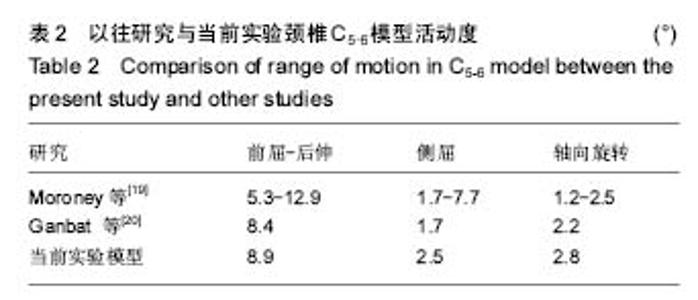
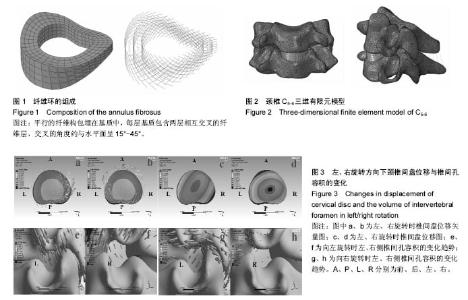
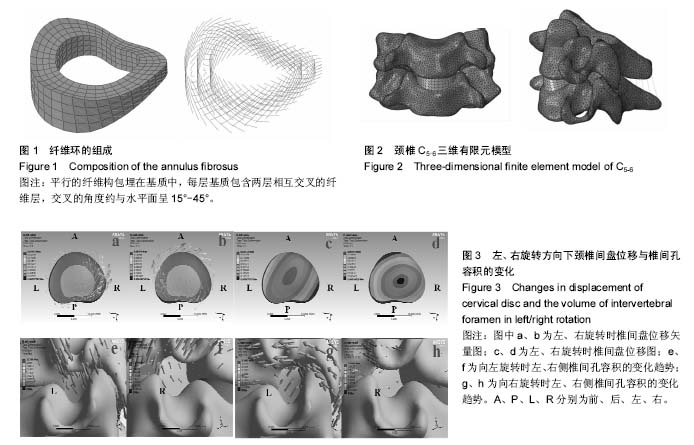
| [1] Ji YY, Jong WK, MD, Young CY, et al. Cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injection for unilateral cervical radiculopathy: comparison of midline and paramedian approaches for efficacy. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16(3): 604-612.[2] Xu W, Wang SQ, Li LH, et al. Clinical evidence of Chinese massage therapy (Tui Na) for cervical radiculopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017; 2017: 9519285.[3] Alentado VJ, Lubelski D, Steinmetz MP, et al. Optimal duration of conservative management prior to surgery for cervical and lumbar radiculopathy: a Literature review. Global Spine J. 2014; 4(4): 279-286.[4] Woods BI, Hilibrand AS. Cervical radiculopathy: epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015; 28(5): e251-259.[5] 王艳国,郭秀琴,张琪,等.手法治疗神经根型颈椎病的系统评价[J].中华中医药杂志,2013,28(2): 499-503.[6] Peterson CK, Pfirrmann CW, Hodler J, et al. Symptomatic, magnetic resonance imaging–confirmed cervical disk herniation patients: a comparative-effectiveness prospective observational study of 2 age- and sex-matched cohorts treated with either imaging-guided indirect cervical nerve root injections or spinal manipulative therapy. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2016; 39(3): 210-217.[7] Peterson CK, Schmid C, Leemann S, et al. Outcomes from magnetic resonance imaging-confirmed symptomatic cervical disk herniation patients treated with high-velocity, low-amplitude spinal manipulative therapy: a prospective cohort study with 3-month follow-up. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2013;36(8): 461-467.[8] Hubka MJ, Phelan SP, Delaney PM, et al. Rotary manipulation for cervical radiculopathy: observations on the importance of the direction of the thrust. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1997;20(9):622-627.[9] 朱巍,贾连顺.神经根型颈椎病根性痛发病机制的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(12): 761-764.[10] Takasaki H, Hall T, Jull G, et al. The influence of cervical traction, compression, and spurling test on cervical intervertebral foramen size. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(16):1658-1662.[11] Abbed KM, Coumans JV. Cervical radiculopathy: pathophysiology, presentation, and clinical evaluation. Neurosurgery. 2007; 60(Supp1): S28-34.[12] Smith AL, Benazzi S, Ledogar JA, et al. Biomechanical implications of intraspecific shape variation in chimpanzee crania: moving towards an integration of geometric morphometrics and finite element analysis.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2015;298(1):122-144.[13] Wang K, Wang H, Deng Z, et al. Cervical traction therapy with and without neck support: A finite element analysis. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2017; 28: 1-9.[14] Mo ZJ, Zhao YB, Wang LZ, et al. Biomechanical effects of cervical arthroplasty with U-shaped disc implant on segmental range of motion and loading of surrounding soft tissue. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23(3): 613-621.[15] Denozière G, Ku DN. Biomechanical comparison between fusion of two vertebrae and implantation of an artificial intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 2006;39(4): 766-775.[16] Du HG, Liao SH, Jiang Z, et al. Biomechanical analysis of press-extension technique on degenerative lumbar with disc herniation and staggered facet joint. Saudi Pharm J. 2016; 24(3): 305-311.[17] Lee SH, Im YJ, Kim KT, et al. Comparison of cervical spine biomechanics after fixed- and mobile-core artificial disc replacement: a finite element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(9): 700-708.[18] Mo Z, Zhao Y, Du C, et al. Does location of rotation center in artificial disc affect cervical biomechanics? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40(8): e469-475.[19] Moroney SP, Schultz AB, Miller JA, et al. Load-displacement properties of lower cervical spine motion segments. J Biomech. 1988; 21(9): 769-779.[20] Ganbat D, Kim YH, Kim K, et al. Effect of mechanical loading on heterotopic ossification in cervical total disc replacement: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2016;15(5): 1191-1199.[21] Wei X, Wang S, Li J, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine for the management of cervical radiculopathy: an overview of systematic reviews. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015: 793649.[22] Zhu L, Wei X, Wang S. Does cervical spine manipulation reduce pain in people with degenerative cervical radiculopathy? A systematic review of the evidence, and a meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(2): 145-155.[23] 毕胜,李义凯,赵卫东,等.腰部推拿手法生物力学和有限元比较研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2002,24(9): 525-528.[24] 王福根,高谦,毕胜,等.腰椎间盘突出症临床治疗机制探讨[J].中国组织工程研究,2003,7(8): 1320-1322.[25] Pyhtinen J, Laitinen J. Cervical intervertebral foramen narrowing and myelographic nerve root sleeve deformities. Neuroradiology.1993; 35(8): 596-597.[26] de Rooij JD, Gadjradj PS, Huygen FJ, et al. Management of symptomatic cervical disk herniation: a survey among dutch neurosurgeons. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(5): 311-317.[27] Wu LP, Huang YQ, Manas D, et al. Real-time monitoring of stresses and displacements in cervical nuclei pulposi during cervical spine manipulation: a finite element model analysis. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2014; 37(8): 561-568.[28] McNally DS, Shackleford IM, Goodship AE, et al. In vivo stress measurement can predict pain on discography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21(22): 2580-2587.[29] Kim HJ, Kang KT, Chun HJ, et al. The influence of intrinsic disc degeneration of the adjacent segments on its stress distribution after one-level lumbar fusion. Eur Spine J.2015; 24(4): 827-837. |