Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (47): 7034-7042.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.47.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteoinductive calcium phosphate ceramics repair alveolar cleft defects
- 1Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2016-08-29Online:2016-11-18Published:2016-11-18 -
Contact:Liang Zhi-gang, Chief physician, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Hao-dong, Master, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Basic Research Program of Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen, No. JCYJ20130401111426275, JCYJ20140414170821224
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Hao-dong, Yao Jin-feng, Liang Zhi-gang. Osteoinductive calcium phosphate ceramics repair alveolar cleft defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(47): 7034-7042.
share this article
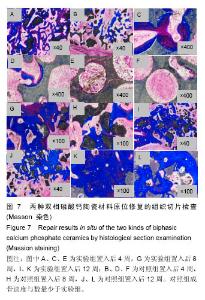
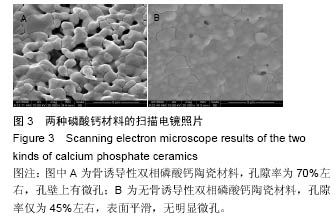
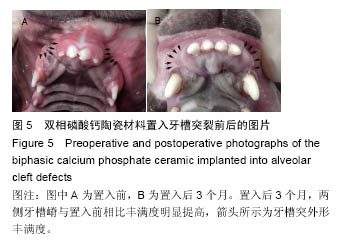
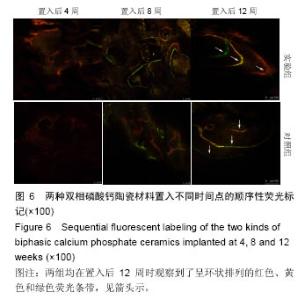
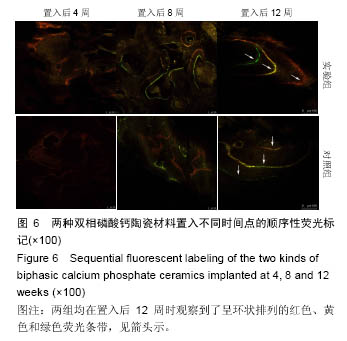
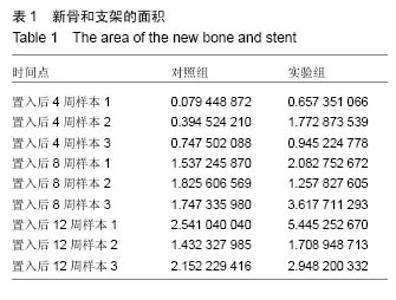
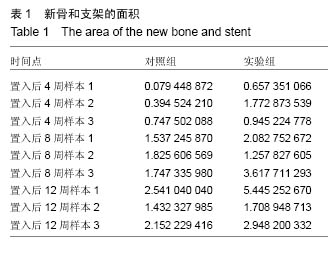
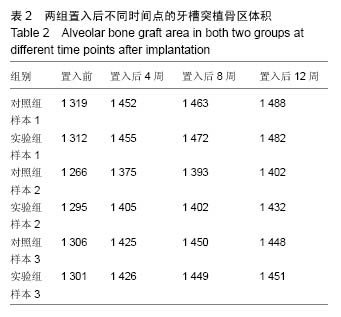
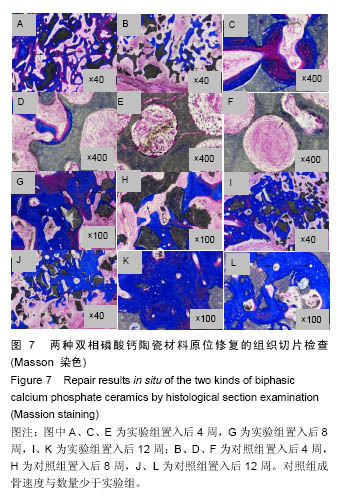
使用南方科技大学Leica TCS SP8共聚焦显微镜(81-1005)观察固有骨诱导性磷酸钙材料原位修复牙槽突裂的成骨情况。两组材料都在置入第4周观察到红色荧光条带,在第8周观察到了红色和黄色荧光条带,而在12周观察到了呈环状排列的红色、黄色和绿色荧光条带。 2.2.3 原位修复(牙槽嵴缺损区)结果 见图7。 实验组:置入4周时,可发现材料近远端成骨表现不尽相同,靠近自体骨的材料孔隙中已有钙化新骨长入(图7A蓝染),贴壁生长,与材料结合紧密,内含有芝麻粒样骨细胞(图7C箭头示),新骨内面边缘可见大量红染胶原成分(图7A红染),为未钙化的骨基质,中心为类似骨髓腔形态,可见小血管;而远离自体骨的材料孔隙中尚未见到钙化新骨生成,但紧贴孔壁可见体积较大的破骨细胞样细胞及沿着孔隙边缘排列的高柱状成骨细胞(图7E箭头示)。 8周时,全部材料内均可见大量新骨长入,形成条索状类似骨小梁结构,成骨活跃(图7G箭头示)。 12周时,成骨速度减慢,骨改建明显,材料逐渐分解,间隙由大量成熟骨组织充填,与剩余材料结合紧密,并可见大量典型哈弗氏管结构(图7I、K箭头示)。 对照组:置入4周时,可见材料与自体骨连接部分有少量新骨形成,亦是从自体骨边缘长入材料间隙(图7B、D箭头示),而材料远端可见少量破骨细胞样细胞(图7F箭头示),未见骨形成和成骨细胞(图7F箭头示),新骨形成启动明显慢于实验组。 8周时,可见材料靠近自体骨的边缘有大量新骨长入,并可见成骨较为活跃(图7H箭头示)。 12周时,材料孔隙由大量成熟骨质充填(图7J箭头示),新骨与材料结合紧密,亦可见少量哈弗氏管结构(图7L箭头示),骨组织形态与实验组相差不大,但成骨速度及成骨量少于实验组。 实验组置入后8,12周的新骨占支架面积的比例均高于对照组(P < 0.05),见表1。"
