Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 2965-2974.doi: 10.12307/2026.660
Previous Articles Next Articles
Glutamine regulates the effect of hormones on the apoptosis of bone microvascular endothelial cells
Zan Yongfeng, Song Keguan, Liu Yuda
- The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-07Accepted:2025-07-31Online:2026-04-28Published:2025-09-28 -
Contact:Song Keguan, Chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Zan Yongfeng, MS candidate, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:Heilongjiang Renxin Bone Health Medical Relief Foundation Project, No. 2022HX031 (to SKG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zan Yongfeng, Song Keguan, Liu Yuda. Glutamine regulates the effect of hormones on the apoptosis of bone microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 2965-2974.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
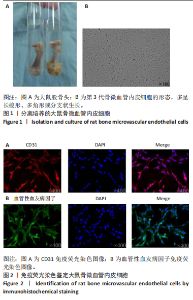
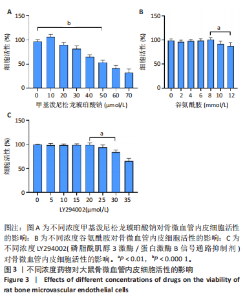
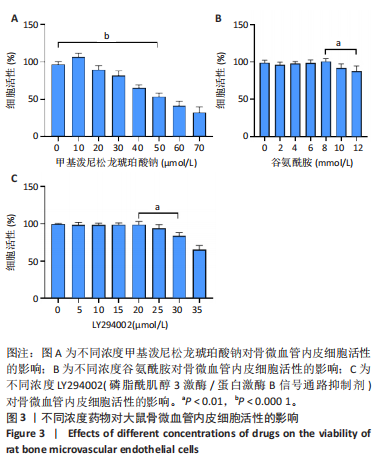
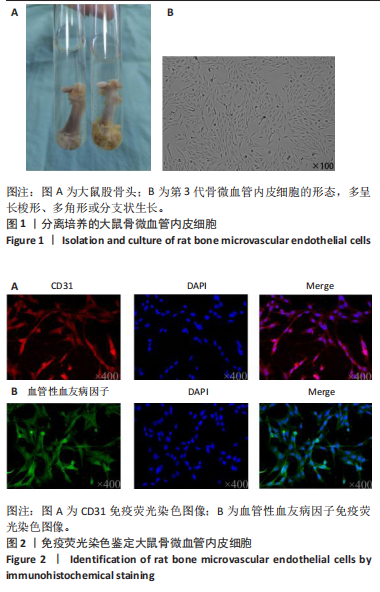
2.1 骨微血管内皮细胞的分离培养及鉴定 首先从大鼠股骨头组织中(图1A)分离培养出骨微血管内皮细胞并进行传代,代至第3代时细胞多呈长梭形、多角形或分支状生长(图1B)。 免疫荧光染色结果显示,分离培养的细胞高表达CD31及血管性血友病因子(图2),表明成功分离并获得骨微血管内皮细胞。 2.2 筛选最适的糖皮质激素、谷氨酰胺、LY294002处理浓度 10 μmol/L糖皮质激素处理后,骨微血管内皮细胞活性展现出轻微提升趋势,然而随着糖皮质激素浓度的逐渐增加,细胞活性开始受到抑制,当糖皮质激素浓度达到50 μmol/L时,骨微血管内皮细胞活性显著降低,见图3A。随着谷氨酰胺浓度从2 mmol/L提升至8 mmol/L,骨微血管内皮细胞活性未见显著改变,当谷氨酰胺浓度进一步增加至10,12 mmol/L时,骨微血管内皮细胞活性较8 mmol/L时显著降低,见图3B。随着LY294002浓度从5 μmol/L逐渐提升至25 μmol/L,骨微血管内皮细胞活性未出现明显变化,当浓度增至30,35 μmol/L时骨微血管内皮细胞活性显著降低,见图3C。所以,最终确定50 μmol/L糖皮质激素、8 mmol/L 谷氨酰胺、20 μmol/L LY294002作为细胞实验最佳药物处理浓度。"
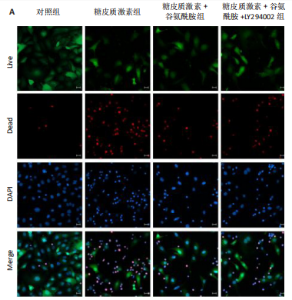
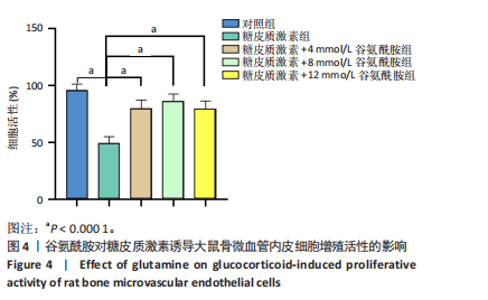
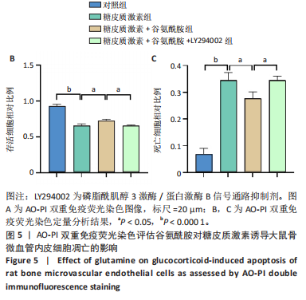
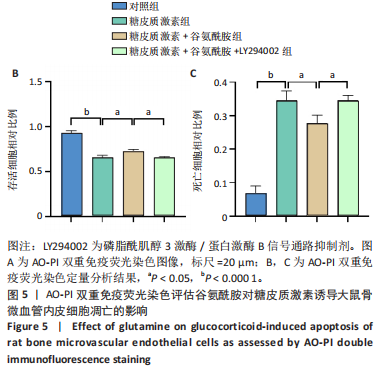
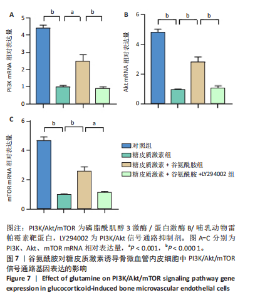
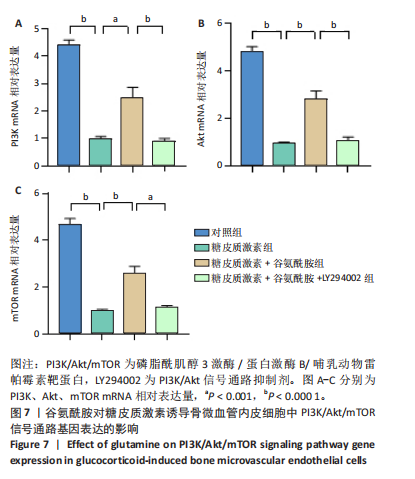
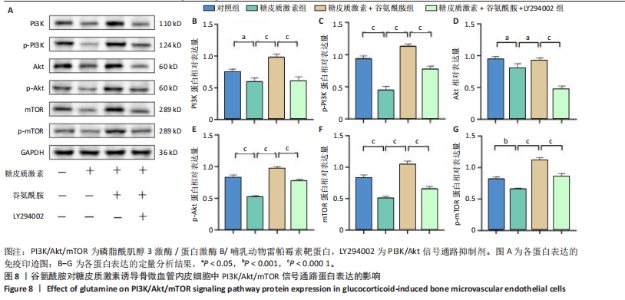
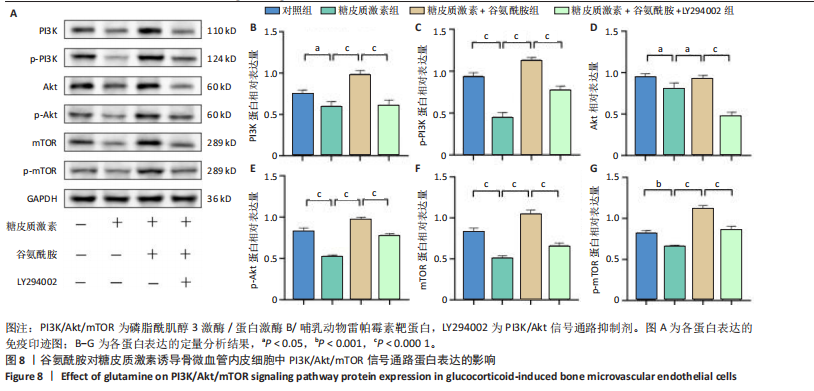
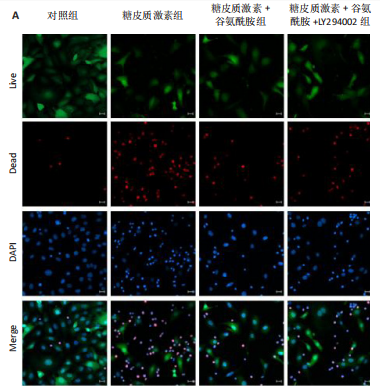
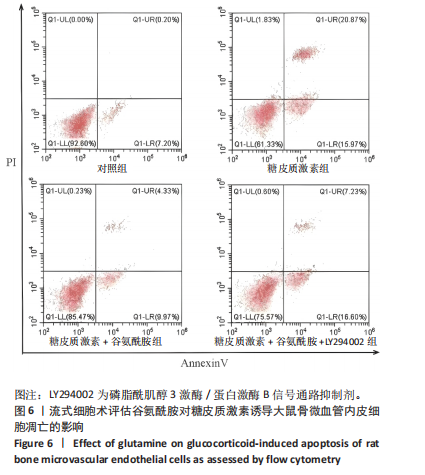
