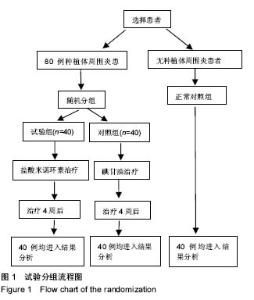
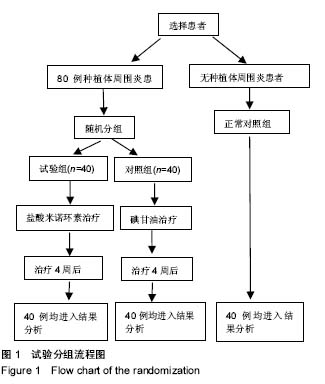
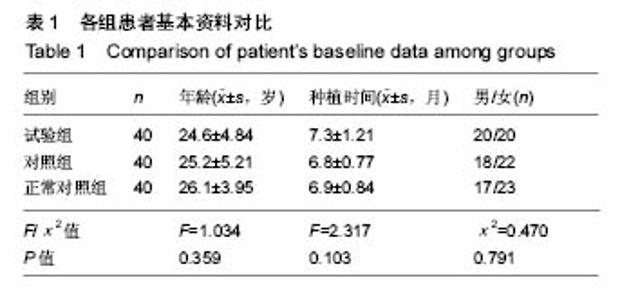
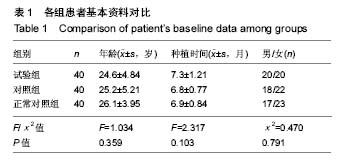
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (6): 852-857.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0058
Previous Articles Next Articles
Minocycline hydrochloride ointment is available for the treatment of peri-implantitis
- Department of Stomatology, Zunyi Municipal Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2017-09-06Online:2018-02-28Published:2018-02-28 -
About author:Liu Ou, Associate chief physician, Department of Stomatology, Zunyi Municipal Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Ou, Gao Zhu, Li Tao, Zhou Bo. Minocycline hydrochloride ointment is available for the treatment of peri-implantitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 852-857.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
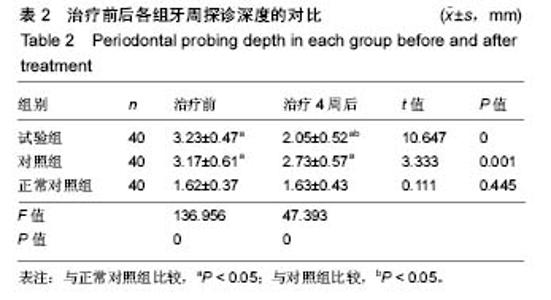
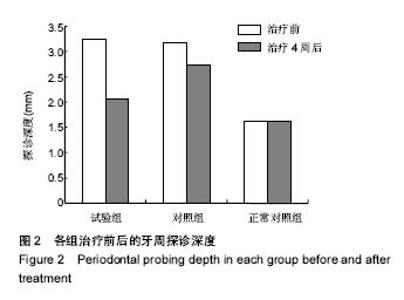
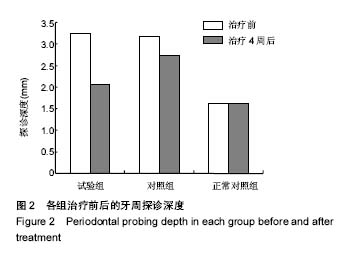
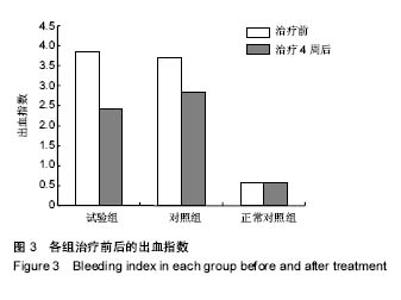
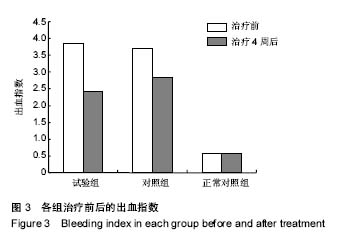
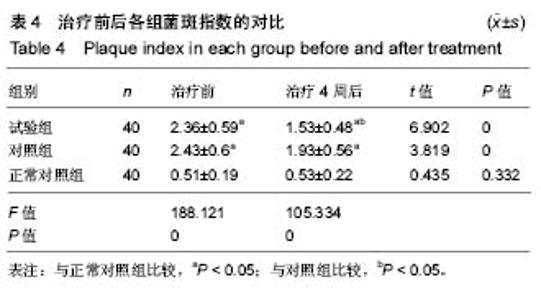
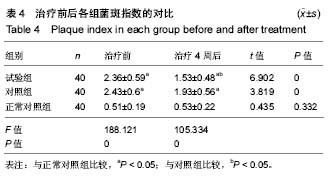
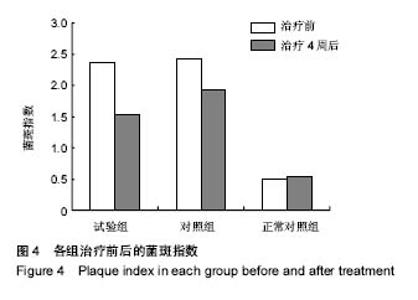
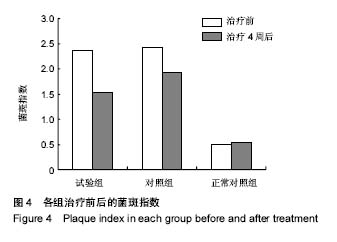
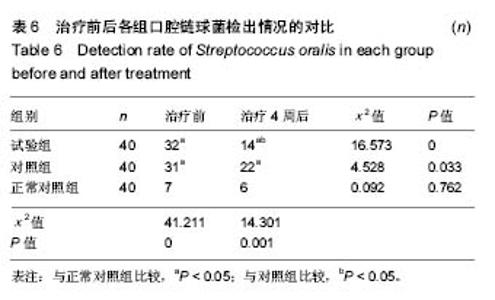
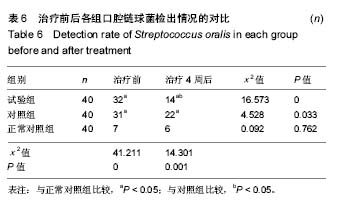
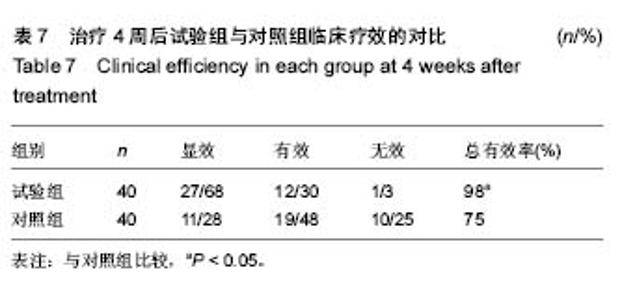
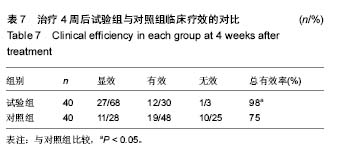
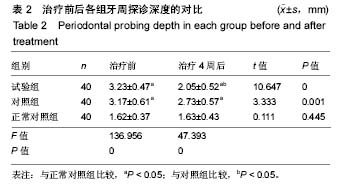
2.4 各组牙周探诊深度的对比 方差分析显示治疗前3组间牙周探诊深度存在显著性差异(P < 0.05);通过独立t 检验显示,正常对照组牙周探诊深度显著低于试验组和对照组(试验组t=17.023,P=0;对照组t=13.740,P=0),试验组和对照组牙周探诊深度无差异(t=0.493,P=0.311)。经过4周的治疗,独立t 检验显示,试验组、对照组牙周探诊深度较治疗前显著降低(P < 0.05),试验组牙周探诊深度低于对照组(t=5.574,P=0),试验组和对照组牙周探诊深度均高于正常对照组(试验组t=3.937,P=0;对照组t=9.744,P=0)。说明试验组和对照组牙周探诊深度相对正常对照组均升高,然经治疗后试验组和对照组探诊深度均有所改善,试验组优于对照组,见表2,图2。"
