Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (22): 5639-5649.doi: 10.12307/2026.170
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transverse tibial bone transfer accelerates healing of foot ulcers in a rabbit model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: involvement and regulation of circular RNA
Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Xu Lin, Li Haojie, Xie Tongliang, Yang Zhihang, Deng Jiang
- Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-05-26Accepted:2025-09-21Online:2026-08-08Published:2025-12-25 -
Contact:Deng Jiang, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Sun Zuyan, MS candidate, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, No. Qian Ke He Ji Chu-ZK[2021] General 387 (to HWL);
Science and Technology Plan Project of Zunyi, No. Zun Shi Ke He HZ(2020)109 (to XL); Guizhou Province Science and Technology Plan Project of Guizhou Province, No. Qian Ke He Chengguo-LC [2024] 019 (to HWL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Xu Lin, Li Haojie, Xie Tongliang, Yang Zhihang, Deng Jiang. Transverse tibial bone transfer accelerates healing of foot ulcers in a rabbit model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: involvement and regulation of circular RNA[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5639-5649.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
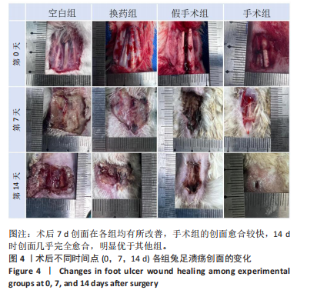
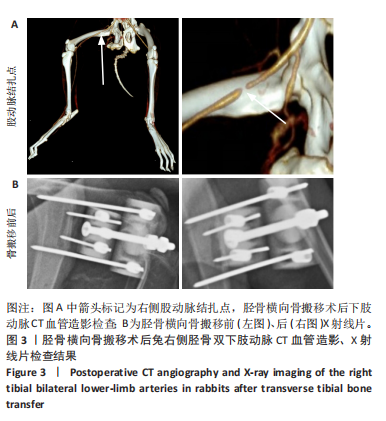
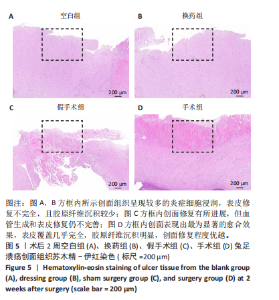
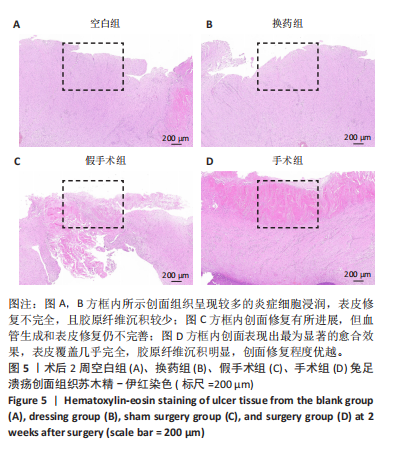
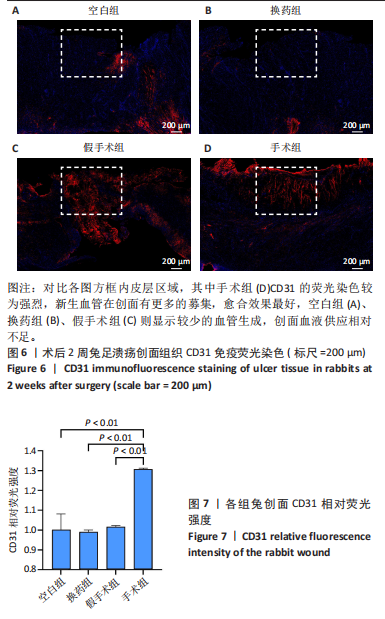
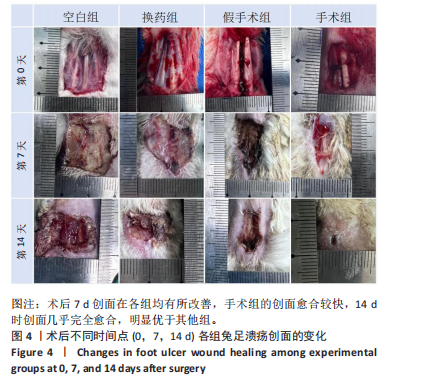
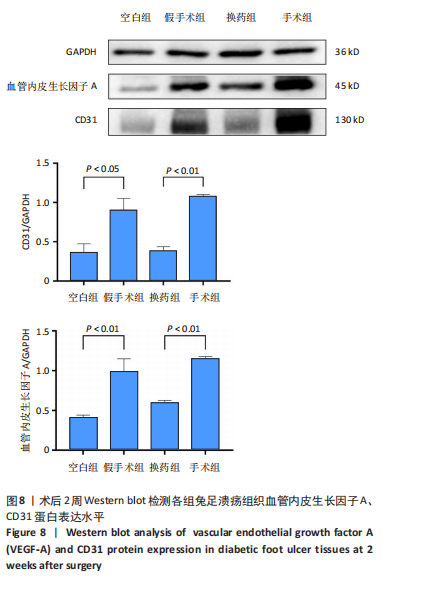
2.3 创面病理检查及创面观察 空白组在术后第7天和第14天创面缩小均为33.33%,未见明显改善。换药组在术后第7天创面缩小了46.88%,而在术后第14天则有显著进展,创面缩小了71.88%。假手术组在术后第7天创面缩小了57.14%,在术后第14天创面缩小了69.64%。手术组在术后第7天创面缩小了50%,但在术后第14天创面缩小达到了96.47%,显示出最佳的愈合效果。手术组促进糖尿病足溃疡愈合的效果最为显著,远超其他组,见图4。术后2周各组溃疡创面组织的苏木精-伊红染色结果,见图5。术后2周各组溃疡创面组织的CD31荧光染色结果,见图6,7。 2.4 Western blot检测溃疡组织血管内皮生长因子A、CD31蛋白表达 术后14 d,血管内皮生长因子A、CD31蛋白量表达如图8所示。手术组血管内皮生长因子A、CD31蛋白表达显著高于其他3组,手术通过促进内皮细胞增殖和血管生成加速了创面愈合。"
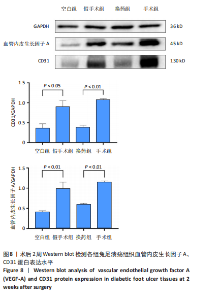
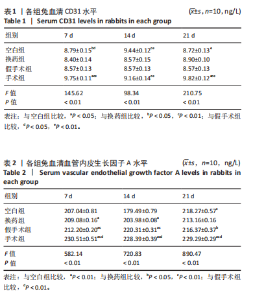
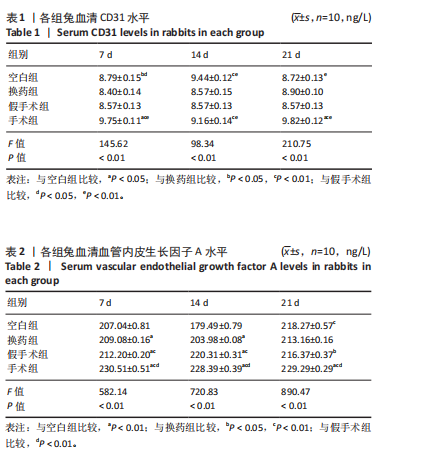
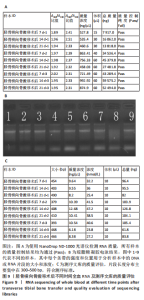
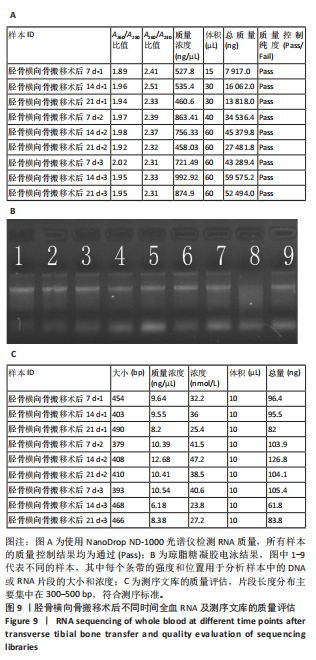