2.4 谷氨酰胺可减少糖皮质激素诱导的骨微血管内皮细胞凋亡 AO-PI双重免疫荧光染色显示,糖皮质激素组细胞存活率低于对照组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.000 1,P < 0.05),糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺+LY294002组细胞存活率低于糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.05);糖皮质激素组细胞死亡率高于对照组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.000 1,P < 0.05),糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺+LY294002组细胞死亡率高于糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.05),见图5。 流式细胞术检测结果显示,对照组、糖皮质激素组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺+LY294002组细胞凋亡率分别为7.40%,36.84%,14.30%,23.83%,糖皮质激素组细胞凋亡率高于对照组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.05),糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺+LY294002组细胞凋亡率高于糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.05),见图6。 2.5 谷氨酰胺对糖皮质激素诱导骨微血管内皮细胞中PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路的影响 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,糖皮质激素组PI3K、Akt、mTOR mRNA表达均低于对照组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1),糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺+LY294002组PI3K、Akt、mTOR mRNA表达低于糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1),见图7。 Western Blot检测结果显示,糖皮质激素组PI3K、Akt、mTOR、p-PI3K、p-Akt、p-mTOR蛋白表达均"
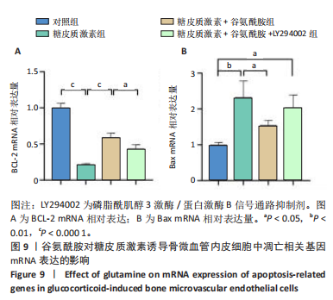
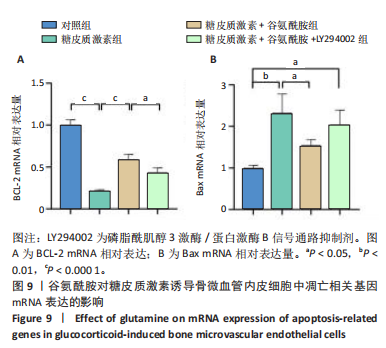
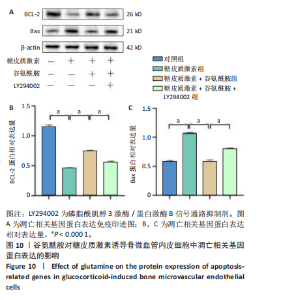
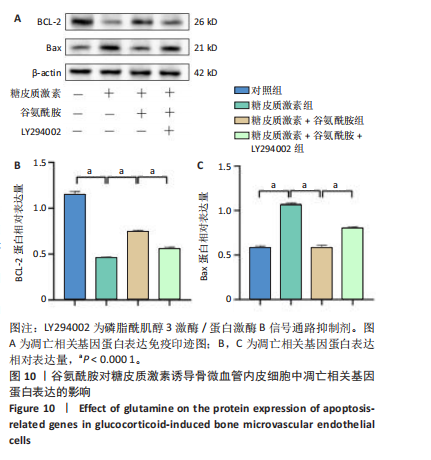
低于对照组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.05,P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1),糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺+LY294002组PI3K、Akt、mTOR、p-PI3K、p-Akt、p-mTOR蛋白表达低于糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.000 1),见图8。 2.6 谷氨酰胺对糖皮质激素诱导骨微血管内皮细胞中凋亡相关基因表达的影响 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,糖皮质激素组BCL-2 mRNA表达低于对照组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.000 1),Bax mRNA表达高于对照组、糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.000 1);糖皮质激素+谷氨酰胺+"
| [1] CHAO PC, CUI MY, LI XA, et al. Correlation between miR-1207-5p expression with steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head and VEGF expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(7):2710-2718. [2] 胡兆林,常峰.激素性股骨头坏死发病机制及相关信号通路研究进展[J].医学综述,2022,28(3):466-470. [3] 柳直,姚五平,李盛华.李盛华教授对非创伤性股骨头坏死的认识[J].西部中医药,2021,34(12):40-43. [4] 王岩,马剑雄,董本超,等.激素性股骨头坏死动物模型的研究进展[J].生物医学工程与临床,2021,25(5):650-656. [5] HINES JT, JO WL, CUI Q, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: an Updated Review of ARCO on Pathogenesis, Staging and Treatment. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(24):e177. [6] CUI Q, JO WL, KOO KH, et al. ARCO Consensus on the Pathogenesis of Non-traumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(10):e65. [7] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today?: A 5-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(12):1084-1099. [8] CHANG C, GREENSPAN A, GERSHWIN ME. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical manifestations of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102460. [9] GEBHARD KL, MAIBACH HI. Relationship between systemic corticosteroids and osteonecrosis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2(6):377-88. [10] JOHNSON EO, SOULTANIS K, SOUCACOS PN. Vascular anatomy and microcirculation of skeletal zones vulnerable to osteonecrosis: vascularization of the femoral head. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004;35(3): 285-291,viii. [11] 张杰,曹建泽,刘永飞,等.激素性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(7):620-624,630. [12] PENG P, NIE Z, SUN F, et al. Glucocorticoids induce femoral head necrosis in rats through the ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(1):312-321. [13] YU QS, GUO WS, CHENG LM, et al. Glucocorticoids Significantly Influence the Transcriptome of Bone Microvascular Endothelial Cells of Human Femoral Head. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(14):1956-1963. [14] YUE J, YU H, LIU P, et al. Preliminary study of icariin indicating prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head by regulating abnormal expression of miRNA-335 and protecting the functions of bone microvascular endothelial cells in rats. Gene. 2021; 766:145128. [15] MAO Z, LIU G, XIAO GY, et al. CircCDR1as Suppresses Bone Microvascular Endothelial Cell Activity and Angiogenesis Through Targeting miR-135b/ FIH-1 Axis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(2):573-582. [16] ALTMAN BJ, STINE ZE, DANG CV. From Krebs to clinic: glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(10):619-634. [17] MASENGA SK, POVIA JP, LWIINDI PC, et al. Recent Advances in Microbiota-Associated Metabolites in Heart Failure. Biomedicines. 2023;11(8):2313. [18] ZHAI Y, SUN Z, ZHANG J, et al. Activation of the TOR Signalling Pathway by Glutamine Regulates Insect Fecundity. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10694. [19] CHEN G, CHEN JL, WU J. Effects of miR-133b on oxLDL-induced vascular endothelial cell injury by targeting SGTB. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2021;37(6):594-600. [20] HUANG J, CHEN L, WU J, et al. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in the Treatment of Human Diseases: Current Status, Trends, and Solutions. J Med Chem. 2022;65(24):16033-16061. [21] MOSCHETTA MG, LEONEL C, MASCHIO-SIGNORINI LB, et al. Evaluation of Angiogenesis Process after Metformin and LY294002 Treatment in Mammary Tumor. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(5):655-666. [22] AGAS D, HANNA R, BENEDICENTI S, et al. Photobiomodulation by Near-Infrared 980-nm Wavelengths Regulates Pre-Osteoblast Proliferation and Viability through the PI3K/Akt/Bcl-2 Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(14):7586. [23] LI H, PREVER L, HIRSCH E, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(14):3517. [24] 卢非凡,王卫国,郭万首,等.糖皮质激素通过PI3K-Akt-mTOR信号通路诱导股骨头骨微血管内皮细胞凋亡的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(5):631-636,669. [25] LEE MS, HSIEH PH, SHIH CH, et al. Non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head - from clinical to bench. Chang Gung Med J. 2010; 33(4):351-360. [26] GÓMEZ-BARRENA E, PADILLA-EGUILUZ NG, ROSSET P, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Safely Healed with Autologous, Expanded, Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in a Multicentric Trial with Minimum 5 Years Follow-Up. J Clin Med. 2021;10(3):508. [27] LI Y, CHEN J, ZHANG Z, et al. The experimental study on treatment of glucocorticoid-induced ischemic necrosis of femoral head by gu fu sheng capsule. J Tradit Chin Med. 2004;24(4):303-307. [28] 胡兆林,常峰.激素性股骨头坏死发病机制及相关信号通路研究进展[J].医学综述,2022,28(3):466-470. [29] TAO SC, YUAN T, RUI BY, et al. Exosomes derived from human platelet-rich plasma prevent apoptosis induced by glucocorticoid-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signal pathway. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):733-750. [30] SUN F, ZHOU JL, WEI SX, et al. Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13319. [31] 彭洁,曹猛,孙慕涵,等.谷氨酰胺代谢在机体免疫调控中作用的研究进展[J]. 癌变.畸变.突变,2023,35(3):231-235,239. [32] NAJUMUDEEN AK, CETECI F, FEY SK, et al. The amino acid transporter SLC7A5 is required for efficient growth of KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2021;53(1):16-26. [33] 吴丹,王超,王子恩,等.