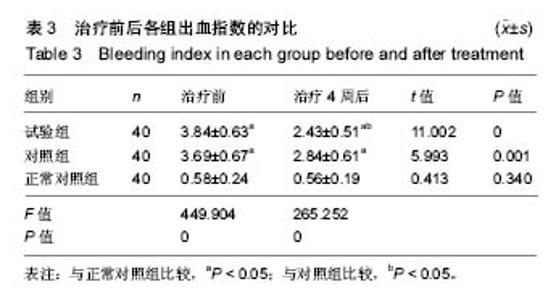
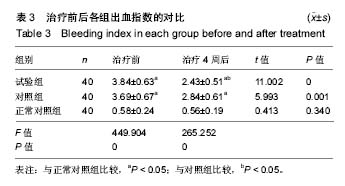
| [1]沈琳,彭国光,夏炜,等.口腔种植修复失败原因探讨[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2014,19(2):84-87.[2]孙志新,张云涛.口腔种植体周围炎与白细胞介素间的关系[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(2):221-224.[3]RoosJansåker AM,Persson GR,Lindahl C,et al.Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using a bone substitute with or without a resorbable membrane: a 5-year follow-up.J Clin Periodontol.2014;41(11):1108-1114.[4]韩月红,成之远,王明德.氧化锆陶瓷与镍铬合金口腔材料的细菌黏附性对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(8):1089-1094.[5]Meng H.Peri-implantitis: risk factors, prevention and treatment.Chin J Stomatol.2014;49(6):328-332.[6]李浪,马锦华,吴亚菲.盐酸米诺环素软膏治疗慢性牙周炎的临床研究[J].现代药物与临床,2015,30(5):531-534.[7]Veitz-Keenan A,Keenan JR.Antibiotic use at dental implant placement.Evid Based Dent.2015;16(2):50-51.[8]Hiraoka R,Sasaki M,Matsushita Y,et al.Mechanical Evaluation of Surrounding Bone with Bone Resorption Model Simulating Peri-Implantitis.Journal of Japanese Society of Oral Implantology. 2014;27:321-330.[9]Arduino PG,Tirone F,Schiorlin E,et al.Single preoperative dose of prophylactic amoxicilin versus a 2-day postoperative course in dental implant surgery:a two-centre randomised controled trial.Eur J Oral Implantol.2015;8(2):143-149.[10]孟田甜,李新.牙龈卟啉单胞菌与病毒的交互作用[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2016,34(4):425-427.[11]王珏,焦艳军,杜晓红,等.牙周炎患者种植修复后可疑致病菌的变化研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志, 2014(6):327-330.[12]熊萍,唐运涛,陈宏刚,等.种植体龈下菌群构成情况分析[J].现代预防医学,2014,41(19):3618-3620.[13]Rams TE,Degener JE,van Winkelhoff AJ.Antibiotic resistance in human peri-implantitis microbiota.