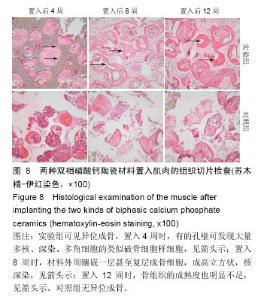
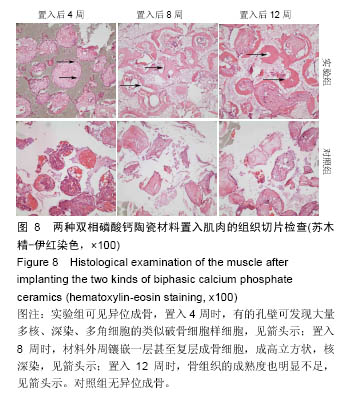
2.2.4 异位修复(大腿肌肉区)结果,见图8。 实验组:各个时间点的所有样本均观察到骨诱导现象。置入4周时,材料孔隙紧贴着支架边缘可见一圈核深染,体积较大,排列紧密的成骨细胞带,分泌旺盛,有未钙化骨基质沉积。有的孔壁可发现大量多核、深染、多角细胞的类似破骨细胞样细胞,仅个别材料孔隙内有少量钙化新骨形成。8周时,所有材料孔腔孔隙均可见新骨生长,新骨厚度大致占孔半径的1/4,有的甚至达到1/3,外周镶嵌一层甚至复层成骨细胞,成高立方状,核深染。12周时,含有骨陷窝的新骨逐渐增厚,在材料孔腔形成条索状的小梁骨,相邻孔腔中的骨小梁已相互连接,还尚未见到典型的哈弗氏管结构,该成骨方式为典型的膜内成骨。与原位中材料成骨相比,其成骨过程非常类似,差别仅是在相同观察期异位成骨厚度明显较薄,新骨量少,骨小梁相对较细,骨组织的成熟度也明显不足。 对照组:所有时间点的所有样本均未观察到异位新骨形成,材料间隙仅可见结缔组织和少量类骨质,可见无诱导性双相磷酸钙陶瓷没有骨诱导性。"
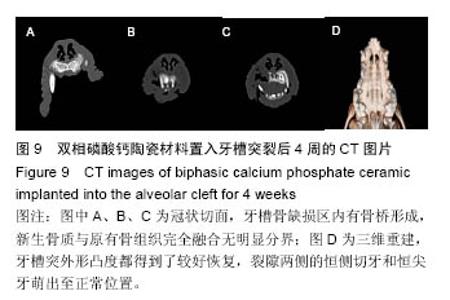
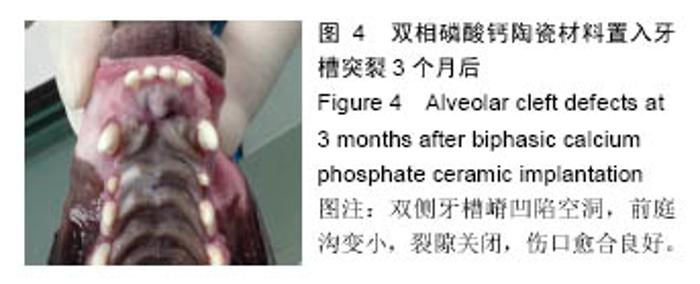
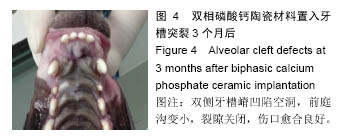
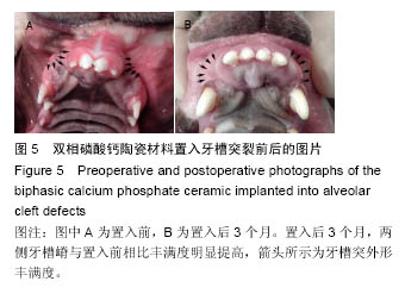
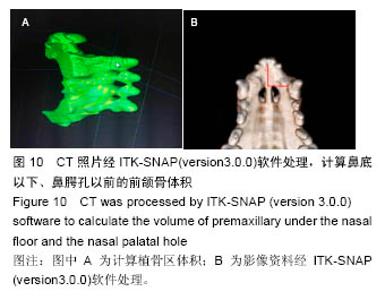
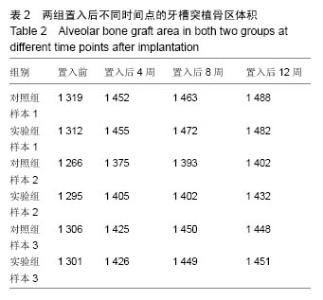
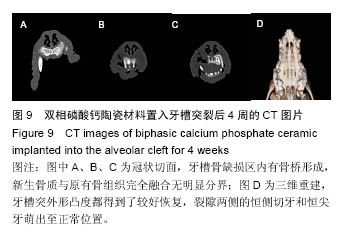
2.2.5 上颌骨螺旋CT观察结果 材料置入前和置入后4周,发现牙槽骨缺损区内有骨桥形成,新生骨质与原有骨组织完全融合无明显分界(图9A);垂直向显示,牙槽突缺损区骨桥高度接近于原有牙槽骨高度(图9B,C)。三维重建显示,两组材料修复的牙槽突外形凸度都得到了较好恢复,裂隙两侧的恒侧切牙和恒尖牙萌出至正常位置(图9D)。 在两种材料置入8,12周,双侧牙槽突外形仍然未见明显吸收凹陷。影像资料由香港中文大学医学影像计算机研究中心经ITK-SNAP(version3.0.0)软件处理(图10A),分别计算两侧植骨区体积(图10B红线所标),用SPSSv18.0软件包先对同种材料不同时期牙槽突总体积进行单因素方差分析。方差齐性检验示P=0.897,证明方差齐性。 方差分析结果显示,同一材料置入后不同时期牙槽突体积无统计学差异(F=0.434,P=0.817);同一时期,两组间的牙槽突体积变化值无差异(P=0.393),见表2,表明不同材料对牙槽裂植骨后牙槽突体积的变化无明显影响。 "
| [1]Boyne PJ,Sands NR.Secondary bone grafting of residual alveolar and palatal clefts. J Oral Surg. 1972; 30(2):87-92. [2]Giannoudis PV,Dinopoulos H,Tsiridis E.Bone substitutes: an update.Injury.2005;36 Suppl 3:S20-S27. [3]Habibovic P,de Groot K.Osteoinductive biomaterials--properties and relevance in bone repair.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2007;1(1):25-32. [4]Moreau JL,Caccamese JF,Coletti DP,et al.Tissue engineering solutions for cleft palates.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2007;65(12):2503-2511. [5]Gimbel M,Ashley RK,Sisodia M,et al.Repair of alveolar cleft defects: reduced morbidity with bone marrow stem cells in a resorbable matrix.J Craniofac Surg. 2007; 18(4):895-901. [6]Thawani JP,Wang AC,Than KD,et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins and cancer: review of the literature.Neurosurgery.2010;66(2):233-246,246. [7]Ravaglioli A,Krajewski A.Bioceramics and the human body[M].London: Elsevier Applied Science, 1992:519. [8]Zhang D,Chu F,Yang Y,et al.Orthodontic tooth movement in alveolar cleft repaired with a tissue engineering bone: an experimental study in dogs.Tissue Eng Part A.2011; 17(9-10):1313-1325. [9]姜宁.扩弓对犬牙槽突裂植骨区改建影响的CT研究[D].上海交通大学,2008. [10]Lexer E.The use of free osteoplasty together with trials on arthrodesis and joint transplantation. Archiv für klin Chirurgie. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;446(8): 1771-1776. [11]Drachter R.Erfahrungen mit dem Friedmannschen Heilmittel bei chirurgischer Tuberkulose1).Dtsch Med Wochenschr.1914;40(28):1422-1425. [12]Sittitavornwong S,Gutta R.Bone graft harvesting from regional sites.Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2010;22(3):317-330. [13]Larossa D,Buchman S,Rothkopf DM,et al.A comparison of iliac and cranial bone in secondary grafting of alveolar clefts.Plast Reconstr Surg.1995; 96(4):789-797,798-799. [14]Segura-Castillo JL,Aguirre-Camacho H,Gonzalez-Ojeda A,et al.Reduction of bone resorption by the application of fibrin glue in the reconstruction of the alveolar cleft.J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16(1):105-112. [15]Feichtinger M,Mossbock R,Karcher H.Evaluation of bone volume following bone grafting in patients with unilateral clefts of lip, alveolus and palate using a CT-guided three-dimensional navigation system.J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2006;34(3):144-149. [16]Berglundh T,Lindhe J,Sterrett JD.Clinical and structural characteristics of periodontal tissues in young and old dogs.J Clin Periodontol.1991;18(8):616-623. [17]Linton JL,Sohn BW,Yook JI,et al.Effects of calcium phosphate ceramic bone graft materials on permanent teeth eruption in beagles.