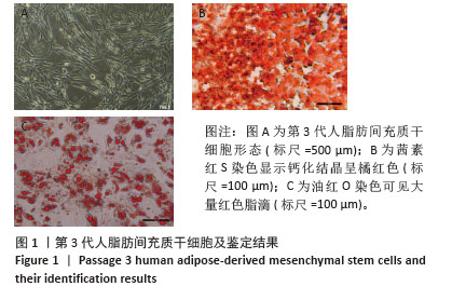
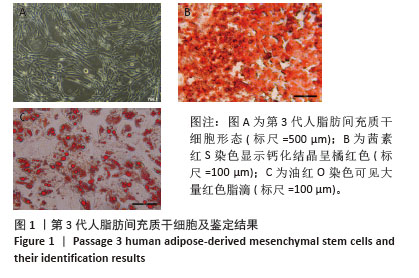
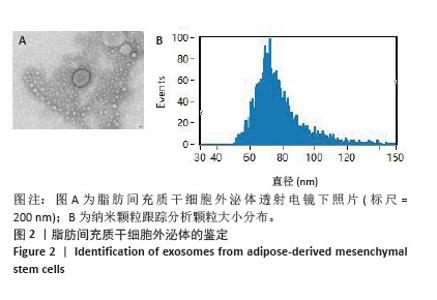
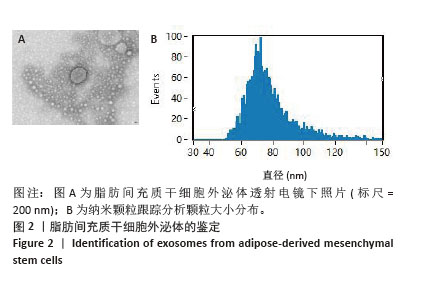
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1699-1710.doi: 10.12307/2026.582
Previous Articles Next Articles
Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing
He Jiale1, 2, Huang Xi2, Dong Hongfei2, Chen Lang1, Zhong Fangyu1, Li Xianhui1, 2
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637002, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, General Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-17Revised:2025-04-30Accepted:2025-05-29Online:2026-03-08Published:2025-08-19 -
Contact:Li Xianhui, PhD, Associate professor, School of Clinical Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637002, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, General Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:He Jiale, Master candidate, School of Clinical Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637002, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, General Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China Huang Xi, Attending physician, Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, General Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China He Jiale and Huang Xi contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Incubation Project of Hospital Management Project of General Hospital of Western Theater Command, No. 2021-XZYG-C36 (to HX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
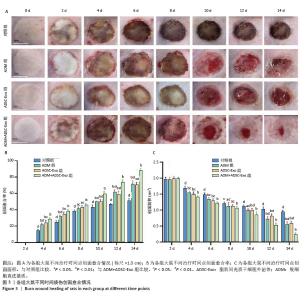
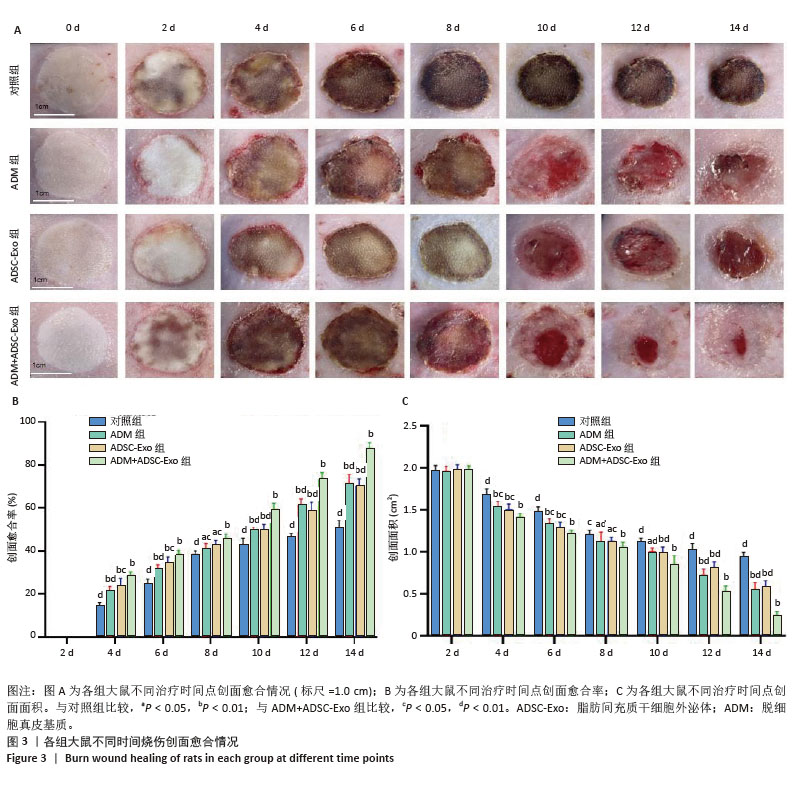
2.3 创面愈合形态学 由于深度烧伤会造成创面在12-24 h内进行性损伤,导致创面逐渐扩大[15],故选择造模后第2天作为创面愈合率和创面愈合面积的起始点。烧伤后立即拍照可见各组大鼠创面均为圆形,呈蜡白色。治疗2,4,6,8 d,各组大鼠创面下出现颜色深度不同的痂壳;治疗10 d,除对照组外,其他3组痂壳均脱落,见黄色渗出液,ADM+ ADSC-Exo组创面上皮化最明显;治疗12,14 d,各组大鼠创面均缩小,ADM+ADSC-Exo组创面面积明显小于其他3组,见图3A。ADM+ADSC-Exo组治疗第4,6,8,10,12,14天的创面愈合率均高于ADSC-Exo组、ADM组及对照组(P < 0.05),ADSC-Exo组、ADM组创面愈合率高于对照组(P < 0.05),见图3B。ADM+ADSC-Exo组治疗第4,6,8,10,12,14天的创面面积均低于ADSC-Exo组、ADM组及对照组(P < 0.05),ADSC-Exo组、ADM组创面面积低于对照组(P < 0.05),见图3C。以上实验结果表明,ADM+ADSC-Exo、ADSC-Exo、ADM均可促进大鼠烧伤创面的愈合,其中ADM+ADSC-Exo的治疗效果最为显著。 "
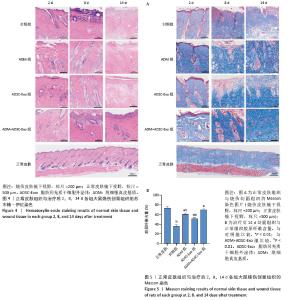
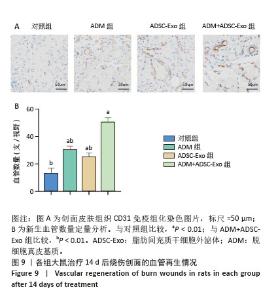
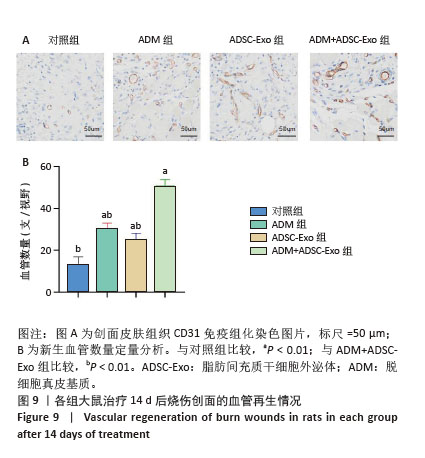
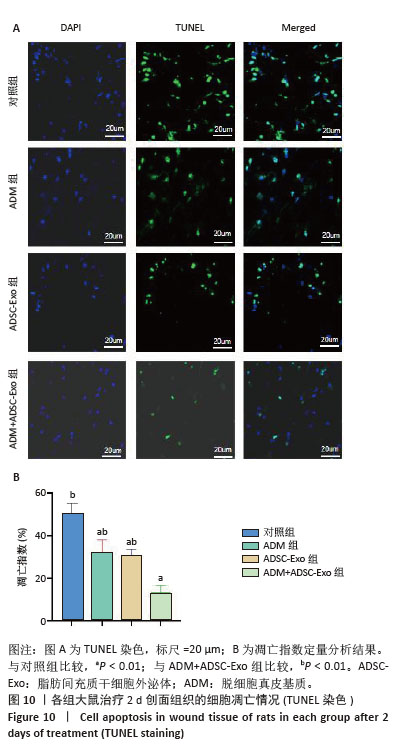
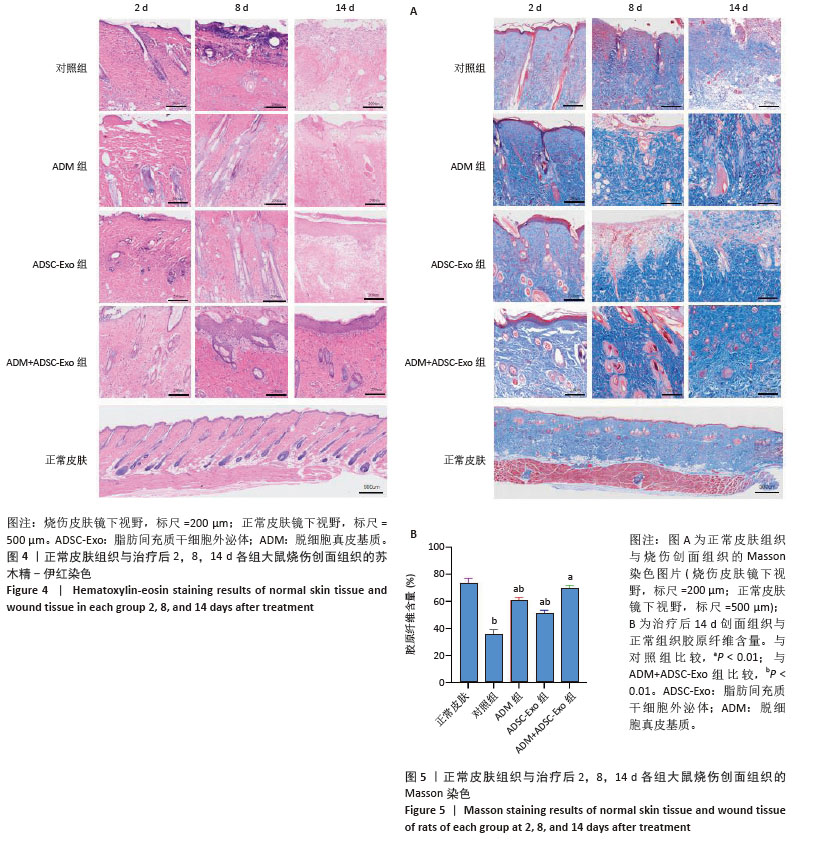
