Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (22): 5770-5781.doi: 10.12307/2026.182
Previous Articles Next Articles
Forkhead box transcription factor O3 affects bone metabolism and participates in the pathological processes of various bone-related diseases
Han Jie1, Hu Tianfa2, Wu Yachao2, Nong Bin2, Yu Kailong2
- 1Department of Joint and Sports Medicine, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-06-06Accepted:2025-09-04Online:2026-08-08Published:2025-12-27 -
Contact:Han Jie, Department of Joint and Sports Medicine, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Han Jie, MS, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Joint and Sports Medicine, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82260858 and 82460872 (to HJ); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2024GXNSFAA010243 (to HJ); Pilot Project of the Construction of High-Level Key Disciplines of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Guangxi, No. GTYKEF[2023]13 (to HJ); Guangxi Key Research Office of Traditional Chinese Medicine Construction Project, No. GTYKEF[2023]9 (to HJ); Guangxi Youth Qihuang Scholars Training Project, No. GTYKEF[2022]13 (to HJ); "Qihuang Project" High-Level Talent Team Cultivation Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. [2024]3 (to HJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Jie, Hu Tianfa, Wu Yachao, Nong Bin, Yu Kailong. Forkhead box transcription factor O3 affects bone metabolism and participates in the pathological processes of various bone-related diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5770-5781.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
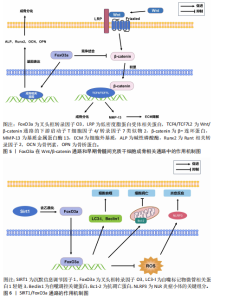
2.1 叉头框转录因子O3与骨组织细胞 2.1.1 叉头框转录因子O3与骨髓间充质干细胞 骨髓间充质干细胞是成骨细胞的前体细胞,在骨组织形成和修复过程中发挥关键作用。叉头框转录因子O3作为一种重要的转录因子,在骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和分化过程中具有复杂的调控作用。在成骨早期,叉头框转录因子O3对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响是复杂的。FATIMA等[4]发现硒纳米颗粒处理的人间充质干细胞的骨标记蛋白表达增加,同时细胞内磷酸化c-Jun N端激酶和叉头框转录因子O3的基因和蛋白表达也相应增加,这表明硒纳米颗粒会诱导激活c-Jun N端激酶/叉头框转录因子O3通路,提高细胞活力,增强人间充质干细胞的成骨潜能。作为一种转录因子,叉头框转录因子O3还能与Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的启动子结合,协助形成成骨谱系[5-6],其中,Runt相关转录因子2是成骨分化中的关键因子,它能触发早期祖细胞中主要骨基质蛋白基因的表达,如Ⅰ型胶原(早期祖细胞)、骨桥蛋白(未成熟成骨细胞)和骨钙素(成熟成骨细胞中编码骨钙素的同源基因),这些因子分别在成骨细胞的不同成熟阶段发挥作用[6]。因此,在早期成骨祖细胞中,叉头框转录因子O3能够协助骨髓间充质干细胞形成成骨谱系,促进骨基质的形成。 叉头框转录因子O3通过调控自噬和脂质代谢促进成骨分化。在骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化过程中,叉头框转录因子O3和碱性磷酸酶水平随成骨分化呈时间依赖性增加,叉头框转录因子O3通过提高微管相关蛋白1轻链3和Beclin1等自噬相关因子的水平,增加了碱性磷酸酶和成骨分化相关因子的表达,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,这说明叉头框转录因子O3在早期成骨过程中通过激活自噬促进成骨[7]。此外,叉头框转录因子O3也能通过抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化促进成骨。例如,叉头框转录因子O3可以通过下调过氧化物酶体增殖激活受体γ和Notch信号来减少骨髓间充质干细胞的脂肪生成并促进成骨,从而防止骨量流失[8]。 2.1.2 叉头框转录因子O3与成骨细胞 成骨细胞源自骨髓间充质干细胞,主要承担骨基质的合成、分泌及矿化等过程,在骨重塑过程中发挥关键作用[9-10]。在成骨细胞中,叉头框转录因子O3会增强抗氧化能力。例如,主动脉羧基肽酶样蛋白可增加成骨细胞中叉头框转录因子O3的核易位,上调叉头框转录因子O3抗氧化基因(如超氧化物歧化酶2和过氧化物还原酶5)的表达,从而促进成骨细胞的分化与存活,促进骨形成过程[11]。硫氨基酸代谢的关键中间体s-腺苷甲硫氨酸在机制上能促使叉头框转录因子O3磷酸化和激活磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/AKT)信号通路,降低衰老间充质干细胞的活性氧水平,进而延缓细胞的整体衰老过程,促进成脂和成骨分化,叉头框转录因子O3参与了这一过程,对调节活性氧水平和促进成骨分化有着显著作用[12]。 YOON等[13]研究显示,烟酰胺处理后成骨前体细胞中沉默信息调节因子3的mRNA表达增加,线粒体抗氧化酶的活性提高,这也是烟酰胺通过激活沉默信息调节因子3并促进叉头框转录因子O3表达的结果,活性氧水平下降,细胞凋亡和骨量流失减少。因此,在成骨细胞中叉头框转录因子O3可通过激活抗氧化基因的表达从而增加抗氧化酶含量,对成骨细胞起到重要的保护作用,有利于维持骨量。 Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路在成骨细胞分化和骨质流失预防中起着至关重要的作用,而叉头框转录因子O3会对其造成干扰。例如,研究发现,铁调素缺乏小鼠与野生型小鼠相比表现出铁积累和骨质流失。