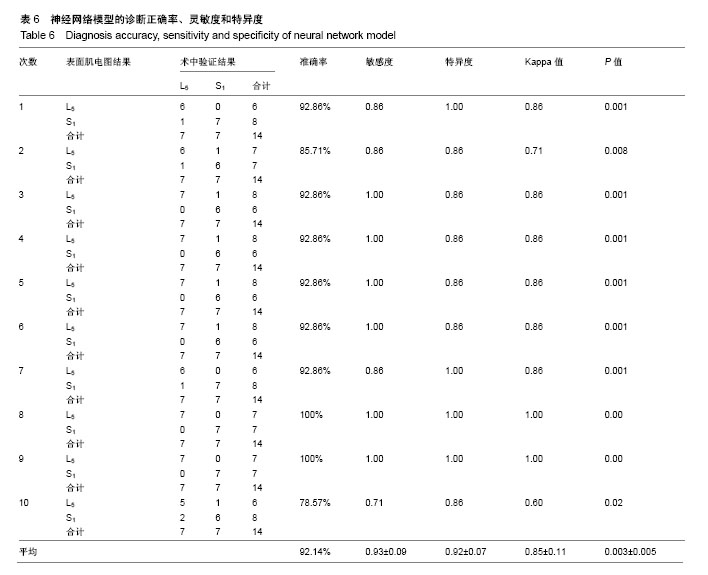
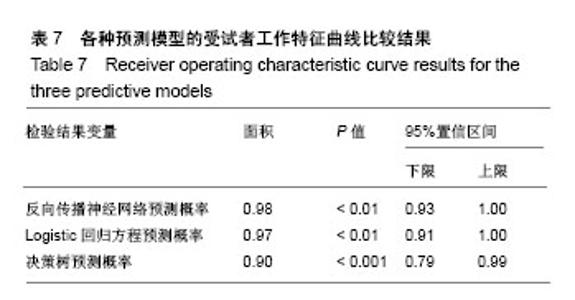
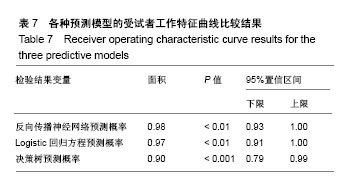
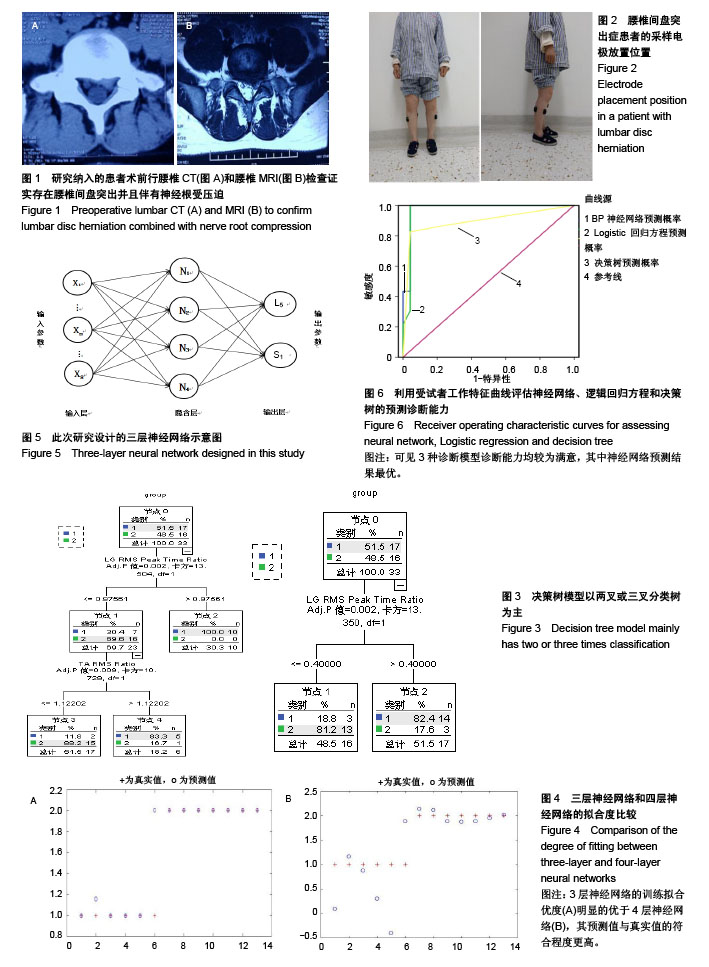
公式中,χ1是胫骨前肌患侧与健侧的均方根峰值的比值;χ2是胫骨前肌患侧与健侧的峰值出现时间的比值;χ2是腓肠肌外侧头患侧与健侧的峰值出现时间的比值。当预测概率值 P < 0.5时,诊断为L5神经根受压;当预测概率值P≥0.5时,诊断为S1神经根受压。 2.2 决策树分类模型 在决策树模型中,分类会在2次分类以内停止,故决策树以二叉和三叉分类居多(图3)。 2.2.1 卡方自交互侦测决策树算法结果 卡方自交互侦测决策树诊断模型的诊断率从42.86%-85.71%,平均为66.43%。该诊断方程的灵敏度和特异度分别为0.77,0.56;Kappa系数无统计学意义(表3)。在建立模型的8个参数中,被选为决策节点最多的是腓肠肌外侧头的峰值出现时间的比值为41.18%,其次是胫骨前肌的峰值出现时间的比值为23.53%,胫骨前肌的均方根峰值的比值为23.53%。 2.2.2 分类回归树算法结果 分类回归树诊断模型的诊断率为57.14%-85.71%,平均为72.14%。该诊断方程的灵敏度和特异度分别为0.71, 0.73;Kappa系数无统计学意义(表4)。在建立模型的8个参数中,被选为决策节点最多的是腓肠肌外侧头的峰值出现时间的比值为54.55%,其次是胫骨前肌的峰值出现时间的比值为18.19%,胫骨前肌均方根峰值的比值为18.19%。 2.3 神经网络诊断模型结果 在此次研究中通过比较3层神经网络和4层神经网络的误差发现3层神经网络,且隐含层神经元节点数为4时,其均方根误差明显的小于其他情况(表5,图4)。故此次研究设定的神经网络为3层,输入参数是8个,输出参数是2个,隐含层1层,隐含层4个神经元节点(图5)。神经网络的诊断率为85.7%-100%,平均为92.14%。该诊断方程的灵敏度、特异度和Kappa系数分别为0.93,0.92和0.85(表6)。 2.4 各种识别模型的比较 在利用受试者工作特征曲线评估神经网络、逻辑回归方程和决策树的预测诊断能力时(图6),结果显示3种决策方法的曲线下面积分别为:神经网络为0.98,逻辑回归方程为0.97,决策树为0.90(表7)。"
| [1] Lee JK, Amorosa L, Cho SK, et al. Recurrent lumbar disk herniation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(6):327-337.[2] Schoenfeld AJ, Laughlin M, Bader JO, et al. Characterization of the incidence and risk factors for the development of lumbar radiculopathy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(3):163-167.[3] 杜金龙. 肌电图在腰椎间盘突出症(L4-5节段)受损神经根定位诊断中的应用[D].宁夏医科大学,2014.[4] Konstantinou K, Dunn KM. Sciatica:review of epidemiological studies and prevalence estimates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(22):2464-2472.[5] Huang YP, Bruijn SM, Lin JH, et al. Gait adaptations in low back pain patients with lumbar disc herniation:trunk coordination and arm swing. Eur Spine J. 2010;20(3):491.[6] Lee JH, An JH, Lee SH, et al. Three-dimensional gait analysis of patients with weakness of ankle dorsiflexor as a result of unilateral L5 radiculopathy. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2010;23(2):49-54.[7] 胡有谷. 腰椎间盘突出症[M]. 4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2011.[8] Kreiner DS, Hwang SW, Easa JE, et al. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Spine J. 2014;14(1):180-191.[9] Al NN, Schneiders AG, Hendrick PA. Neurological examination of the peripheral nervous system to diagnose lumbar spinal disc herniation with suspected radiculopathy:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2013;13(6):657-674.