2.4 治疗后不同时间点各组大鼠创面组织学观察结果 见图4。治疗后2 d,各组大鼠创面组织均出现表皮层细胞核固缩,真皮层胶原纤维破裂、融合,可见坏死的皮肤附属器。治疗后8 d,对照组坏死的胶原纤维出现断裂,断裂处以下可见部分再生的胶原纤维;ADM组与ADSC-Exo组坏死胶原纤维断裂处可见不连续的部分新生表皮层,下方可见有较多疏松的胶原纤维再生;ADM+ADSC-Exo组可见连续的表皮层,且颜色明显深于其他3组,表皮层下可见大量再生的胶原纤维,并可见新生的少量皮肤附属器。治疗后14 d,ADM+ADSC-Exo组表皮层更为完整、连续,并与真皮层贴合度更高,胶原纤维粗大,排列有序,皮肤附属器完整,新生组织覆盖范围大于其他3组;其他3组可见不同程度的炎症细胞浸润,胶原纤维相对细小并杂乱;ADM+ADSC-Exo组皮肤组织及形态最接近于正常皮肤。 2.5 不同治疗时间点各组大鼠Masson染色观察结果 见图5。治疗后2 d,各组大鼠创面胶原纤维均坏死、融合,排列紊乱。治疗后8 d,对照组创面组织下方可见疏松的再生胶原纤维,以及少量坏死的皮肤附属器,还未生成表皮层;ADM组与ADSC-Exo组可见不连续的表皮层再生,以及大量再生的胶原纤维,其中ADM组胶原纤维颜色深于ADSC-Exo组,而ADM+ADSC-Exo组胶原纤维颜色比他3组更深,可见部分再生的皮肤附属器。治疗后14 d,ADM+ADSC-Exo组相较其他3组,胶原纤维为深蓝色且分布更为均匀,胶原纤维粗大、排列整齐有序、间隙清晰;ADM+ADSC-Exo组胶原纤维结构及含量最接近正常皮肤组织,而其他3组胶原纤维排列相对紊乱,细胞浸润及组织空泡较多。对正常皮肤组织及治疗后14 d创面组织通过Image J定量分析胶原纤维含量,结果显示:正常皮肤胶原纤维含量均高于ADM+ADSC-Exo组、ADSC-Exo组、ADM组及对照组,其中ADM+ADSC-Exo组创面新生组织中胶原纤维含量显著高于另外3组(P < 0.01),最接近正常皮肤。而ADSC-Exo组与ADM组创面新生组织中胶原纤维含量均高于对照组(P < 0.01)。 "
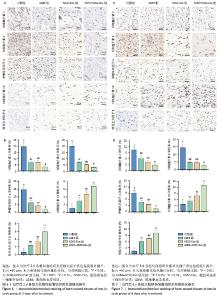
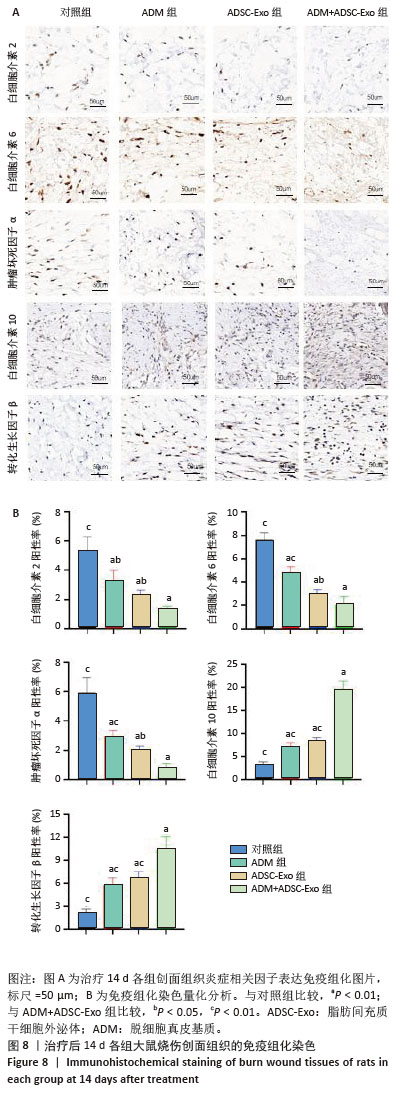
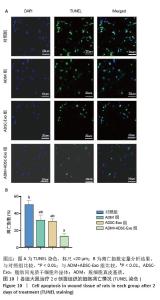
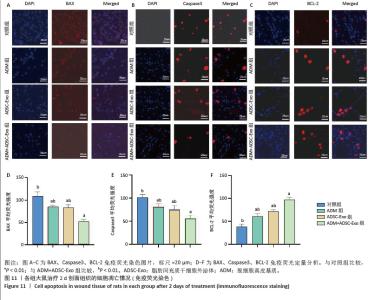
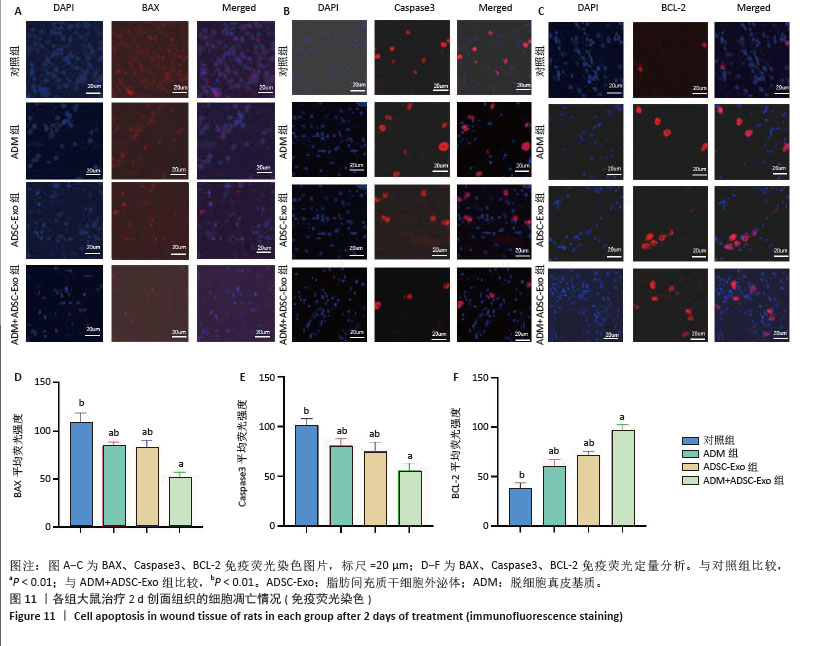
2.6 各组大鼠皮肤创面中相关炎症因子表达 见图6-8。治疗后2 d,ADM+ADSC-Exo组、ADSC-Exo组、ADM组大鼠创面中白细胞介素2、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α表达均明显低于对照组(P < 0.01),ADM+ADSC-Exo组低于ADSC-Exo组、ADM组(P < 0.05);ADM+ADSC-Exo组大鼠创面中白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β表达均高于其他3组,ADM组、ADSC-Exo 组高于对照组(P < 0.05)。治疗后8 d,ADM+ADSC-Exo组大鼠创面中白细胞介素2、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α表达低于其他3组,ADSC-Exo组、ADM组低于对照组(P < 0.01);ADM+ADSC-Exo组大鼠创面中白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β表达均高于其他3组,ADM、ADSC-Exo 组高于对照组(P < 0.01)。治疗14 d,ADM+ADSC-Exo组、ADSC-Exo组、ADM组大鼠创面中白细胞介素2、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α表达明显低于对照组(P < 0.01);ADM+ADSC-Exo组低于ADSC-Exo组、ADM组(P < 0.05)。ADM+ADSC-Exo组、ADSC-Exo组、ADM组大鼠创面中白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β表达高于对照组(P < 0.01),ADM+ADSC-Exo组高于ADM组、ADSC-Exo组(P < 0.01)。 "

| [1] KESHRI VR, PEDEN M, SINGH P, et al. Health systems research in burn care: an evidence gap map. Inj Prev. 2023;29(5):446-453. [2] JESCHKE MG, VAN BAAR ME, CHOUDHRY MA, et al. Burn injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):11. [3] ŻWIEREŁŁO W, PIORUN K, SKÓRKA-MAJEWICZ M, et al. Burns: Classification, Pathophysiology, and