与野生型小鼠的骨髓间充质干细胞相比,铁调素缺乏小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力明显减弱。然而,在铁调素缺乏时,β-连环蛋白、T细胞因子4/转录因子7类似物2(T cell factor 4/Transcriptional factor 7-like 2,TCF4/TCF7L2)和叉头框转录因子O3在骨组织中的表达没有改变,但β-连环蛋白与叉头框转录因子O3的结合强烈,抑制了β-连环蛋白与T细胞因子4/转录因子7类似物2的结合,这表明铁调素缺乏可能通过叉头框转录因子O3表达干扰Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路,进而影响成骨分化过程[14]。抑制叉头框转录因子O3可能是治疗铁调素缺乏性骨质流失的一种可能方法。 药物显著抑制叉头框转录因子O3的表达能改善Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路。例如,在微重力条件下,螺旋藻能降低叉头框转录因子O3表达,增加Wnt信号分子和β-连环蛋白的表达,进而激活Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路,促进成骨细胞的骨形成[15]。益肾壮骨汤能抑制绝经后骨质疏松大鼠叉头框转录因子O3的升高,激活Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路[16]。在上述过程中,叉头框转录因子O3会对Wnt/β-连环蛋白成骨通路进行干扰,从而影响成骨过程,而通过药物抑制其表达,能逆转这一过程。 然而亦有研究结论相反,叉头框转录因子O3可促进机械力诱导的成骨分化。研究发现,在机械力诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中,叉头框转录因子O3的表达水平显著上调。与对照组相比,正畸牙齿运动侧叉头框转录因子O3阳性细胞数量持续增加,并伴有成骨增强。值得注意的是,叉头框转录因子O3敲低可有效抑制机械力诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,而叉头框转录因子O3的过表达可增强这一作用。在机制上,研究揭示了叉头框转录因子O3可能通过与Runt相关转录因子2合作激活其启动子来促进骨钙素转录的一种新的调控模式,这表明叉头框转录因子O3在机械力诱导的成骨分化过程中,能以有效的方式直接调节下游成骨细胞分化[17]。上述研究说明叉头框转录因子O3对成骨分化过程具有双向调控作用,见表1。叉头框转录因子O3在成骨分化中的作用可能存在差异,这取决于不同的分子微环境,将其作为分子靶点进行治疗仍需进一步探究。 2.1.3 叉头框转录因子O3与破骨细胞 破骨细胞源自骨造血祖细胞,对骨骼生长、重塑及骨结构维持至关重要。活性氧对细胞信号传递和生理功能有显著影响,过量活性氧会导致氧化应激和多种疾病,同时,活性氧也是调节破骨细胞分化的重要因素之一。有研究表明,一种新生DNA甲基转移酶能通过调控叉头框转录因子O3启动子的甲基化抑制叉头框转录因子O3的表达,增加活性氧水平,进而促进破骨细胞形成,表明叉头框转录因子O3通过调控细胞内活性氧来影响破骨细胞分化的过程[18]。在高龄骨质疏松小鼠模型中,核因子κB受体活化因子配体基因表达增加,破骨细胞数量明显高于低龄小鼠。随着"
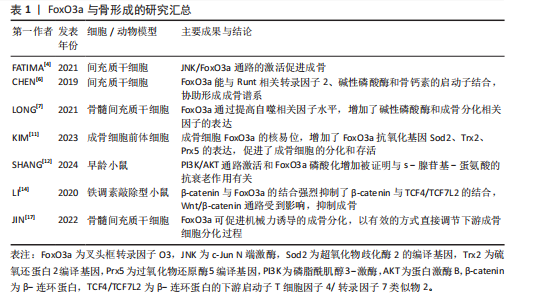

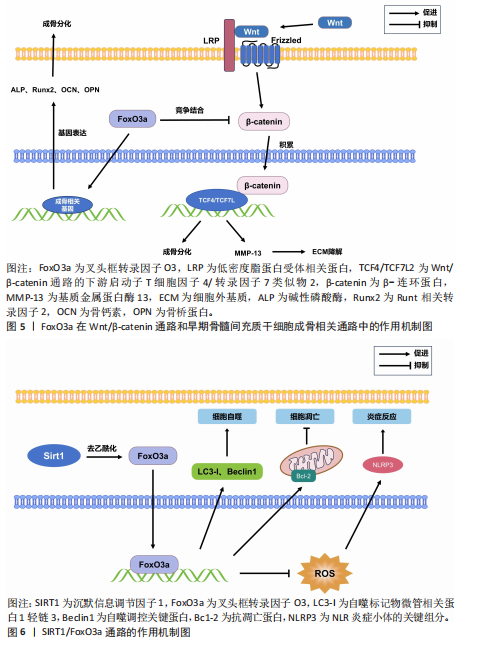
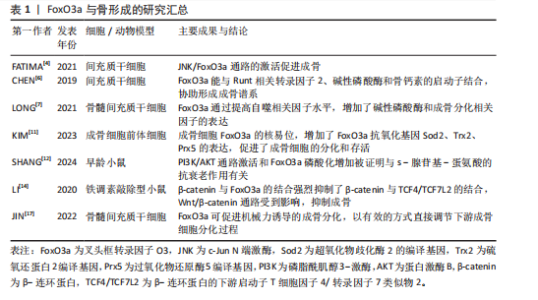
周龄的增长,小鼠衰老和炎症相关基因(如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素13)的表达增加,而氧化应激相关基因(如超氧化物歧化酶编译基因)、叉头框转录因子O3基因的表达随年龄增长而降低,这种情况是由衰老、炎症、氧化应激和转化生长因子β1信号通路等因素所驱动的,更加支持叉头框转录因子O3抵抗氧化应激而抑制破骨细胞形成的作用[19]。 不仅如此,叉头框转录因子O3还能通过调控自噬过程抑制破骨细胞形成。ZHENG等[20]研究表明辅酶Q10导致小鼠单核巨噬细胞中的磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)通路失活,显著提高细胞内叉头框转录因子O3和自噬相关蛋白的表达水平,从而促进自噬,阻止破骨细胞生成。此外,CAO等[21]还发现叉头框转录因子O3亚型2是破骨细胞分化的重要抑制因子,它能通过延缓端粒磨损、促进细胞更新和维持基因组稳定性来发挥抗衰老作用,对调控破骨细胞有着重要作用。不仅如此,叉头框转录因子O3也能以一条新通路抑制破骨细胞生成:例如在类风湿关节炎中,转录抑制因子RBP-J/促破骨转录因子-促炎性miR-182是介导破骨细胞生成的新的调节网络,该网络在肿瘤坏死因子诱导的破骨细胞发生和炎症性骨吸收中起重要作用。其中,RBP-J能抑制miR-182进而促进叉头框转录因子O3的表达,抑制破骨细胞形成。而在类风湿关节炎中,在肿瘤坏死因子诱导下,RBP-J的表达被抑制,而破骨细胞调节因子(活化T细胞核因子1和miR-182)的表达增强,叉头框转录因子O3的表达也被抑制,促进破骨细胞生成[22]。综上,在多数情况下,叉头框转录因子O3对破骨细胞的形成起着抑制作用。叉头框转录因子O3是调控破骨细胞生成的重要调控因子,它的作用通常受到氧化应激和炎症因子的影响,见表2。 2.1.4 叉头框转录因子O3与骨细胞 叉头框转录因子O3在高糖环境下保护骨细胞。研究表明,使用脂联素处理后高糖环境下小鼠骨样细胞MLO-Y4细胞中磷酸化腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)显著激活以及细胞质中磷酸化叉头框转录因子O3显著增加,这提示更多的叉头框转录因子O3核定位和叉头框转录因子O3磷酸化。此外,在脂联素诱导的MLO-Y4细胞中促凋亡蛋白半胱天冬酶3和半胱天冬酶8的表达降低,而抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的表达增加。这些数据表明,腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶/叉头框转录因子O3轴在糖尿病诱导的骨细胞凋亡中具有调控作用,可通过减轻高糖诱导的MLO-Y4细胞的氧化应激来抑制骨细胞凋亡[23]。 叉头框转录因子O3的乙酰化促使骨细胞衰老。1,25-二羟基维生素D缺乏通过维生素D受体介导下调沉默信息调节因子1的表达、增加叉头框转录因子O3的乙酰化和氧化应激、激活p16和p53信号通路、诱导衰老相关的分泌表型增加,促使骨细胞衰老,从而导致下颌骨骨质流失[24]。因此,叉头框转录因子O3的表达可通过抑制氧化应激、减缓骨细胞衰老从而减少骨质流失。 2.1.5 叉头框转录因子O3与软骨细胞 叉头框转录因子O3在骨关节炎中对软骨细胞具有保护作用。例如,DL-3-n-丁基黄嘌呤能够抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路,上调叉头框转录因子O3的表达,进而抑制人骨关节炎软骨细胞的凋亡,促进软骨细胞外基质合成,抑制骨关节炎[25]。经典卵巢切除诱导的骨关节炎大鼠软骨中,成骨细胞分泌的富含半胱氨酸的酸性分泌蛋白可下调腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶/叉头框转录因子O3信号通路,从而促进软骨细胞变性,而腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶激动剂可改善骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞的分解代谢,这也体现了叉头框转录因子O3对软骨细胞的保护作用,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B和腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶等上游通路因子分别对叉头框转录因子O3起到调控作用[26]。 