Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (20): 3147-3151.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.20.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
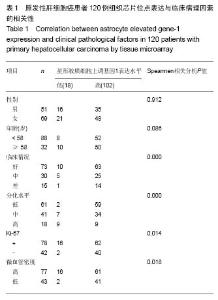
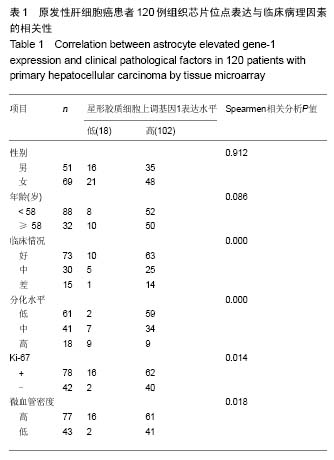
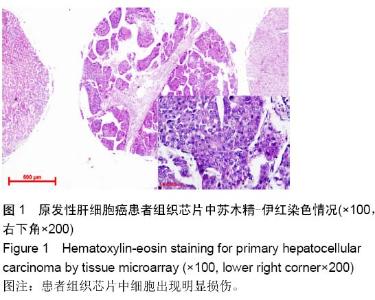
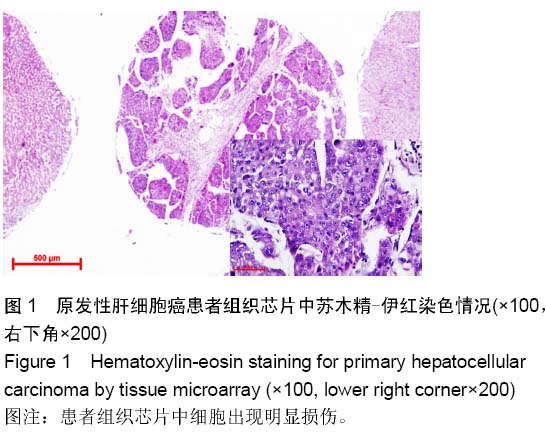
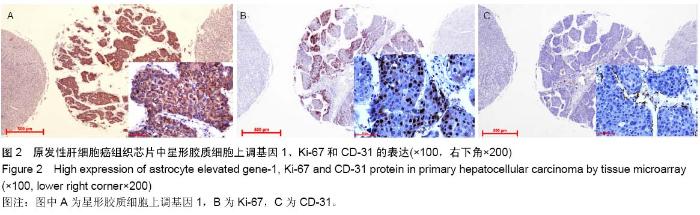
Tissue microarray detection for astrocyte elevated gene-1 and its correlation with pathological factors in primary hepatocellular carcinoma
Li Cong1, Zhang Wei2, Liu Xue-zhi3, Liu Bo-jun1, Zhang Hong-hai1, Yang Geng-xia1, Sheng Shou-peng1, Sun Yu1, Yuan Chun-wang1, Zheng Jia-sheng1
- 1Center of Oncology and Minimally Invasive Intervention, Beijing YouAn Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, General Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Laishui County Hospital, Baoding 071002, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2015-05-14Published:2015-05-14 -
Contact:Zheng Jia-sheng, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Center of Oncology and Minimally Invasive Intervention, Beijing YouAn Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China -
About author:李聪,男,1985年生,山东省人,汉族,2014年哈尔滨医科大学毕业,博士,医师,主要从事腹部实体肿瘤的临床和基础研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81472328; YouAN Fund for Liver Diseases and AIDS, No. BJYAH-2011-034; the National Science and Technology Support Program, No. 2012BAI15B08; the National Special Fund for Infectious Diseases, No. 2012ZX10002015-002
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Cong, Zhang Wei, Liu Xue-zhi, Liu Bo-jun, Zhang Hong-hai, Yang Geng-xia, Sheng Shou-peng, Sun Yu, Yuan Chun-wang, Zheng Jia-sheng. Tissue microarray detection for astrocyte elevated gene-1 and its correlation with pathological factors in primary hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(20): 3147-3151.
share this article
| [1] Bernard WS, Christopher PW. The World Cancer Report 2014. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). 2014.
[2] 张思维,郑荣寿,李霓,等.中国肝癌发病的趋势分析和预测[J].中华预防医学杂志,2012,46(7):587-592.
