Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (18): 3374-3380.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.18.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Systematic evaluation of extracorporeal bioartificial liver support system for the treatment of liver failure
Gu Jin-yang1, 2, Shi Xiao-lei1, 2, Ren Hao-zhen1, Xiao Jiang-qiang1, Ding Yi-tao1, 2
- 1 Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China
2 Jiangsu Clinical Center of Hepatobiliary Disease, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2012-10-19Revised:2013-01-21Online:2013-04-30Published:2013-04-30 -
Contact:Ding Yi-tao, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Clinical Center of Hepatobiliary Disease, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China dingyitao@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Gu Jin-yang☆, Doctor, Attending physician, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Clinical Center of Hepatobiliary Disease, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China gjynyd@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gu Jin-yang, Shi Xiao-lei, Ren Hao-zhen, Xiao Jiang-qiang, Ding Yi-tao. Systematic evaluation of extracorporeal bioartificial liver support system for the treatment of liver failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(18): 3374-3380.
share this article
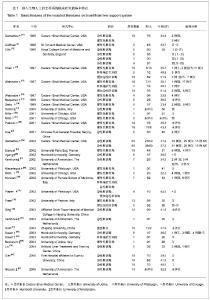
2.1 文献检索结果 在PubMed数据库共检索到2 812篇文章,Cochrane数据库检索到10篇论文。其中3篇因非英语论文被排除,另有2 778篇研究为摘要、评论、综述、动物实验或非相关研究。剩余41篇相关研究经进一步筛选后,发现尚有9项研究由于数据不足而无法纳入,1篇为重复发表论文,故最终共有31篇文献纳入本项研究。 2.2 纳入研究特征 纳入的研究及患者特征详见表1。 其中美国14项[11-12, 14-22, 24, 28-29, 31],中国5项[23, 33, 35, 39-40],意大利4项[19, 30, 32, 38],德国3项[26, 36-37],荷兰3项[27, 34, 41],英国和法国各1项[13,25]。"
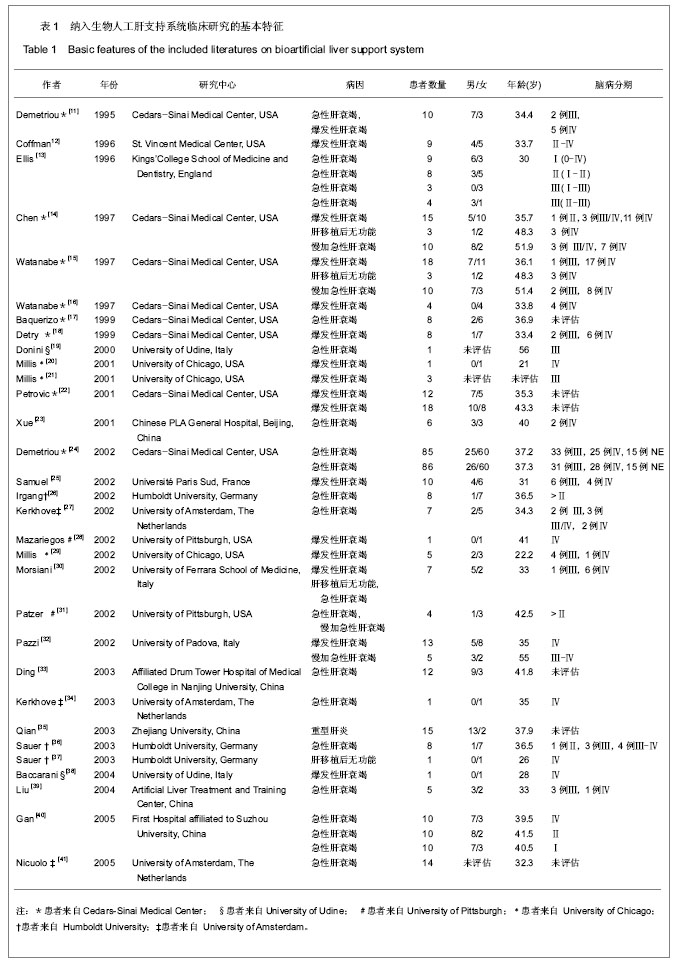
2项随机对照试验进行了有关ELAD和HepatAssist研究[13, 24]。除去以上4项研究,剩余29篇文献均为BAL安全性和有效性的观察。共10种BAL装置应用于临床研究,分别为HepatAssist[11-12, 14-18,22, 24-25,32],ELAD[13, 20-21,29],TECA-HALSS[23, 33, 35, 40],AMC-BAL[27, 34, 41],LSS[26, 36],BLSS[28, 31],RFB[30, 38],MELS[37],HBL和BHS[19,39]。481例患者的年龄范围从21-56岁,男女比例为1∶1.35,大部分患者有脑病分期(26/31),Ⅲ期和Ⅳ期比例分别为21.62% 和33.47%。31项研究中肝脏疾病的类型有:急性肝衰竭[11, 13, 17, 19, 23-24, 26-27, 30-31, 33-34, 36, 39, 41],爆发性肝衰竭[11-12, 14-16, 18, 20-22, 25, 28-30, 32, 38],肝移植后无功 能 [14-15, 30, 37],慢加急性肝衰竭和重症肝炎[14-15, 31-32, 35]。 2.3 BAL治疗情况 见表2。"

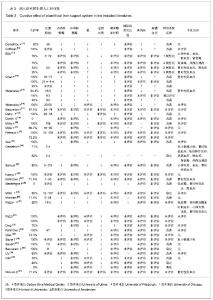
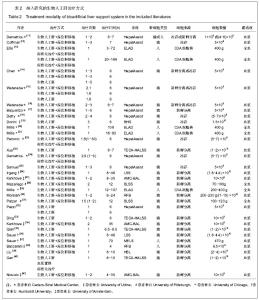
大多数患者接受了一二次BAL治疗,最多者接受了9次治疗[24]。每次治疗时间根据不同的系统,3-168 h不等。不同的系统使用的细胞数量也不同,如HepatAssist系统使用了5×109个细胞,而MELS则需要470 g细胞,一般来说以10×109到 20×109个肝脏细胞数为最多见。在细胞类型选择方面,大多数的BAL系统选择新鲜分离的猪肝细胞,除此之外,还有使用低温冻存的猪肝细胞、低温冻存或新鲜分离的人肝细胞及C3A肝细胞株等。 2.4 BAL治疗结果 大多数作者描述了临床和生化指标、肝移植过渡期、存活率和不良反应事件,以评估BAL治疗效果。大体而言,上述指标均有不同程度改善,包括转氨酶、血氨、总胆红素、凝血酶原时间、国际标准化比值、颅内压和脑灌注压。大部分患者神经系统的功能状态也得到了改善或稳定。其中肝移植过渡期从3 h到8 d不等。值得一提的是,两项随机对照试验结果不尽如人意。Ellis等[13]报道了生物人工肝联合原位肝移植治疗组与单纯原位肝移植手术组在生存期方面统计并无明显差异。Demetriou等[24]报道了在使用HepatAssist系统治疗的患者中,只有因过量摄入对乙酰氨基酚引起急性肝衰竭这一亚组的患者,他们的生存率才有明显改善。另外,5个BAL系统报道发生了不良反应,其中暂时性低血压最为常见。BAL治疗效果列于表3。"