叉头框转录因子O3的去磷酸化抑制了软骨细胞凋亡。小C末端结构域磷酸酶4(small C‐terminal domain phosphatase‐4,SCP4)缺失会导致促凋亡蛋白表达水平上调,此时伴有叉头框转录因子O3的磷酸化在小鼠生长板的软骨细胞中升高,这说明小C末端结构域磷酸酶4可通过维持叉头框转录因子O3的去磷酸化状态进而抑制软骨细胞凋亡,这对软骨发育和成骨过程至关重要[27]。因此,叉头框转录因子O3的去磷酸化状态可促进软骨细胞外基质合成,抑制软骨细胞的分解代谢,对软骨细胞体现重要的保护作用。不仅如此,在软骨细胞的肥大中,叉头框转录因子O3也具有抑制作用。HUANG等[28]发现,骨形态发生蛋白结合内皮调节因子(bone morphogenetic protein binding endothelial regulator,BMPER)作为骨形态发生蛋白4激动剂,能激活骨形态发生蛋白结合内皮调节因子/骨形态发生蛋白4信号通路,促进软骨细胞肥大。而5,7,3’,4’-四甲基黄酮可通过激活叉头框转录因子O3表达,抑制骨形态发生蛋白结合内皮调节因子/骨形态发生蛋白4信号通路,进而抑制软骨细胞肥大。研究指出,肥大前软骨细胞和肥大软骨细胞中活性氧水平较高,这与叉头框转录因子O1、叉头框转录因子O3和叉头框转录因子O4失活导致的小鼠生长板异常有关,这说明叉头框转录因子O3很可能通过调节活性氧水平来抑制软骨细胞肥大。与之相反,叉头框转录因子O3也可促使软骨细胞肥大。例如,叉头框转录因子O3与Runt相关转录因子1在软骨细胞中的高度共表达会促进软骨祖细胞的早期软骨形成和终末肥大,促进了软骨基质的钙化和软骨组织的退行性变,从而加重骨关节炎的发生[29]。 综上,叉头框转录因子O3对软骨细胞起到重要的保护作用,叉头框转录因子O3与不同的因子结合,可对软骨细胞肥大起到完全相反的作用,见表3。 2.2 叉头框转录因子O3通过作用于Wnt/β-连环蛋白与磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B等通路影响骨疾病 通过以上研究发现,叉头框转录因子O3通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白与磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B等通路在各类骨组织细胞中充当着枢纽的作用。叉头框转录因子O3作为骨代谢调控的核心转录因子,其功能实现不仅依赖于自身核-质穿梭的动态平衡,更深度整合于Wnt/β-连环蛋白与磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B等经典"

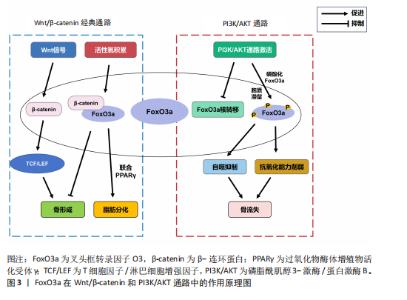
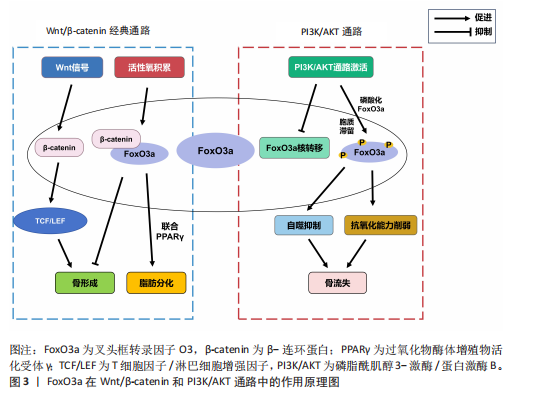
通路的交互网络中。例如,在生理状态下,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路通过磷酸化叉头框转录因子O3诱导其在胞质滞留,抑制其转录活性,从而协调成骨细胞分化与破骨细胞活化的动态平衡。同时,Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路与叉头框转录因子O3也形成双向调控作用:β-连环蛋白可增强叉头框转录因子O3对氧化应激应答基因(如超氧化物歧化酶2)的转录激活,而叉头框转录因子O3则通过上调Wnt拮抗剂限制β-连环蛋白过度活化,亦可竞争性抑制β-连环蛋白积累,防止骨形成失控。这种精密互作在骨关节炎、骨质疏松等疾病中发生紊乱。例如,炎症微环境中蛋白激酶B异常激活导致叉头框转录因子O3功能抑制,削弱其抗氧化能力并加剧软骨细胞凋亡;而在衰老性骨丢失中,Wnt信号衰减与叉头框转录因子O3核聚集共同驱动成骨前体细胞向脂肪分化偏移。值得注意的是,叉头框转录因子O3还通过调控自噬-溶酶体系统及线粒体代谢重编程,直接参与骨组织细胞的能量稳态维持,它与线粒体能量代谢核心因子的协同作用,为理解骨疾病中代谢-信号交叉调控提供了新视角。上述机制表明,叉头框转录因子O3不仅是骨组织细胞命运决定的“分子开关”,更能通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白和磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B等通路密切影响诸多骨疾病的发病和治疗过程,见图3。 2.3 叉头框转录因子O3与骨相关疾病 2.3.1 叉头框转录因子O3与骨关节炎 叉头框转录因子O3可抑制软骨细胞外基质降解。在骨关节炎中,5,7,3’,4’-四甲基黄酮可以激活骨关节炎软骨细胞中的沉默信息调节因子1/叉头框转录因子O3信号通路,抑制CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白β对骨关节炎软骨细胞的作用,进而防止软骨细胞外基质的降解,延缓骨关节炎的进展[30]。转谷氨酰胺酶2的激活可以稳定β-连环蛋白,增强典型的Wnt信号,促使腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶和叉头框转录因子O3的磷酸化,这一"
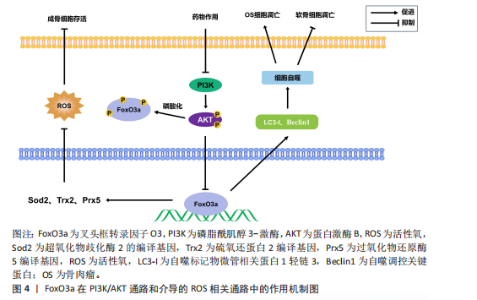
过程促使产生了基质金属蛋白酶13,加速了骨关节炎的发生[31],而叉头框转录因子O3作为Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路的干扰分子,可抑制Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路,抑制基质金属蛋白酶13的产生,对骨关节炎的治疗是有益的。在这两个过程中,叉头框转录因子O3分别参与不同通路进而阻止软骨细胞外基质的降解,延缓骨关节炎进展。 叉头框转录因子O3通过促进自噬抑制骨关节炎进展。在骨关节炎中,腺苷A2A受体刺激增加叉头框转录因子O3的激活和核定位,促进自噬通量的增加,改善软骨细胞的代谢功能,进而抑制软骨细胞凋亡。其中,叉头框转录因子O3上调参与自噬的激活,抑制了骨关节炎中软骨细胞的减 少[32]。此外,叉头框转录因子O3作为血清糖皮质激素调节激酶1的下游靶标,亦可通过去磷酸化促进血清糖皮质激素调节激酶1的表达,激活自噬和提高成骨细胞活力,促进软骨细胞存活[33]。综上,叉头框转录因子O3在骨关节炎中,可以保护软骨细胞外基质免受降解,亦可通过激活自噬抑制软骨细胞凋亡,延缓了骨关节炎进展。 叉头框转录因子O3可抑制炎性体激活。研究发现,过表达沉默信息调节因子1或抑制核因子κB可通过促进叉头框转录因子O3来缓解miRNA-30b-5p诱导的细胞凋亡和炎性体的激活,而下调沉默信息调节因子1或叉头框转录因子O3可逆转miRNA-30b-5p抑制剂诱导的抗炎和细胞凋亡抑制作用。因此,miRNA-30b-5p可抑制沉默信息调节因子1/叉头框转录因子O3通路加重骨关节炎进展,而叉头框转录因子O3a的表达则可抑制细胞凋亡和炎症反应[34]。 2.3.2 叉头框转录因子O3与骨质疏松症 骨质疏松症是一种以骨平衡失调为特征的骨骼疾病,而氧化应激是导致此疾病的重要原因。在这一病理过程中,氧化应激可诱导β-连环蛋白与叉头框转录因子O3和过氧化物酶体增殖物活化受体γ共同作用,从而使得主通路由β-连环蛋白转录因子家族介导的转录转变为叉头框转录因子O3介导的转录,抑制骨髓的成骨分化,进而转化为脂肪分化,导致骨质疏松症[35]。叉头框转录因子O3参与了氧化应激所导致的骨质疏松过程,可对成骨过程起到抑制作用。 反之,叉头框转录因子O3还能通过促进线粒体自噬来维持骨量。