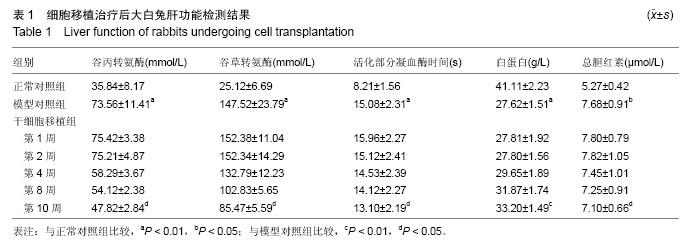
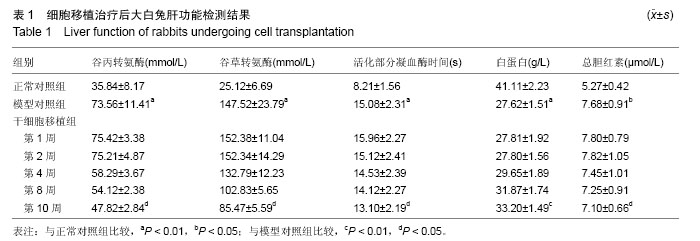
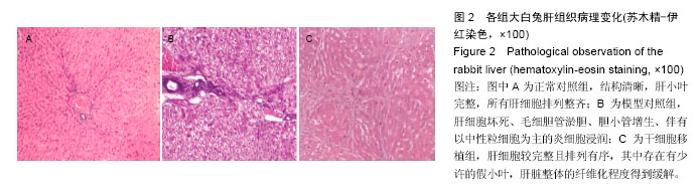
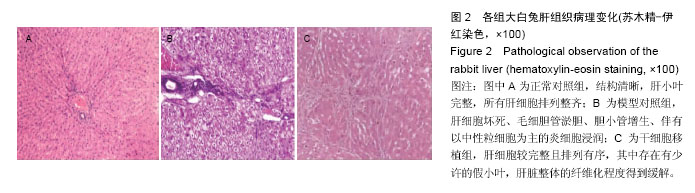
| [1] 李小红,叶军.中医及中西医结合治疗肝硬化研究进展[J].实用中医内科杂志,2011,25(12):49-51.
[2] 范婷婷,谢渭芬.肝纤维化和肝硬化治疗进展[J].国际消化病杂志,2010,30(6):349-351.
[3] 张海苗.不同干预方法对肝硬化住院患者心理社会状况、生活质量及疗效的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2011.
[4] 卢昆云,杨晋辉.干细胞移植治疗肝硬化的移植途径及优缺点比较[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2011,27(11): 1226-1228, 1232.
[5] Yao P, Zhan Y, Xu W, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor-induced proliferation of hepatic stem-like cells depends on activation of NF-kappaB. J Hepatol. 2004; 40(3):391-398.
[6] 姚鹏,詹轶群,许望翔,等.细胞生长因子在体外对大鼠肝干细胞的影响[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2003,11(1):33-36.
[7] Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, et al. Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999;284(5417):1168-1170.
[8] Miyazaki M, Akiyama I, Sakaguchi M, et al. Improved conditions to induce hepatocytes from rat bone marrow cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002; 298(1):24-30.
[9] Wollert KC, Meyer GP, Lotz J, et al. Intracoronary autologous bone-marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: the BOOST randomised controlled clinical trial. Lancet. 2004;364(9429):141-148.
[10] 金博,程留芳,孙涛,等.兔四氯化碳实验性肝硬化模型的建立[J].海军总医院学报,2005,18(3):129-131.
[11] 熊全,冯吉,王军,等.3种不同途径移植骨髓间充质干细胞治疗肝硬化模型大鼠的效果比较[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2011,33(8):804-808.
[12] Kania G, Blyszczuk P, Jochheim A, et al. Generation of glycogen- and albumin-producing hepatocyte-like cells from embryonic stem cells. Biol Chem. 2004;385(10): 943-953.
[13] 李力,滕皋军.肝细胞移植实验研究中大鼠肝细胞的冻存与复苏初探[J].中华放射学杂志,2002,36(4):369-372.