CD31水平:手术组 > 空白组、换药组、假手术组(P < 0.01);空白组与换药组比较无显著差异(P > 0.05);空白组、换药组 > 假手术组(P < 0.01),见表1。 术后7 d血管内皮生长因子A水平:手术组 > 空白组、换药组、假手术组(P < 0.01);假手术组 > 空白组、换药组(P < 0.01);换药组 > 空白组(P < 0.01)。术后14 d血管内皮生长因子A水平:手术组 > 空白组、换药组、假手术组(P < 0.01);假手术组 > 空白组、换药组(P < 0.01);换药组 > 空白组(P < 0.01);术后21 d血管内皮生长因子A水平:手术组 > 空白组、换药组、假手术组(P < 0.01);假手术组 > 换药组(P < 0.05);空白组 > 换药组(P < 0.01),见表2。 2.6 高通量测序 首先使用NanoDrop ND-1000光谱仪检测术后7,14,21 d采集的RNA质量,RNA样本的A260/A280比值在1.89-2.02之间,A260/A230比值在2.32-2.51之间,符合RNA测序要求,样本质量"
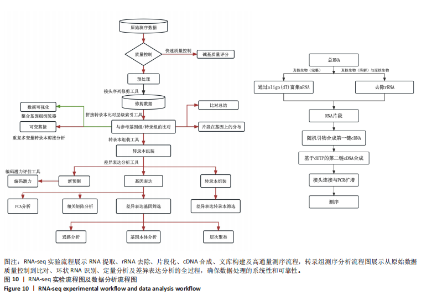
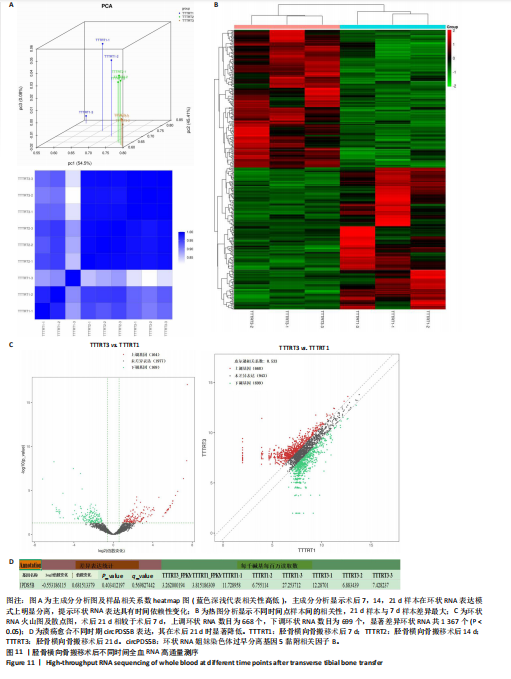
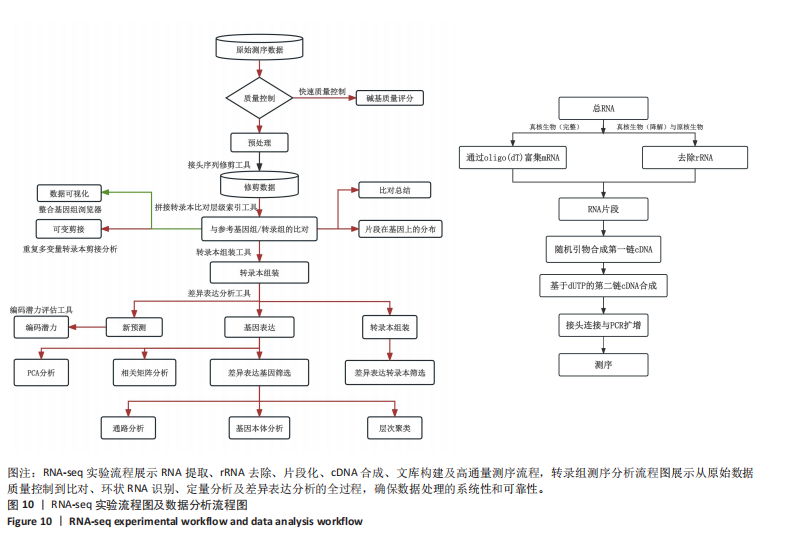
转录组测序实验流程展示RNA提取、rRNA去除、片段化、cDNA合成、文库构建及高通量测序流程,确保数据可重复性。转录组测序分析流程图说明从原始数据质量控制到比对、环状RNA识别、定量分析及差异表达分析的全过程,确保数据处理的系统性和可靠性,见图10。 主成分分析显示术后7,14,21 d样本在环状RNA表达模式上明显分离,提示环状RNA表达具有时间依赖性变化,见图11A。热图分析显示不同时间点样本间的相关性,21 d的样本与7 d样本差异最大,见图11B。环状RNA散点图及表达分析展示术后不同时间点的环状RNA表达情况,进一步验证环状RNA在手术组的动态变化。其中环状RNA姐妹染色体过早分离基因5黏附相关因子B在术后21 d显著下调,与糖尿病足溃疡愈合过程密切相关。环状RNA差异表达火山图,红色点代表显著上调的环状RNA,绿色点代表显著下调的环状RNA。术后21 d相较于术后7 d,上调环状RNA数目为668个,下调环状RNA数目为699个,显著差异环状RNA共1 367个(P < 0.05),见图11C。数据表明,环状RNA姐妹染色体过早分离基因5黏附相关因子B的表达在术后显著降低,尤其是在术后21 d(7.428 237),相较于术后7 d (12.287 01),环状RNA姐妹染色体过早分离基因5黏附相关因子B的表达逐渐减少,见图11D。"
| [1] VOELKER R. What Are Diabetic Foot Ulcers? JAMA. 2023;330(23):2314. [2] HUANG F, LU X, YANG Y, et al. Microenvironment-Based Diabetic Foot Ulcer Nanomedicine. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(2):e2203308. [3] ARMSTRONG DG, TAN TW, BOULTON AJM, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(1):62-75. [4] ZHU D, WEI W, ZHANG J, et al. Mechanism of damage of HIF-1 signaling in chronic diabetic foot ulcers and its related therapeutic perspectives. Heliyon. 2024;10(3):e24656. [5] 李文惠,柳国斌.国际糖尿病足研究知识图谱:基于CiteSpace的文献可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20):3178-3184. [6] SENNEVILLE É, ALBALAWI Z, VAN ASTEN SA, et al. IWGDF/IDSA guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes-related foot infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024;40(3):e3687. [7] TIAN W, ZHANG L, WANG Y, et al. Tibial transverse transport promotes wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers by stimulating endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and homing mediated neovascularization. Ann Med. 2024;56(1):2404186. [8] WEI W, JIANG T, HU F, et al. Tibial transverse transport combined with platelet-rich plasma sustained-release microspheres activates the VEGFA/VEGFR2 pathway to promote microcirculatory reconstruction in diabetic foot ulcer. Growth Factors. 