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(1):82-90.[14]倪欢胜,王镶珊,韩翔,等.口腔种植体周围菌群分布及耐药性分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2014, 24(3):594-595.[15]Fritoli A,Goncalves C,Faveri M,et al.The effect of systemic antibiotics administered during the active phase of non-surgical periodontal therapy or after the healing phase: a systematic review. J Appl Oral Sci.2015;23(3):249-254. [16]王萃萃.盐酸米诺环素软膏联合甲硝唑药膜治疗牙周病的临床观察[J].北方药学,2015,12(10):63.?[17]陈新,谭新伟,刘洪臣,等.盐酸米诺环素联合替硝唑治疗 2 型糖尿病合并牙周病的临床研究[J].现代药物与临床,2014,29(6): 664-667?.[18]张红艳,胡迎新,崔粲,等.甲硝唑药膜联合盐酸米诺环素软膏治疗牙周病的临床疗效分析[J].现代生物医学进展,2017, 17(4): 746-749.[19]Zhang H,Yang X,Li C,et al.Effects of minocycline-HCl paste root conditioning on periodontal surgery: in vitro and in vivo studies.Int JClin Exp Med.2015;8(3):4080-4086.[20]马晶.盐酸米诺环素软膏治疗牙周炎患者的临床疗效[J].临床药学,2017,12(1):62-64.[21]毛小琴,周光,张樱,等.不同耐药表型鲍氏不动杆菌的蛋白质表达图谱的建立研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2014,24(2):261-263.[22]Chiappe VB,Gómez MV,Rodríguez C,et al.Subgingivally applied minocycline microgranules in subjects with chronic periodontitis: A randomized clinical and microbiological trial.Acta Odontológica Latinoamericana Aol.2015;28(2): 122-131.[23]肖艳,谭小兵,徐静舒.米诺环素辅助治疗侵袭性牙周炎对血清炎性因子的影响[J].重庆医学, 2015,44(9):1208-1210.[24]杜艳,陈正辉,陈瑞春,等.2012年中国云南地区革兰阴性杆菌耐药监测[J].中国抗生素杂志,2014, 39(8):629-634.[25]何艳阳.奥硝唑碘甘油糊剂治疗急性智齿冠周炎对冠周袋内菌群的影响及疗效分析[J].中国微生态学杂志, 2015,27(9): 1041-1043.[26]顾明,廖天安,邢孔才,等.牙周炎患者局部应用盐酸米诺环素软膏与碘甘油的临床效果对比研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2013, 13(29):5761-5764.[27]胡瑶瑶.盐酸米诺环素在种植体周围炎中的应用[J].临床合理用药,2017,3(10):108-109.[28]刘敏,曲进.盐酸米诺环素缓释剂治疗老年牙周炎的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,31(17):3223-3224.[29]徐燕.盐酸米诺环素治疗种植体周围黏膜炎疗效观察[J].中国美容医学,2017,6(26):72-74. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||