Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2618-2628.doi: 10.12307/2026.627
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visualization analysis of lumbar spondylolisthesis treatment research from a bibliometric perspective
Huang Hailun, Wei Yatao, Liu Yongai, Wu Junzhe, Gao Heng, Sun Kui, Cao Zhenwen
- Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2025-05-06Accepted:2025-06-10Online:2026-04-08Published:2025-08-30 -
Contact:Liu Yongai, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Hailun, MS candidate, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Hailun, Wei Yatao, Liu Yongai, Wu Junzhe, Gao Heng, Sun Kui, Cao Zhenwen. Visualization analysis of lumbar spondylolisthesis treatment research from a bibliometric perspective[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2618-2628.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
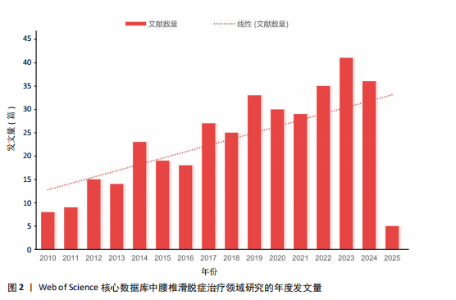
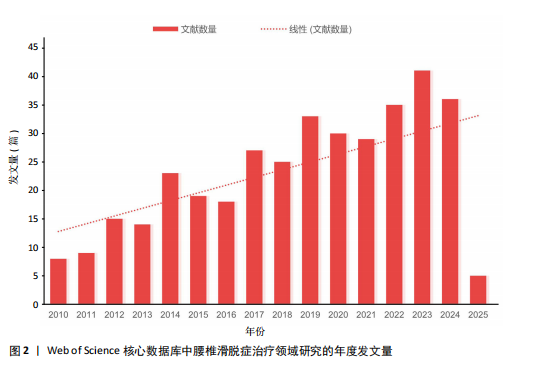
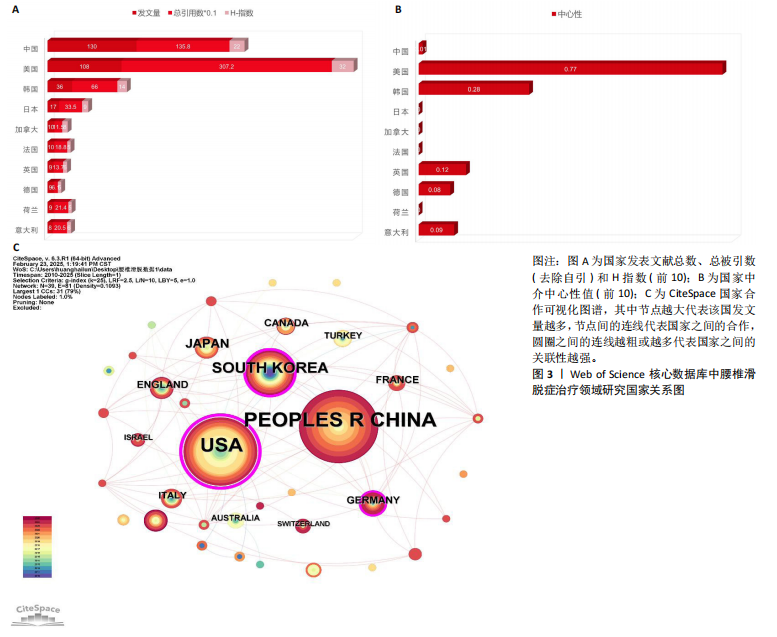
2.1 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域研究发文量分析 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域年度发文量见图2。在学术研究领域,绘制年度发文量图表是一种有效的分析手段,通过统计每年在特定领域发表的文献数量并以图表形式呈现,能够直观地展示该领域在不同年份的研究活跃程度。2010-2011年间,发文量在个位数,表明该领域的研究处于雏形阶段。2012-2024年间,共计发文量345篇,虽然有部分年份发文量有所减少,但总体仍呈现飞速增长的趋势,年平均发文量26.5篇,表明关于腰椎滑脱症的治疗越来越受全球研究者的关注。