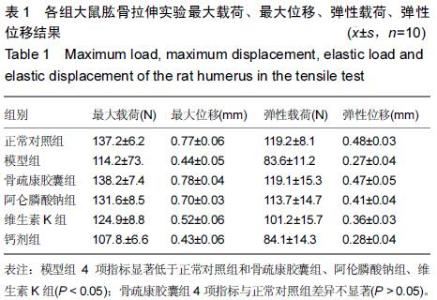
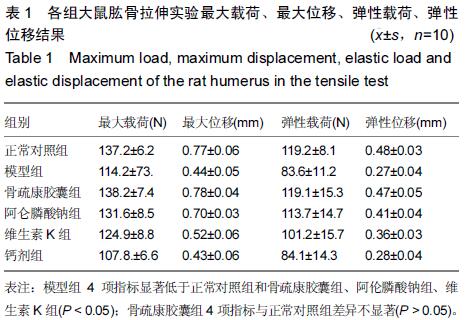
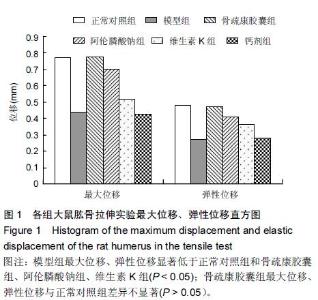
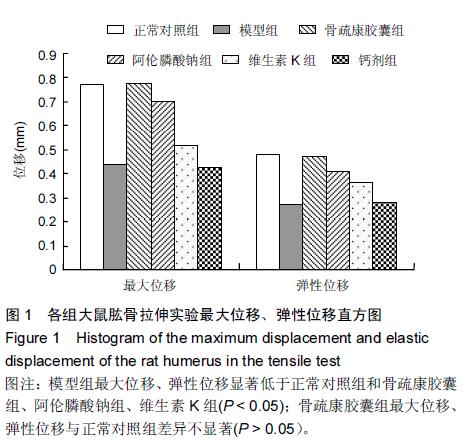
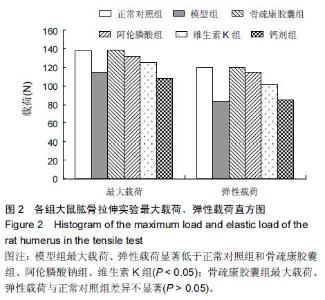
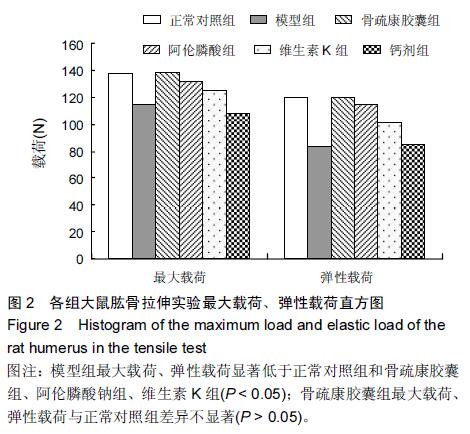
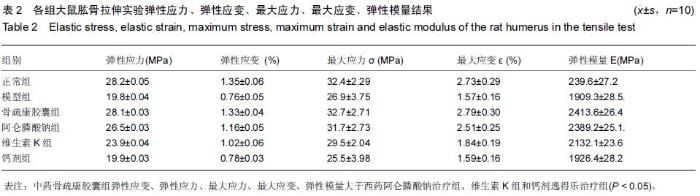
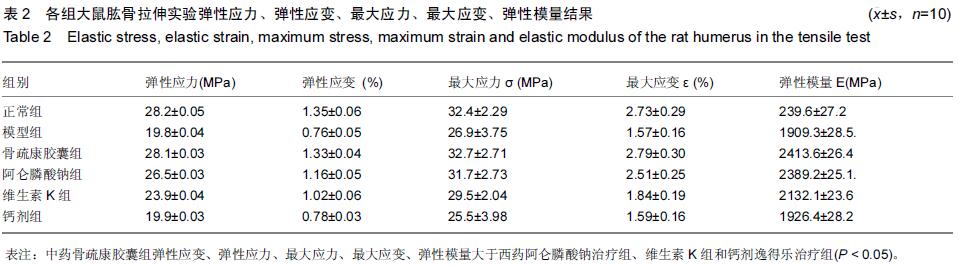
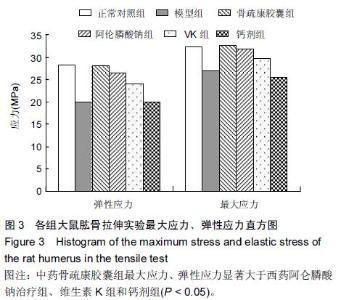
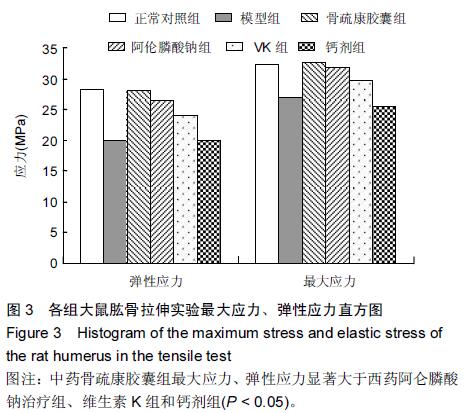
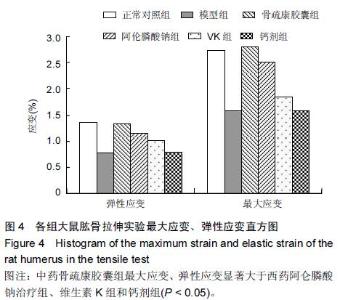
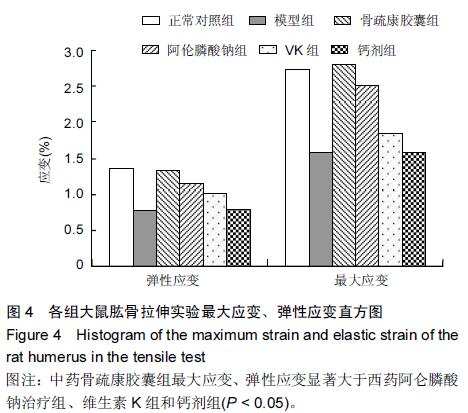
| [1] 刘忠厚.骨质疏松学[M].北京:科学出版社,1999:142-143.
[2] 高凤展.运动与中药淫羊菌对骨质疏松大鼠骨髓组织细胞件黏附分子表达的影响[D]. 武汉:武汉体育粮食学院,2008.
[3] Reeve J, Davies UM, Hesp R, et al.Treatment of osteoporosis with human parathyroid peptide and observations on effect of sodium fluoride. BMJ.1990;301:314-318.
[4] Riond JL. Modulation of the anabolic effect of synthetic human parathyroid hormone fragment (1-34) in the bone of growing rats by variations in the dosage regimen. Clin Sci.1993;85(2): 223-228.
[5] Shen V, Dempster D W, Birchmen R, et al.Loss of cancellous bone mass and connectivity in ovariectomized rats can be restoredby combined treatment with parathyroid hormone and estradiol. J Clin Invest.1993;91(6):2479-2487.
[6] Fukata S, Hagino H, Okano T, et al..Effect of intermittent administration of human parathyroid hormone on bone mineral density and arthritis in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rrheumatism.2004;50(12):4060-4069.
[7] Vignery A, and Baron. R. Dynamic histomorphometry of alveolar bone remodeling in the adult rat. Anat Rec.1990;196(2):191-200.
[8] Wronski TJ, and Yen CF, Anabolic effects of parathyroid hormone on cortical bone in ovariectomized rats. Bone. 1994; 15(1):51-58.
[9] Wronski TJ, Yen CF, Qi H, et al.Parathyroid hormone is more effective than estrogen or bisphosphonates for restoration of lost bone mass in ovariectomized rats.Endocrinology.1993; 132(2): 823-831.
[10] Frost HM.Why do bone strength and “mass” in aging adults become unresponsive to vigorous exercise Insights of the Utah paradigm.J Bone Miner Metab. 1999;17(2):90-97.
[11] Frost HM.From Wolff’s Law to the Utah paradigm: insights about bone physiology and its clinical applications. Anat Rec. 2001;262:398-419.
