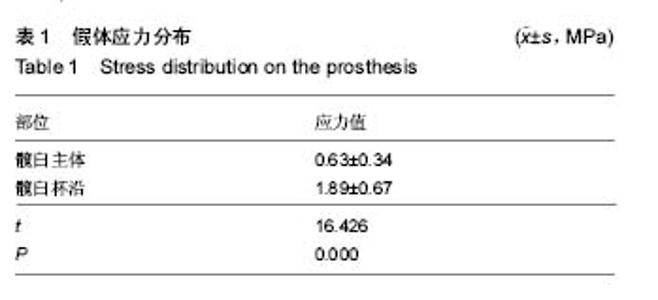
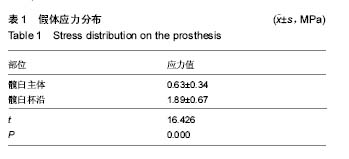
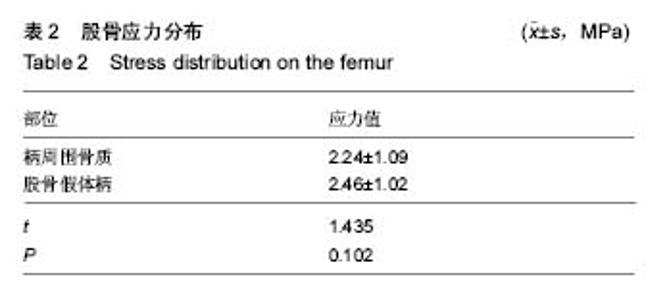
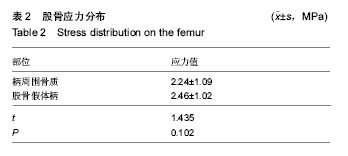
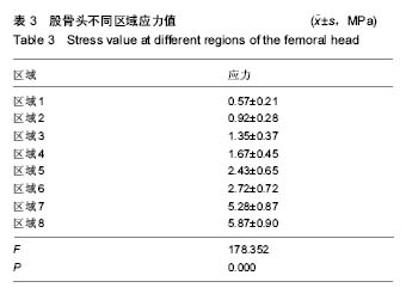
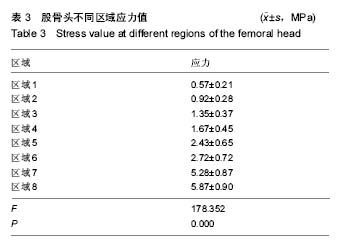
| [1] Stiehler M, Goronzy J, Günther KP.Total hip arthroplasty in overweight osteoarthritis patients.Orthopade. 2015;44(7): 523-530. [2] Müller M, Wassilew G, Perka C.Diagnosis and therapy of particle disease in total hip arthroplasty.Z Orthop Unfall. 2015; 153(2):213-229. [3] 赵红莲,刘晓丽,冯向春,等.全髋关节置换术和半髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(23):6671-6672. [4] 区广鹏,肖军,郑佐勇,等.金属大头全髋关节置换术和半髋关节置换术治疗老年人股骨颈骨折的近期疗效比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(14):3292-3293.[5] Lavernia CJ, Iacobelli DA, Brooks L,et al.The Cost-Utility of Total Hip Arthroplasty: Earlier Intervention, Improved Economics.J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(6):945-949. [6] 李嘉,戴海峰,陈永良,等.全髋关节置换术治疗老年严重骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折疗效观察[J].山东医药,2015,55(39): 37-38,39. [7] Liu XW, Zi Y, Xiang LB, et al.Total hip arthroplasty: areview of advances, advantages and limitations.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):27-36.[8] 常三来.23例全髋关节置换术早期失败因素分析[J].中国医药导刊,2013,15(10):1719-1720. [9] 罗福昌,邱华文,王一民,等.全髋关节置换术后Segawa 4型感染一期翻修术临床疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014, 29(6):580-581.[10] Howard JJ.Balancing innovation and medical device regulation: the case of modern metal-on-metal hipreplacements. Med Devices (Auckl). 2016;9:267-275. [11] Engh CA Jr, Sritulanondha S, Korczak A,et al.No Difference in Reoperations at 2 Years Between Ceramic-on-metal and Metal-on-metal THA: A Randomized Trial.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(2):447-455. [12] Lin ZL, Li PF, Pang ZH,et al.Influence of Regional Difference in Bone Mineral Density on Hip Fracture Site in Elderly Females by Finite Element Analysis.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;73(2):405-412. [13] 范鑫斌,张岩,杨铁毅,等.胫骨平台后外侧骨折3种内固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(22):3510-3516. [14] Sofuoglu H, Cetin ME. An investigation on mechanical failure of hip joint using finite element method. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2015;60(6):603-616. [15] 刘骞,王万春,姚长海,等.构建Cam型髋关节撞击综合征有限元模型及力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(40):6513-6518. [16] 马安邦,王东,吴慧慧,等.基于贝叶斯决策的髋关节自动分割方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(39):5873-5878. [17] Rüdiger HA, Parvex V, Terrier A.Impact of the Femoral Head Position on Moment Arms in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A ParametricFinite Element Study.J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(3): 715-720. [18] 潘浩,胡庆丰,肖鲁伟,等.髋关节发育不良髋臼假体位置与稳定的三维有限元分析[J].浙江医学,2015,37(1):44-48. [19] Ni M, Niu W, Wong DW,et al.Finite element analysis of locking plate and two types of intramedullary nails for treating mid-shaft clavicle fractures. Injury. 2016;47(8):1618-1623. [20] 陈林威,赵京涛,郑挺渠,等.儿童肱骨髁上骨折残留移位复位模型:力学响应的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(13): 2125-2132. [21] 王国栋,姜海波,张元民,等.髓内持骨动力性髓内钉固定股骨干骨折的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(40): 6524-6530.[22] Ike H, Inaba Y, Kobayashi N,et al. Effects of rotational acetabular osteotomy on the mechanical stress within the hip joint in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a subject-specific finite element analysis. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97-B(4):492-497. [23] 陈少明,邱玉金,卢斌,等.