2025年截至2025-03-25,已有5篇相关研究产出。全球关于腰椎滑脱治疗领域发文量在增长过程中存在一定起伏,但是该研究领域总体呈现向上发展趋势,这表明未来在该领域的研究趋势值得进一步关注和深入分析。 2.2 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域研究国家分析 从文献计量学视角来看,中国在腰椎滑脱症治疗领域的研究产出量居全球首位,2010-2025年间累计发表文献130篇,高于美国(108篇)、韩国(36篇)、日本(17篇)等国家(图3A)。然而,在学术影响力层面美国仍占据主导地位,其总被引频次高达3 072次,H指数为32,均位列第一;中国以1 358次被引和H指数22紧随其后,通过CiteSpace软件的中介中心性分析发现美国的中介中心性系数高达0.77,远超其他国家(图3B),表明美国在全球科研合作网络中扮演核心枢纽角色,主导着知识传播与技术协同创新。相比之下,中国虽发文量领先,但中介中心性系数值仅为0.1,表明中国在该领域的研究成果在引用层面相对不足,可能在研究质量、创新性及成果传播范围方面存在一定的进步空间。这一差距可能与欧美国家长期积累的学术话语权、多学科协作机制及高质量临床转化能力密切相关。 图3C展示了2010-2025年腰椎滑脱症领域研究的全球合作格局,美国和中国的节点直径最大,文献产出量及科研活跃度领先。美国与韩国、日本及德国、瑞士等国合作紧密,中国则与澳大利亚、意大利等多国协作,但合作广度不及美国。整体网络呈“双极驱动”结构,以美、中为关键节点,推动多区域科研合作,彰显高度国际"
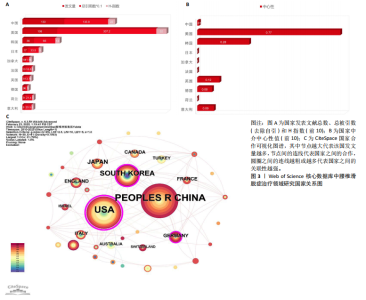
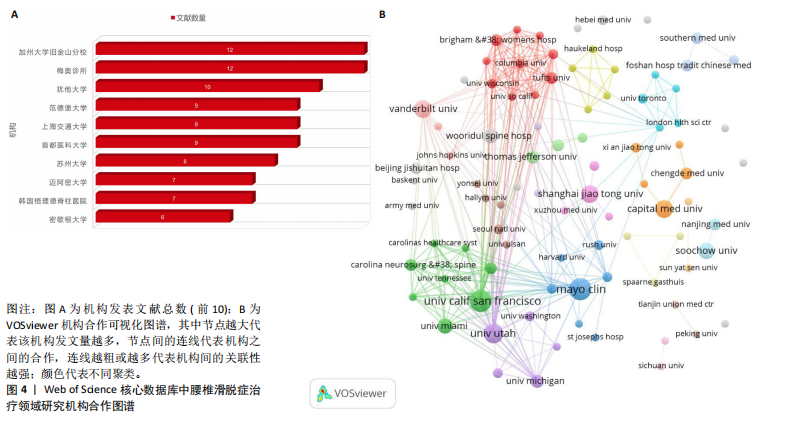
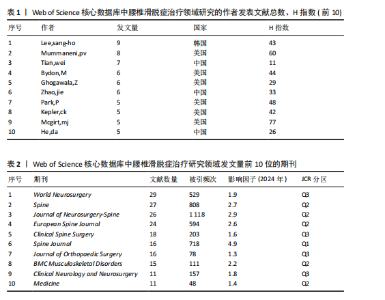
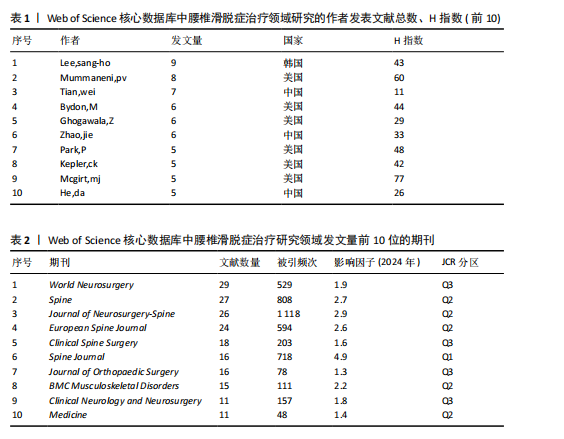
化的知识共享与创新生态,但部分高发文量国家如法国在合作网络中相对孤立,说明需进一步加强国际间的交流合作。 2.3 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域研究机构分析 从机构的发文数量方面看(图4A),加州大学旧金山分校和梅奥诊所文献数量均为12 篇,并列第一,说明这两所机构在相关领域研究中活跃度极高,投入较多资源开展研究;犹他大学文献量为10篇,范德堡大学、上海交通大学、首都医科大学文献量均为9篇,这些机构也属于该领域的核心研究力量;上海交通大学、首都医科大学、苏州大学等国内机构展现出不错的研究实力,与部分国外知名机构的文献产出差距较小,表明国内在该领域的研究发展态势良好。根据VOSviewer软件对研究机构分布进行分析(图4B),Mayo Clin(梅奥诊所)、Univ Calif San Francisco(加州大学旧金山分校)等节点较大,是领域内的核心研究机构,红色聚类内机构联系紧密,可能在某细分方向深入合作;整体看,各聚类间也有连线,说明领域内机构合作广泛且多元化。