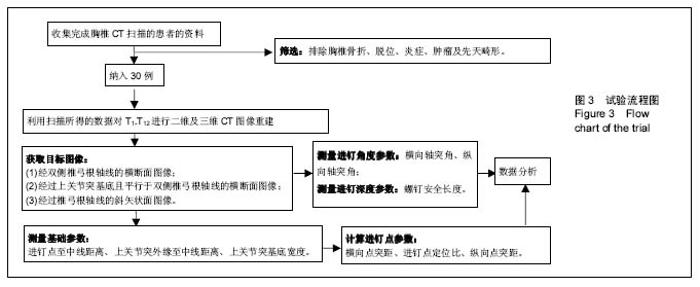
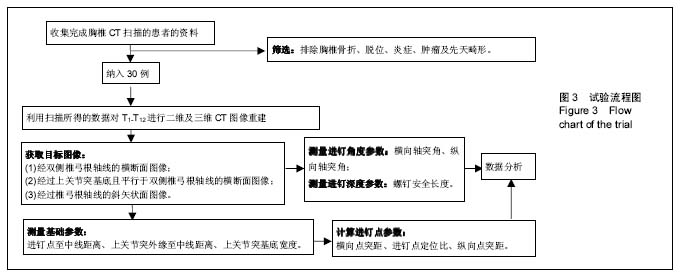
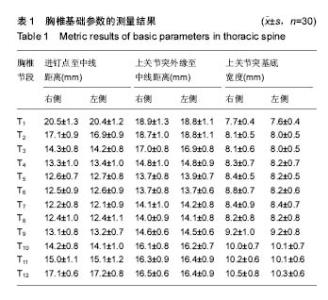
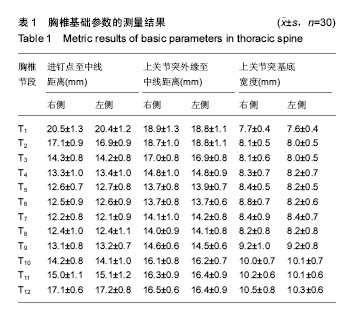
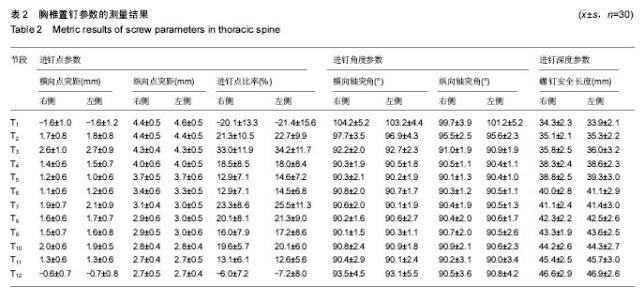
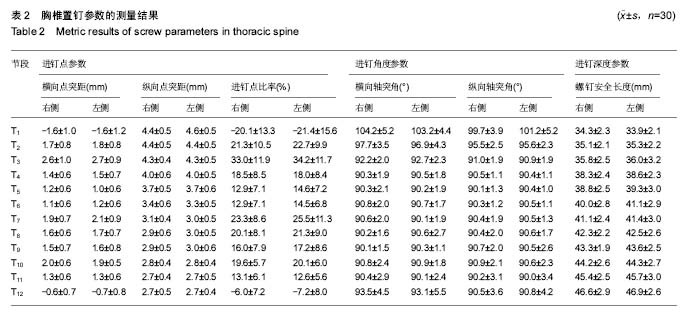
| [1] Kim JH,Choi GM,Chang IB,et al.Pedicular and extrapedicular morphometric analysis in the Korean population: computed tomographic assessment relevance to pedicle and extrapedicle screw fixation in the thoracic spine. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009;46(3):181-188.[2] 刘建伟,邹海波,肖奇,等.胸椎椎弓根螺钉与椎弓根外侧螺钉固定治疗胸椎骨折的比较研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010, 25(7):580 -582.[3] Wang H,Wang HF,Sribastav SS,et al. Comparison of pullout strength of the thoracic pedicle screw between intrapedicular and extrapedicular technique: a meta-analysis and literature review.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(12):22237-22245.[4] 程鑫华,余永桂,曹洪.后路复位椎弓根钉棒系统治疗胸椎骨折脱位[J].湖北医药学院学报,2016,35(5): 491-494. [5] Gonzalvo A, Fitt G, Liew S, et al. Correlation between pedicle size and the rate of pedicle screw misplacement in the treatment of thoracic fractures: Can we predict how difficult the task will be? Br J Neurosurg. 2015;29(4):508-512.[6] Ikeuchi H, Ikuta K. Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion in the thoracic and lumbar spine: a comparative study between percutaneous screw insertion and conventional open technique. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(9): 1195-1202.[7] Hyun SJ,Kim YJ,Cheh G,et al.Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine without any radiographic guidance: technical note,a cadaveric study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012;51(1):66-70.[8] 孙志峰,曹晓建.胸椎椎弓根螺钉技术的现状及研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2015,21(5):432-435.[9] Elliott MJ,Slakey CJ.Thoracic pedicle screw placement: analysis using anatomical landmarks without image guidance. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27(5):582-586.[10] Roy-camille R,Saillant G,Mazel C. Plating of thoracic, thoraoclumbar and lumbar injuries with pedicle screw plates. Orthop Clin North Am. 1986;17(1):147-159.[11] 杨明坤,刘川,张旭,等.上胸椎椎弓根螺钉固定并发症的探讨[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(6):500-503.[12] 王志焘,肖玉周.上胸椎椎弓根螺钉置入技术的研究进展[J].医学综述,2012,18(18):2995-2998.[13] Ishii K,Shiono Y,Funao H,et al. A noval Groove-Entry technique for inserting thoracic percutanous pedicle screws. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(2):57-64.[14] Gang C, Haibo L, Fancai L, et al. Learning curve of thoracic pedicle screw placement using the free-hand technique in scoliosis: how many screws needed for an apprentice? Eur Spine J. 2012;21(6):1151-1156.[15] WaschkeA, Walter J, Duenisch P, et al. CT-navigation versus fluoroscopy-guided placement of pedicle screws at the thoracolumbar spine: single center experience of 4,500 screws. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3): 654-660.[16] 盛红枫,徐卫星,卢笛,等.上中胸椎经椎弓根-肋骨单元途径置钉的安全性及稳定性研究[J].中医正骨, 2017, 29(2):1-5.[17] 秦毅,李勇,李振宇,等.微创后路固定联合前路病灶清除植骨融合治疗胸腰段脊柱结核[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014, 22(7): 659-661,667. [18] 卢政好,欧军,苏小桃,等.微创经皮置钉技术治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2016,19(5): 518-521.[19] Kira F, Aimee E, Charles E, et al. Upper thoracic pedicle screw loss of fixation causing spinal cord injury: a review of the literature and multicenter case series. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013;33(1):75-79.[20] Louis R. Spine internal fixation with Louis instrumentation. In An HS, Cotler JM eds. Spine Instrumentation. Baltimore: Wiliams and Wilkins, 1992:183-196.[21] Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Balderston RA, et al. Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part Ⅱ:Anatomical and radio-graphic assessment. Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1995;77(8): 1200-1206.[22] Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Ahmad M, et al. Projection of the thoracic pedicle and its morphometric analysis. Spine. 1997; 22(3):233-238.[23] Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(3):333-342.[24] 徐丽明,顾锐,朱庆三,等. 徒手与在计算机导航下中上胸椎椎弓根螺钉置入技术的前瞻性对比研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010,25(9):778-780.[25] 叶斌,孟祥龙,刘玉增,等.徒手置钉技术在脊柱畸形矫正中的准确性与安全性研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2014,12(1):25-34.[26] Modi HN,Suh SW,Fernandez H,et al. Accuracy and safety of pedicle screw placement in neuromuscular scoliosis with free-hand technique. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(12):1686-1696.[27] 王学文,李艳超,郑海龙.漏斗技术结合徒手椎弓根探针技术在椎弓根置钉术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(3): 213-215.[28] 田大胜,荆珏华,钱军,等.漏斗技术结合探针技术置入胸椎椎弓根螺钉在脊椎畸形矫形术中的应用[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(6): 431-434.[29] 刘显宏,欧云生,权正学,等.“漏斗技术”置入胸椎椎弓根螺钉在青少年特发性脊柱侧弯矫形术中的应用[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2012, 36(10):1264-1267.[30] 梁春祥,李浩淼,陈克冰,等.Balltip技术置入中上胸椎椎弓根螺钉的准确性评价[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2012,33(1): 116-120.[31] 唐绍峰,姚女兆,夏曦,等.统一解剖标志徒手胸椎椎弓根置钉技术的初步应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(5):588-592.[32] 潘定康,罗军,单永兴.横突上嵴椎弓根螺钉置入治疗胸椎骨折的疗效[J].武警医学,2015,26(11):1141-1144.[33] Larson AN,Polly DW Jr,Guidera KJ,et al. The accuracy of navigation and 3D image-guided placement for the placement of pedicle screws in congenital spine deformity. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(6):e23-29. [34] Allam Y,Silbermann J,Riese F,et al. Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in thoracic spine: comparison between free hand and a generic 3D-based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):648-653.[35] 常志强,张沛,吴一民,等. CT多平面三维重建条件下颈椎椎弓根置钉减少偏差的应用价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(48): 7833-7837. |