Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (13): 2033-2038.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0494
Previous Articles Next Articles
Isolation and identification of human adipose-derived stem cells and its exosomes
Li Hong-chao1, Jin Yin-peng2, Wang Xi1, Li Li2, Wang Xiao-jin2, Zhou Rong2, Chen Cheng-wei2, Fu Qing-chun2, Cheng Ming-liang3
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2the 85th Hospital of PLA, Shanghai Research Center for Hepathopathy, Shanghai 200235, China; 3Department of Infection, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Revised:2018-01-20Online:2018-05-08Published:2018-05-08 -
Contact:Fu Qing-chun, Master, Chief physician, the 85th Hospital of PLA, Shanghai Research Center for Hepathopathy, Shanghai 200235, China; Cheng Ming-liang, Chief physician, Department of Infection, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Hong-chao, Master candidate, School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China. Jin Yin-peng, Master, the 85th Hospital of PLA, Shanghai Research Center for Hepathopathy, Shanghai 200235, China. Li Hong-chao and Jin Yin-peng contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the Medical Innovation Project of the Nanjing Military Region, No. 14ZX01; the Chinese Foundation for Hepatitis Prevention and Control-Sunshine Foundation for Hepatitis, No. TQGB20150104
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Hong-chao, Jin Yin-peng, Wang Xi, Li Li, Wang Xiao-jin, Zhou Rong, Chen Cheng-wei, Fu Qing-chun, Cheng Ming-liang. Isolation and identification of human adipose-derived stem cells and its exosomes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(13): 2033-2038.
share this article
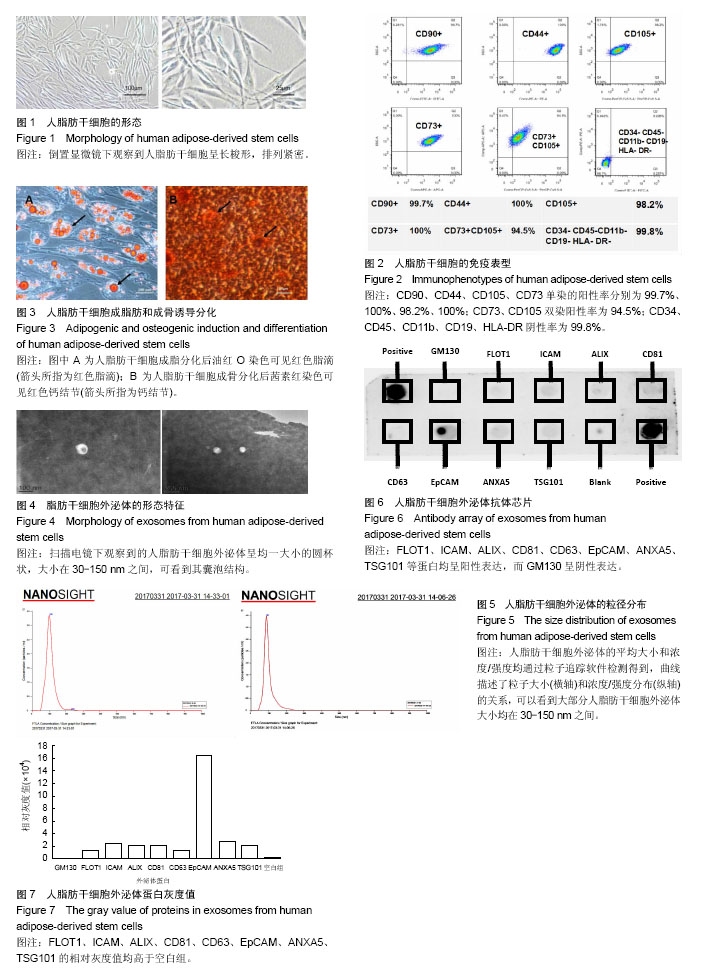
2.1 人脂肪干细胞的形态与流式细胞仪检测结果 第2代以后人脂肪干细胞维持成纤维样形态,大小均一且排列紧密,呈漩涡状或放射状生长(图1)。流式细胞仪检测结果显示,超过90%的细胞阳性表达CD73(100%)、CD44(100%)、CD90(99.7%)、CD105(98.2%),而造血细胞系分子标记物CD34、CD45、CD19等呈阴性表达的细胞占99.8%(图2)。 2.2 人脂肪干细胞的成骨、成脂分化能力 人脂肪干细胞成脂诱导3周后可以在镜下观察到细胞浆内有大量透亮、折光性好的脂滴,油红O染色呈红色(图3A);人脂肪干细胞成骨诱导3周后进行茜素红染色,倒置显微镜下观察可见成骨细胞特征性的红色密集的钙结节(图3B)。 2.3 人脂肪干细胞外泌体的形态特征 利用超滤浓缩离心方法收集得到人脂肪干细胞外泌体,置于扫描电镜下观察可见呈大小均一的圆杯形态,大小在30-150 nm之间,可看到其囊泡结构(图4)。 2.4 人脂肪干细胞外泌体数量和大小分布 利用颗粒粒度分析仪检测到人脂肪干细胞外泌体的大小如图5所示,横坐标代表直径范围,纵坐标代表人脂肪干细胞外泌体的浓度/强度,可以看出大多数外泌体均处于30-150 nm直径范围内。 2.5 抗体芯片检测人脂肪干细胞外泌体蛋白表达 抗体芯片显示人脂肪干细胞外泌体特殊蛋白FLOT1(Flotillin 1)、ICAM1(Intercellular adhesion molecule 1)、ALIX、CD81、CD63、EpCAM(Epithelial cell adhesion molecule)、ANXA5(Annexin A5)、TSG101(Tumor susceptibility gene 101)均为阳性表达,而GM130(cis-Golgi matrix protein)呈阴性表达(图6)。蛋白芯片的灰度值柱形图也显示FLOT1、ICAM、ALIX、CD81、CD63、EpCAM、ANXA5、TSG101的灰度值均高于空白组(图7)。"
| [1] Chen G, Jin Y, Shi X, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell-based treatment for acute liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6: 40.[2] Furuta T, Miyaki S, Ishitobi H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Fracture Healing in a Mouse Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(12):1620-1630.[3] Zhang B, Wang M, Gong A, et al. HucMSC-Exosome Mediated-Wnt4 Signaling Is Required for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells. 2015;33(7):2158-2168.[4] Park HY, Kim EY, Lee SE, et al. Effect of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal-stem-cell bioactive materials on porcine embryo development. Mol Reprod Dev. 2013;80(12): 1035-1047. [5] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[6] Favaro E, Carpanetto A, Caorsi C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells and derived extracellular vesicles induce regulatory dendritic cells in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2016;59(2):325-333.