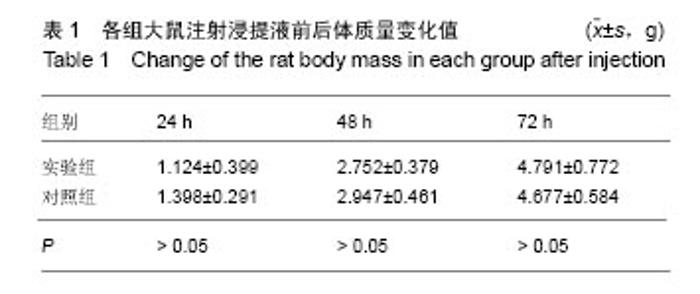
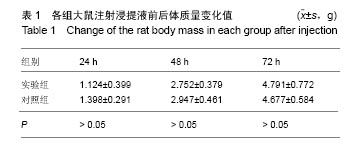
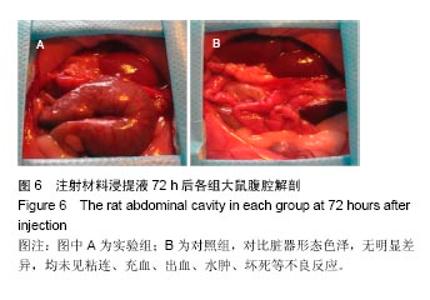
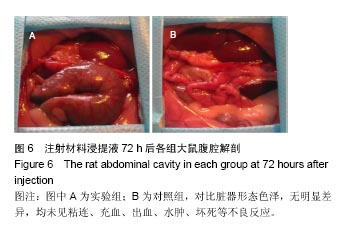
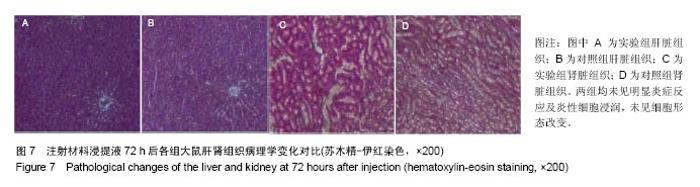
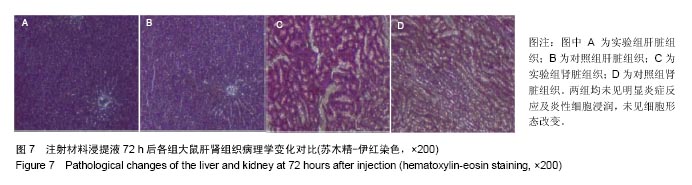
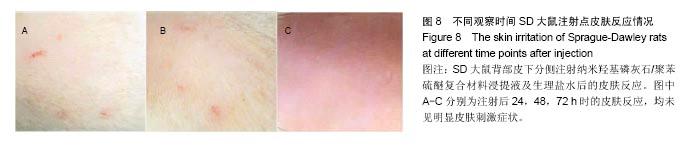
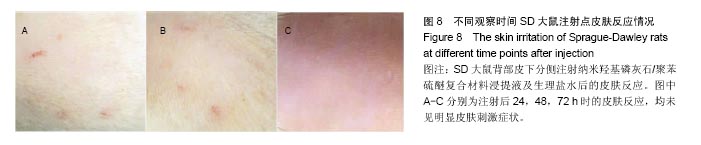
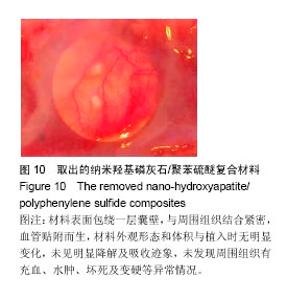
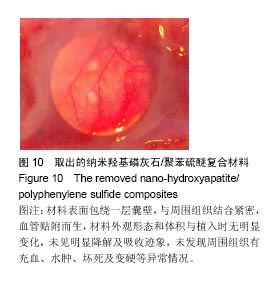
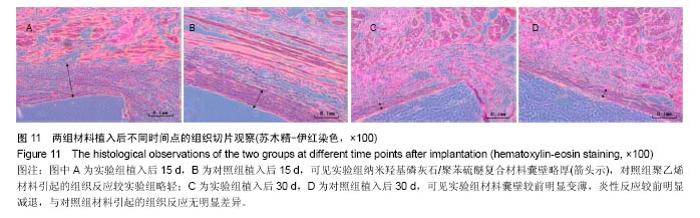
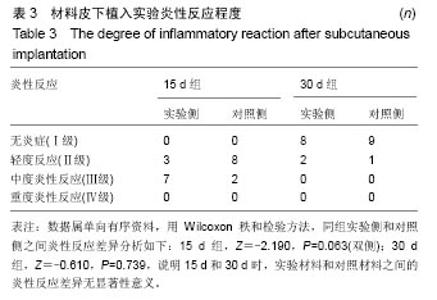
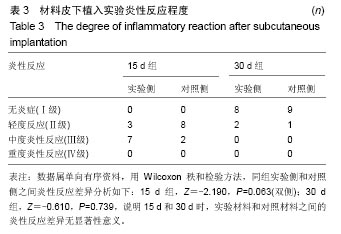
| [1]王翊民,张春,罗道友.我国聚苯硫醚市场概况及发展趋势[J].塑料工业,2009,37(8): 81-83.[2]徐桂花,沈凌云.聚苯硫醚的应用与市场展望[J].新材料产业, 2009,29(11):561-563.[3]汪家铭.新型工程塑料聚苯硫醚发展概况市及场分析[J].石油化工技术与经济,2008, 24(1): 21-25.[4]Li S,Huang B,Chen Y,et al.Hydroxyapatite-coated femoral stems in primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Surg.2013; 11(6):477-482.[5]Oonishi H.A long term histological analysis of effect of interposed hydroxyapatite between bone and bone cement in THA and TKA.J Long Term Eff Med Implants.2012;22(2): 165-176.[6]Munzinger U,Guggi T,Kaptein B,et al.A titanium plasma-sprayed cup with and without hydroxyapatite- coating:a randomised radiostereometric study of stability and osseointegration.Hip Int.2013;23(1):33-39.[7]Cossetto DJ.Mid-term outcome of a modular, cementless, proximally hydroxyapatite-coated, anatomic femoral stem.J Orthop Surg. 2012;20(3):322-326.[8]Herrera A,Mateo J,Lobo-Escolar A,et al.Long-term outcomes of a new model of anatomical hydroxyapatite-coated hip prosthesis.J Arthroplasty.2013;28(7):1160-1166.[9]Eschen J,Kring S,Brix M,et al.Outcome of an uncemented hydroxyapatite coated hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a clinical and radiographic 2-year follow-up study.Hip Int.2012;22(5):574-579.[10]Lazarinis S,Kärrholm J,Hailer NP.Effects of hydroxyapatite coating of cups used in hip revision arthroplasty.Acta Orthop. 2012;83(5):427-435.[11]Melton JT,Mayahi R,Baxter SE,et al.Long-term outcome in an uncemented, hydroxyapatite-coated total knee replacement:a 15- to 18-year survivorship analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(8):1067-1070.[12]Chris Arts JJ,Verdonschot N,Schreurs BW,et al.The use of a bioresorbable nano-crystalline hydroxyapatite paste in acetabular bone impaction grafting. Biomaterials. 2006; 27(7):1110-1118.[13]范珂夏,马原,余思逊,等.羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料的制备及体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(52): 8443-8449. [14]曹谊林.组织工程学[M].北京:科学出版社,2008:381-382.[15]矫树生,李兵仓,陈建梅,等.嗅鞘细胞与聚乳酸-聚羟基乙酸共聚物材料的细胞相容性研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2008, 30(5): 370-373.