Treatment: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):3749. [4] KALLMEYER K, ANDRÉ-LÉVIGNE D, BAQUIÉ M, et al. Fate of systemically and locally administered adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their effect on wound healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(1): 131-144. [5] XIE F, TENG L, LU J, et al. Interleukin-10-Modified Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Hypertrophic Scar Formation via Regulating the Biological Characteristics of Fibroblasts and Inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:6368311. [6] 王一希,陈俊杰,岑瑛,等.脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体促进糖尿病创面愈合的研究进展[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022,38(5):491-495. [7] HEO JS, KIM S. Human adipose mesenchymal stem cells modulate inflammation and angiogenesis through exosomes. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1): 2776. [8] GE L, WANG K, LIN H, et al. Engineered exosomes derived from miR-132-overexpresssing adipose stem cells promoted diabetic wound healing and skin reconstruction. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11: 1129538. [9] WANG Y, PIAO C, LIU T, et al. Effects of the exosomes of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on apoptosis and pyroptosis of injured liver in miniature pigs. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;169:115873. [10] TRZYNA A, BANAŚ-ZĄBCZYK A. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Secretome and Its Potential Application in “Stem Cell-Free Therapy”. Biomolecules. 2021;11(6):878. [11] XIANG K, CHEN J, GUO J, et al. Multifunctional ADM hydrogel containing endothelial cell-exosomes for diabetic wound healing. Mater Today Bio. 2023;23:100863. [12] ZHU W, CAO L, SONG C, et al. Cell-derived decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds for articular cartilage repair. Int J Artif Organs. 2021; 44(4):269-281. [13] REDDY MSB, PONNAMMA D, CHOUDHARY R, et al. A Comparative Review of Natural and Synthetic Biopolymer Composite Scaffolds. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(7):1105. [14] GONZÁLEZ-CUBERO E, GONZÁLEZ-FERNÁNDEZ ML, GUTIÉRREZ-VELASCO L, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Anat. 2021;238(5): 1203-1217. [15] LU M, ZHAO J, WANG X, et al. Research advances in prevention and treatment of burn wound deepening in early stage. Front Surg. 2022;9: 1015411. [16] LIN JC, CHEN XD, XU ZR, et al. Association of the Circulating Supar Levels with Inflammation, Fibrinolysis, and Outcome in Severe Burn Patients. Shock. 