研究发现,烟草毒素能通过磷酸化蛋白激酶B抑制叉头框转录因子O3和PTEN诱导激酶1/E3泛素连接酶(PTEN-induced kinase 1/Parkin,PINK1/Parkin)通路的表达,抑制线粒体自噬,促进骨髓间充质干细胞衰老和耗竭,进而导致骨质疏松症的发生;此外,为研究叉头框转录因子O3是否可以逆转烟草毒素引起的衰老,还使用了蛋白激酶B活性抑制剂抑制蛋白激酶B的磷酸化而上调叉头框转录因子O3蛋白的表达,结果显示,随着蛋白激酶B抑制剂浓度的升高,叉头框转录因子O3的核定位增加,恢复了PTEN诱导激酶1的mRNA表达,缓解了烟草毒素引起的衰老。其中,叉头框转录因子O3的表达降低了烟草毒素诱导的线粒体氧化应激,促进线粒体自噬,显著下调骨髓间充质干细胞中衰老标志物的表达,恢复成骨分化,减轻了烟草毒素暴露小鼠的骨质流失[36]。此外,亦有研究表明,17β-雌二醇可诱导成骨细胞中沉默信息调节因子1上调,进而提高自噬相关蛋白、抗凋亡蛋白和叉头框转录因子O3表达,降低促凋亡蛋白表达,促进细胞自噬,从而抑制细胞凋亡[37]。可见,叉头框转录因子O3能通过激活自噬减少骨量流失。 叉头框转录因子O3通过减轻氧化应激延缓骨质流失。研究表明,在体内,miRNA-29a能够促进叉头盒O途径的转录并维持氧化还原状态,抑制氧化应激和叉头框转录因子O3的丢失,从而延缓成骨细胞衰老和骨质流失,逆转年龄诱导的骨髓基质细胞的成骨功能丧失。而在体外实验中,miRNA-29a能够中断DNA甲基转移酶介导的叉头框转录因子O3启动子甲基化和降低衰老相关的β-半乳糖苷酶活性,从而减轻氧化应激、衰老和矿化基质的不足[38]。因此,叉头框转录因子O3可以作为治疗骨质疏松症的一个潜在靶点。 总之,叉头框转录因子O3在骨质疏松症不同的通路中,似乎表现为相反的作用,一方面,它能够在氧化应激的条件下干扰Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路,导致骨量流失。另一方面,它又能激活线粒体自噬过程,恢复成骨分化。叉头框转录因子O3功能的差异可能与它所在通路的主导分子相关联,在氧化应激条件下,β-连环蛋白会被诱导与叉头框转录因子O3和过氧化物酶体增殖物共同作用,抑制成骨分化;而叉头框转录因子O3与沉默信息调节因子1的结合则会促进线粒体自噬,抑制细胞凋亡和骨质流失,这归咎于多个分子的协同作用。因此,叉头框转录因子O3的功能往往受到多个分子的协同调控,这与细胞所处的病理环境与分化状态相关。而对于将叉头框转录因子O3作为直接靶点的药物,则受到叉头框转录因子O3的主要结合分子的影响,这仍需要进一步探究。 2.3.3 叉头框转录因子O3与恶性骨肿瘤 恶性骨肿瘤是一种生长在骨骼及软骨组织的恶性肿瘤疾病,主要分为骨肉瘤、软骨肉瘤和尤文氏肉瘤,在临床中,继发性恶性骨肿瘤的发生占多数。而叉头框转录因子O3能够抑制恶性骨肿瘤的转移。研究表明,在骨肉瘤中,叉头框转录因子O3的激活会导致促凋亡基因p53的转录,进而诱导骨肉瘤细胞凋亡[39]。碳离子辐照、miRNA-34和哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白抑制剂的多模式治疗也能促进叉头框转录因子O3高表达从而抑制软骨肉瘤[40]。此外,亦有实验证明叉头框转录因子O3的表达能诱导活性氧介导的骨肉瘤细胞凋亡,抑制骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和迁移能力[41]。miRNA-29a-3p也可通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路从而提高叉头框转录因子O3水平,促进骨肉瘤细胞的自噬凋亡,抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖、集落形成、迁移和侵袭[42]。因此,叉头框转录因子O3表达对于恶性骨肿瘤转移的控制有着积极作用[43]。 叉头框转录因子O3可抑制骨肉瘤细胞生长。环状RNA的过表达能与赖氨酸乙酰转移酶6B(lysine acetyltransferase 6B,KAT6B)相互作用,增加叉头框转录因子O3启动子上组蛋白H3第23位赖氨酸乙酰化修饰(histone H3 lysine 23 acetylation,H3K23ac)的富集,从而激活叉头框转录因子O3的表达,增强微管相关蛋白1轻链3和Beclin1等自噬相关蛋白的表达水平,增加了骨肉瘤细胞的凋亡率。在骨肉瘤细胞中,环状RNA通过赖氨酸乙酰转移酶6B/组蛋白H3第23位赖氨酸乙酰化修饰/FoxO3a通路抑制了骨肉瘤的生长,叉头框转录因子O3在这一过程中对骨肉瘤细胞发挥促凋亡和促自噬的作用[44]。除此之外,一种有效的蛋白酶体抑制剂,能够下调抗凋亡蛋白的表达,上调促凋亡蛋白和叉头框转录因子O3等在骨肉瘤细胞中的表达,从而激活细胞的凋亡信号通路,亦可发挥抗癌作用[45]。这也佐证了叉头框转录因子O3对骨肉瘤细胞生长的抑制作用。 恶性骨肿瘤相关疼痛是严重影响晚期乳腺癌、肺癌和前列腺癌患者的常见症状。氧化应激在恶性骨肿瘤相关疼痛的发展中起着至关重要的作用,因此,活性氧的清除是治疗恶性骨肿瘤相关疼痛的一个重要途径,而叉头框转录因子O3能通过抗氧化作用对恶性骨肿瘤相关疼痛有显著影响。例如,沉默信息调节因子2能通过抑制叉头框转录因子O3乙酰化、磷酸化和泛素化,上调叉头框转录因子O3和抗氧化基因的表达(如超氧化物歧化酶2和过氧化氢酶的编译基因),从而抑制氧化应激,缓解恶性骨肿瘤相关疼痛[46]。这种对恶性骨肿瘤相关疼痛的治疗作用是基于叉头框转录因子O3的抗氧化作用实现的。综上,叉头框转录因子O3能通过促自噬、促凋亡或抗氧化的作用对恶性骨肿瘤的生长、扩散迁移与临床症状进行有效控制。 2.3.4 叉头框转录因子O3与股骨头坏死 股骨头坏死是一种影响年轻人的毁灭性疾病,可导致明显的疼痛、关节表面塌陷和致残功能障碍。现已确定,股骨头坏死是由于血液供应不足导致骨细胞和骨髓细胞死亡,但是股骨头坏死的具体发病机制尚不完全清楚[47]。而叉头框转录因子O3同样能参与骨代谢影响股骨头坏死的发病过程,不仅如此,叉头框转录因子O3的编码基因还是影响股骨头坏死发病过程的枢纽基因之一[48]。 叉头框转录因子O3通过调节脂质代谢影响股骨头坏死。高脂血症导致外周血脂肪栓子形成,引起骨微血管闭塞,增加骨内压力,加重骨微循环功能障碍,这是股骨头坏死产生原因的重要假说之一。研究发现,股骨头坏死小鼠模型中伴随着高密度脂蛋白胆固醇的减少和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的增加,两者的比值是股骨头坏死发展的一个危险因素[49]。而叉头框转录因子O3可通过靶向自噬促进分化的小鼠前脂肪细胞的脂质积累和炎症反应。因此,叉头框转录因子O3的抑制可能是治疗股骨头坏死的一个方向,能在一定程度上抑制脂质积累,改善股骨头血供。然而,叉头框转录因子O3抑制的同时也能影响成骨分化,例如,在类固醇相关性骨坏死患者的骨髓间充质干细胞中,miR-29a-3p可促使叉头框转录因子O3下调,进而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,抑制Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素等成骨分化标志物的表达,抑制碱性磷酸酶活性,促进细胞凋亡和细胞周期阻滞。这表明miR-29a-3p可以作用于叉头框转录因子O3的靶基因,从而抑制叉头框转录因子O3表达和Wnt/β-连环蛋白的信号传导,抑制了成骨分化过程[50]。因此,叉头框转录因子O3在股骨头坏死中的靶向治疗作用有待进一步明确研究。 2.3.5 FoxO3a与腰椎间盘突出症 随着人口老龄化的发展,腰椎间盘突出症的发病率正逐年上升。腰椎间盘突出症是一种以椎间盘退变为主要病理变化的病症。有研究发现,不同年龄组和退化组的人类髓核样本中,叉头框转录因子O3蛋白水平随着年龄的增长和退化而下降[51],这也一定程度上解释了随着患者年龄升高,腰椎间盘突出症发病率逐渐上升的现象。不仅如此,叉头框转录因子O3与椎间盘退变的骨代谢关系也密切影响着腰椎间盘突出症的发生。 叉头框转录因子O3通过激活自噬预防椎间盘退变。