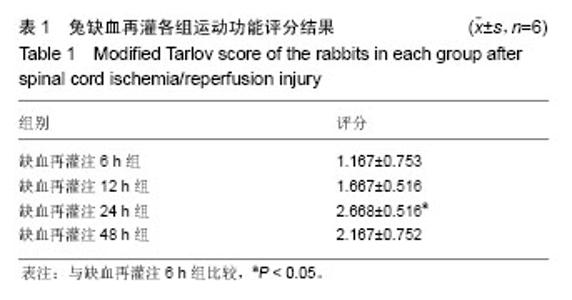
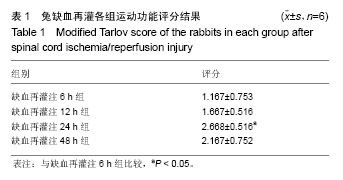
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (24): 3845-3850.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.24.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression and clinical significance of protein disulfide-isomerase A3 in a rabbit model of spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury
Li Chun-xu, Zhang Shan-yong, Qi Zhi-ping, Xia Peng, Pan Su, Zan Chun-fang, Yang Xiao-yu
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Revised:2017-05-23Online:2017-08-28Published:2017-08-30 -
Contact:Zan Chun-fang, Master, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China; Yang Xiao-yu, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Liu Chun-xu, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31572217 and 81350013; the Technology Innovation Foundation of Small and Medium-Sized Technology-Based Enterprise in Jilin Province, No. SC201502001; the Innovation Foundation for the Graduate in Jilin University, No. 2017176
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Chun-xu, Zhang Shan-yong, Qi Zhi-ping, Xia Peng, Pan Su, Zan Chun-fang, Yang Xiao-yu. Expression and clinical significance of protein disulfide-isomerase A3 in a rabbit model of spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(24): 3845-3850.
share this article
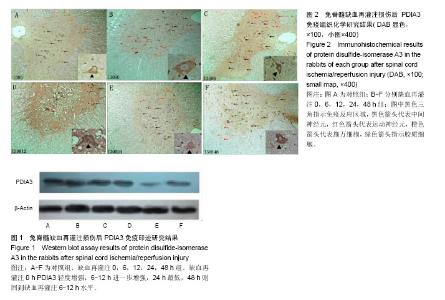
2.3 PDIA3免疫印迹研究结果 对照组PDIA3表达有清晰印迹显示,缺血再灌注0 h印迹轻度增强,缺血再灌注6-12 h进一步增强,缺血再灌注24 h显著减弱至最低,缺血再灌注48 h则回到缺血再灌注6-12 h水平(图1)。 2.4 PDIA3免疫组织化学研究结果 对照组中间神经元及前角运动神经元可见轻度免疫反应(+),后角神经元未见免疫反应(见图2A);缺血再灌注0 h组中间神经元及前角运动神经元免疫反应强度未变但后角神经元出现轻度免疫反应(+) (见图2B);相比之下,缺血再灌注6 h组神经元免疫反应增强至中度(++),后角神经元仍为轻度(+)(见图2C);缺血再灌注12 h组中间神经元免疫反应明显增强(+++),前角运动神经元免疫反应不明显(见图2D);实验组缺血再灌注24 h组神经元免疫反应明显减轻,中间神经元免疫反应下降至对照组水平以下(+),前角运动神经元 免疫反应减轻(+)而后角神经元免疫反应消失(-)(见图2E);缺血再灌注48 h组神经元免疫反应强度与缺血再灌注6 h组水平相近(++),明显可见中间神经元免疫反应增强(++)(见图2F)。"
| [1] Geng CK,Cao HH,Ying X,et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells transplantation combining with hyperbaric oxygen therapy on rehabilitation of rat spinal cord injury. Asian Pac J Trop Med.2015; 8(6):468-473.[2] Haapanen H,Herajärvi J,Arvola O,et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning protects the spinal cord against ischemic insult: An experimental study in a porcine model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151(3): 777-785.[3] Kieffer E,Chiche L,Cormier E, et al.Recurrent spinal cord ischemia after endovascular stent grafting for chronic traumatic aneurysm of the aortic isthmus.J Vasc Surg.2007; 45(4): 831-833.[4] Svensson LG, Von Ritter CM, Groeneveld HT, et al. Cross-clamping of the thoracic aorta: influence of aortic shunts, laminectomy, papaverine, calcium channel blocker, allopurinol, and superoxide dismutase on spinal cord blood flow and paraplegia in baboons. Ann Surg.1986; 204(1): 38-47.[5] Lang-Lazdunski L, Matsushita K, Hirt L, et al. Spinal cord ischemia. Development of a model in the mouse. Stroke. 2000; 31: 208-213.[6] Smith PD, Puskas F, Meng X, et al. The evolution of chemokine release supports a bimodal mechanism of spinal cord ischemia and reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2012; 126(11 Suppl 1): S110-S117.[7] Allen AR. Surgery of experimental lesion of spinal cord equivalent to crush injury of fracture dislocation of spinal column: preliminary report. JAMA. 1911; 57: 878 -880.[8] Panthee N,Ono M. Spinal cord injury following thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic repairs. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2015; 23(2): 235-246.[9] Katsargyris A,Oikonomou K,Kouvelos G,et al.Spinal cord ischemia after endovascular repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms with fenestrated and branched stent grafts. J Vasc Surg. 2015;62(6):1450-1456.[10] Kato M,Motoki M, Isaji T, et al.Spinal cord injury after endovascular treatment for thoracoabdominal aneurysm or dissection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2015; 48(4): 571-577.[11] Etz DC, Luehr M, Aspern KV, et al. Spinal cord ischemia in open and endovascular thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair: new concepts. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2014; 55 (2 Suppl 1): 159-168. [12] Hetz C, Russelakis-Carneiro M, Walchli S, et al. The disulfide isomerase Grp58 is a protective factor against prion neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 2005; 25(11): 2793- 2802.