[10] Micankova AB, Vohanka S, Dusek L, et al. Prediction of long-term clinical outcome in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(12):2611-2619.[11] Chawalparit O, Churojana A, Chiewvit P, et al. The limited protocol MRI in diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation. J Med Assoc Thai. 2006;89(2): 182-189.[12] Tawa N, Rhoda A, Diener I. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting lumbo-sacral nerve root compromise:a systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):386.[13] Oikawa Y, Eguchi Y, Inoue G, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of lumbar spinal nerve in subjects with degenerative lumbar disorders. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;33(8):956-961.[14] Kuijper B, Tans JT, van der Kallen BF, et al. Root compression on MRI compared with clinical findings in patients with recent onset cervical radiculopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82(5):561-563.[15] Reinhold M, Ederer C, Henninger B, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of patients with lumbar nerve root entrapment syndromes:results from a pilot study. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(2):319-326.[16] 向为. 生物视觉启发下的特征提取和目标分类方法研究[D].北京交通大学,2009.[17] 黄晓霞,严玉洁,尉敏琦,等. logistic回归、决策树和神经网络在脑卒中高危筛查中的性能比较[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2016,24(6):412-415.[18] Delen D, Walker G, Kadam A. Predicting breast cancer survivability:a comparison of three data mining methods. Artif Intell Med. 2005; 34(2): 113-127.[19] Barr K. Electrodiagnosis of lumbar radiculopathy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2013;24(1):79-91.[20] Wang Y, Nataraj A. Foot drop resulting from degenerative lumbar spinal diseases:clinical characteristics and prognosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014;117:33-39.[21] Boccia G, Dardanello D, Rosso V, et al. The Application of sEMG in Aging:A Mini Review. Gerontology. 2015;61(5):477-484.[22] 李云超,邱虹,陈广,等. 颅内动脉瘤破裂的临床危险因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2012,15(21):2388-2390.[23] 来丹飞,陈雪东. 基于决策树的门脉高压脾切术并发门脉血栓的早期诊断与预测[J]. 湖州师范学院学报,2013,35(6):69-74.[24] 王剑,刘殿武,曹国玉,等. 树模型在慢性乙肝与肝硬化和肝癌临床诊断中的应用[J]. 医学争鸣,2008,29(12):1135-1137.[25] Wickenberg-Bolin U, Göransson H, Fryknäs M, et al. Improved variance estimation of classification performance via reduction of bias caused by small sample size. Bmc Bioinformatics. 2006;7(1):1-8.[26] Mordohai P. Dimensionality Estimation, Manifold Learning and Function Approximation using Tensor Voting. J Mach Learn Res. 2010;11(1):411-450.[27] 陈卉,王晓华. 