[3] Zheng J, Li J, Cui X, et al. Comparison of diagnostic sensitivity of C-arm CT, DSA and CT in detecting small HCC. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60(126):1509-1512.
[4] 郑加生,李建军,崔雄伟,等.肝动脉化疗栓塞联合CT引导下射频消融术治疗肝癌的疗效分析[J].介入放射学杂志,2009(5):324-327.
[5] Zheng JS, Long J, Sun B, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation can improve survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumour thrombosis: extending the indication for ablation? Clin Radiol. 2014;69(6):e253-263.
[6] Wang H, Chen L. Tumor microenviroment and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28 Suppl 1:43-48.
[7] Yoo BK, Emdad L, Su ZZ, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(3):465-477.
[8] Srivastava J, Siddiq A, Emdad L, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis: novel insights from a mouse model. Hepatology. 2012;56(5):1782-1791.
[9] Emdad L, Das SK, Dasgupta S, et al. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC: signaling pathways, downstream genes, interacting proteins, and regulation of tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 2013; 120:75-111.
[10] 李聪,龙江,生守鹏,等.星形细胞上调基因1(AEG-1)在肝细胞癌中的研究进展[J].实用肿瘤学杂志,2014(1):61-65.
[11] Zheng J, Li C, Wu X, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) shRNA sensitizes Huaier polysaccharide (HP)-induced anti-metastatic potency via inactivating downstream P13K/Akt pathway as well as augmenting cell-mediated immune response. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(5):4219-4224.
[12] Zheng J, Li C, Wu X, et al. Huaier polysaccharides suppresses hepatocarcinoma MHCC97-H cell metastasis via inactivation of EMT and AEG-1 pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;64:106-110.
[13] Zheng J, Li C, Wu X, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel biomarker of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in two China regions. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(3):2265-2269.
[14] Zerbini A, Pilli M, Penna A, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma liver nodules can activate and enhance tumor-specific T-cell responses. Cancer Res. 2006;66(2):1139-1146.
[15] Su ZZ, Kang DC, Chen Y, et al. Identification and cloning of human astrocyte genes displaying elevated expression after infection with HIV-1 or exposure to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein by rapid subtraction hybridization, RaSH. Oncogene. 2002;21(22):3592-3602.
[16] Kang DC, Su ZZ, Sarkar D, et al. Cloning and characterization of HIV-1-inducible astrocyte elevated gene-1, AEG-1. Gene. 2005;353(1):8-15.
[17] Qian BJ, Yan F, Li N, et al. MTDH/AEG-1-based DNA vaccine suppresses lung metastasis and enhances chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011;60(6):883-893.
[18] Zhu K, Dai Z, Pan Q, et al. Metadherin promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17(23): 7294-7302.
[19] Brown DM, Ruoslahti E. Metadherin, a cell surface protein in breast tumors that mediates lung metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2004; 5(4):365-374.
[20] Thirkettle HJ, Mills IG, Whitaker HC, et al. Nuclear LYRIC/AEG-1 interacts with PLZF and relieves PLZF-mediated repression. Oncogene. 2009;28(41):3663-3670.
[21] Kikuno N, Shiina H, Urakami S, et al. Knockdown of astrocyte-elevated gene-1 inhibits prostate cancer progression through upregulation of FOXO3a activity. Oncogene. 2007; 26(55): 7647-7655.
[22] Li C, Wu X, Zhang H, et al. A Huaier polysaccharide restrains hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by suppression angiogenesis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;75:115-120.
[23] Zhou Z, Deng H, Yan W, et al. Expression of metadherin/AEG-1 gene is positively related to orientation chemotaxis and adhesion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines of different metastatic potentials. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2012;32(3):353-357.
[24] Yuan L, Shi RR, Rao SM, et al. Reversal of resistance to adriamycin in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7/ADM by silencing AEG-1 gene and its mechanism. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2014;66(5):625-630.
[25] Ding L, Tian C, Feng S, et al. Small sized EGFR1 and HER2 specific bifunctional antibody for targeted cancer therapy. Theranostics. 2015;5(4):378-398.