研究表明,核磷酸化蛋白p300可以提高叉头框转录因子O3的表达,进而让叉头框转录因子O3和沉默信息调节因子1启动子结合,增加沉默信息调节因子1的表达,抑制Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路。通过这种机制,可以促进椎间盘退变组织来源髓核细胞的自噬和细胞凋亡衰减,抑制椎间盘退变的进展[52]。原花青素C1已被证实对髓核细胞具有保护作用。在椎间盘退变中,原花青素C1通过激活沉默信息调节因子3/叉头框转录因子O3信号通路,进而改善髓核细胞线粒体动力学失衡、线粒体自噬和线粒体介导的凋亡作用,保留了髓核细胞的细胞外基质[53]。间充质干细胞能够将miR-217转移到髓核细胞中,进而提高叉头框转录因子O3表达,促进肿瘤坏死因子干预髓核细胞中的自噬水平,阻碍细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解[54]。因此,叉头框转录因子O3可通过激活髓核细胞自噬过程抑制椎间盘退变。 叉头框转录因子O3可防止椎间盘细胞外基质的降解。在椎间盘退变中,活性氧暴露会激活YTH N6-甲基腺苷RNA结合蛋白2(YTH domain family protein 2,YTHDF2),促进了N6-甲基腺苷修饰的叉头框转录因子O3的降解,损害了叉头框转录因子O3激活基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂1的能力,这种降解加剧了基质金属蛋白酶的活性,导致椎间盘细胞外基质的降解。反之,使用YTH N6-甲基腺苷RNA结合蛋白2抑制剂可显著提高叉头框转录因子O3和基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂1的表达量,降低基质金属蛋白酶活性,减轻椎间盘变性[55]。此外,叉头框转录因子O3的磷酸化也可抑制细胞外基质降解。17β-雌二醇可诱导磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路的激活,从而促使叉头框转录因子O3磷酸化,导致基质金属蛋白酶启动子活性降低,上调了Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白的表达,抑制细胞外基质的降解,预防椎间盘退变的发生[56]。综上,在腰椎间盘突出症中,叉头框转录因子O3可通过激活髓核细胞的自噬过程,抑制细胞凋亡和细胞外基质的降解,最终延缓腰椎间盘突出症的发病进展。"
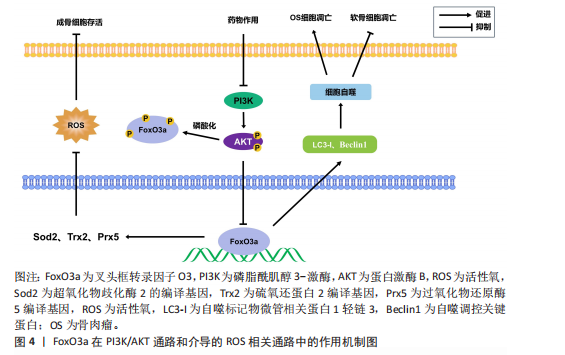
| [1] WANG C, TU X, JIANG Y, et al. Prognostic value of high FoxO3a expression in patients with solid tumors: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Int J Biol Markers. 2022; 37(2):210-217. [2] CHANDRA A, RAJAWAT J. Skeletal Aging and Osteoporosis: Mechanisms and Therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3553. [3] 张亚楠,陈保民,高阳,等.FoxO3a转录因子与机体氧化应激损伤的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2016,29(3):327-331. [4] FATIMA S, ALFRAYH R, ALRASHED M, et al. Selenium Nanoparticles by Moderating Oxidative Stress Promote Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Osteoblasts. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:331-343. [5] DHOKE NR, GEESALA R, DAS A. Low Oxidative Stress-Mediated Proliferation Via JNK-FoxO3a-Catalase Signaling in Transplanted Adult Stem Cells Promotes Wound Tissue Regeneration. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018; 28(11):1047-1065. [6] CHEN D, GONG Y, XU L, et al. Bidirectional regulation of osteogenic differentiation by the FOXO subfamily of Forkhead transcription factors in mammalian MSCs. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12540. [7] LONG C, CEN S, ZHONG Z, et al. FOXO3 is targeted by miR-223-3p and promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing autophagy. Hum Cell. 2021;34(1):14-27. [8] YU W, TONG MJ, WU GH, et al. FoxO3 Regulates Mouse Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell Fate and Bone-Fat Balance During Skeletal Aging. Stem Cells Dev. 2024;33(13-14):365-375. [9] PONZETTI M, RUCCI N. Osteoblast Differentiation and Signaling: Established Concepts and Emerging Topics. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6651. [10] AMARASEKARA DS, KIM S, RHO J. Regulation of Osteoblast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):2851. [11] KIM H, KIM MJ, MOON SA, et al. Aortic carboxypeptidase-like protein, a putative myokine, stimulates the differentiation and survival of bone-forming osteoblasts. FASEB J. 2023;37(8):e23104. [12] SHANG L, LI X, DING X, et al. S-Adenosyl-l-Methionine Alleviates the Senescence of MSCs Through the PI3K/AKT/FoxO3a Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells. 2024;42(5): 475-490. [13] YOON H, PARK SG, KIM HJ, et al. Nicotinamide enhances osteoblast differentiation through activation of the mitochondrial antioxidant defense system. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55(7):1531-1543. [14] LI G, ZHANG H, WU J, et al. Hepcidin deficiency causes bone loss through interfering with the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway via Forkhead box O3a. J Orthop Translat. 2020;23:67-76. [15] ZHANG J, HUANG Y, BAI N, et al. Spirulina platensis components mitigate bone density loss induced by simulated microgravity: A mechanistic insight. Food Chem. 2025; 463(Pt 3):141361. [16] LI B, JIANG C, ZHAN X. Combined Therapy of Yishen Zhuanggu Decoction and Caltrate D600 Alleviates Postmenopausal Osteoporosis by Targeting FoxO3a and Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022; 2022:7732508. [17] JIN A, HONG Y, YANG Y, et al. FOXO3 Mediates Tooth Movement by Regulating Force-Induced Osteogenesis. J Dent Res. 2022;101(2):196-205. [18] ZHANG W, LI W, DU J, et al. Dnmt3a-mediated hypermethylation of FoxO3 promotes redox imbalance during osteoclastogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025;122(12):e2418023122. [19] MA Z, QIU L, LI J, et al. Construction a novel osteoporosis model in immune-deficient mice with natural ageing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;735:150820. [20] ZHENG D, CUI C, YE C, et al. Coenzyme Q10 prevents RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by promoting autophagy via inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024;57:e13474. [21] CAO G, LIN M, GU W, et al. The rules and regulatory mechanisms of FOXO3 on inflammation, metabolism, cell death and aging in hosts. Life Sci. 2023;328:121877. [22] INOUE K, HU X, ZHAO B. Regulatory network mediated by RBP-J/NFATc1-miR182 controls inflammatory bone resorption. FASEB J. 2020;34(2):2392-2407. [23] ZENG Y, LIANG H, GUO Y, et al. Adiponectin regulates osteocytic MLO-Y4 cell apoptosis in a high-glucose environment through the AMPK/FoxO3a signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(10):7088-7096. [24] CHEN H, HU X, YANG R, et al. SIRT1/FOXO3a axis plays an important role in the prevention of mandibular bone loss induced by 1,25(OH)2D deficiency. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(14):2712-2726. [25] ZHANG Y, DAI J, YAN L, et al. DL-3-N-Butylphthalide Promotes Cartilage Extracellular Matrix Synthesis and Inhibits Osteoarthritis Development by Regulating FoxO3a. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:9468040. [26] JIANG A, XU P, YANG Z, et al. Increased Sparc release from subchondral osteoblasts promotes articular chondrocyte degeneration under estrogen withdrawal. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(1):26-38. [27] WANG P, ZOU K, CAO J, et al. Protein phosphatase SCP4 regulates cartilage development and endochondral osteogenesis via FoxO3a dephosphorylation. Cell Prolif. 2024;57(9):e13691. [28] HUANG J, REN Q, JIAO L, et al. TMF suppresses chondrocyte hypertrophy in osteoarthritic cartilage by mediating the FoxO3a/BMPER pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2024;28(1):283. [29] YUAN S, ZHANG L, JI L, et al. FoxO3a cooperates with RUNX1 to promote chondrogenesis and terminal hypertrophic of the chondrogenic progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;589:41-47. [30] WANG Z, SHI W, WU L, et al. TMF inhibits extracellular matrix degradation by regulating the C/EBPβ/ADAMTS5 signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;174:116501. [31] HAN MS, JUNG YK, KIM GW, et al. Transglutaminase-2 regulates Wnt and FoxO3a signaling to determine the severity of osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):13228. [32] FRIEDMAN B, CORCIULO C, CASTRO CM, et al. Adenosine A2A receptor signaling promotes FoxO associated autophagy in chondrocytes. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):968. [33] YU XH, XU XM, ZHANG SX. Low-dose dexamethasone promotes osteoblast viability by activating autophagy via the SGK1/FoxO3a signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2023;47(3):669-678. [34] XU H, ZHANG J, SHI X, et al. NF-κB inducible miR-30b-5p aggravates joint pain and loss of articular cartilage via targeting SIRT1-FoxO3a-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(16):20774-20792. [35] ZOU DB, MOU Z, WU W, et al. TRIM33 protects osteoblasts from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in osteoporosis by inhibiting FoxO3a ubiquitylation and degradation. Aging Cell. 2021;20(7): e13367. [36] XIANG K, REN M, LIU F, et al. Tobacco toxins trigger bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells aging by inhibiting mitophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;277:116392. [37] WANG Y, MEI R, HAO S, et al. Up-regulation of SIRT1 induced by 17beta-estradiol promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis in osteoblasts. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(20):23652-23671. [38] LIAN WS, WU RW, CHEN YS, et al. MicroRNA-29a Mitigates Osteoblast Senescence and Counteracts Bone Loss through Oxidation Resistance-1 Control of FoxO3 Methylation. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(8):1248. [39] OYAMA T, BRASHEARS CB, RATHORE R, et al. PHGDH inhibition and FOXO3 modulation drives PUMA-dependent apoptosis in osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 2025;16(1):89. [40] VARES G, AHIRE V, SUNADA S, et al. A multimodal treatment of carbon ions irradiation, miRNA-34 and mTOR inhibitor specifically control high-grade chondrosarcoma cancer stem cells. Radiother Oncol. 2020;150:253-261. [41] CHA HS, LEE HK, PARK SH, et al. Acetylshikonin induces apoptosis of human osteosarcoma U2OS cells by triggering ROS-dependent multiple signal pathways. Toxicol In Vitro. 2023;86:105521. [42] QI S, XU L, HAN Y, et al. miR-29a-3p mitigates the development of osteosarcoma through modulating IGF1 mediated PI3k/Akt/FOXO3 pathway by activating autophagy. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(18):1980-1995. [43] JURKOVICOVA D, MAGYERKOVA M, SESTAKOVA Z, et al. Evaluation of expression profiles of microRNAs and two target genes, FoxO3a and RUNX2, effectively supports diagnostics and therapy predictions in breast cancer. Neoplasma. 2016;63(6): 941-951. [44] JIANG C, JIANG Z, ZHANG X. Circular RNA circMRPS35 regulates progression and autophagy in osteosarcoma cells by recruiting KAT6B to govern FOXO3. Anticancer Drugs. 2022;33(7):607-613. [45] LEE HK, PARK SH, NAM MJ. Proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021;40(11):1985-1997. [46] YANG C, KANG F, HUANG X, et al. Spinal sirtuin 2 attenuates bone cancer pain by deacetylating FoxO3a. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024;1870(4):167129. [47] LI Z, SHAO W, LV X, et al. Advances in experimental models of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Translat. 2023; 39:88-99. [48] SHI W, ZHANG X, XU C, et al. Identification of Hub Genes and Pathways Associated with Oxidative Stress of Cartilage in Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Using Bioinformatics Analysis. Cartilage. 