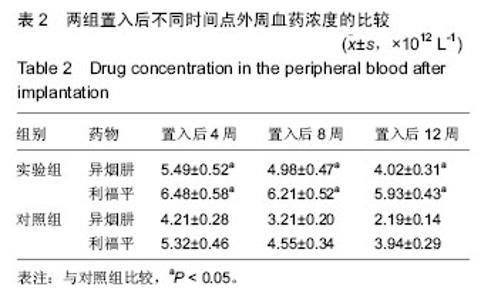
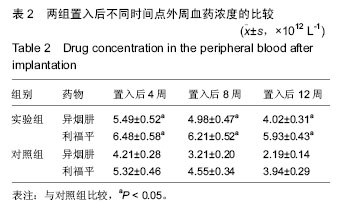
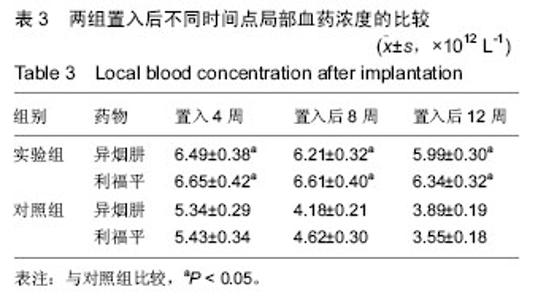
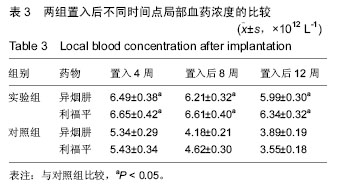
| [1]张宏其,高琪乐,郭虎兵,等. 人同种异体骨载异烟肼-壳聚糖缓释微球的制备和体内外释药特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(3):479-483.
[2]Ouellet H,Ouellet Y,Richard C,et al.Truncated hemoglobin HbN protects Mycobacterium bovis from nitric oxide.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:5902-5907.
[3]全国结核病流行病学抽样调查技术指导组. 第四次全国结核病流行病学抽样调查报告[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2002,25(1):3-8.
[4]Ma YZ,Xue HD,Surgical strategy for spinal tuberculosis. Chin J Spine Spinal Cord, 2009;19(11): 805-807.
[5]孙洁.脊柱结核患者围术期的护理需求及护理干预[J].实用临床医药志,2012,16(6):63-70.
[6]陆宇,王彬,郑梅琴,等.应用AlamarBlue和MTT测定抗结核药物最低抑菌浓度的研究[J].中国防痨杂志, 2007, 29(6): 499-501.
[7]德向研,施建党,王自力,等.载三联抗结核药硫酸钙/氨基酸聚合物人工骨体内缓释实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(6):531-536.
[8]中华结核和呼吸疾病杂志编委会,抗结核药物引起的毒副作用综合报道[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2000,21(1): 40-43.
[9]燕荣帅,李力韬,张泽华.耐利福平脊柱结核的分子药敏检测及药物缓释系统的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(21):1807-1809.
[10]Ma Y,Cui X,Li H,et al.The outcome of anterior or posterior instrumentation under different surgical procedure in the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis in adults.Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):299-305.
[11]崔旭,马远征,陈兴,等.不同手术方法治疗脊柱结核及其疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(10):807-812.
[12]折胜利.PLA/PLGA共聚物在组织工程中的应用[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2011,7(4):235-237.
[13]赵锡江,齐新生,董寅生. rhBMP-2/PLGA缓释支架的制备及对MSCs细胞成骨活性的体外研究[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2010,33(3):147-151.
[14]Chono S,Tanino T,Seki T,et al.Efficient drug delivery to alveolar macrophages and lung epithelial lining fluid following pulmonary administration of liposomal ciprofloxacin in rats with pneumonia and estimation of its antibacterial effects.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009; 34(10):1090-1096.
[15]张海晴,刘成勇,孙庆,等.Mtb耐异烟肼基因变异株的在体外最小抑菌浓度[J].中华防痨杂志,2012,34(7):452-454
[16]安汝玉,易洪城,唐良华.载抗结核药缓释剂的临床效应[J].贵阳中医学院学报,2012,34(5):215-217.