2024;42(3):128-144. [9] OU S, XU C, YANG Y, et al. Transverse Tibial Bone Transport Enhances Distraction Osteogenesis and Vascularization in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2170-2179. [10] 刘杰,花奇凯,李山郎,等.骨膜牵张技术用于糖尿病足治疗的理论基础及临床结果验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5236-5241. [11] CHEN LL. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):475-490. [12] YAO R, YAO Y, LI C, et al. Circ-HIPK3 plays an active role in regulating myoblast differentiation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;155: 1432-1439. [13] ZHONG G, ZHAO Q, CHEN Z, et al. TGF-β signaling promotes cervical cancer metastasis via CDR1as. Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):66. [14] ASHRAFIZADEH M, ZARRABI A, MOSTAFAVI E, et al. Non-coding RNA-based regulation of inflammation. Semin Immunol. 2022;59:101606. [15] HUANG Q, CHU Z, WANG Z, et al. circCDK13-loaded small extracellular vesicles accelerate healing in preclinical diabetic wound models. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):3904. [16] MISIR S, WU N, YANG BB. Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(3):481-491. [17] ULSHÖFER CJ, PFAFENROT C, BINDEREIF A, et al. Methods to study circRNA-protein interactions. Methods. 2021;196:36-46. [18] HWANG HJ, KIM YK. Molecular mechanisms of circular RNA translation. Exp Mol Med. 2024;56(6):1272-1280. [19] LI X, LI N, LI B, et al. Noncoding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in diabetic wound healing. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021;50:128311. [20] WANG Y, ZHAO R, SHEN C, et al. Exosomal CircHIPK3 Released from Hypoxia-Induced Cardiomyocytes Regulates Cardiac Angiogenesis after Myocardial Infarction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8418407. [21] GAREEV I, KUDRIASHOV V, SUFIANOV A, et al. The role of long non-coding RNA ANRIL in the development of atherosclerosis. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022;7(4):212-216. [22] ZHANG S, TU D, LIU W, et al. circELP2 reverse-splicing biogenesis and function as a pro-fibrogenic factor by targeting mitochondrial quality control pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(3):e18098. [23] LI Z, ZHANG W, ZHANG H. Hsa_circ_0000129 knockdown attenuates proliferation and migration in keloid fibroblasts by targeting miR-485-3p/SGMS2 pathway. Burns. 