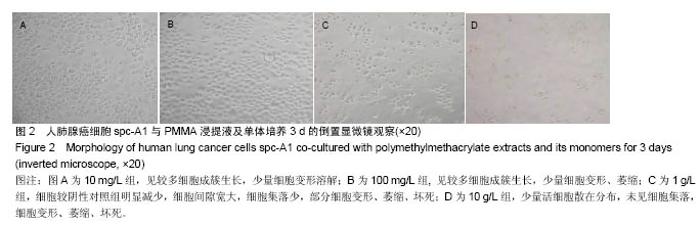
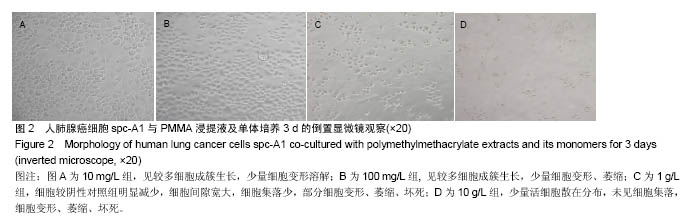
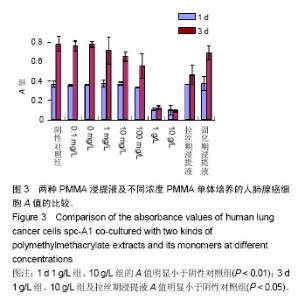
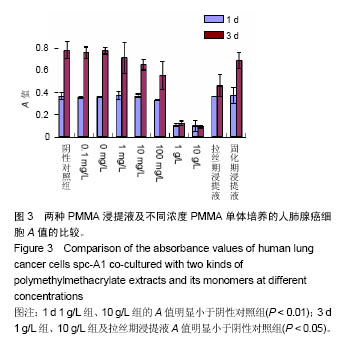
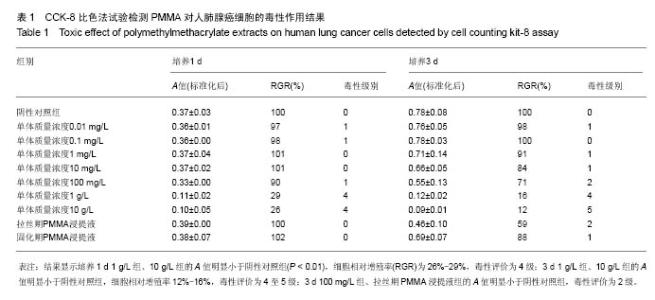
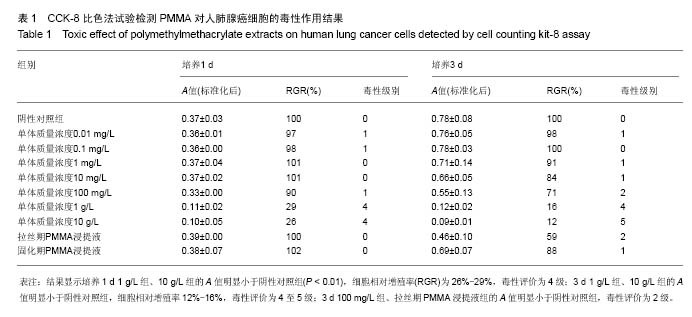
| [1]Boland PJ, Lane JM, Sundaresan N.Metastatic disease of the spine.Clin Orthop.1982;169:95-102.[2]Perrin RG, Laxton AW. Metastatic spine disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and evaluation of patients. NeurosurgClin N Am.2004;15(4):365-373.[3]宋奇志,李涛,奉成斌,等.经皮椎体成形使用骨水泥对心血管系统的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(21):3374-3379.[4]郝和平.生物医学材料生物学评价标准实施指南[M].北京:中国标准出版社.2000.[5]Do HM,Kim BS,Marcellus ML,et al.Prospective analysis ofclinical outcomes after pereutaneousvertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral body fractures.Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(7):1623-1628.[6]Dahl OE,Garvik LJ,Lyberg T.Toxic effects of methylmethacrylate monomer onleukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro.ActaOrthop Scand.l994;65:147-153.[7]Belkofl'SM, Molloy S.Temperature measurement during polymerization of polymethylmethacrylate cement used for vertebroplasty. Spine. 2003;28:1555-1559.[8]Azhar DA,Syed S,Luqman M,et al. Evaluation of methyl methacrylatemonomer cytotoxicity in dental lab technicians using buccal micronucleuscytome assay. Dent Mater J.2013; 32(3):519 -521.[9]Lai PL,Chen LH,Chen WJ,et al. Chemical and physical properties ofbone cement for vertebroplasty. Biomed J.2013; 36(4):162 -167.[10]Webb JC,Gbejuade H,Lovering A,et al. Characterisation of in vivorelease of gentamicin from polymethyl methacrylate cement using a novelmethod. IntOrthop.2013;37(10): 2031 -2036.[11]Dahl OE,Westvik AB, Kierulf P, et al. Effect of monomethylmethacrylateonprocoagulant activities of human monocytes and umbilical vein endothelial cells invitro.Thromb Res.1994;56: 377-387.[12]Dahl OE,Garvik LJ,Lyberg T.Toxic effects of methylmethacrylate monomer onleukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro.ActaOrthop Scand.1994;65:147-153.[13]Nishimiya H,Yamada M,Ueda T,et al. N-acetyl cysteine alleviatesinflammatory reaction of oral epithelial cells to poly (methyl methacrylate)extract. Acta Odontol Scand.2015:1-10.[14]Drozdz K,Wysokinski D,Krupa R,et al. Bisphenol A - glycidyl methacrylateinduces a broad spectrum of DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Arch Toxicol.2011;85(11):1453 -1461.[15]Radin EL,Rubin CT,Thrasher EL. Changes in the bone cement interface after total hip replacement.J Bone Joint Surg.1982;64:188-1200.[16]San Millan Ruiz D, Burkhardt K, Jean B, et al. Pathology findings with acrylic implants.Bone.1999;25:85-90.[17]Togada D,Bauer TW,Lieberman IH,et al.Histologic evaluation of human vertebral bodies after vertebral augmentation with polymethylmethacrylate. Spine. 2003;28:1521-1527.[18]Razuin R, Effat O, Shahidan MN, et al. Bone cement implantation syndrome. Malays J Pathol.2013;35(1):87-90.[19]Pikis S, Goldstein J, Spektor S.Potential neurotoxic effects of polymethylmethacrylate during cranioplasty. ClinNeurosci. 2015;22(1): 139-143.[20]陈珑. 经皮椎体成形术注射骨水泥对椎体肿瘤细胞毒作用的临床和实验研究[D]. 第二军医大学,2010年.[21]孙强,梁庆晨,郑加法,等. 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥混合唑来膦酸对乳腺癌细胞的细胞毒性研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(9):913-915.[22]Liu B M, Li M, Yin B S, et al. Effects of Incorporating Carboxymethyl Chitosan into PMMA Bone Cement Containing Methotrexate.Plos One. PLoS One. 2015;10(12): e0144407. |