[7] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[8] Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):845-854.[9] Aggarwal S, Moggio A, Bussolati B. Concise review: stem/progenitor cells for renal tissue repair: current knowledge and perspectives. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013; 2(12):1011-1019.[10] Marfia G, Navone SE, Hadi LA, et al. The Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Inhibits Inflammatory Responses of Microglia: Evidence for an Involvement of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signalling. Stem Cells Dev. 2016; 25(14):1095-1107.[11] Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, et al. Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int. 2010;78(9):838-848.[12] Gauthier SA, Pérez-González R, Sharma A, et al. Enhanced exosome secretion in Down syndrome brain - a protective mechanism to alleviate neuronal endosomal abnormalities. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017;5(1):65.[13] Zhou Y, Zhou G, Tian C, et al. Exosome-mediated small RNA delivery for gene therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016; 7(6):758-771.[14] Xu AT, Lu JT, Ran ZH, et al. Exosome in intestinal mucosal immunity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31(10):1694-1699.[15] He M, Zeng Y. Microfluidic Exosome Analysis toward Liquid Biopsy for Cancer. J Lab Autom. 2016;21(4):599-608.[16] Qin Y, Sun R, Wu C, et al. Exosome: A Novel Approach to Stimulate Bone Regeneration through Regulation of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(5): E712.[17] Kilchert C, Wittmann S, Vasiljeva L. The regulation and functions of the nuclear RNA exosome complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(4):227-239.[18] Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N Jr, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63-70.[19] Pan BT, Johnstone RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(3):967-978.[20] Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.[21] Hessvik NP, Llorente A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Jul 21. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2595-9. [Epub ahead of print] [22] Wang Y, Wang Q, Wei X, et al. Global scientific trends on exosome research during 2007-2016: a bibliometric analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(29):48460-48470.[23] Jia Y, Chen Y, Wang Q, et al. Exosome: emerging biomarker in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(25):41717-41733.[24] Fares J, Kashyap R, Zimmermann P. Syntenin: Key player in cancer exosome biogenesis and uptake. Cell Adh Migr. 2017;11(2):124-126.[25] Tomasetti M, Lee W, Santarelli L, et al. Exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer metabolism: possible implications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(1): e285.[26] Koyama Y, Ito T, Hasegawa A, et al. Exosomes derived from tumor cells genetically modified to express Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen: a novel vaccine for cancer therapy. Biotechnol Lett. 2016;38(11):1857-1866.[27] Yu H, Lu K, Zhu J, et al. Stem cell therapy for ischemic heart diseases. Br Med Bull. 2017;121(1):135-154.[28] Suzuki E, Fujita D, Takahashi M, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes as a therapeutic tool for cardiovascular disease. World J Stem Cells. 2016;8(9):297-305.