Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (18): 3366-3373.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.18.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Streptozocin affects the hepatorenal function of type 1 diabetes mini-pigs
Tian Zhong, Cui Yong-chun, Li Kai, Li Ju-bo, Wang Kun, Tang Yue
- State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Medicine, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Disease, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100037, China
-
Received:2013-02-18Revised:2013-03-08Online:2013-04-30Published:2013-04-30 -
Contact:Tang Yue, Doctor, Chief physician, State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Medicine, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Disease, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100037, China tangyue1226@vip.sina.com Cui Yong-chun, Doctor, Assistant researcher, State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Medicine, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Disease, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100037, China cyc_fuwai@sina.com -
About author:Tian Zhong★, Studying for master’s degree, Attending physician, State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Medicine, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Disease, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100037, China xunzhaotian@yeah.net -
Supported by:Science and Technology Planning Project of Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, No. Z101107052210004; Union Youth Foundation, No. 2012-XHQN04
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Zhong, Cui Yong-chun, Li Kai, Li Ju-bo, Wang Kun, Tang Yue. Streptozocin affects the hepatorenal function of type 1 diabetes mini-pigs[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(18): 3366-3373.
share this article
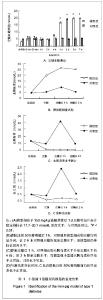
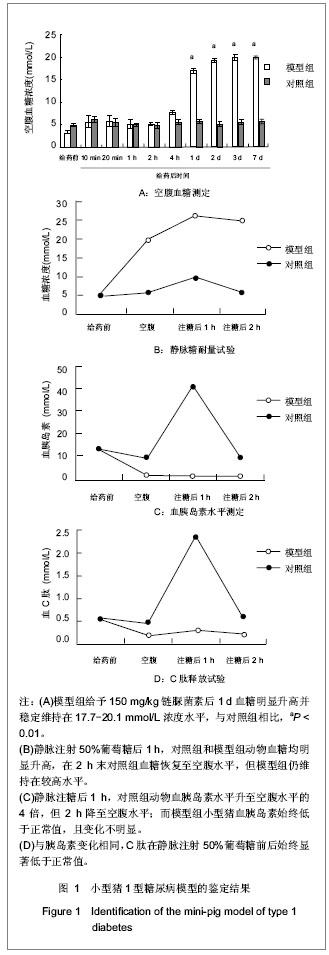
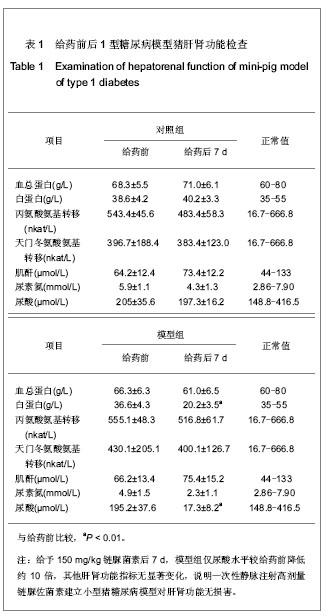
为了进一步确定糖尿病分型,实验于给药后1周进行了静脉葡萄糖耐量试验和C肽释放试验。静脉葡萄糖耐量试验实验结果表明,与给药前水平相比,模型组链脲佐菌素处理后7 d空腹血糖水平明显高于7 mmol/L的糖尿病诊断标准,空腹胰岛素水平显著下降;对照组注射等体积0.1 mol/L柠檬酸钠前后的空腹血糖和胰岛素水平差异不明显。 静脉注射50%葡萄糖后1 h,对照组和模型组动物血糖均明显升高,模型组达到28 mmol/L左右(>11.1 mmol/L临界值),对照组9.5 mmol/L左右(<11.1 mmol/L临界值);在注糖2 h后对照组血糖恢复至空腹水平,但模型组仍维持在较高水平(约25 mmol/L);在静脉注糖后1 h,对照组动物血胰岛素水平升至空腹水平的4倍,但2 h降至空腹水平;而模型组小型猪在静脉注糖前后,血胰岛素始终变化不明显。见图1B,C。 C肽释放规律检测结果与血胰岛素变化情况相近,见图1D。链脲佐菌素处理后1周,模型猪血胰岛素空腹水平较给药前明显降低;注糖后一两小时与空腹水平比较,差异均无显著性意义。 根据2010年ADA糖尿病诊断标准,上述参数变化特征符合1型糖尿病标准:空腹血糖大于等于7 mmol/L; 静脉葡萄糖耐量试验经脉注射50%葡萄糖1 h后血糖浓度>11.1 mmol/L,血糖2 h后血糖浓度未降至空腹水平;空腹胰岛素和C肽水平明显降低,静脉注射50%葡萄糖前后2 h内,二者血液水平始终变化不显著。说明小型猪静脉一次性注射高剂量链脲佐菌素(150 mg/kg)可成功建立1型糖尿病模型。 2.3 给药前后1型糖尿病猪模型的肝肾功能 为说明一次性静脉注射高剂量链脲佐菌素建立小型猪糖尿病模型是否能够造成肝肾功能损伤,实验分别在给药前和给药后1周采集了各组实验小型猪的静脉血,进行肝肾功的检查。 结果表明,给药前实验小型猪的各项指标均正常。给药后1周,血总蛋白、丙氨酸氨基转移酶、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶、肌酐水平均在正常范围内;而白蛋白和尿素氮较给药前略有降低,但尚未达到显著水平;仅尿酸水平与正常值相比差异有显著性意义,较给药前降低约10倍,见表1。"
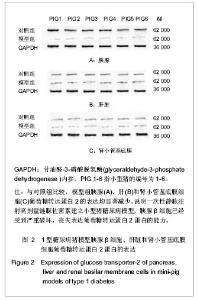
2.4 1型糖尿病猪模型胰腺β细胞、肝脏和肾小管基底膜细胞葡萄糖转运蛋白2蛋白的表达 为说明糖尿病小型猪胰腺β细胞、肝脏和肾小管基底膜细胞葡萄糖转运蛋白2蛋白表达情况,解释模型组血尿酸降低的可能机制,实验分别采集对照组和模型组小型猪的胰腺、肝脏和肾皮质组织,通过western blot方法检测其中葡萄糖转运蛋白2蛋白的表达水平。 结果如图2所示,给药后1周,链脲佐菌素处理组小型猪胰腺组织几乎无葡萄糖转运蛋白2蛋白表达,说明胰腺β细胞已经受到严重破坏,丧失表达葡萄糖转运蛋白2蛋白的能力,见图2A。与胰腺组织比较,对照组小型猪肝细胞和肾小管基底膜细胞葡萄糖转运蛋白2蛋白的表达丰度相对较低,经链脲佐菌素处理后葡萄糖转运蛋白2蛋白仍有痕量表达,见图2 B,C。"