[26] Srivastava J, Siddiq A, Emdad L, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis: novel insights from a mouse model. Hepatology. 2012;56(5):1782-1791.
[27] Zhang C, Li HZ, Qian BJ, et al. MTDH/AEG-1-based DNA vaccine suppresses metastasis and enhances chemosensitivity to paclitaxel in pelvic lymph node metastasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;70:217-226.
[28] Song E, Yu W, Xiong X, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes progression of cervical squamous cell carcinoma by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt signaling. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015;25(3):345-355.
[29] Liu K, Guo L, Guo Y, et al. AEG-1 3'-untranslated region functions as a ceRNA in inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-30a activity. Eur J Cell Biol. 2015;94(1):22-31.
[30] Wang P, Yin B, Shan L, et al. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and increases the chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in renal cancer Caki-1 cells. Mol Cells. 2014; 37(12):857-864.
[31] Zhao J, Wang W, Huang Y, et al. HBx elevates oncoprotein AEG-1 expression to promote cell migration by downregulating miR-375 and miR-136 in malignant hepatocytes. DNA Cell Biol. 2014;33(10):715-722.
[32] Huang Y, Ren GP, Xu C, et al. Expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) as a biomarker for aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:479.
[33] Gnosa S, Zhang H, Brodin VP, et al. AEG-1 expression is an independent prognostic factor in rectal cancer patients with preoperative radiotherapy: a study in a Swedish clinical trial. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(1):166-173.
[34] Vartak-Sharma N, Gelman BB, Joshi C, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel modulator of HIV-1-associated neuroinflammation via regulation of nuclear factor-κB signaling and excitatory amino acid transporter-2 repression. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(28):19599-19612.
[35] Yang G, Zhang L, Lin S, et al. AEG-1 is associated with tumor progression in nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31(6):986.
[36] Yuan L, Shi RR, Rao SM, et al. Reversal of resistance to adriamycin in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7/ADM by silencing AEG-1 gene and its mechanism. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2014;66(5):625-630.
[37] Hu B, Emdad L, Bacolod MD, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 interacts with Akt isoform 2 to control glioma growth, survival, and pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 2014;74(24):7321-7332.
[38] Wang F, Ke ZF, Wang R, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) promotes osteosarcoma cell invasion through the JNK/c-Jun/MMP-2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;452(4):933-939.
[39] Robertson CL, Srivastava J, Siddiq A, et al. Genetic deletion of AEG-1 prevents hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(21):6184-6193.
[40] Bhatnagar A, Wang Y, Mease RC, et al. AEG-1 promoter- mediated imaging of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(20):5772-5781.
[41] Srivastava J, Robertson CL, Rajasekaran D, et al. AEG-1 regulates retinoid X receptor and inhibits retinoid signaling. Cancer Res. 2014;74(16):4364-4377.
[42] Li G, Wang Z, Ye J, et al. Uncontrolled inflammation induced by AEG-1 promotes gastric cancer and poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2014;74(19):5541-5552.
[43] Zhao J, Wang W, Huang Y, et al. HBx elevates oncoprotein AEG-1 expression to promote cell migration by downregulating miR-375 and miR-136 in malignant hepatocytes. DNA Cell Biol. 2014;33(10):715-722.
[44] Huang Y, Li LP. Progress of cancer research on astrocyte elevated gene-1/Metadherin (Review). Oncol Lett. 2014;8(2): 493-501.
[45] Huang Y, Ren GP, Xu C, et al. Expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) as a biomarker for aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:479.
[46] Vartak-Sharma N, Gelman BB, Joshi C, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel modulator of HIV-1-associated neuroinflammation via regulation of nuclear factor-κB signaling and excitatory amino acid transporter-2 repression. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(28):19599-19612.
[47] Yang G, Zhang L, Lin S, et al. AEG-1 is associated with tumor progression in nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31(6):986.
[48] Li S, Guo X, Ma X, et al. Expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 closely correlates with the angiogenesis of gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(5):1447-1454.
[49] Song H, Tian Z, Qin Y, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 activates MMP9 to increase invasiveness of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(7):6679-6685.
[50] Liu X, Wang D, Liu H, et al. Knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) in cervical cancer cells decreases their invasiveness, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and chemoresistance. Cell Cycle. 2014;13(11):1702-1707.
