Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (18): 3247-3254.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.18.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Serum cystatin C is considered to monitor the renal function of urinary tract obstruction patients after renal transplantation
Zhang Xin-tao1, Dai Cheng1, Zhang Qing2
- 1 Department of Urology, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
2 Department of Transplantation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2013-01-19Revised:2013-03-08Online:2013-04-30Published:2013-04-30 -
About author:Zhang Xin-tao★, Master, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Urology, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China zhangxt75@sohu.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xin-tao, Dai Cheng, Zhang Qing. Serum cystatin C is considered to monitor the renal function of urinary tract obstruction patients after renal transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(18): 3247-3254.
share this article

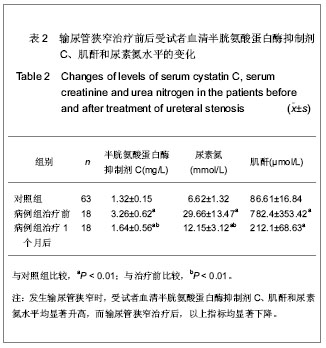
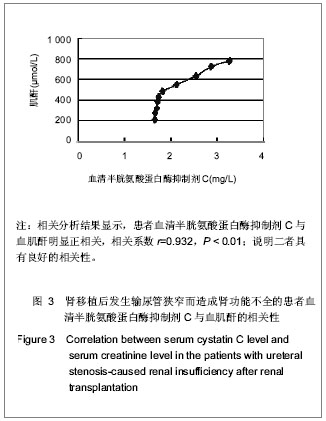
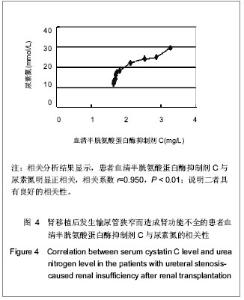
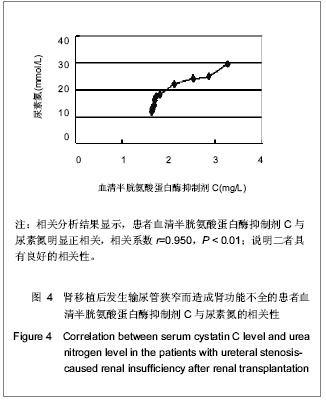
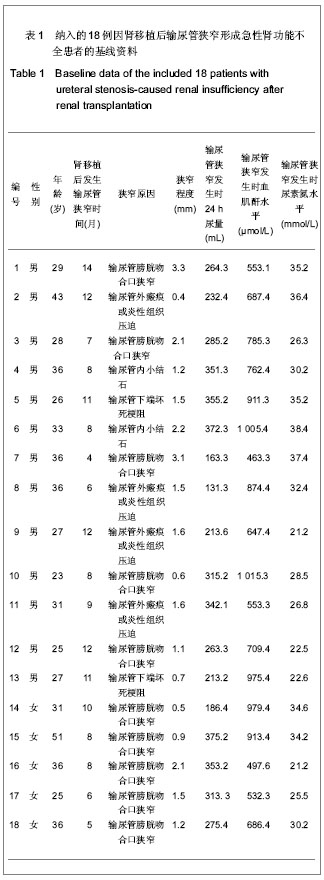
2.1 研究对象数量分析 研究共纳入18例因肾移植后输尿管狭窄形成急性肾功能不全患者和63名健康对照者,均进入结果分析。 2.2 因肾移植后输尿管狭窄形成急性肾功能不全患者的基线资料 共纳入18例肾移植后发生输尿管狭窄的患者,基线资料见表1。 2.3 因肾移植后输尿管狭窄形成急性肾功能不全患者血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C水平的变化 在对照组中,血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C呈正态分布,半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C随年龄增长呈上升趋势。肾移植后发生输尿管狭窄患者经手术治疗后,尿量明显增多,肾功能均有改善,恢复至正常参考范围。与对照组比较,病例组输尿管狭窄治疗前半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C显著增高(P < 0.01),经治疗后,病例组半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C水平显著降低(P < 0.01),见表2。"
| [1] Song J, Lu YP, Chen SZ, et al. Jujie Shoushuxue Zazhi. 2011; 20(6):653-655.宋珺,卢一平,陈世瞻,等.双侧上尿路梗阻致肾功能不全200例分析[J].局解手术学杂志,2011,20(6):653-655.[2] Xie LL, Liu J, Gao Q, et al. Tianjin Yiyao. 2010;38(7): 582-583.谢丽莉,刘娟,高强,等.肾移植术后动态监测血清胱抑素C变化的临床意义[J].天津医药,2010,38(7):582-583.[3] Ma Y, Xu XG, Huang HY, et al. Xibao yu Fenzi Mianyixue Zazhi. 2010;26(11):1140-1142.马樱,许晓光,黄海燕,等.定量检测血和尿中Cystatin C含量在肾移植患者肾功能评价中的应用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2010, 26(11):1140-1142.[4] Gu CY, Zheng L, Wang Q. Guowai Yixue Linchuang Shengwu Huaxue yu Jianyanxue Fence. 2004;25(6):559-561.顾春瑜,郑磊,王前.血清胱抑素C在评价肾移植患者肾功能中的应用[J].国外医学临床生物化学与检验学分册,2004,25(6): 559-561.[5] Sun YH, Zeng ZJ, Jiang C, et al. Zhonghua Shenzangbing Zazhi. 2006;22(8):503-505.孙艳虹,曾智杰,姜偿,等.血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C在肾病患者肾功能评估中的应用[J] .中华肾脏病杂志,2006,22(8): 503-505.[6] Baxmann AC, Ahmed MS, Marques NC, et al. Influence of muscle mass and physical activity on serum and urinary creatinine and serum cystatin C. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3(2):348-354.[7] Li YY, Yang ZK, Li Q. Guoji Jianyan Yixue Zazhi. 2006;27(9): 812-813.李玉艳,杨振坤,李强.胱抑素C 在临床中的应用进展[J] .国际检验医学杂志,2006,27(9) :812-813.[8] Liu XM, Yu HF, Zhang HX. Shandong Yiyao. 2008;48(28): 76-77.刘雪梅,于华凤,张洪霞.儿童肾功能损害不同时期血清胱抑素C 的变化及意义[J] .山东医药,2008,48(28):76-77.