| [1] Preiss D, Sattar N. Pharmacotherapy: Statins and new-onset diabetes--the important questions. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012;9(4): 190-192. [2] Tan DA. Changing disease trends in the Asia-Pacific. Climacteric. 2011;14(5):529-534. [3] Maeda H, Hanazaki K. Pancreatogenic diabetes after pancreatic resection. Pancreatology. 2011;11(2):268-276. [4] Lehach EI, Bodnar Iu I, Bozhok HA. Prophylaxis of a specific type diabetes mellitus development using pancreatic insuli autotranspiantation after pancreatic resection. Klin Khir. 2011; (12):63-67. [5] Guan ZA, Sun MX, Guan DS, et al. Tianjin: Tianjin Kexue Jishu Chubanshe. 2001.关子安,孙茂欣,关大顺,等.现代糖尿病学[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社,2001. [6] Du GH, Li XJ, Zhang YX, et al. Beijing Science Press. 2001.杜冠华,李学军,张永祥,等.药理学实验指南-新药发现和药理学评价[M].北京:科学出版社,2001.[7] Jaidane H, Sane F, Gharbi J, et al. Coxsackievirus B4 and type 1 diabetes pathogenesis: contribution of animal models. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009;25(7):591-603. [8] Colli ML, Nogueira TC, Allagnat F, et al. Exposure to the viral by-product dsRNA or Coxsackievirus B5 triggers pancreatic beta cell apoptosis via a Bim/Mcl-1 imbalance. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7(9):e1002267. [9] Sauter P, Hober D. Mechanisms and results of the antibody-dependent enhancement of viral infections and role in the pathogenesis of coxsackievirus B-induced diseases. Microbes and infection/Institut Pasteur. 2009;11 (4):443-451. [10] Diz R, Garland A, Vincent BG, et al. Autoreactive effector/memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells infiltrating grafted and endogenous islets in diabetic NOD mice exhibit similar T cell receptor usage. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52054. [11] Bortell R, Yang C. The BB rat as a model of human type 1 diabetes. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;933:31-44. [12] Zhao YY, Huang XY, Chen ZW. Daintain/AIF-1 (Allograft Inflammatory Factor-1) accelerates type 1 diabetes in NOD mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;427(3):513-517. [13] Grant CW, Duclos SK, Moran-Paul CM, et al. Development of standardized insulin treatment protocols for spontaneous rodent models of type 1 diabetes. Comp Med. 2012;62(5): 381-390. [14] Wu J, Kakoola DN, Lenchik NI, et al. Molecular phenotyping of immune cells from young NOD mice reveals abnormal metabolic pathways in the early induction phase of autoimmune diabetes. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46941. [15] Wszola M, Berman A, Fabisiak M, et al. TransEndoscopic Gastric SubMucosa Islet Transplantation (eGSM-ITx) in pigs with streptozotocine induced diabetes-technical aspects of the procedure - preliminary report. Ann Transplant. 2009; 14(2):45-50. [16] Strauss A, Moskalenko V, Tiurbe C, et al. Goettingen Minipigs (GMP): Comparison of Two Different Models for Inducing Diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012;4(1):7.[17] Szkudelski T. Themechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol Res. 2001;50(6): 537-546. [18] Liu YQ, Li CH, Chen H. Shiyan Dongwu Kexue. 2007;24(5): 24-26.刘亚千,李春海,陈华.三个品系实验用小型猪部分血液生化指标比较[J].实验动物科学,2007,24(5):24-26. [19] Chen H. Zhongguo Shiyan Dongwu Xuebao. 2009;16(6): 458-462.陈华.小型猪糖尿病模型[J].