[51] Xia X, Du R, Zhao L, et al. Expression of AEG-1 and microvessel density correlates with metastasis and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2014;45(4):858-865.
[52] Huang S, Wu B, Li D, et al. Knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1 inhibits tumor growth and modifies microRNAs expression profiles in human colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;444(3):338-345.
[53] Deng H, Zhou Z, Tu W, et al. Knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1 inhibits growth through suppression of IL-6 secretion in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(1):101-106.
[54] Huang K, Li LA, Meng Y, et al. High expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is associated with progression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and unfavorable prognosis in cervical cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:297.
[55] Yan JW, Lin JS, He XX. The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(5):1011-1018.
[56] Guo J, Xia B, Meng F, et al. miR-137 suppresses cell growth in ovarian cancer by targeting AEG-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441(2):357-363.
[57] Guo F, Zhang LJ, Liu W, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 overexpression in histologically favorable Wilms tumor is related to poor prognosis. J Pediatr Urol. 2014;10(2):317-323.
[58] Ma J, Xie SL, Geng YJ, et al. In vitro regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma cell viability, apoptosis, invasion, and AEG-1 expression by LY294002. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014;38(1):73-80.
[59] Son HS, Kwon HY, Sohn EJ, et al. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase3 β mediate ursolic acid induced apoptosis in HepG2 liver cancer cells. Phytother Res. 2013; 27(11):1714-1722.
|
| [1] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [2] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [3] | Zhao Shuangdan, Zheng Jiahua, Qi Wenbo, Huang Xianghua. Role and mechanism of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in reproductive system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3097-3102. |
| [4] | Long Qian, Guan Xiaoyan, Wang Qian, Hu Huan, Liu Jianguo. Transcriptome sequencing technology and its application in oral diseases, dental implants and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1791-1798. |
| [5] | Xu Zhuqing, Wang Zhuhui, Zhang Xinyu, Zheng Jianjin. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and tongue squamous carcinoma cells: promoting growth or targeting biotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 128-132. |
| [6] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [7] | Zhang Xinyu, Wang Zhuhui, Xu Zhuqing, Zheng Jianjin. Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of tongue squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5392-5395. |
| [8] | Yan Zhiwen, Li Shuofeng, Li Ao, Hu Ziqi, Ma Litao, Zhang Ershuai, Li Jingwu, Yao Fanglian, Che Pengcheng, Sun Hong. Preparation and biocompatibility evaluation of modified thermosensitive xyloglucan hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4841-4847. |
| [9] | Han Fei, Qin Haixia. Effects of microRNA-9 on proliferation and migration of thyroid papillary cancer stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3404-3409. |
| [10] | Dai Senlin, Li Xiaoqian, Wu Jie, Yue Changwu, Li Yajun. CNE2 stem-like cells of nasopharyngeal carcinoma have stem cell characteristics and high level of autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2703-2708. |
| [11] | Ren Hao, Dong Jing, Liu Li-wei, Chen Zhao-lin, Pan Jin-jin, Chen Xi, Song Hai-yan, Zhang Jun-fei, Chen Cong-xin, Liu Bo. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B cirrhosis patients given treatment with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1350-1356. |
| [12] | Chen Hao1, Zhang Wu2, Wang Hao1, Zhang Heng-yi1, Xu Zhi-wei1. Mechanism by which endothelin-1 regulates the differentiation of P19 cells into cardiac conduction cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(12): 1915-1921. |
| [13] | Wang Mei-jiang, Qi Lin. Immunological impact of autologous peripheral blood stem cell infusion on lung adenocarcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(9): 1402-1407. |
| [14] | Fan Hui-fang, Chen Fang, Ma Feng-xia, Chi Ying, Lu Shi-hong, Han Zhong-chao. Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of NB4 leukemic cells affected by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(25): 3949-3955. |
| [15] | Lv Wei-dong, Cai Lin, Zhang Jia-dong, Lei Guang-yan, Liu Zhi-gang, Zhang Xin-wei, Lu Jian-rong. Acellular embryoid bodies in mice: preparation and effect of promoting differentiation of Lewis lung carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(20): 2972-2978. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||