[17]崔旭,马远征,李大伟,等.复合骨形态发生蛋白缓释材料修复兔桡骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(51): 9558-9562.
[18]Jutte PC,Rutgers SR,Van Altena R,et al.Penetration of isoniazid,rifampicin and pyrazinamide in tuberculous pleural effusion and psoas abscess.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis.2004;8(11):1368-1372.
[19]Li JQ,Wang SL,Xu F,et al.Therapeutic effectiveness of slow-release PLGA-oxaliplatin microsphere on human colorectal tumor-bearing mice,Anticancer Drugs. 2010; 21:600-608.
[20]袁凯,陈建庭.脊柱结核外科治疗植骨材料的临床应用与研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(21): 1957-1959.
[21]伍卫刚,郑启新,郭晓东.利福平-异烟肼-控释型载药人工骨的实验研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2010,29(1): 137-142.
[22]赵莉,何晨光,高永娟,等.PLGA的不同组成对支架材料性能的影响研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2008,28(5):22-28.
[23]Yang F,Cui W, Xiong Z,et al.Poly/tricalcium phosphate composite scaffold and its various changes during degradation in vitro.Polym Degrad Stabil. 2006;91(12): 3065-3073.
[24]Zhu M,Wang H,Liu J,et al.A mesoporous silica nanoparticulate/β-TCP/BG composite drug delivery system for osteoarticular tuberculosis therapy. Biomaterials.2011;32(7):1986-1965.
[25]胡杨,马莹,何惠宇.β-磷酸三钙支架材料即刻植入对保存剩余牙槽嵴的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(16):2905-2910.
[26]万蕾蕾,刘宏伟.β-磷酸三钙复合骨髓基质细胞构建组织工程骨的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2010,26(4): 497-500.
[27]陈永锋,王林,张扬,等.以β-磷酸三钙为支架组织工程骨在兔脊柱后外侧融合中的作用研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2012,9(1):8-12.
[28]Shu CC,Lee CH,Lee MC,et al.Hepatotoxicity due to first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs: a five-year experience in a Taiwan medical centre.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013; 17(7):934-939.
[29]Nuermberger EL,Rosenthal IM,Tasneen R,et al.Reply to "Contradictory results with high-dosage rifamycin in mice and humans".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(2):1104-1105.
[30]贾平平,余利岩,岑山.抗结核一线药物及结核分枝杆菌的耐药分子机制[J].中国抗生素杂志,2011,36(7):487-491.
[31]童叶青,侯双翼,叶建君,等.抗结核药物研究进展[J].中国药师,2013,16(8):1236-1239.
[32]Zumla A,Nahid P,Cole ST.Advances in the development of new tuberculosis drugs and treatment regimens.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2013;12(5):388-404.
[33]崔玉彬,曹胜华,蒋晓磊.抗结核药物的研究新进展[J].中国抗生素杂志,2010,35(5):321-333.
[34]Ahmad S,Mokaddas E.Current status and future trends in the diagnosis and treatment of drug-susceptible and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.J Infect Public Health. 2014;7(2):75-91.
[35]Sekiguchi J,Disratthakit A,Maeda S,et al.Characteristic resistance mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to DC-159a,a new respiratory quinolone.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2011;55(8):3958-3960.
[36]钟洪兰,李祥,李卫,等.三种护肝药治疗结核病药物性肝损害的成本-效果分析[J].现代医院,2012,12(12):50-51.
[37]邵红,杜玲玲,孙晋翠,等.用甲硫氨酸维B1联合护肝片治疗脂肪肝的临床研究[J].求医问药:学术版, 2011,9(8): 257-257.
[38]李红山,陈少东.多烯磷脂酰胆碱改善脂肪肝新西兰大白兔肝脏脂质沉积的作用机制研究[J].医学研究杂志, 2010,39(12):73-77.
[39]刘鸿凌,尹明红,游绍丽,等. 甘草酸制剂治疗药物性肝损害患者疗效观察[J].实用肝脏病杂志, 2013,16(3): 257-258.
[40]冯悦静,陈裕,闫振富.硫普罗宁治疗抗结核药物所致肝损害35例疗效观察[J].中西医结合肝病杂志, 2013,23(1): 56-57. |