[16]刘学勇,刘吉泉,邓纯博,等.聚醚醚酮/羟基磷灰石/碳纤维复合材料的组织相容性初步研究[J].生物医学工程与临床, 2010,14(6): 481-484.[17]郝和平.医疗器械生物学评价标准实施指南[M].北京:中国标准出版社,2000.[18]GB/T 16886-2005,医疗器械生物学评价第12部分:样品制备与参照样品[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2005.[19]GB/T 16886-2005,医疗器械生物学评价第10部分:刺激与致敏试验[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2005.[20]Lewandowska-Szumiel M,Komender J.Interaction between tissues and implantable materials.Front Med Biol Eng.2000; 10(2):79-82.[21]Xu L P, Pan F, Yu G, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the surface bioactivity of a calcium phosphate coated magnesium alloy.Biomaterials.2009;30(8):1512-1523.[22]Müller HD,Cvikl B,Lussi A,et al.Chemokine expression of oral fibroblasts and epithelial cells in response to artificial saliva. Clin Oral Investig.2016;20(5):1035-1042. [23]Aykent F,Yondem I,Ozyesil AG,et al.Effect of different finishing techniques for restorative materials on surface roughness and bacterial adhesion.J Prosthet Dent. 2010;103(4):221-227. [24]Eger M,Sterer N,Liron T,et al.Scaling of titanium implants entrains inflammation-induced osteolysis.Sci Rep.2017;7: 39612. [25]Kulkarni GH,Jadhav P,Kulkarni K,et al.Assessment of Myeloperoxidase and Nitric Levels around Dental Implants and Natural Teeth as a Marker of Inflammation: A Comparative Study.J Contemp Dent Pract.2016;17(11): 934-938.[26]Gulati K,Prideaux M,Kogawa M,et al.Anodized 3D-printed titanium implants with dual micro- and nano-scale topography promote interaction with human osteoblasts and osteocyte-like cells.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2016.doi: 10.1002/term.2239. [Epub ahead of print][27]Jämsen E,Kouri VP,Ainola M,et al.Correlations between macrophage polarizing cytokines, inflammatory mediators, osteoclast activity, and toll-like receptors in tissues around aseptically loosened hip implants.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(2):454-463. [28]Samelko L,Landgraeber S,McAllister K,et al.Cobalt Alloy Implant Debris Induces Inflammation and Bone Loss Primarily through Danger Signaling, Not TLR4 Activation: Implications for DAMP-ening Implant Related Inflammation.PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0160141. [29]Gibon E, Amanatullah DF, Loi F, et al.The biological response to orthopaedic implants for joint replacement: Part I: Metals.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2016.doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33734. [Epub ahead of print].[30]邹昌,张帅,段宏,等.注射型可吸收聚氨基酸/硫酸钙复合材料动物体内的安全及组织相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(8): 220-223. |