[14] Malhi H, Gupta S. Hepatocyte transplantation: new horizons and challenges. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2001;8(1):40-50.
[15] Avital I, Feraresso C, Aoki T, et al. Bone marrow-derived liver stem cell and mature hepatocyte engraftment in livers undergoing rejection. Surgery. 2002;132(2):384-390.
[16] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.
[17] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al. Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature. 2001; 410(6829):701-705.
[18] Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, et al. Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999;284(5417):1168-1170.
[19] Oh SH, Miyazaki M, Kouchi H, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor induces differentiation of adult rat bone marrow cells into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;279(2):500-504.
[20] Zhou YM, Hu DR, Yao P, et al. Study of mouse marrow cells differentiation into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2004;12(12):722- 725.
[21] Theise ND, Badve S, Saxena R, et al. Derivation of hepatocytes from bone marrow cells in mice after radiation-induced myeloablation.Hepatology. 2000; 31(1):235-240.
[22] Avital I, Inderbitzin D, Aoki T, et al. Isolation, characterization, and transplantation of bone marrow-derived hepatocyte stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;288(1):156-164.
[23] Mitchell C, Fausto N. Bone marrow-derived hepatocytes : rare but promising. Am J Pathol. 2002; 161(2):349-350.
[24] Schwartz RE, Reyes M, Koodie L, et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Clin Invest. 2002; 109(10):1291-1302.
[25] Okumoto K, Saito T, Haga H, et al. Characteristics of rat bone marrow cells differentiated into a liver cell lineage and dynamics of the transplanted cells in the injured liver. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41(1):62-69.
[26] Theise ND, Badve S, Saxena R, et al. Derivation of hepatocytes from bone marrow cells in mice after radiation-induced myeloablation. Hepatology. 2000; 31(1):235-240.
[27] Cantz T, Sharma AD, Jochheim-Richter A, et al. Reevaluation of bone marrow-derived cells as a source for hepatocyte regeneration. Cell Transplant. 2004;13(6):659-666.
[28] Yannaki E, Athanasiou E, Xagorari A, et al. G-CSF-primed hematopoietic stem cells or G-CSF per se accelerate recovery and improve survival after liver injury, predominantly by promoting endogenous repair programs. Exp Hematol. 2005;33(1):108-119.
[29] Kuo TK, Hung SP, Chuang CH, et al. Stem cell therapy for liver disease: parameters governing the success of using bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(7):2111-2121.
[30] Mohamadnejad M, Namiri M, Bagheri M, et al. Phase 1 human trial of autologous bone marrow-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13(24):3359-3363.
[31] Yao P, Zhan Y, Xu W, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor-induced proliferation of hepatic stem-like cells depends on activation of NF-kappaB. J Hepatol. 2004; 40(3):391-398.
[32] Kushida T, Inaba M, Hisha H, et al. Crucial role of donor-derived stromal cells in successful treatment for intractable autoimmune diseases in mrl/lpr mice by bmt via portal vein. Stem Cells. 2001;19(3):226-235.
[33] 张强,李京雨,徐力扬,等.经肝动脉骨髓干细胞移植治疗肝硬化的初步临床应用[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2005, 2(4):261-263.
[34] 曹葆强,林继宗,钟跃思,等.自体骨髓细胞经门静脉移植治疗肝硬化与肝功能不全的临床研究[J].中华普通外科杂志, 2007,22(5):386-389.
[35] 潘兴南,沈建坤,庄岳鹏,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗终末期肝病临床研究[J].南方医科大学学报,2008,28(7): 1207-1209.
[36] Terai S, Ishikawa T, Omori K, et al. Improved liver function in patients with liver cirrhosis after autologous bone marrow cell infusion therapy. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(10):2292-2298.
[37] Gordon MY, Levicar N, Pai M, et al. Characterization and clinical application of human CD34+ stem/ progenitor cell populations mobilized into the blood by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(7):1822-1830.
[38] Kharaziha P, Hellström PM, Noorinayer B, et al. Improvement of liver function in liver cirrhosis patients after autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection: a phase I-II clinical trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21(10):1199-1205. |