2022; 13(1):19476035221074000. [49] ZHANG X, LIU Q, ZHANG X, et al. FoxO3a regulates lipid accumulation and adipocyte inflammation in adipocytes through autophagy : Role of FoxO3a in obesity. Inflamm Res. 2021;70(5):591-603. [50] WANG C, ZHU M, YANG D, et al. MiR-29a-3p Inhibits Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Targeting FOXO3 and Repressing Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis. Int J Stem Cells. 2022;15(3):324-333. [51] WANG Y, YANG Y, ZUO R, et al. FOXO3 protects nucleus pulposus cells against apoptosis under nutrient deficiency via autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;524(3):756-763. [52] HAO Y, REN Z, YU L, et al. p300 arrests intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the FOXO3/Sirt1/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Aging Cell. 2022;21(8): e13677. [53] HUA W, XIE L, DONG C, et al. Procyanidin C1 ameliorates acidic pH stress induced nucleus pulposus degeneration through SIRT3/FOXO3-mediated mitochondrial dynamics. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):1071. [54] HAO Y, ZHU G, YU L, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells confer protection against intervertebral disc degeneration through a microRNA-217-dependent mechanism. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(11): 1455-1467. [55] WANG F, WANG Y, ZHANG S, et al. YTHDF2-dependent m6A modification of FOXO3 mRNA mediates TIMP1 expression and contributes to intervertebral disc degeneration following ROS stimulation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81(1):477. [56] GAO XW, SU XT, LU ZH, et al. 17β-Estradiol Prevents Extracellular Matrix Degradation by Downregulating MMP3 Expression via PI3K/Akt/FOXO3 Pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(5):292-299. |
| [1] | Chen Haojie, Wang Dai, Shen Shan. Immune inflammatory microenvironment mechanisms in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [2] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [3] | Han Nianrong, Huang Yifei, Akram · Osman, Liu Yanlu, Hu Wei . Programmed cell death receptor-1 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a high-glucose microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1649-1657. |
| [4] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [5] | Chen Ju, Zheng Jinchang, Liang Zhen, Huang Chengshuo, Lin Hao, Zeng Li. Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [6] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [7] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [8] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [9] | Zhu Kuicheng, Du Chunyan, Zhang Jintao. Mechanism by which hairless gene mutation promotes white adipose tissue browning in hairless mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1424-1430. |
| [10] | Li Hao, Tao Hongcheng, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Ding Qiang, Niu Chicheng, Huang Kai, Kang Hongyu. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway regulates the development of osteoarthritis: guiding targeted therapy with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [11] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [12] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [13] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [14] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [15] | Xu Jiamu, Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Wang Chunqing. Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||