2023;49(8):2007-2017. [24] YANG L, FU J, HAN X, et al. Hsa_circ_0004287 inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation in an N6-methyladenosine-dependent manner in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149(6):2021-2033. [25] ZHOU JL, DENG S, FANG HS, et al. Circular RNA circANKRD36 regulates Casz1 by targeting miR-599 to prevent osteoarthritis chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(1):120-131. [26] 周俊丽,王小俊,王海焦,等.新型医用敷料治疗糖尿病足溃疡疗效比较的网状Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(16):2562-2569. [27] 邓晓慧,张增增,张执华,等.间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰microRNA治疗糖尿病足的机制及应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(31):5076-5084. [28] JIN Y, MENG M, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparative study on the efficacy of PRP gel and UC-MSCs gel as adjuvant therapies in the treatment of DFU wounds. Skin Res Technol. 2024;30(1):e13549. [29] LO ZJ, HARISH KB, TAN E, et al. A feasibility study on the efficacy of a patient-owned wound surveillance system for diabetic foot ulcer care (ePOWS study). Digit Health. 2023;9:20552076231205747. [30] 郭国庆,陈林海,郭明君,等.胫骨横向骨搬移技术对糖尿病兔下肢溃疡创面促细胞趋化水平的研究[J].中国医疗美容,2021, 11(7):50-53. [31] WANG F, ZHANG X, ZHANG J, et al. Recent advances in the adjunctive management of diabetic foot ulcer: Focus on noninvasive technologies. Med Res Rev. 2024;44(4):1501-1544. [32] 刘星余,刘日光,李光第,等.内源性竞争RNA调控骨性关节炎的发生[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(28):4559-4565. [33] WANG XF, YU CQ, YOU ZH, et al. A feature extraction method based on noise reduction for circRNA-miRNA interaction prediction combining multi-structure features in the association networks. Brief Bioinform. 2023;24(3):bbad111. [34] JIANG Z, JIANG Y. Circular RNA CircPDS5B impairs angiogenesis following ischemic stroke through its interaction with hnRNPL to inactivate VEGF-A. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;181:106080. |
| [1] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [2] | Gao Yanguo, Guo Xu, Li Xiaohan, Chen Shiqi, Zhu Haitao, Huang Liangyong, Ye Fang, Lu Wei Wang Qibin, Zheng Tao, Chen Li. Optimization of prescription ratio of “Honghuangbai” gel by orthogonal test in diabetic skin wound mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [3] | Han Teng, Ma Hong, Yang Ruoyi, Luo Yi, Li Chao. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal delivery of angiopoietin-2 is involved in tumor angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1755-1767. |