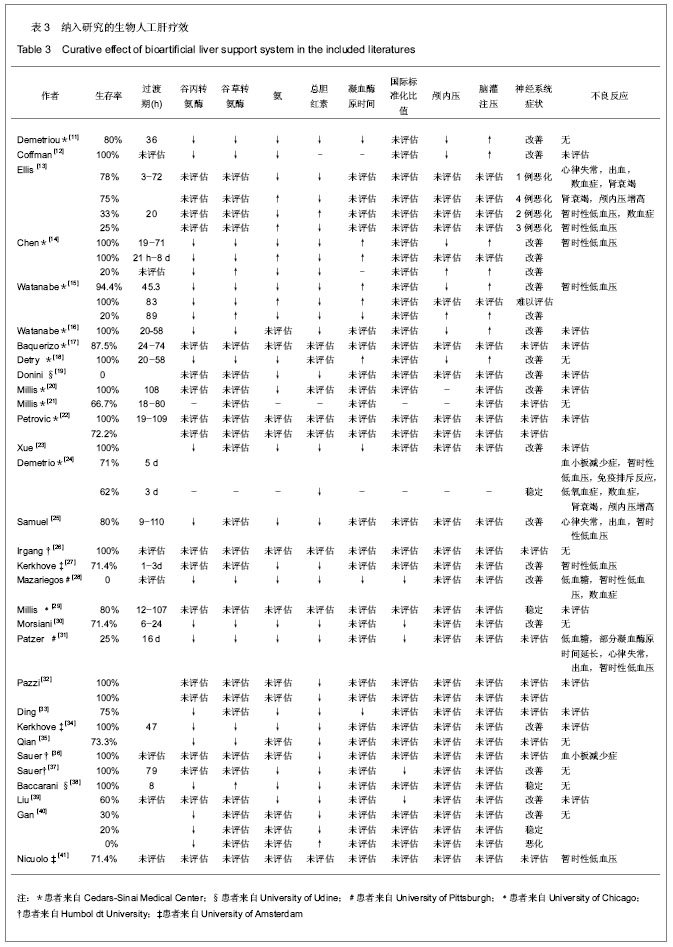
| [1] Lee WM. Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:1862-1872.[2] Shakil AO,Mazariegos GV,Kramer DJ.Fulminant hepatic failure. Surg Clin North Am.1999;79:77-108.[3] Jalan R, Stadlbauer V, Sen S, et al. Natural history of acute decompensation of cirrhosis: the basis of the definition, prognosis and pathophysiology of acute on chronic liver failure. Hepatology.2006:44:371A.[4] Millis JM,Losanoff JE. Technology insight: liver support systems. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol.2005;2:398-405,434.[5] Harper AM,Rosendale JD.The UNOS OPTN Waiting List and Donor Registry: 1988-1996. Clin Transpl.1996:69-90.[6] Fishman JA,Rubin RH.Infection in organ-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1741-1751.[7] Larson AM,Polson J,Fontana RJ,et al. Acetaminophen- induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2005;42: 1364-1372 [8] Yarmush ML,Dunn JC,Tompkins RG.Assessment of artificial liver support technology.Cell Transplant.1992;1:323-241.[9] Strain AJ,Neuberger JM.A bioartificial liver--state of the art. Science. 2002; 295:1005-1009.[10] Matsumura KN,Guevara GR,Huston H,et al.Hybrid bioartificial liver in hepatic failure: preliminary clinical report.Surgery. 1987;101:99-103.[11] Demetriou AA,Rozga J,Podesta L,et al.Early clinical experience with a hybrid bioartificial liver. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl.1995; 208:111-117.[12] Coffman KL,Hoffman A,Rosenthal P,et al. eurological and psychological sequelae in transplant recipients after bridging with the bioartificial liver.Gen Hosp Psychiatry.1996;18:20S-24S.[13] Ellis AJ,Hughes RD,Wendon JA,et al.Pilot-controlled trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 1996; 24:1446-5141.[14] Chen SC,Mullon C,Kahaku E,et al. Treatment of severe liver failure with a bioartificial liver.Ann N Y Acad Sci.1997; 831: 350-360.[15] Watanabe FD,Mullon CJ,Hewitt WR,et al.Clinical experience with a bioartificial liver in the treatment of severe liver failure. A phase I clinical trial. Ann Surg.1997; 225:484-494.[16] Watanabe FD,Shackleton CR,Cohen SM,et al.Treatment of acetaminophen-induced fulminant hepatic failure with a bioartificial liver. Transplant Proc.1997;29:487-488. [17] Baquerizo A,Mhoyan A,Kearns-Jonker M,et al. Characterization of human xenoreactive antibodies in liver failure patients exposed to pig hepatocytes after bioartificial liver treatment: an ex vivo model of pig to human xenotransplantation.Transplantation.1999; 67:5-18.