2021;56(6):948-955. [17] KNUTH CM, AUGER C, JESCHKE MG. Burn-induced hypermetabolism and skeletal muscle dysfunction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021; 321(1):C58-C71. [18] REZAEI S, NILFOROUSHZADEH MA, AMIRKHANI MA, et al. Preclinical and Clinical Studies on the Use of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Mol Pharm. 2024;21(6):2637-2658. [19] MA J, YONG L, LEI P, et al. Advances in microRNA from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome: focusing on wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(46):9565-9577. [20] LIN Z, LIN D, LIN D. The Mechanisms of Adipose Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Wound Healing and Regeneration. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024;48(14):2730-2737. [21] HU N, CAI Z, JIANG X, et al. Hypoxia-pretreated ADSC-derived exosome-embedded hydrogels promote angiogenesis and accelerate diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2023;157:175-186. [22] DOLIVO D, XIE P, HOU C, et al. Application of decellularized human reticular allograft dermal matrix promotes rapid re-epithelialization in a diabetic murine excisional wound model. Cytotherapy. 2021;23(8):672-676. [23] LINGYAN L, HAN Z, JIALU L, et al. Acellular Dermal Matrix for Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2023:15347346231201696. [24] CAMPITIELLO F, MANCONE M, CAMMAROTA M, et al. Acellular Dermal Matrix Used in Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Clinical Outcomes Supported by Biochemical and Histological Analyses. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):7085. [25] HU P, ARMATO U, FREDDI G, et al. Human Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Co-Cultured on Silk Fibroin Scaffolds Exosomally Overrelease Angiogenic and Growth Factors. Cells. 2023;12(14):1827. [26] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, LI T, et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Promote Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Embedded in Collagen/Platelet-Rich Plasma Scaffold and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2023;35(40):e2303642. [27] QI M, ZHU X, YU X, et al. Preparation of W/O Hypaphorine-Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application on Promoting Chronic Wound Healing via Alleviating Inflammation Block. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(11):2830. [28] 郑凡,蔡玉娥,李黎,等.黄芪多糖在深Ⅱ度烧伤大鼠创面愈合中的作用及其机制[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022,38(5):491-495. [29] CHANG TH, WU CS, CHIOU SH, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes as a Novel Anti-Inflammatory Agent and the Current Therapeutic Targets for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines. 2022;10(7):1725. [30] CASADO-DÍAZ A, QUESADA-GÓMEZ JM, DORADO G. Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) in Regenerative Medicine: Applications in Skin Wound Healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:146. [31] ROSTAMI Z, KHORASHADIZADEH M, NASERI M. Immunoregulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: Micro-RNAs. Immunol Lett. 2020;219:34-45. [32] WANG B, LI L, YU R. Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Suppress the Progression of Chronic Endometritis. Cell Transplant. 2023;32:9636897231173736. [33] HE X, LI D, CHEN T. Porcine Acellular Dermal Matrix Promotes Migration and Suppresses Inflammation of Keratinocytes by Mediating the AKT Signaling Pathway. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2023;71(12):852-858. [34] AHANGAR P, MILLS SJ, SMITH LE, et al. Treatment of murine partial thickness scald injuries with multipotent adult progenitor cells decreases inflammation and promotes angiogenesis leading to improved burn injury repair. Wound Repair Regen. 2021;29(3):380-392. [35] HSU LC, PENG BY, CHEN MS, et al. The potential of the stem cells composite hydrogel wound dressings for promoting wound healing and skin regeneration: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(2):278-285. [36] CAO Y, SHI X, ZHAO X, et al. Acellular dermal matrix decorated with collagen-affinity peptide accelerate diabetic wound healing through sustained releasing Histatin-1 mediated promotion of angiogenesis. Int J Pharm. 2022;624:122017. [37] TORUN KARADERE M, ACUNER B, ISIKTEKIN E, et al. The effect of Tarantula cubensis D6 on zone of stasis in a rat burn model. Burns. 2023;49(2):444-454. [38] URALOĞLU M, URAL A, EFE G, et al. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on the Zone of Stasis and Apoptosis in an Experimental Burn Model. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2019;27(2):173-181. [39] ZHOU H, FANG Q, LI N, et al. ASMq protects against early burn wound progression in rats by alleviating oxidative stress and secondary mitochondria‑associated apoptosis via the Erk/p90RSK/Bad pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):390. [40] LI W, CHEN L, XIAO Y. Apigenin protects against ischemia-/hypoxia-induced myocardial injury by mediating pyroptosis and apoptosis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(4):307-312. [41] ASUKU M, SHUPP JW. Burn wound conversion: clinical implications for the treatment of severe burns. J Wound Care. 2023;32(Sup5):S11-S20. [42] V G R, ELLUR G, A GABER A, et al. 4-aminopyridine attenuates inflammation and apoptosis and increases angiogenesis to promote skin regeneration following a burn injury in mice. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10(1):428. [43] KARI S, SUBRAMANIAN K, ALTOMONTE IA, et al. Programmed cell death detection methods: a systematic review and a categorical comparison. Apoptosis. 2022;27(7-8):482-508. [44] ZONG L, LIANG Z. Apoptosis-inducing factor: a mitochondrial protein associated with metabolic diseases-a narrative review. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2023;13(3):609-622. [45] COSTIGAN A, HOLLVILLE E, MARTIN SJ. Discriminating Between Apoptosis, Necrosis, Necroptosis, and Ferroptosis by Microscopy and Flow Cytometry. Curr Protoc. 2023;3(12):e951. |
| [1] | Wang Qisa, Lu Yuzheng, Han Xiufeng, Zhao Wenling, Shi Haitao, Xu Zhe. Cytocompatibility of 3D printed methyl acrylated hyaluronic acid/decellularized skin hydrogel scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [2] | Gao Yanguo, Guo Xu, Li Xiaohan, Chen Shiqi, Zhu Haitao, Huang Liangyong, Ye Fang, Lu Wei Wang Qibin, Zheng Tao, Chen Li. Optimization of prescription ratio of “Honghuangbai” gel by orthogonal test in diabetic skin wound mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [3] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [4] | Yang Lixia, Diao Liqin, Li Hua, Feng Yachan, Liu Xin, Yu Yuexin, Dou Xixi, Gu Huifeng, Xu Lanju. Regulatory mechanism of recombinant type III humanized collagen protein improving photoaging skin in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1988-2000. |