| [4] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [5] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [6] | Yan Chengbo, Luo Qiuchi, Fan Jiabing, Gu Yeting, Deng Qian, Zhang Junmei. Effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on orthodontic tooth movement and bone microstructure parameters on the tension side in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 824-831. |
| [7] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [8] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [9] | Yang Wenyan, Wang Huayu, Yang Like, Pang Xue, Wang Yutao. Biomarkers for diabetic foot ulcers: single-cell transcriptomics bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5694-5706. |
| [10] | Lin Kejian, Chai Yinghong, Zou Jie, Huang Ruixin, Fang Yongchao, Huang Jing, Yang Qin, Luo Xia, Zhang Hong. Preparation of Cu2+-containing microarc oxidation functional coating on medical magnesium alloy and its anti-tumor and angiogenesis-promoting effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5103-5114. |
| [11] | Niu Qi, Chen Junji, Tu Haining, Mo Weibin, Zhong Yujin, Li Mingliang. Effect of swimming exercise combined with probiotic intervention on anti-inflammatory and apoptotic gene expression in renal tissue of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4105-4114. |
| [12] | Fan Meirong, Li Guangqi, Song Xumei, Yan Xin, Sui Ruizhi. Chemokine receptor 7-bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with porcine small intestinal submucosa promote skin repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3242-3249. |
| [13] | Yao Jinfeng, Deng Mengzhao, Xie Tian, Chen Kan, Wang Haixia. Reduced graphene oxide improves endothelial differentiation efficiency and angiogenesis ability of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3270-3279. |
| [14] | Shi Yuxin, Kaiwusail · Tursun, Liu Jia. Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor-loaded composite bioscaffold on angiogenesis of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3343-3349. |
| [15] | Yao Lijuan, Wang Yinfeng, Ma Zhennan, Chen Leqin. Exercise-induced extracellular vesicles: action and mechanisms in occurrence and development of insulin resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3412-3423. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||