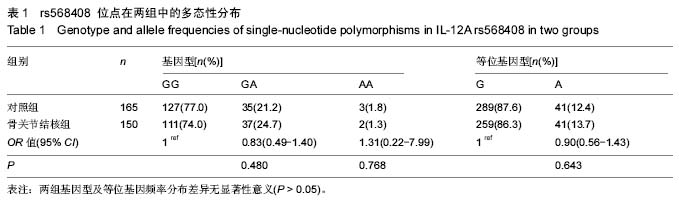
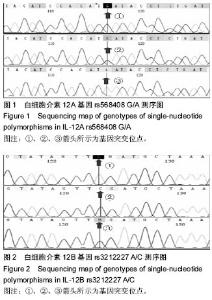
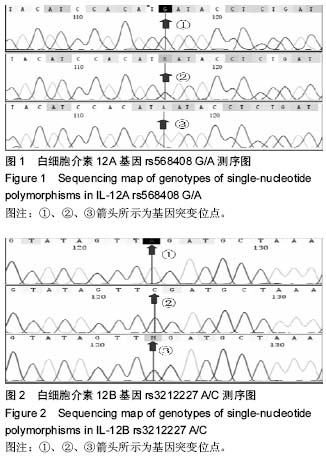
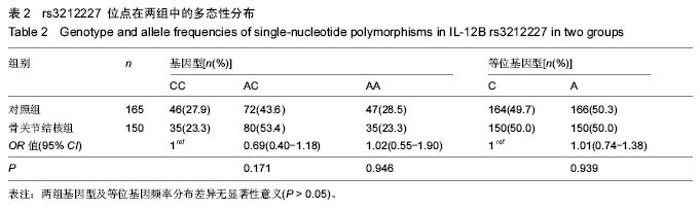
| [1] |
Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin.
Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339.
|
| [2] |
Liu Cong, Liu Su.
Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074.
|
| [3] |
Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei.
In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141.
|
| [4] |
Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian.
The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812.
|
| [5] |
Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting.
Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820.
|
| [6] |
Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong.
Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515.
|
| [7] |
Ma Zhijie, Li Jingyu, Cao Fang, Liu Rong, Zhao Dewei.
Influencing factors and biological property of novel biomedical materials: porous silicon carbide coated with bioactive tantalum
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 558-563.
|
| [8] |
Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui.
Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569.
|
| [9] |
Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng.
Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599.
|
| [10] |
Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han.
Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606.
|
| [11] |
Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He.
Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620.
|
| [12] |
Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei.
Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631.
|
| [13] |
Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia.
Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643.
|
| [14] |
Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian.
Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650.
|
| [15] |
Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong.
Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430.
|