Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (12): 1940-1945.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.12.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ghrelin participates in bone metabolism: the newest research progress
Chen Hong1, Bi Ran-ran2, Chen Liang1, Zhu Qiong1
- 1Xuhui District Lingyun Community Health Service Center of Shanghai, Shanghai 200237, China; 2Yangpu Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University, Shanghai 200090, China
-
Received:2017-02-24Online:2017-04-28Published:2017-05-16 -
Contact:Bi Ran-ran, Master, Attending physician, Yangpu Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University, Shanghai 200090, China -
About author:Chen Hong, Attending physician, Xuhui District Lingyun Community Health Service Center of Shanghai, Shanghai 200237, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Hong1, Bi Ran-ran2, Chen Liang1, Zhu Qiong1. Ghrelin participates in bone metabolism: the newest research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(12): 1940-1945.
share this article
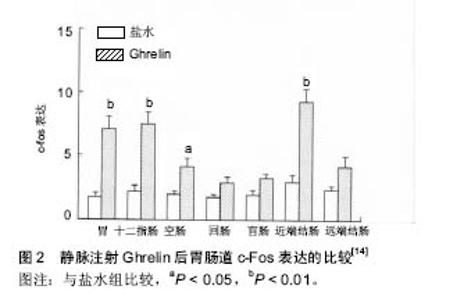
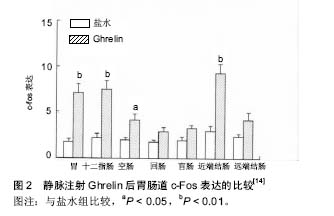
2.1 Ghrelin的概况 1999年日本科学家Kojima等[1]利用免疫组织化学的方法在小鼠和人的胃内分泌细胞及下丘脑弓状核发现了一种含有28个氨基酸残基的多肽,它 是 生 长 激 素 促 分 泌 素 受 体的内源性配体,Ghrelin 在体内的多个组织中均有表达,但是以胃黏膜内的表达量最高[2]。Ghrelin全肽的半衰期是 27-31 min,酰基化的Ghrelin半衰期是9-13 min[3]。 2.1.1 Ghrelin的合成与分布 Ghrelin由28个氨基酸残基组成,相对分子质量为3 314,它有2种形式:Ghrelin-25和Des-Gln14-Ghrelin[4]。Des-Glnl4-Ghrelin生物学活性与Ghrelin相同,第14位上是谷氨酞胺。大鼠和人类Ghrelin氨基酸序列具有较高的同源性,Ghrelin第3位丝氨酸残基被辛酰基化,该辛酰基结构是Ghrelin生物活性所必需的[1]。Date等[5]研究发现:胃肠道黏膜均有Ghrelin分泌细胞,即X/A样内分泌细胞,主要位于胃底黏膜泌酸腺的体部和底部,十二指肠、回肠、盲肠、结肠的分泌量很少;其释放Ghrelin的机制可能是胃肠道的Ghrelin细胞与固有层的毛细血管网紧密接触,接受胃肠道管腔的物理刺激和/或基底膜外侧的化学刺激,从而释放Ghrelin。Gnanapavan等[5-6]通过免疫组织化学和原位杂交研究发现:胃肠道黏膜均有Ghrelin mRNA的表达.Ghrelin的mRNA存在于胃底泌酸腺的颈部和底部[1]。也有人通过原位杂交和RT-PCR均证实Ghrelin mRNA在中枢神经系统也有表达,下丘脑弓状核、垂体、脑干等中枢神经系统亦有Ghrelin的分泌[1,7],故称之为脑-肠肽。Gnanapavan等[6]研究发现:机体许多组织器官均有Ghrelin mRNA表达。这些发现说明Ghrelin分布较广泛。 2.1.2 Ghrelin的受体促生长激素分泌物受体 研究表明Ghrelin通过与细胞表面相应的受体促生长激素分泌物受体结合发挥生物学作用。促生长激素分泌物受体属于α螺旋7次跨膜的G蛋白偶联受体[8],主要G蛋白是Gq蛋白,主要的信号传递分子是磷脂酶C(phospholipase C,PLC)、三磷酸肌醇(inositol-triphosphate,IP3)和蛋白激酶C(protein kinase C,PKC)。促生长激素分泌物受体存在促生长激素分泌物受体1α和促生长激素分泌物受体1b两种亚型[4]。其中1α型由366个氨基酸组成,含7个跨膜结构域(transmembrane domains,TMD),是受体功能的主要形式。研究表明,Ghrelin是与1α型促生长激素分泌物受体结合而发挥其生物学作用的[9]。Ghrelin与促生长激素分泌物受体1α结合后,主要激活磷脂酶C、三磷酸肌醇和蛋白激酶C、有丝分裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)等信号通路而发挥相应的效应。1b型由289个氨基酸组成,含5个跨膜结构域;1b不介导生物学效应。促生长激素分泌物受体1a在多种组织中均有表达,主要在垂体表达,同时在下丘脑弓状核、甲状腺、胰腺、脾、心肌、肾上腺也有低水平表达,促生长激素分泌物受体1b也在多种组织中有广泛表达[10] 2.2 Ghrelin的生理作用 2.2.1 对消化系统的影响 Ghrelin参与胃功能的中枢和外周调节。新近研究发现,脑室和室旁核注入Ghrelin可促进大鼠摄食,增加与摄食相关核团,如下丘脑室旁核、背内侧核、弓状核、延髓孤束核和最后区的c-Fos表达[11-12]。同时,Ghrelin可加速胃排空、增加胃酸分泌及促进结肠运动[13]。Ghrelin也可以促进小肠转运,其促动力作用由其受体促生长激素分泌物受体所介导;静脉给予Ghrelin可通过肠神经系统和中枢神经系统调节小肠运动[14](图2)。Ghrelin受体的激活可发挥多种生理学作用,可刺激胃酸分泌和胃排空、加快小肠蠕动、改善术后肠梗阻症状[15]。 2.2.2 对内分泌系统的影响 Ghrelin与血糖调节有关。李丽等[16]研究表明:糖尿病大鼠血浆Ghrelin水平显著升高。Ghrelin 可影响肝脏糖代谢及胰岛素水平,进而调节外周血糖稳态[17]。Gauna等[18]研究表明,非酰化"