[9] Huber AR, Risch L. Recent developments in the evaluation of glomerular filtration rate: is there a place for beta-trace? Clin Chem. 2005;51(8):1329-1330.[10] Sundaram CP, Martin GL, Guise A, et al. Complications after a 5-year experience with laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: the Indiana University experience. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(5): 724-728.[11] Elwagdy S, Ghoneim S, Moussa S, et al. Three-dimensional ultrasound (3D US) methods in the evaluation of calcular and non-calcular ureteric obstructive uropathy. World J Urol. 2008; 26(3):263-274.[12] Wu SQ, Wen DL, Cao WP. Zhongguo Xiandai Yiyao Zazhi. 2009;11(5):62-64.吴少卿,文道林,曹文平.肾移植后在肾功能监测中血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C同血清肌酐的应用比较[J].中国现代医药杂志, 2009,11(5):62-64.[13] Ding Y, Wang ZB, Yu J, et al. Zhonghua Yixue Chaosheng Zazhi: Dianzi Ban. 2010;7(6):941-947.丁媛,王正滨,禹静,等.超声显像对输尿管狭窄的定位与定性诊断[J].中华医学超声杂志(电子版),2010,7(6):941-947.[14] Lin L, Bagley DH, Liu JB. Role of endoluminal sonography in evaluation of obstruction of the ureteropelvic junction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191(4):1250-1254.[15] Wang ZB, Yuan M, Hou SC, et al. Zhonghua Yixue Chaosheng Zazhi: Dianzi Ban. 2004,1(4):178-180.王正滨,袁梅,侯四川,等.超声显像对输尿管下端梗阻病因的诊断评价[ J] .中华医学超声杂志(电子版),2004,1(4):178-180.[16] Ingram MD, Sooriakumaran P, Palfrey E, et al. Evaluation of the upper urinary tract using transureteric ultrasound--a review of the technique and typical imaging appearances. Clin Radiol. 2008;63(9):1026-1034.[17] Wang W. Linchuang Miniao Waike Zazhi. 2009;24(4):294-296.王威.磁共振水成像在上尿路梗阻疾病诊断中的应用价值[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2009,24(4):294-296.[18] Shi L, Wei YF, Sun WQ, et al. Gansu Yiyao. 2011;30(3): 156-157.石磊,魏玉峰,孙文勤,等.磁共振水成像在上尿路梗阻中的应用[J].甘肃医药,2011,30(3):156-157.[19] Sun J, Yang Y. Guoji Jianyan Yixue Zazhi.2011;32(9):991-992.孙剑,杨燕.应用Westgard多规则进行生化室内质量控制数据分析[J].国际检验医学杂志 2011,32(9):991-992.[20] He M, Xu JH, Huang XZ, et al. Linchuang Gongcheng. 2012; 27(1):64-67,71.何敏,徐建华,黄宪章,等.Realtime 实时质控结合Westgard多规则理论[J].临床工程,2012,27(1):64-67,71.[21] Jia W, Liu XS, Zhu Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of mabs against different epitopes of CD226 (PTA1). Hybridoma. 2000;19(6):489-494.[22] Qin J, Zhang P. Anhui Yufang Yixue Zazhi. 2009;15(4): 303-304.秦晶,张鹏.酶法和Jaffe速率法测定血清肌酐结果比较[J].安徽预防医学杂志,2009,15(4):303-304.[23] Xie B, Jiang LP, Dai CY, et al. Shiyan yu Jianyan Yixue. 2009; 27(1):89-90.解冰,江利萍,戴晨英,等.酶法与Jaffe 速率法测定肌酐在计算内生肌酐清除率时的差异[J].实验与检验医学,2009,27(1):89-90.[24] Tan XM, Zhang XL. Xiandai Yiyuan. 2008;8(1):60-61.谭晓明,张小玲.酶法与Jaffe法测定血清肌酐结果偏倚的估计[J].现代医院,2008,8(1):60-61.[25] Ge L, Cheng XM, Mao SH. Bengbu Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2011; 36(12):1382-1384.葛玲,程训民,毛诗海.血清胱抑素C测定在肾病早期诊断中的应用[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2011,36(12):1382-1384.[26] Zeng GH, Li X, Lei M, et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2005;26(3):145-147.曾国华,李逊,雷鸣,等.移植肾输尿管膀胱吻合口梗阻的腔内手术处理[J].中华器官移植杂志,2005,26(3):145-147.[27] Dharnidharka VR, Kwon C, Stevens G. Serum cystatin C is superior to serum creatinine as a marker of kidney function: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;40(2):221-226.