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2002;39(2): 197-207. [18]Hossain MZ,Kyomen S,Tanne K.Biologic responses of autogenous bone and beta-tricalcium phosphate ceramics transplanted into bone defects to orthodontic forces.Cleft Palate Craniofac J.1996;33(4):277-283. [19]Ahuja RB.Radical correction of secondary nasal deformity in unilateral cleft lip patients presenting late.Plast Reconstr Surg.2001;108(5):1127-1135. [20]王炜.整形外科学[M].浙江:浙江科学技术出版社, 1999: 694-695. [21]Frost HM,Villaneuva AR.Tetracycline staining of newly forming bone and mineralizing cartilage in vivo.Stain Technol.1960;35:135-138. [22]Harris WH,Jackson RH,Jowsey J.The in vivo distribution of tetracyclines in canine bone.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1962;44-A:1308-1320. [23]Treharne RW,Brighton CT.The use and possible misuse of tetracycline as a vital stain.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1979;(140):240-246. [24]Johnson RH,Mitchell DF.The effects of tetracyclines on teeth and bones.J Dent Res.1966;45(1):86-93. [25]Habibovic P,Sees TM,van den Doel MA,et al. Osteoinduction by biomaterials--physicochemical and structural influences.J Biomed Mater Res A.2006; 77(4): 747-762. [26]Habibovic P,Yuan H,van den Doel M,et al.Relevance of osteoinductive biomaterials in critical-sized orthotopic defect.J Orthop Res.2006;24(5):867-876. [27]Newlands LC.Secondary alveolar bone grafting in cleft lip and palate patients. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2000; 38(5):488-491. [28]Ramstad T,Semb G.The effect of alveolar bone grafting on the prosthodontic/reconstructive treatment of patients with unilateral complete cleft lip and palate.Int J Prosthodont.1997;10(2):156-163. [29]Long RJ,Spangler BE,Yow M.Cleft width and secondary alveolar bone graft success. Cleft Palate Craniofac J.1995;32(5):420-427. [30]Shen Y, Ma HY, Zhang YS, et al.Orthodontic surgery with alveolar cleft grafting in patients with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate: a feasibility analysis based on cone-beam CT three-dimensional reconstruction.Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2015;19(11): 1678-1682. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||