| [1] Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature.1999;402: 656-660. [2] Han D,Huang W,Ma S,et al.Ghrelin improves functional survival of engrafted adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in ischemic heart through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int.2015;2015: 858349. [3] Akamizu T, Takaya K, IrakoT, et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and endocrine and appetite effects of Ghrelin administration in young health subjects. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;150:447-455. [4] Hosoda H, Kojima M, Matsuo H, et al. Purification and characterization of rat des-Gln14-Ghrelin, a second endogenous ligand for the growth secretagogue receptor. Biol Chem. 2000;275: 21995-22000. [5] Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, et al. Ghrelin,a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide,is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology. 2000;141: 4255-4261.[6] Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, et al. The tissue distribution of the mRNA of Ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor,GHS-R,in humans. Clin Endocrinol Metab.2002;87: 2988.[7] Cowley MA, Smith RG, Diano S, et al. The distribution and mechanism of action of Ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron. 2003;37: 649-661.[8] Wang G, Lee HM. Ghrelin not just another stomach hormone. Regulatory Peptide. 2002;105:75-81.[9] Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cully DF,et al. A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science.1996;273:974-977.[10] Nogueiras R, Tovar S, Mitchell SE, et al. Regulation of growth hormone secretagogue receptor gene expression in the arcuate nuclei of the rat by leptin and Ghrelin. Diabetes.2004; 53: 2552-2558. [11] Sakurazawa N, Mano-Otagiri A, Nemoto T,et al. Effects of intracerebroventricular Ghrelin on food intake and Fos expression in the arcuate nucleus of the thpothalamus in female rats vary with estrous cycle phase.Neurosci Lett. 2013;541:204-208.[12] Cone JJ, McCutcheon JE, Roitman MF. Ghrelin acts as an interface between physiological state and phasic dopamine signaling.J Neurosci.2014;34(14): 4905 -4913.[13] Cheung CK, Wu JC. Role of Ghrelin in the pathophysiology of gastrointestinal disease. Gut Liver.2013;7(5): 505-512. [14] 王燕,史海涛,秦斌, 等.Ghrelin对大鼠小肠转运的作用及对中枢和胃肠道c-Fos表达的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版,2014, 35(5):611-617.[15] Bron R, Yin L, Russo D, et al. Expression of the Ghrelin receptor gene in neurons of the medulla oblongata of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2013;521(12): 2680-2702.[16] 李丽,徐珞.Ghrelin对糖尿病大鼠摄食的影响[J],青岛大学医学院院报,2014, 50(1): 13-18.[17] Stark R,Reichen bach A,Lockie SH,et al.Acyl Ghrelin acts in the brain to control liver function and peripheral glucose homeostasis in male mice.Endocrinology.2015;156(3) : 858-868.[18] Gauna C, Kiewiet RM, Janssen JA, et al. Unacylated Ghrelin acts as apotent insulin secretagogue in glucose-stimulated conditions. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2007;293: E697-E704.