[28] Filler G, Priem F, Lepage N, et al. Beta-trace protein, cystatin C, beta(2)-microglobulin, and creatinine compared for detecting impaired glomerular filtration rates in children. Clin Chem. 2002;48(5):729-736.[29] National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1-266.[30] Kazama JJ, Kutsuwada K, Ataka K, et al. Serum cystatin C reliably detects renal dysfunction in patients with various renal diseases. Nephron. 2002;91(1):13-20.[31] Li HX, Zhang CL, Xu GB, et al. Zhonghua Jianyan Yixue Zazhi. 2006;29(11):970- 974.李海霞,张春丽,徐国宾,等.健康人群血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C与肌酐分布及其评价慢性肾脏病患者肾小球滤过率功能的比较研究[J].中华检验医学杂志,2006,29(11):970- 974.[32] Wu JP. Shandong Kexue Jishu Chubanshe. 2004.吴阶平.吴阶平泌尿外科学[M].山东科学技术出版社,2004.[33] Gökku?u CA, Ozden TA, Gül H, et al. Relationship between plasma Cystatin C and creatinine in chronic renal diseases and Tx-transplant patients. Clin Biochem. 2004;37(2):94-97.[34] Mostafa SA, Abbaszadeh S, Taheri S, et al. Percutaneous nephrostomy for treatment of posttransplant ureteral obstructions. Urol J. 2008;5(2):79-83.[35] Xiao L, Liu FY, He DR, et al. Yixue yu Zhexue: Linchuang Juece Luntan Ban. 2007;28(7):45-47.肖力,刘伏友,贺达仁,等.终末期肾病治疗方法的比较[J] .医学与哲学:临床决策论坛版,2007,28(7):45-47.[36] Liang XL, Shi W, Ye ZM, et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2006;22(1):177-181.梁馨苓,史伟,叶智明,等.血清半胱氨酸蛋白抑制剂C与急性肾衰竭预后关系的研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2006,22(1):177-181.[37] Qin WZ. Guangxi Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2008;5(3):544.覃文周.血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C检测对诊断早期肾功能损害的价值[J].广西医科大学学报,2008,5(3):544.[38] Xie H, Lin HL. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Shenbing Zazhi. 2006;7(9):514-516.谢华,林洪丽.血清Cystatin C评价慢性肾脏病患者肾小球滤过功能的对照研究[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2006,7(9):514-516.[39] Zhong JQ, Jiang SK, Song LM. Jiangxi Yiyao. 2007;42(1): 26-27.钟久庆,蒋叔凯,宋乐明.梗阻肾尿液pH值与HCO3测定对梗阻解除后肾功能的评价研究[J]. 江西医药,2007,42(1):26-27.[40] Zhao ZX, Bi ZQ. Guowai Yixue: Miniao Xitong Fence. 2002; 22(2):103-104.赵子秀,毕增祺.血清胱蛋白酶抑制剂C测定的临床意义[J].国外医学:泌尿系统分册,2002,22(2):103-104.[41] Mojiminiyi OA, Abdella N. Evaluation of cystatin C and beta-2 microglobulin as markers of renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2003; 17(3):160-168.[42] Jovanovi? D, Krstivojevi? P, Obradovi? I, et al. Serum cystatin C and beta2-microglobulin as markers of glomerular filtration rate. Ren Fail. 2003;25(1):123-133.[43] Tian J. Jinan: Shandong Daxue Chubanshe. 2003:67-93.田军.临床血液净化肾移植[M].济南:山东大学出版社, 2003: 67-93.[44] Risch L, Herklotz R, Blumberg A, et al. Effects of glucocorticoid immunosuppression on serum cystatin C concentrations in renal transplant patients. Clin Chem. 2001; 47(11):2055-2059.[45] Christensson A, Ekberg J, Grubb A, et al. Serum cystatin C is a more sensitive and more accurate marker of glomerular filtration rate than enzymatic measurements of creatinine in renal transplantation. Nephron Physiol. 2003;94(2):p19-27.[46] Deinum J, Derkx FH. Cystatin for estimation of glomerular filtration rate? Lancet. 2000;356(9242):1624-1625.