数据挖掘技术在计算机辅助肺癌诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2007,11(5):879-881.[28] 黄晓霞,严玉洁,尉敏琦,等. Logistic回归、决策树和神经网络在脑卒中高危筛查中的性能比较[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2016,24(6):412-415.[29] 刘绿. Logistic回归模型、神经网络模型和决策树模型在乳腺癌的彩超影像诊断中的比较研究[D].南华大学,2013.[30] Chou HL, Yao CT, Su SL, et al. Gene expression profiling of breast cancer survivability by pooled cDNA microarray analysis using logistic regression, artificial neural networks and decision trees. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013; 14(1):100.[31] Jenhani I, Amor NB, Elouedi Z. Decision trees as possibilistic classifiers. Int J Approx Reason. 2008;48(3):784-807.[32] Amini P, Ahmadinia H, Poorolajal J, et al. Evaluating the high risk groups for suicide:A comparison of Logistic regression, support vector machine, decision tree and artificial neural network. Iran J Public Health. 2016;45(9):1179-1187.[33] Monta ÃO, Moreno JJ, Palmer PA, et al. Artificial neural networks applied to forecasting time series. Psicothema. 2011;23(2):322-329.[34] Delen D, Oztekin A, Tomak L. An analytic approach to better understanding and management of coronary surgeries. Dec Support Syst. 2012;52(3):698-705.[35] Wang J, Li M, Hu YT, et al. Comparison of hospital charge prediction models for gastric cancer patients:neural network vs. decision tree models. Bmc Health Serv Res. 2009;9(1):161.[36] Aguilar C, Westman E, Muehlboeck JS, et al. Different multivariate techniques for automated classification of MRI data in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Psychiatry Res. 2013;212(2): 89-98.[37] Chen H, Zhang J, Xu Y, et al. Performance comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression model for differentiating lung nodules on CT scans. Exp Syst Appl. 2012;39(13):11503-11509.[38] Ayer T, Chhatwal J, Alagoz O,et al. Informatics in radiology:comparison of logistic regression and artificial neural network models in breast cancer risk estimation. Radiographics. 2010;30(1):13-22.[39] Pai DR, Lawrence KD, Klimberg RK, et al. Experimental comparison of parametric, non-parametric, and hybrid multigroup classification. Exp Syst Appl. 2012;39(10):8593-8603. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Yang Qin, Zhou Honghai, Chen Longhao, Zhong Zhong, Xu Yigao, Huang Zhaozhi. Research status and development trend of pelvic reconstruction techniques: a bibliometric and visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3718-3724. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||