[19] Barzon L, Pacenti M, Masi G, et al. Loss of growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a and overexpression of type 1b receptor transcripts in human adrenocortical tumors. Oncology. 2005;68: 414-421.[20] Shi L, Bian X, Qu Z, et al.Peptide hormone Ghrelin enhances neuronal excitability by inhibition of Kv7/ KCNQ channels. Nature Communications.2013;4:1435.[21] Wang Q, Liu C, Uchida A, et al. Arcuate AgRP neurons mediate orexigenic and glucoregulatory actions of Ghrelin. Mol Metab.2013;3(1):64-72.[22] Stoyanova II. Ghrelin: a link between ageing, metabolism and neurodegenerative disorders. Neurobiology Disease. 2014; 72(Pt A):72-83.[23] Li E, Kim Y, Kim S, et al. Ghrelin stimulates proliferation, Migration and differentiation of neural progenitors from the Subventricular zone in the adult mice.Experimental Neurology. 2014;252:75-84.[24] Li E, Kim Y, Kim S et al. Ghrelin-induced hippocampal neurogenesis and enhancement of cognitive function are mediated independently of GH/IGF-1 axis: lessons from the spontaneous dwarf rats. Endocrine Journal.2013;60(9): 1065-1075. [25] Kadoglon NP,Fotiadis G,Lambadiari V,et al. Serum levels of novel adipokines in patients with acute ischemic stroke : potential contribution to diagnosis and prognosis. Peptides. 2014;57(7): 12-16. [26] Müller TD, Nogueiras R, Andermann ML,et al. Ghrelin. Molecular Metabolism.2015;4(6): 437-460.[27] Qi Y, Inoue K, Fu M, et al.Chronic overproduction of Ghrelin in the hypothalamus leads to temporal increase in food intake and body weight.Neuropeptides. 2015;50(4): 23-28.[28] Barazzoni R,Bosutti A,Stebel M,et al. Ghrelin regulates mitochondrial-lipid metabolism gene expression and tissue fat distribution in liver and skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2005;288(1):E228-E235.[29] Murphy KG, Bloom SR. Gut hormones and the regulation of energy homeostasis. Nature. 2006;444(12):854-859.[30] Lely AJ, Tschop M, Heiman ML. Biological, Physiological, PathophySiological, and Pharmacological Aspects of Ghrelin. Endocrine Review.2004;25(10):426-457.[31] Leite-Moreira AF, Soares JB. Adelino F. Physiological, Pathological and potential therapeutic roles of Ghrelin. Drug Discovery Today. 2007;12(4):276-288.[32] Thompson NM, Gill DA, Davies R, et al. Ghrelin and desoctanoyl Ghrelin promote adipogenesis directlyin vivoby a mechanism independent of the type 1a growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology. 2004;145(1):234-242.[33] Kojima M, Kangawa K. Ghrelin: Structure and Function. Physiological Review.2005;85(2): 495-522.[34] Amini P, Cahill F, Wadden D, et al. Beneficial association of serum Ghrelin and peptide YY with bone mineral density in the Newfoundland population.BMC Endocrine Disorder.2013; 12(9): 35.[35] Kim SW, Her SJ, Park SJ. Ghrelin stimulates proliferation and differentiation and inhibits apoptosis in osteoblastic MC3T3- E1 cells.Bone.2005;3:359-369. [36] Dellhanty PJ, van der Eerden BC, van Leeuwe JP. Ghrelin and bone. Biofacts.2014;40(1): 41-48.