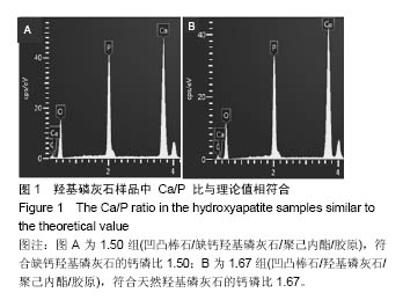
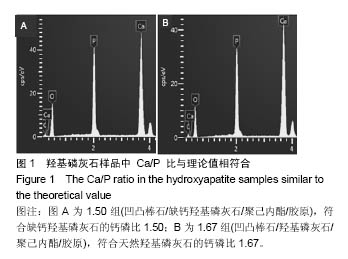
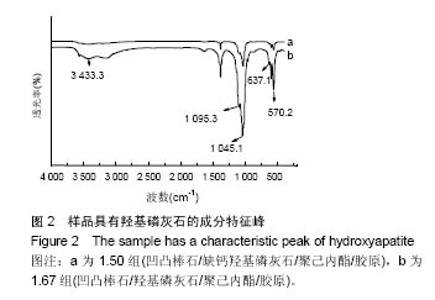
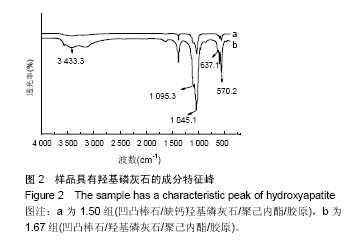
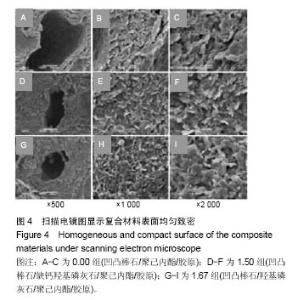
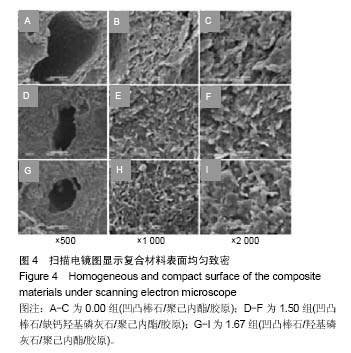
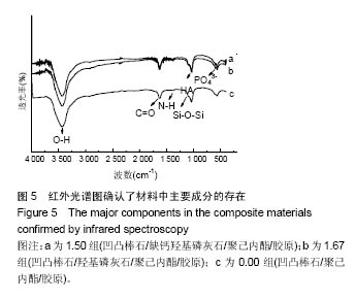
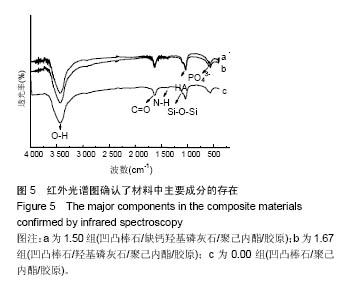
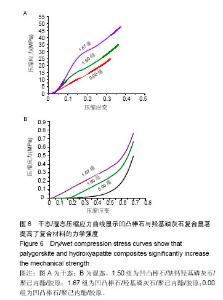
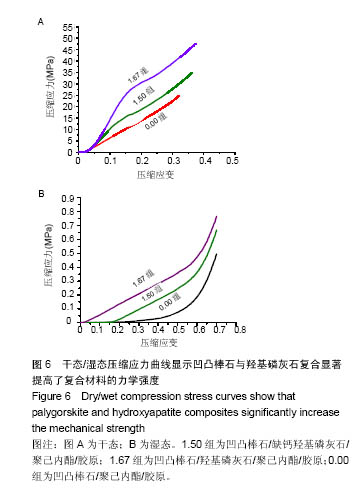
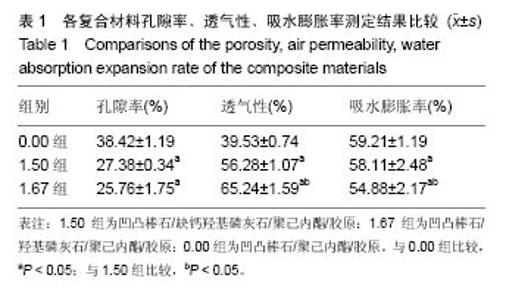
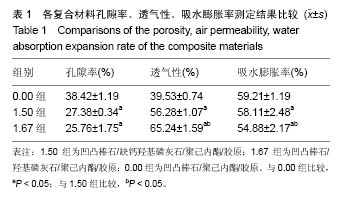
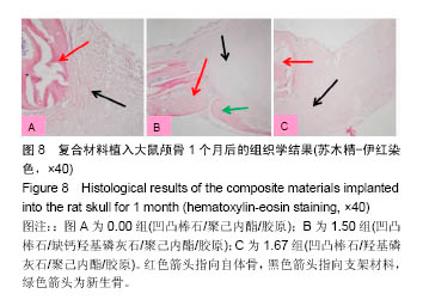
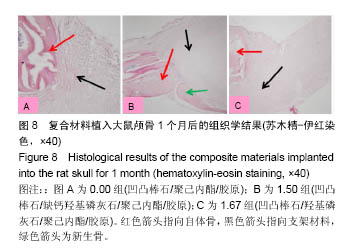
| [1]Neufurth M, Wang X, Schröder HC, et al. Engineering a morphogenetically active hydrogel for bioprinting of bioartificial tissuederived from humanosteoblast-like SaOS-2 cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35(31): 8810-8819.[2]Hashemibeni B, Dehghani L, Sadeghi F, et al. Bone Repair with Differentiated Osteoblasts from Adipose-derived Stem Cells in Hydroxyapatite/Tricalcium Phosphate In vivo. Int J Prev Med. 2016;7:62.[3]徐世希,欧阳丽娜,丁劲松. 凹凸棒石黏土及其应用进展[J].中南药学, 2009,7(6): 441-445.[4]王浩,张里程,石涛,等. 胶原-羟基磷灰石-硫酸软骨素-骨形态发生蛋白骨修复材料的性质评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(5):730-734.[5]Castilho M, Moseke C, Ewald A, et al. Direct 3D powder printing of biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds for substitution of complex bone defects. Biomaterial. 2014;6(1):015006. [6]Xue J, He M, Liu H, et al. Drug loaded homogeneous electrospun PCL/gelatin hybrid nanofiber structures for anti-infective tissue regeneration membranes. Biomaterials. 2014;35(34):9395-9405.[7]艾合麦提,玉素甫,陈统一,等. 可降解聚己内酯修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2005, 19(6): 439-442.[8]张达江,王亮.Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的结构、功能及其应用研究的现状与前景[J]. 生物技术通讯,2006,17(2):265-269.[9]何立志,冯祖德. 不同Ca/P纳米缺钙羟基磷灰石的微波合成和表征[J]. 广州化工,2009,37(4):74-76.[10]王学江,李玉宝. 羟基磷灰石纳米针晶与聚酰胺仿生复合生物材料研究[J]. 高技术通讯,2001,11(5):1-5.[11]王迎军, 杜昶, 赵娜如, 等. 仿生人工骨修复材料研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报,2012,40(10):51-58.