[29] Safari S, Malekvandfard F, Babashah S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: A novel potential therapeutic avenue for cardiac regeneration. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016;62(7):66-73.[30] Santhakumar R, Vidyasekar P, Verma RS. Cardiogel: a nano-matrix scaffold with potential application in cardiac regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e114697.[31] 张鉴清,季佳霖,崔新明,等. 小鼠附睾脂肪干细胞的分离培养及鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(28): 4535-4541.[32] Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):116-125.[33] Huang L, Ma W, Ma Y, et al. Exosomes in mesenchymal stem cells, a new therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2015;11(2):238-245.[34] Li P, Kaslan M, Lee SH, et al. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):789-804.[35] Del Fattore A, Luciano R, Pascucci L, et al. Immunoregulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on T Lymphocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(12): 2615-2627.[36] Zhou Y, Zhou G, Tian C, et al. Exosome-mediated small RNA delivery for gene therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016; 7(6):758-771.[37] Xu AT, Lu JT, Ran ZH, et al. Exosome in intestinal mucosal immunity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31(10):1694-1699.[38] Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, et al. Exosomes from breast cancer cells can convert adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblast-like cells. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(1): 130-138.[39] Vrijsen KR, Maring JA, Chamuleau SA, et al. Exosomes from Cardiomyocyte Progenitor Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulate Angiogenesis Via EMMPRIN. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(19):2555-2565.[40] Guo SC, Tao SC, Yin WJ, et al. Exosomes from Human Synovial-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in the Rat. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(10):1262-1272.[41] Penfornis P, Vallabhaneni KC, Whitt J, et al. Extracellular vesicles as carriers of microRNA, proteins and lipids in tumor microenvironment. Int J Cancer. 2016;138(1):14-21.[42] Azevedo LC, Pedro MA, Laurindo FR. Circulating microparticles as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular diseases. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2007;2(1): 41-51.[43] Song JQ, Liu ML, Liu YX. Microvesicle as a novel mediator of cell-to-cell communication and its roles in cardiovascular diseases. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2010;41(5):376-379.[44] Bruschi M, Ravera S, Santucci L, et al. The human urinary exosome as a potential metabolic effector cargo. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015;12(4):425-432.[45] Zhao W, Zheng XL, Zhao SP. Exosome and its roles in cardiovascular diseases. Heart Fail Rev. 2015;20(3):337-348.[46] Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13-27.[47] Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, et al. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820(7):940-948.[48] Simpson RJ, Jensen SS, Lim JW. Proteomic profiling of exosomes: current perspectives. Proteomics. 2008;8(19): 4083-4099.[49] Kim HS, Choi DY, Yun SJ, et al. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. Proteome Res. 2012;11(2):839-849.[50] Loyer X, Vion AC, Tedgui A, et al. Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 2014;114 (2):345-353. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||