[37] Liang Q H,Liu Y,Wu S S,et al. Ghrelin inhabits the apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells through ERK and AKT signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2013;272(3): 591 -597.[38] Bachrach L. Acquisition of optimal bone mass in childhood and adolescence. Trends Endocrinol Metab.2001;12(1): 22-28.[39] Biller B, Saxe V, Herzog D, et al. Mechanisms of osteoporosis in adult and adolescent women with anorexia nervosa. Clin Endocrinol Metab.1989;68(3): 548-549.[40] Delhanty PJ, van der Eerden BC, van der Velde M, et al. Ghrelin and unacylated Ghrelin stimulate human osteoblast growth via mitogenactivated protein kinase (MAPK)/ phosphoin-ositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways in the absence of GHS-R1a. Endocrinol. 2006;188(1):37-47.[41] Caminos JE, Gualillo O, Lago F, et al.The endogenous growth hormone secretagogue (Ghrelin) is synthesized and secreted by chondrocytes. Endocrinology. 2005;146(3): 1285 -1292.[42] Cocchi D, Maccarinelli G, Sibilia V. GH-releasing peptides and bone. Endocrinol Invest.2005;28 (8 Suppl):11-14. [43] schop M, Weyer C, Tataranni PA, et al. Circulating Ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes.2001;50(4): 707-709.[44] Zhang W, Zhao L, Lin TR, et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Ghrelin. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15(5):2484-2491.[45] Higuchi C, Myoui A, Hashimoto N, et al. Continuous inhibition of MAPK signaling promotes the early osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization of the extracellular matrix. Bone Miner Res.2002;17(10):1785-1794. [46] Shelton JG, Steelman LS, White ER, et al. Synergy between PI3K/Akt and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in IGF-1R mediated cell cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis in hematopoietic cells. Cell Cycle.2004;3(3): 372-379. [47] Kazama JJ. Osteoprotegerin and bone mineral metabolism in renal failure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens.2004;13(4): 411-415.[48] Chua CC, Chua BH, Chen Z, et al. Dexamethasone induces caspase activation in murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.2003;1642(1-2): 79-85.[49] Sang WK, Ok KC, Ju YJ, et al. Ghrelin Inhibits Early Osteogenic Differentiation of C3H10T1/2 Cells by Suppressing Runx2 Expression and Enhancing PPARg and C/EBPa Expression. Cellular Biochemistry.2009;106(4): 626-632. [50] 周华, 杨曦, 张雅鸥,等. Ghrelin抑制小鼠骨髓基质细胞成脂分化[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2007, 27(6): 886-890.[51] Kim MS, Yoon CY, Jang PG, et al. The mitogenic and anti-apoptotic actions of Ghrelin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Endocrinol.2004;18(9): 2291-2301. [52] Nuttall ME, Gimble JM. Controlling the balance between Osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis and the consequent therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Pharmacol.2004; 4(3): 290-294.[53] Pei L, Tontonoz P. Fat’s loss is bone’s gain. J Clin Invest. 2004;113(6): 805-806 |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [14] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||