不稳定股骨转子间骨折不同内固定方式的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(26): 3890-3896. [24] 张海峰,尹爱华,董毅,等.有限元法分析不同负荷下髋臼区的应力分布[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(39):5867-5872.[25] Hellwig FL, Tong J, Hussell JG.Hip joint degeneration due to cam impingement: a finite element analysis.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016;19(1):41-48. [26] 王昊森,郝智秀,林剑浩,等.基于有限元方法的全髋关节假体个体化选型分析[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(3):219-226. [27] Kaku N, Tabata T, Tsumura H. Influence of cup-center-edge angle on micro-motion at the interface between the cup and host bone in cementless total hip arthroplasty: three-dimensional finite element analysis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(8):1271-1277. [28] 蔡春元,李永奖,张美超,等.股骨柄假体与骨固定界面三维有限元模型的构建及其生物力学意义[J].医学研究杂志,2013,42(3): 65-69. [29] 斯海波,曾羿,兰平文,等.有限元分析应用于全髋关节置换中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(24):2256-2260.[30] Miles B, Kolos E, Walter WL,et al.Subject-specific finite element model with an optical tracking system in total hip replacement surgery. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2015;229(4): 280-290. [31] Junnila M, Kostensalo I, Virolainen P,et al.Hip resurfacing arthroplasty versus large-diameter head metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty:comparison of three designs from the Finnish Arthroplasty Register.Scand J Surg. 2014;103(1):54-59.[32] 朱建炜,刘璠,董启榕,等.中青年髋关节疾病行金属对金属全髋关节表面置换术的疗效及安全性[J].山东医药,2014,54(1):11-13. [33] 李明,何志勇,陶崑,等.全髋表面置换术后与正常股骨近端生物力学比较[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(3):213-218. [34] Emmanuel AR, Bergin KM, Kelly GE,et al.The effect of acetabular inclination on metal ion levels following metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(1): 186-191. [35] Munro JT, Masri BA, Duncan CP,et al.High complication rate after revision of large-head metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(2):523-528. [36] Liudahl AA, Liu SS, Goetz DD, et al.Metal on metal total hip arthroplasty using modular acetabular shells.J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(5):867-871. [37] Kostensalo I, Seppänen M, Mäkelä K,et al.Early results of large head metal-on-metal hip arthroplasties.Scand J Surg. 2012;101(1):62-65.[38] 吴传龙,孙蕊心,朱振安,等.金属对金属髋关节置换术后金属离子相关问题研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(3): 33-36,39.[39] 马立峰,郭艾.金属对金属髋关节表面置换术的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2014,9(5):537-540. [40] Oshima Y, Fetto JF.Mechanical failure of metal-polyethylene sandwich liner in metal-on-metal total hip replacement. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(1):5383. [41] Berstock JR, Baker RP, Bannister GC,et al.Histology of failed metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty; three distinct sub-types.Hip Int. 2014;24(3):243-248. [42] Daniel J, Pynsent PB, McMinn DJ. Metal-on-metal resurfacing of the hip in patients under the age of 55 years with osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2):177-184.[43] Amstutz HC,Campbell PA, LeDuff MJ.Fracture of the neck of the femur after surface arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86 (9):1874-1877.[44] Beaul PE,Campbell PA,Hoke R,et al.Notching of the femoral neck during resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip.Avascular study . J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(1):35-39. [45] Little CP,Ruiz AL,Harding IJ,et al.Osteonecrosis inretrieved femoral heads after failed resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(3):320-323. |