[18] Detry O,Arkadopoulos N,Ting P,et al.Clinical use of a bioartificial liver in the treatment of acetaminophen-induced fulminant hepatic failure.Am Surg. 1999;65:934-938.[19] Donini A,Baccarani U,Risaliti A,et al.Temporary neurological improvement in a patient with acute or chronic liver failure treated with a bioartificial liver device. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:1102-1104.[20] Millis JM,Cronin DC,Johnson R,et al.Bioartificial liver support: report of the longest continuous treatment with human hepatocytes.Transplant Proc. 2001;33:1935.[21] Millis JM,Cronin DC,Johnson R,et al.Safety of continuous human liver support.Transplant Proc.2001; 33:1954.[22] Petrovic LM,Arkadopoulos N,Demetriou AA.Activation of hepatic stellate cells in liver tissue of patients with fulminant liver failure after treatment with bioartificial liver. Hum Pathol. 2001; 32:1371-1375.[23] Xue YL,Zhao SF,Luo Y,et al.TECA hybrid artificial liver support system in treatment of acute liver failure.World J Gastroenterol.2001; 7:826-29.[24] Demetriou AA,Brown RJ,Busuttil RW,et al.Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg.2004;239:660-670.[25] Samuel D,Ichai P,Feray C,et al.Neurological improvement during bioartificial liver sessions in patients with acute liver failure awaiting transplantation. Transplantation.2002; 73: 257-264.[26] Irgang M,Sauer IM,Karlas A,et al.Porcine endogenous retroviruses: no infection in patients treated with a bioreactor based on porcine liver cells. J Clin Virol.2003;28:141-154.[27] van de Kerkhove MP,Di Florio E,Scuderi V,et al. Phase I clinical trial with the AMC-bioartificial liver. Int J Artif Organs. 2002;25:950-959.[28] Mazariegos GV,Patzer JN,Lopez RC,et al.First clinical use of a novel bioartificial liver support system (BLSS).Am J Transplant.2002;2:260-266.[29] Millis JM, Cronin DC, Johnson R, et al. Initial experience with the modified extracorporeal liver-assist device for patients with fulminant hepatic failure: system modifications and clinical impact.Transplantation.2002; 74:1735-1746.[30] Morsiani E,Pazzi P,Puviani AC,et al.Early experiences with a porcine hepatocyte-based bioartificial liver in acute hepatic failure patients.Int J Artif Organs.2002;25:192-202.[31] Patzer IJ,Lopez RC,Zhu Y,et al.Bioartificial liver assist devices in support of patients with liver failure. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2002; 1:18-25.[32] Pazzi P,Morsiani E,Vilei MT,et al.Serum bile acids in patients with liver failure supported with a bioartificial liver.