[12]李强. 可注射骨组织工程材料的制备与性能研究[D]. 华中科技大学,2009.[13]帅丽. 缺钙纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原复合支架材料的制备[D]. 重庆大学,2010[14]吴晓东. 生物活性骨组织工程支架的研究及介孔羟基磷灰石的初步探讨[D]. 吉林大学,2012.[15]朱爱臣. 一种可用于引导组织再生技术的淀粉/PVA膜的制备及性能研究[D].北京化工大学,2010.[16]Park HJ, Yu SJ, Yang K, et al. Paper-based bioactive scaffolds for stem-mediated bone tissue engineering. Biomaterial. 2014;35(37):9811-9823.[17]Li H, Xue K, Kong N, et al. Silicate bioceramics enhanced vascularization and osteogensis through stimulating in teractions between endothelia cells and bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35(12):3803-3818.[18]Hettiaratchi MH, Miller T, Temenoff JS, et al. Heparin microparticle effects on presentation and bioactivity of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomaterials. 2014;35(25):7228-7238.[19]Cholas R, Kunjalukkal Padmanabhan S, et al. Scaffolds for bone regeneration made of hydroxyapatite microspheres in a collagen matrix. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;63: 499-505.[20]Castilho M, Moseke C, Ewald A, et al. Direct 3D powder printing of biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds for substitution of complex bone defects. Biofabrication. 2014;6(1):015006. [21]Xue J, He M, Liu H, et al. Drug loaded homogeneous electrospun PCL/gelatin hybrid nanofiber structures for anti-infective tissue regeneration membranes. Biomaterials. 2014;35(34):9395-9405. [22]贾帅军. 定向结构软骨支架复合骨髓基质干细胞修复兔关节软骨缺损的研究[D]. 第四军医大学,2012.[23]Han B, Perelman N, Tang B, et al. Collagen-targeted BMP3 fusion proteins arrayed on collagen matrices or porous ceramics impregnated with Type I collagen enhance osteogenesis in a rat cranial defect model. Orthop Res.2002;20(4):747-755.[24]Kume S, Kato S, Yamagishi S, et al. Advanced glycation end-products attenuate human mesenchymal stem cells and prevent cognate differentiation into adipose tissue, cartilage, and bone. Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(9):1647-1658. |