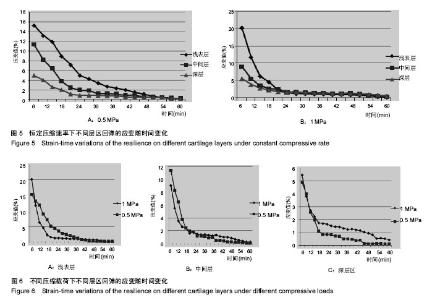
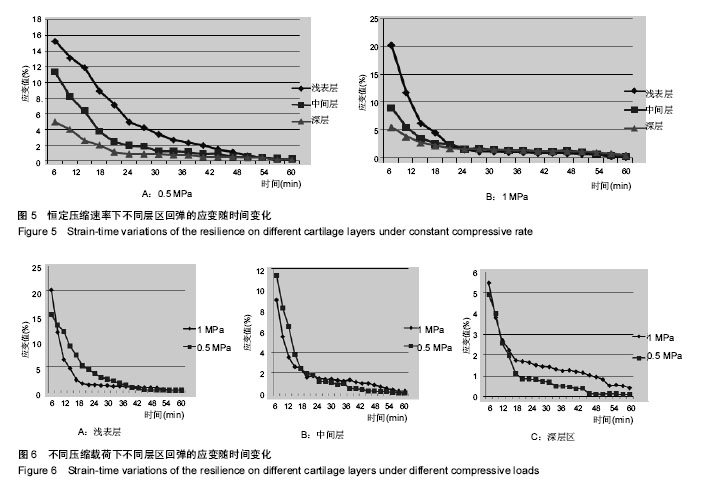
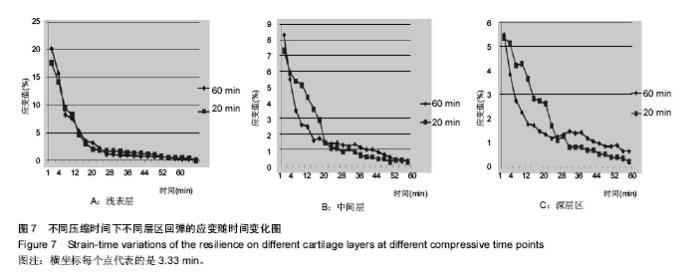
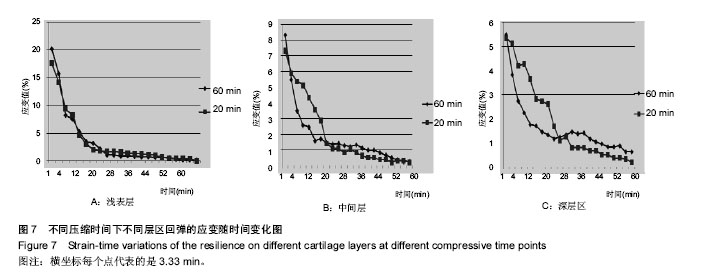
| [1] 2015年中国骨关节炎防治认知白皮书[EB/OL]. http://health.sohu.com/s2015/guguanjieyan/ [2] 王成学,赵宝林,白岩,等.人体肩、髋及膝关节软骨蠕变对比研究[J].吉林大学学报:医学版, 2004, 30(4): 586-588.[3] Li F, Su Y, Wang J,et al. Influence of dynamic load on friction behavior of human articular cartilage, stainless steel and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel as artificial cartilage.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(1):147-154.[4] Gao LL, Zhang CQ, Dong LM, et al. Description of depth-dependent nonlinear viscoelastic behavior for articular cartilage in unconfined compression. Materials Science & Engineering C. 2012; 32(2):119-125.[5] Mow VC, Kuei SC, Lai WM, et al. Biphasic creep and stress relaxation of articular cartilage in compression? Theory and experiments.J Biomech Eng. 1980;102(1):73-84.[6] Li LP, Soulhat J, Buschmann MD, et al. Nonlinear analysis of cartilage in unconfined ramp compression using a fibril reinforced poroelastic model.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1999;14(9):673-682.[7] Wilson W, van Donkelaar CC, van Rietbergen B, et al. A fibril-reinforced poroviscoelastic swelling model for articular cartilage.J Biomech. 2005;38(6):1195-1204.[8] 陈凯,张德坤,戴祖明,等.牛膝关节软骨的力学承载特性及其有限元仿真分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2012,27(6):675-680.[9] Halonen KS, Mononen ME, Jurvelin JS, et al. Deformation of articular cartilage during static loading of a knee joint--experimental and finite element analysis.J Biomech. 2014;47(10):2467-2474.[10] 周海宇,李元超,王成焘. 关节软骨胶原纤维增强特性[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(4):460-465.[11] 刘琳琳.不同年龄组兔关节软骨细胞黏弹性研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2007.[12] 刘志动,高丽兰,张春秋,等.关节软骨不同层区的率相关性能研究[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(2):141-145.[13] 高丽兰,张春秋,刘志动,等.滑动载荷作用下关节软骨不同层区的法向位移[J]. 医用生物力学,2014,29(1):20-24.[14] 刘志动.压缩载荷作用下关节软骨准静态力学性能的研究[D]. 天津:天津理工大学,2014.[15] 刘蕾. 静力性负重对人体身高影响的实验研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2011.[16] 包呼日查. 内、外侧半月板后根部完全撕裂对膝关节生物力学影响的有限元分析[D].长春:吉林大学, 2013. |