谷氨酰胺对严重烧伤小鼠骨骼肌膜修复的影响及作用机制[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2019, 35(5): 341-350. [34] ZHANG W, LI W, ZHANG C, et al. Effects of Vitamin A on Expressions of Apoptosis Genes Bax and Bcl-2 in Epithelial Cells of Corneal Tissues Induced by Benzalkonium Chloride in Mice with Dry Eye. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:4583-4589. [35] 芮翊馨,谢红潇,李丹,等.中乌宁通过BAX/BCL-2/Caspase 3信号通路抑制细胞凋亡改善慢性肾衰竭大鼠肾纤维化[J].中药药理与临床,2024,40(5):42-48. [36] 张恒,李康宁,董海峰,等. LY294002通过PI3K/Akt通路对结直肠癌RKO细胞增殖及凋亡的影响[J]. 中国现代医药杂志,2024, 26(1):22-27. |
| [1] | Chen Haojie, Wang Dai, Shen Shan. Immune inflammatory microenvironment mechanisms in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [2] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [3] | Yuan Xiaoshuang, Yang Xu, Yang Bo, Chen Xiaoxu, Tian Ting, Wang Feiqing, Li Yanju, Liu Yang, Yang Wenxiu. Effect of conditioned medium of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells on proliferation and apoptosis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1632-1640. |
| [4] | Han Nianrong, Huang Yifei, Akram · Osman, Liu Yanlu, Hu Wei . Programmed cell death receptor-1 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a high-glucose microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1649-1657. |
| [5] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [6] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [7] | Chen Ju, Zheng Jinchang, Liang Zhen, Huang Chengshuo, Lin Hao, Zeng Li. Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [8] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [9] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [10] | Zhu Kuicheng, Du Chunyan, Zhang Jintao. Mechanism by which hairless gene mutation promotes white adipose tissue browning in hairless mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1424-1430. |
| [11] | Jia Jinwen, Airefate·Ainiwaer, Zhang Juan. Effects of EP300 on autophagy and apoptosis related to allergic rhinitis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1439-1449. |
| [12] | Li Hao, Tao Hongcheng, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Ding Qiang, Niu Chicheng, Huang Kai, Kang Hongyu. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway regulates the development of osteoarthritis: guiding targeted therapy with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [13] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [15] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||