[47] Le Bricon T, Thervet E, Froissart M, et al. Plasma cystatin C is superior to 24-h creatinine clearance and plasma creatinine for estimation of glomerular filtration rate 3 months after kidney transplantation. Clin Chem. 2000;46(8 Pt 1): 1206-1207.[48] Bökenkamp A, Domanetzki M, Zinck R, et al. Cystatin C serum concentrations underestimate glomerular filtration rate in renal transplant recipients. Clin Chem. 1999;45(10): 1866-1868.[49] Pöge U, Stoschus B, Stoffel-Wagner B, et al. Cystatin C as an endogenous marker of glomerular filtration rate in renal transplant patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2003;26(1): 55-60. |
| [1] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [2] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [3] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [4] | Wu Kai, Liu Kun, Xie Lin, Lu Guanjun, Ma Shengchao, Li Guizhong, Cao Jun, Jie Yuzhen, Jiang Yideng, Hao Yinju. Mechanism of hyperhomocysteinemia induced renal injury in Cbs+/- mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1728-1732. |
| [5] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [6] | Cao Houran, Deng Peng, Ye Pengcheng, Jie Ke, Zeng Jianchun, Feng Wenjun, Chen Jinlun, Qi Xinyu, Li Jie, Tan Xueqiu, Zhang Haitao, Zeng Yirong. Platelet count as a novel potential predictor of periprosthetic joint infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4795-4801. |
| [7] | Cui Jiaming, Yang Dazhi. Treatment strategies for spinal metastases: advantages of 3D printing and precise treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5875-5881. |
| [8] | Wang Jicheng1, 2, Liu Shizhang1, Zhao Song1, 2, Yi Zhi1. Relationship between miRNA and occurrence and development of chondrosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5697-5702. |
| [9] | Wu Jiaxin, Pei Xibo. Advance in research on peri-implantitis in diabetic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5558-5564. |
| [10] | Luo Hong1, Liu Fang1, Li Shunhua1, Qiu Bing1, Liu Fuyao1, Zhang Yu2, Ma Limin3. Significance of gait analysis in the diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4969-4973. |
| [11] | Mo Fan1, Zhao Jinmin2, Sha Ke2, Yang Yuan1, Huang Weifeng1, Wei Wu1, Xie Qi1. Treatment and research progress of adult brachial plexus injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5072-5078. |
| [12] | Kong Lingyao, Li Tao, Zeng Xinglin, Li Jian, Xiong Yan. Synovial chondromatosis: how to improve the diagnosis accuracy and clearance rate of tumor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4570-4575. |
| [13] |
Wang Jicheng, Yi Zhi.
Correlation between miRNA and pathological development of osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3875-3881.
|
| [14] | Cai Qiucheng, Fan Hongkai, Xiong Rihui, Jiang Yi. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects liver function following fatty liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2625-2629. |
| [15] | Hu Xiaoli, Gu Ying, Cai Yan, Xie Jin, Liu Chan. Assessment of seven joint ultrasound score for early rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2523-2528. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||