[13] Garbi N, Tanaka S, Momburg F, et al. Impaired assembly of the major histocompatibility complex class I peptide-loading complex in mice deficient in the oxidoreductase ERp57. Nat Immunol. 2006; 7(1): 93-102. [14] Bennett CF,Balcarek JM,Varrichio A,et al. Molecular cloning and complete amino-acid sequence of form-I phosphoinositide specific phospholipase C.Nature. 1988; 334(6179): 268-270.[15] Matsushita T,Lankford KL, Arroyo EJ, et al. Diffuse and persistent blood-spinal cord barrier disruption after contusive spinal cord injury rapidly recovers following intravenous infusion of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Neurol. 2015; 267: 152-164.[16] Yang MC,Zhang HZ,Wang Z,et al.The molecular mechanism and effect of cannabinoid-2 receptor agonist on the lood-spinal cord barrier permeability induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Res.2016; 1636: 81-92.[17] Zhang C,Ma J,Fan L, Zou Y, et al.Neuroprotective effects of safranal in a rat model of traumatic injury to the spinal cord by anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory and edema-attenuating. Tissue Cell.2015; 47(3): 291-300. [18] Matsushita Y, Shima K, Nawashiro H, et al. Real-time monitoring of glutamate following fluid percussion brain injury with hypoxia in the rat. J Neurotrauma. 2000; 17(2): 143-153.[19] Segal JL, Gonzales E, Yousefi S, et al. Circulating levels of IL-2R, ICAM-1, and IL-6 in spinal cord injuries. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997; 78(1): 44 -47.[20] Salzman SK, Acosta R, Beck G, et al. Spinal endothelin content is elevated after moderate local trauma in the rat to levels associated with locomotor dysfunction after intrathecal injection. J Neurotrauma.1996;13(2): 93-101.[21] Zhang S, Wu D, Wang J, et al. Stress protein expression in early phase spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(24): 2225-2235.[22] Gao Q, Liang Y, Yang X, et al. Differential protein expression in spinal cord tissue of a rabbit model of spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2012; 7(20): 1534-1539.[23] Wang J, Pearse DD, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia in spinal cord injury: the status of its use and open questions. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(8):16848-16879.[24] Zhilai Z, Biling M, Sujun Q, et al. Preconditioning in lowered oxygen enhances the therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2016; 1642: 426-435.[25] Zivin JA, DeGirolami U. Spinal cord infarction: a highly reproducible stroke model. Stroke.1980;11(2): 200-202.[26] Li GL, Farooque M,Olsson Y,et al. Changes of Fas and Fas ligand immunoreactivity after compression trauma to rat spinal cord. Acta Neuropathol Berl. 2000; 100(1): 75-81.[27] Ekshyyan O, Aw TY. Apoptosis in acute and chronic neurological disorders. Front Biosci. 2004; 1(9): 1567-1576.[28] Pahl HL. Signal transduction from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell nucleus. Physiol Rev. 1999; 79(3): 683-701.[29] Szegezdi E,Logue SE,Gorman AM,et al. Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2006;7(9): 880-885.[30] Lee AS. The glucose-regulated proteins: stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001; 26(8): 504-510.[31] Yamauchi T, Sakurai M, Abe K, et al. Impact of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in spinal cord after transient ischemia. Brain Res. 2007; 1169: 24-33. [32] Rao RV, Bredesen DE. Misfolded proteins, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004; 16(6): 653-662. [33] Yu ZF, Mattson MP. Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration reduce focal ischemic brain damage and improve behavioral outcome: evidence for a preconditioning mechanism. J Neurosci Res.1999; 57(6): 830-839. [34] Hoozemans JJ, Veerhuis R, Van Haastert ES, et al. The unfolded protein response is activated in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2005;110(2):165-172. [35] Yamauchi T, Sakurai M, Abe K, et al. Ubiquitin-mediated stress response in the spinal cord after transient ischemia. Stroke. 2008; 39(6): 1883-1889. [36] Hetz CA, Soto C. Stressing out the ER: a role of the unfolded protein response in prion-related disorders. Curr Mol Med. 2006; 6(1): 37-43. [37] Pendyala G, Ninemire C, Fox HS. Protective Role for the Disulfide Isomerase PDIA3 in methamphetamine neurotoxicity. PLoS One. 2012; 7(6): e38909. [38] Takata H, Kudo M, Yamamoto T, et al. Increased expression of PDIA3 and its association with cancer cell proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2016; 12(6): 4896-4904.