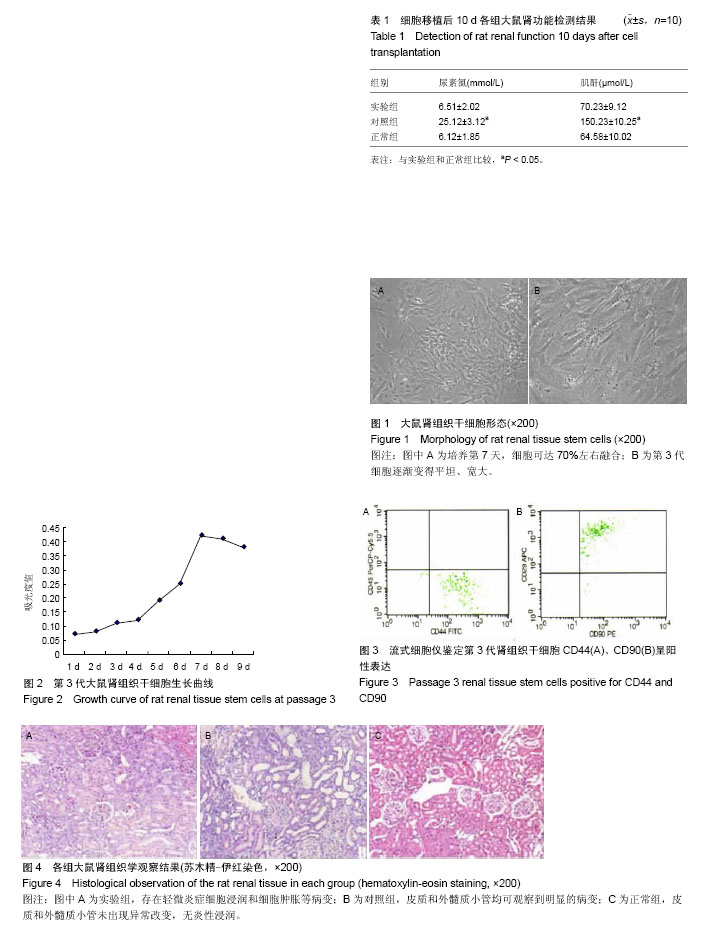
| [1] 王共先,汪泱,张中华,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺血再灌注肾损伤的保护作用[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2005,26(8):535- 538.[2] 王琼,卢慕峻.低氧诱导成体干细胞血管化[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2015,11(4):274-277.[3] Westover AJ, Buffington DA, Humes HD. Enhanced propagation of adult human renal epithelial progenitor cells to improve cell sourcing for tissue-engineered therapeutic devices for renal diseases. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012; 6(8):589-597.[4] Dankers PY, Boomker JM, Meijer EW, et al. From kidney development to drug delivery and tissue engineering strategies in renal regenerative medicine. J Control Release. 2011;152(1):177-185.[5] 杨光.高糖对肾组织干细胞的影响及其损伤机制初探[D].北京:中国人民解放军医学院,2014.[6] Eirin A, Zhu XY, Krier JD, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve revascularization outcomes to restore renal function in swine atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Stem Cells. 2012;30(5):1030-1041.[7] Roemeling-van Rhijn M, Reinders ME, de Klein A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue are not affected by renal disease. Kidney Int. 2012;82(7):748- 758.[8] Vanikar AV, Trivedi HL, Gopal SC, et al. Pre-transplant co-infusion of donor-adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells may help in achieving tolerance in living donor renal transplantation. Ren Fail. 2014;36(3):457-460.[9] 姜燕,王葳,李泽争,等.黄芪甲苷孵育的脂肪源性干细胞对顺铂诱导的急性肾损伤小鼠的保护作用[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2014,15(2):114-117.[10] Semedo P, Wang PM, Andreucci TH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate tissue damages triggered by renal ischemia and reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc. 2007;39(2): 421-423.[11] Zhuo W, Liao L, Fu Y, et al. Efficiency of endovenous versus arterial administration of mesenchymal stem cells for ischemia- reperfusion-induced renal dysfunction in rats. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(2): 503-510.[12] Zhu XY, Urbieta-Caceres V, Krier JD, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells decrease renal injury in experimental swine renal artery stenosis through different mechanisms. Stem Cells. 2013;31(1):117-125.[13] Aggarwal S, Moggio A, Bussolati B. Concise review: stem/progenitor cells for renal tissue repair: current knowledge and perspectives. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013; 2(12):1011-1019.[14] 李建秋,杨琴,党西强,等.新生儿急性肾损伤研究进展[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2014,29(17):1345-1348.[15] Katsuno T, Ozaki T, Saka Y, et al. Low serum cultured adipose tissue-derived stromal cells ameliorate acute kidney injury in rats. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(2):287-297.[16] Genheimer CW, Ilagan RM, Spencer T, et al. Molecular characterization of the regenerative response induced by intrarenal transplantation of selected renal cells in a rodent model of chronic kidney disease. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012; 196(4):374-384.[17] Swetha G, Chandra V, Phadnis S, et al. Glomerular parietal epithelial cells of adult murine kidney undergo EMT to generate cells with traits of renal progenitors. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(2):396-413.[18] 刘荣福,高加胜,付国,等.可分化为肾小管上皮细胞的脂肪间充质干细胞对大鼠急性肾损伤的修复作用研究[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2014,35(10):778-781.[19] Angelotti ML, Ronconi E, Ballerini L, et al. Characterization of renal progenitors committed toward tubular lineage and their regenerative potential in renal tubular injury. Stem Cells. 2012; 30(8):1714-1725.[20] 刘少鹏.脂肪干细胞(ASCs)在急性肾损伤(AKI)动物模型治疗中的作用研究进展[J].复旦学报:医学版,2014,41(3):400-404.[21] Tarantal AF, Lee CC, Batchelder CA, et al. Radiolabeling and in vivo imaging of transplanted renal lineages differentiated from human embryonic stem cells in fetal rhesus monkeys. Mol Imaging Biol. 2012;14(2):197-204.[22] Li K, Han Q, Yan X, et al. Not a process of simple vicariousness, the differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to renal tubular epithelial cells plays an important role in acute kidney injury repairing. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(8):1267-1275.[23] 杨光,程庆砾,李春霖,等.大鼠肾组织干细胞的分离培养与鉴定[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2015,46(5):667-672.[24] Vanikar AV, Trivedi HL, Feroze A, et al. Effect of co-transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells as compared to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation alone in renal transplantation to achieve donor hypo-responsiveness. Int Urol Nephrol. 2011;43(1): 225-232.[25] Huang HC, Chang YJ, Chen WC, et al. Enhancement of renal epithelial cell functions through microfluidic-based coculture with adipose-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19 (17-18):2024-2034.[26] Romagnani P, Lazzeri E, Mazzinghi B, et al. Nephrotic syndrome and renal failure after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: novel molecular diagnostic tools for a challenging differential diagnosis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005; 46(3): 550-556.[27] Oliver JA, Maarouf O, Cheema FH, et al. The renal papilla is a niche for adult kidney stem cells. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(6): 795-804.[28] Zhao ZK, Yu HL, Xiao F, et al. Muscle-derived stem cells differentiate into functional smooth muscle cells for ureter tissue engineering: An experimental study. Biotechnology & Bioprocess Engineering. 2012; 17(3):456-464.[29] Pelekanos RA, Li J, Gongora M, et al. Comprehensive transcriptome and immunophenotype analysis of renal and cardiac MSC-like populations supports strong congruence with bone marrow MSC despite maintenance of distinct identities. Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(1):58-73.[30] Zhuo W, Liao L, Xu T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal dysfunction by improving the antioxidant/oxidant balance in the ischemic kidney. Urol Int. 2011;86(2): 191-196.[31] 杨光,程庆砾,李春霖,等.肾组织干细胞向肾小管上皮细胞的诱导分化[J].南方医科大学学报,2015,35(2):163-167.[32] 温静,程庆砾,马强,等.肾组织干细胞对人肾小管上皮细胞损伤修复的作用[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2013,45(4): 619-624.[33] 温静.老年急性肾损伤的临床研究及肾组织干细胞对肾小管上皮细胞损伤修复的影响[D].北京:军医进修学院解放军总医院, 2012.[34] 温静,程庆砾,马强,等.肾组织干细胞对人肾小管上皮细胞损伤修复的作用[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2013, 45(4): 619-624. |