[12] Huiskes R, Ruimerman R, van Lenthe GH,et al. Effects of mechanical forces on maintenance and adaptation of form in trabecular bone. Nature.2000;405:704-706.
[13] 彭建,李万逸,李海平,等. 补肾健骨方治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折的临床疗效分析[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(17):42-44.
[14] 向科明,庄琼,黄玉梅,等. 独活寄生汤联合唑来膦酸治疗绝经后肝肾亏虚型骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].贵阳中医学院学报, 2013, 35(4):27-30.
[15] 张上上,刘心昱,郑姝宁,等. 骨碎补醇提物对骨质疏松预防作用的大鼠尿液UPLC-MS/MS代谢组学研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2012, 37(5):658-662
[16] 石继祥,曹成福,纪斌,等.补阳还五汤对急性脊髓损伤大鼠神经功能康复作用的研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2012,11(21): 1684-1686.
[17] Lingard EA, Mitchell SY, Francis RM, et al. The prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with severe hip and knee osteoarthritis awaiting joint arthroplasty. Age Ageing. 2010;39(2): 234-239.
[18] 牛放,赵雨,徐云凤,等.鹿角脱盘胶原蛋白对去卵巢所致骨质疏松大鼠的治疗作用[J].中国现代应用药学,2012,29 (2):93-97
[19] 李亚楠,刘红,刘梅洁,等.无比山药丸对去卵巢大鼠腰椎骨密度和股骨生物力学性能的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2012 ,18(10 ): 1085-1086.
[20] 张戈,宋太咏.补肾益精方提高绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠模型松质骨骨质量的作用极其机制的研究[J].医用生物力学,2001,16(1):18-22.
[21] 陆声,徐永清,张关超,等.骨质疏松椎体增强后对相邻椎体,生物力学影响的有限元研究[J],中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,15(9): 996-998.
[22] 李晋平,章明放,李忠武,等.补钙对骨质疏松并发骨折大鼠的生物力学研究[J],中国骨质疏松杂志,2005 11(2):126-128
[23] 吕雅平,冯铁键,马洪顺.氟中毒动物模型蠕变实验研究[J].中国地方病防治杂志,2010,25(4):95.
[24] 张远石,张忠君,王溪原,等.氟中毒大鼠腰椎压缩蠕变实验研究[J].中国地方病防治杂志,2011,26 (2):107-108.
[25] 王溪原,张远石,苑福生,等.正常与病态股骨头应力松弛特性的对比分析[J].生物医学工程研究,2011,30(1):49-52.
[26] 罗民,李新颖,马洪顺.股骨下端松质骨横向与纵向的蠕变特性[J]. 生物医学工程研究, 2012, 31(1):24- 27.
[27] 钟显春,罗民,李新颖.几种药物治疗骨质疏松模型大鼠股骨蠕变特性的对比分析[J].生物医学工程研究, 2012, 31(3): 180-183.
[28] 彭传刚,杨琦,李鹏. C3-4、T9-10、L2-3椎间盘与相邻椎体弯曲(屈曲)的力学特性[J].生物医学工程研究,2013,32(2):94-96.
[29] 李亚军,王亚芬,罗民.气管软骨蠕变的实验研究[J].生物医学工程研究,2013,32(2):91-93.
[30] 李爽,李鹏,袁毅.正常与病态眼角膜应力松弛特性的对比分析[J].生物医学工程研究,2013,32(3):174-179.
[31] 鞠晓伟,赵卫东,李义凯.在研发防治骨质疏松药物动物实验中生物力学方法的评价[ J] .颈腰痛杂志, 2005, 26(4):310-312.
[32] 李鹏,罗民,马洪顺.药物治疗老龄骨质疏松大鼠骨显微结构与骨组织形态学指标的变化[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(140):3975-3977.
[33] 吴俊哲,曾元桂,王伟群,等.中医药治疗脊髓损伤及骨质松疏的研究进展[J].中药材,2014,37(10):1893-1896.
[34] 王锡娟,梁目欣,赵璐中药复方骨疏康防治骨质疏松症研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2007,3(27) :3-5.
[35] 高美霞,陈康,赵志红.骨疏康对绝经后骨质疏松骨代谢的调节作用[J].中医正骨,2003,11(15):11-13. |