[39] He Y, Shao F, Pi W, et al. Largescale Transcriptomics Analysis Suggests Over-Expression of BGH3, MMP9 and PDIA3 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS One. 2016; 11(1): e0146530.[40] Zhu Y, Cai L, Guo J, et al. Depletion of Dicer promotes epithelial ovarian cancer progression by elevating PDIA3 expression. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37(10): 14009-14023.[41] Su BB, Zhou SW, Gan CB, et al. MiR-330-5p regulates tyrosinase and PDIA3 expression and suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in cutaneous malignant melanoma. J Surg Res. 2016; 203(2): 434-40.[42] Zhuang Z, Zhang L, Wang X, et al. PDIA3 gene induces visceral hypersensitivity in rats with irritable bowel syndrome through the dendritic cell-mediated activation of T cells. PeerJ. 2016; 17(4): e2644.[43] Yuan G, Hua B, Yang Y, et al. The Circadian Gene Clock Regulates Bone Formation Via PDIA3. J Bone Miner Res. 2017; 32(4): 861-871.[44] Xu S, Sankar S, Neamati N. Protein disulfide isomerase: a promising target for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2014; 19(3): 222-240.[45] Trnková L, Ricci D, Grillo C, et al. Green tea catechins can bind and modify ERp57/PDIA3 activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1830(3): 2671-2682. [46] Hoffstrom BG, Kaplan A, Letso R, et al. Inhibitors of protein disulfide isomerase suppress apoptosis induced by misfolded proteins. Nat Chem Biol. 2010; 6(12): 900-906.[47] Frasconi M, Chichiarelli S, Gaucci E, et al. Interaction of ERp57 with calreticulin: analysis of complex formation and effects of vancomycin. Biophys Chem. 2012; 160(1): 46-53.[48] Khan MM, Simizu S, Lai NS, et al. Discovery of a small molecule PDI inhibitor that inhibits reduction of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. ACS Chem Biol. 2011; 6(3): 245-251.[49] Jasuja R, Passam FH, Kennedy DR, et al. Protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors constitute a new class of antithrombotic agents.J Clin Invest.2012; 122 (6):2104-2113.[50] ?iplys E,?itkus E, Slibinskas R. Native signal peptide of human ERp57 disulfide isomerase mediates secretion of active native recombinant ERp57 protein in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Protein Expr Purif.2013; 89(2): 131-135. |
| [1] | Wang Shuo, Liu Wenying, Lü Chaofan, Li Jiacong, Geng Yi, Zhao Yungang. Cardioprotective effect of 3-nitro-N-methyl salicylamide on the isolated rat heart under cold ischemia preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1194-1201. |
| [2] | Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209. |
| [3] | Yang Shenglin, Pu Xingwei, Luo Chunshan, Yang Jianwen. Neuroprotective effects of tetrandrine preconditioning in rabbits with spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1223-1227. |
| [4] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1286-1292. |
| [5] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [6] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [8] | Li Wanhai, Dong Yuhang, Shi Chao, Jiang Yiyao, Liu Ge, Diao Wenjie, Wu Zhen. Ligustrazine furoxan complex protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 205-210. |
| [9] | Lai Han, Wang Jiao, Dong Miaomiao, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Electroacupuncture intervenes with changes of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion due to middle cerebral artery occlusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 225-231. |
| [10] | Xing Hongchang, Cao Jianping, Zhu Jing, Yao Kun. Mechanism by which enalapril alleviates myocardial injury in a rat model of limb ischemia-reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1747-1751. |
| [11] | Mei Yunyun, Zhang Jianjun, Wang Dong. Hyperbaric oxygen combined with NgR gene silencing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 12-19. |
| [12] | Xie Xingqi, Hu Wei, Tu Guanjun. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes combined with chondroitinase ABC for treating spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 20-26. |
| [13] | Zhao Xu, Mao Xin, Li Chuntian, Wang Feng. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 130-134. |
| [14] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [15] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||