中国实验动物学报,2009,16(6): 458-462. [20] Dutta T, Chai HS, Ward LE, et al. Concordance of changes in metabolic pathways based on plasma metabolomics and skeletal muscle transcriptomics in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61(5):1004-1016. [21] Yu X, Park BH, Wang MY, et al. Making insulin-deficient type 1 diabetic rodents thrive without insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37):14070-14075. [22] Galan M, Kassan M, Choi SK, et al. A novel role for epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and its downstream endoplasmic reticulum stress in cardiac damage and microvascular dysfunction in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Hypertension. 2012;60(1):71-80. [23] Gunawardana SC, Piston DW. Reversal of type 1 diabetes in mice by Brown adipose tissue transplant. Diabetes. 2012; 61(3):674-682. [24] Dufrane D, van Steenberghe M, Guiot Y, et al. Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in large animals (pigs/primates): role of GLUT2 transporter and [beta]-cell Plasticity. Transplantation. 2006;81(1):36-45. [25] Jensen-Waern M, Andersson M, Kruse R, et al. Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in domestic pigs with focus on the amino acid metabolism. Lab Anim. 2009;43(3):249-254. [26] Von Wilmowsky C, Stockmann P, Metzler P, et al. Establishment of a streptozotocin-induced diabetic domestic pig model and a systematic evaluation of pathological changes in the hard and soft tissue over a 12-month period. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(7):709-717.[27] Lee PY, Park SG, Kim EY, et al. Proteomic analysis of pancreata from mini-pigs treated with streptozotocin as a type I diabetes models. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;20(4): 817-820. [28] Hara H, Lin YJ, Zhu X, et al. Safe induction of diabetes by high-dose streptozotocin in pigs. Pancreas. 2008;36(1):31-38. [29] Wang YT, Wang ZB. Zhongguo Bijiao Yixue Zazhi. 2012;21 (12):70-73.王月婷,王宗保.小型猪糖尿病模型研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2012,21(12):70-73. [30] Aschenbach J, Steglich K, Gäbel G, et al. Expression of mRNA for glucose transport proteins in jejunum, liver, kidney and skeletal muscle of pigs. J Physiol Biochem. 2009;65(3): 251-266. [31] Freitas HS, Schaan BD, Seraphim PM, et al. Acute and short-term insulin-induced molecular adaptations of GLUT2 gene expression in the renal cortex of diabetic rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005;237(1-2):49-57. [32] Goestemeyer A, Marks J, Srai S, et al. GLUT2 protein at the rat proximal tubule brush border membrane correlates with protein kinase C (PKC)-βl and plasma glucose concentration. Diabetologia. 2007;50(10):2209-2217. [33] Park S-K, Haase VH, Johnson RS. von Hippel Lindau tumor suppressor regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by controlling expression of glucose transporter 2 and glucose 6-phosphatase. Int J Oncology. 2007;30(2):341-348. [34] Schmidt C, Höcherl K, Bucher M. Regulation of renal glucose transporters during severe inflammation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292(2):F804-F11. [35] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[36] Strauss A, Tiurbe C, Chodnevskaja I, et al. Use of the continuous glucose monitoring system in Goettingen Minipigs, with a special focus on the evaluation of insulin-dependent diabetes. Transplant Proc. 2008;40(2):536-539. [37] Ludvigsson J. C-peptide in diabetes diagnosis and therapy. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2013;5:214-223. [38] Wang S, Wei W, Zheng Y, et al. The role of insulin c-peptide in the coevolution analyses of the insulin signaling pathway: a hint for its functions. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52847. [39] Wang Z, Gleichmann H. GLUT2 in pancreatic islets: crucial target molecule in diabetes induced with multiple low doses of streptozotocin in mice. Diabetes. 1998;47(1):50-56. [40] Vallon V, Thomson SC. Renal function in diabetic disease models: the tubular system in the pathophysiology of the diabetic kidney. Ann Rev Physiol. 2012;74:351-375.[41] Kramer J, Moeller EL, Hachey A, et al. Differential expression of GLUT2 in pancreatic islets and kidneys of New and Old World nonhuman primates. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;296(3):R786-R793. |
| [1] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [2] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [3] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [4] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [5] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin. Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3275-3280. |
| [6] | Xia Wenshen, He Renjiao, Ai Jinwei, Wang Jun, Li Desheng, Pei Bin. Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3110-3116. |
| [7] | Luo Yicai, Li Hao. Effect of enhanced aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression on inflammatory response and healing of alveolar bone defects in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2166-2171. |
| [8] | Hu Sheng, Yuan Haiyan, Hu Meng, Jin Shanhu. Effects of moderate treadmill exercise on alpha-smooth muscle actin and type IV collagen in the liver of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1723-1727. |
| [9] | Bai Xue, Wang Bin, He Sirong. Research focus and application advantages in encapsulating biomaterial for islet transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1585-1591. |
| [10] | Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Suo Jinrong, Li Yingrui, Huang Lei, Ma Munan, Li Jingjing, Fu Songtao. Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 78-83. |
| [11] | Bu Yueli, Wang Fang, Zhang Jianguo, Li Xiaolin, Cao Zijun, Li Xuemei. Plantar pressure and gait characteristics in older adult patients with diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 736-740. |
| [12] | Yu Peiyuan, Zhang Zhida, Liang Lichang, Yang Zhidong, Huang Jinjing, Peng Jiancheng, Liang Ziyang, He Jiahui, Zhao Wenhua, Yu Fuyong, Chen Guifeng, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing . Difference in the effect of metformin on bone strength of lumbar vertebrae and hind limbs in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 657-661. |
| [13] | Xie Xiufeng, Zhang Yue, Qu Ze. Clinical outcomes of drug-eluting balloons and drug-eluting stents for the treatment of in-stent restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 555-560. |
| [14] |
Zheng Haijun, Jin Hui, Cui Hongling, Zhu Yakun, Zeng Hui, Han Fengjie, Qiu Cuiting, Liu Jing.
Safety of drug-coated balloon versus drug-eluting stents in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by coronary artery small vessel disease in older adult patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4573-4579. |
| [15] |
Geng Kang, Ding Xiaobin, Tian Xinli, Wang Xue, Yang Yuting, Yan Hong.
Electrical stimulation promotes wound healing and angiogenesis in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4152-4156. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||