| [5] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [6] | Han Teng, Ma Hong, Yang Ruoyi, Luo Yi, Li Chao. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal delivery of angiopoietin-2 is involved in tumor angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1755-1767. |
| [7] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [8] | Cao Yong, Teng Hongliang, Tai Pengfei, Li Junda, Zhu Tengqi, Li Zhaojin. Interactions between cytokines and satellite cells in muscle regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [9] | Huang Jiawen, Pan Zhiyi, Xue Wenjun, Lian Yuanpei, Xu Jianda. Plant-derived vesicles and malignant tumor therapy: cross-species communication and modulation of host cell responses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1828-1838. |
| [10] | Wang Baiyan, Yang Shu, Wang Yiming, Wu Mengqing, Xiao Yu, Guo Zixuan, Zhang Boyi, Feng Shuying. Exosome-delivered CRISPR/Cas system enables gene editing in target cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1839-1849. |
| [11] | Wang Zhenze, Liu Fende, Zhang Rui, Li Wujun. Mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of arteriosclerosis obliterans of lower extremities: systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1869-1876. |
| [12] | Song Puzhen, Ma Hebin, Chen Hongguang, Zhang Yadong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined with transforming growth factor beta 1 on macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [13] | Cai Ziming, Yu Qinghe, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Zhang Chongyang, Lin Wenping. Heme oxygenase-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [14] | Yuan Xiaoshuang, Yang Xu, Yang Bo, Chen Xiaoxu, Tian Ting, Wang Feiqing, Li Yanju, Liu Yang, Yang Wenxiu. Effect of conditioned medium of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells on proliferation and apoptosis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1632-1640. |
| [15] | Wang Qiuhua, Du Ziwei, Wang Wenshuang, Zhao Dongmei, Zhang Xiaoqing. Differences in metabolism, proliferation, differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, and differentiation into vascular smooth muscle cells between male and female rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1687-1698. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||