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 16:1547-1554. [33] Ding YT,Qiu YD,Chen Z,et al. The development of a new bioartificial liver and its application in 12 acute liver failure patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2003; 9:829-832. [34] van de Kerkhove MP, Di Florio E, Scuderi V, et al. Bridging a patient with acute liver failure to liver transplantation by the AMC-bioartificial liver. Cell Transplant.2003;12:563-568.[35] Qian Y,Lanjuan L,Jianrong H,et al.Study of severe hepatitis treated with a hybrid artificial liver support system.Int J Artif Organs.2003; 26:507-513.[36] Sauer IM,Kardassis D,Zeillinger K,et al.Clinical extracorporeal hybrid liver support--phase I study with primary porcine liver cells. Xenotransplantation. 2003;10:460-469. [37] Sauer IM,Zeilinger K,Pless G,et al.Extracorporeal liver support based on primary human liver cells and albumin dialysis--treatment of a patient with primary graft non-function. J Hepatol. 2003; 39:649-53.[38] Baccarani U,Donini A,Sanna A,et al.First report of cryopreserved human hepatocytes based bioartificial liver successfully used as a bridge to liver transplantation.Am J Transplant.2004; 4:286-289.[39] Liu Q,Duan ZP,Huang C,et al. Evaluation of effect of hybrid bioartificial liver using end-stage liver disease model.World J Gastroenterol.2004; 10:1379-1381.[40] Gan JH,Zhou XQ,Qin AL,et al.Hybrid artificial liver support system for treatment of severe liver failure. World J Gastroenterol.2005;11:890-894.[41] Di Nicuolo G,van de Kerkhove MP,Hoekstra R,et al.No evidence of in vitro and in vivo porcine endogenous retrovirus infection after plasmapheresis through the AMC-bioartificial liver. Xenotransplantation.2005;12:286-292.[42] Lo CM,Fan ST,Liu CL,et al.Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation using extended right lobe grafts. Ann Surg. 1997; 226:261-270. |
| [1] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [2] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [3] | Huang Zeling, Shi Shanni, He Junjun, Gao Hongjian, Ge Haiya, Hong Zhenqiang. Meta-analysis of safety and effectiveness of proximal fibular osteotomy and high tibial osteotomy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2945-2952. |
| [4] | Lu Ming, Wang Chunhong, Li Min, Luo Tao, Lin Yongsui, Zhou Weili, Sha Baoxue, Wang Mingxin, Meng Deqiang, Gao Zhenchao, Yang Guangling, Zhao Xingcheng, Chen Qiu. Efficacy and prognosis of transforaminal endoscopy in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: a non-randomized, controlled, two-year follow-up clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2375-2379. |
| [5] | Wu Cunshu, Zhan Xiaoxuan, Zhao Siyi, Huang Fan, Zhang Yue, Qiu Mingwang, Xia Jingxian, Lu Xiaobo. Gait training for spinal cord injury based on radar plotting: an overview of systematic reviews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2287-2296. |
| [6] | Wang Shao, Yuan Dajiang, Li Yanyan, Li Xiaoya. Dexmedetomidine combined with local anesthetic for brachial plexus block: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1951-1958. |
| [7] | Liu Yali, Wang Huan, Yan Qiong, Wang Gang, Hou Boru, Wang Dengfeng, Ma Bin, Ren Haijun. Therapeutic effect of stem cells in chronic temporal lobe epilepsy: a systematic review of animal studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 152-158. |
| [8] | Deng Jinman, Fang Guanjun, Wang Yu, Ding Shaobo. Efficacy and characteristics of parecoxib and celecoxib in the treatment of pain after orthopedic surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1471-1476. |
| [9] | Ruan Zhe, Zhu Yong, Lin Zhangyuan, Long Haitao, Zhao Ruibo, Lu Bangbao, Sun Buhua, Cheng Liang, Zeng Min, Zhao Shushan. Systematic review of triangle versus inverted triangle-configurated cannulated screws in the treatment of femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 924-930. |
| [10] | Zhang Jinhuan, Yuan Weiqu, Chen Chen, Huang Xingxian, Yu Haibo. Different acupuncture therapies for treating periarthritis of the shoulder: overview of systematic reviews and network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5723-5732. |
| [11] | Huangfu Zhimin, Wei Daiqing, Ao Yunong. Systematic evaluation and meta-analysis of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4414-4420. |
| [12] |
Yang Jiayi, Zhang Guanghao, Zhang Cheng, Li Ke, Huo Xiaolin, Wu Changzhe.
Stem cell expansion and hepatic differentiation: measurement of related indicators and detection methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4039-4045. |
| [13] |
Shang Zhizhong, Jiang Yanbiao, Yao Lan, Wang Anan, Wang Hongxia, Tian Yuanxin, Liu Dengrui, Ma Bin .
Feasibility of stem cell therapy for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: a systematic review based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4094-4100. |
| [14] | Qiu Mingwang, Fang Wanyi, Song Jiaying, Huang Fan, Zhao Siyi, Wen Junmao, Tian Qiang, Fan Zhiyong, Guo Rusong, Wu Shan. Multiple evaluation of radar plot on acupuncture for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review/meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3904-3910. |
| [15] | Fan Zhirong, Su Haitao, Jiang Tao, Zhou Junde, Peng Jiajie, Hong Weiwu, Zhou Lin, Huang Huida. Safety of intraarticular corticosteroid injections after arthroscopic shoulder surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3931-3936. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||