图中包含国内外众多机构,国内如Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ(上海交通大学)、Capital Med Univ(首都医科大学)等在网络中有一定位置,表明国内研究力量在该领域有参与度。 2.4 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域研究作者分析 总体而言,共有1 999位作者对腰椎滑脱症治疗展开了研究,表1详细列出了产出最高的前10位作者的具体信息,其中发文量位居前三的作者分别是:韩国学者Lee,Sang-Ho(9篇)、美国学者Mummaneni,PV(8篇)"

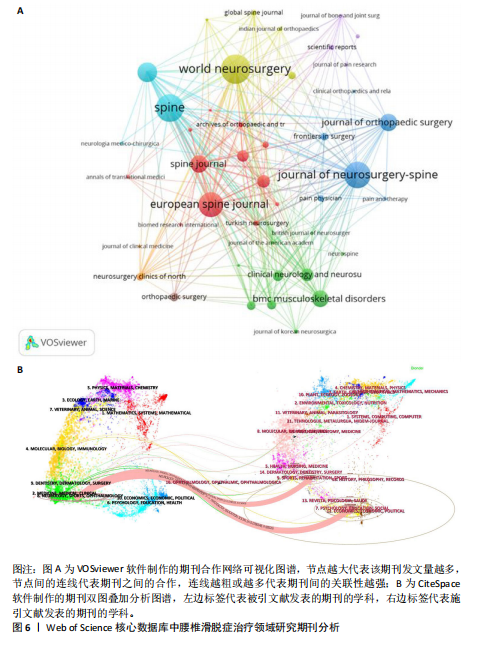
及中国学者Tian,Wei(7篇)。在前10名高产作者中,有6位来自美国,3位来自中国,1位来自韩国,说明对于该领域的研究主要以美国和中国的作者为主。另外,H指数能够准确地反映出作者的学术成就,其中美国学者McGirt,MJ以最高的H指数位居榜首,彰显了该作者在这一特定研究领域中的巨大影响力。图5展示了由VOSviewer生成的覆盖可视化结果,对作者共现现象进行了深入分析,颜色相同且连线密集的作者群体构成了不同的研究团队,图谱中显示主要以绿色和红色聚类的作者合作较为紧密,绿色聚类中的作者彼此紧密相连,说明他们在研究上有频繁合作,形成了以美国学者Mummaneni,pv为核心的研究团队;红色聚类的作者围绕美国学者Bydon,M也形成了一个合作紧密的团队,表明这些团队在研究方向上携手共进,已经取得了一系列显著的成果。 2.5 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域研究期刊分析 如图6A所示,期刊《World neurosurgery》在节点图中占据最大位置,这表明该期刊所发表的文献拥有最高的被引用率,不仅显示了该期刊在研究领域的领导地位,也意味着其文章内容紧密围绕研究方向展开。高被引用文献数量彰显了期刊在学术界的影响力,证明其研究成果已获得国际学术界的广泛认可。结合表2数据更清楚地看到,发文量最多的10大期刊在科研论文总数中占据了52.59%的份额,总计达到193篇,其中《World neurosurgery》以29篇的发文量位居榜首,领先于《Spine》(27篇)和《Journal of neurosurgery-spine》(26篇)。从期刊影响因子角度分析,《Spine journal》以高达4.9的影响因子值脱颖而出,展示了该期刊在腰椎滑脱症治疗领域的显著影响力和学术权威性。值得注意的是,尽管前10大期刊中影响力显著,但其中没有一本期刊的影响因子值达到5.0。具体来看,5种期刊的影响因子值处于2.0-5.0之间,其余5种的影响因子值则低于2.0。期刊《Journal of"

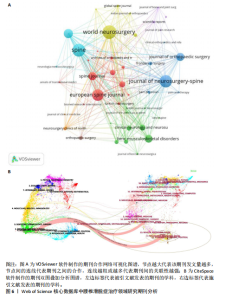
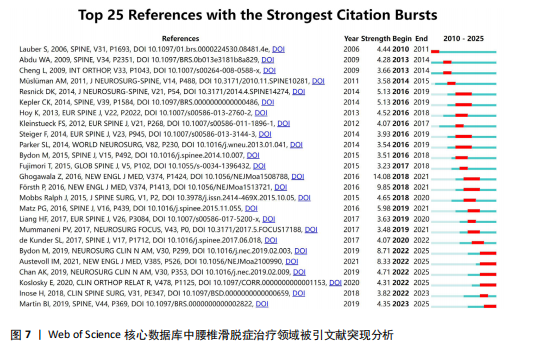
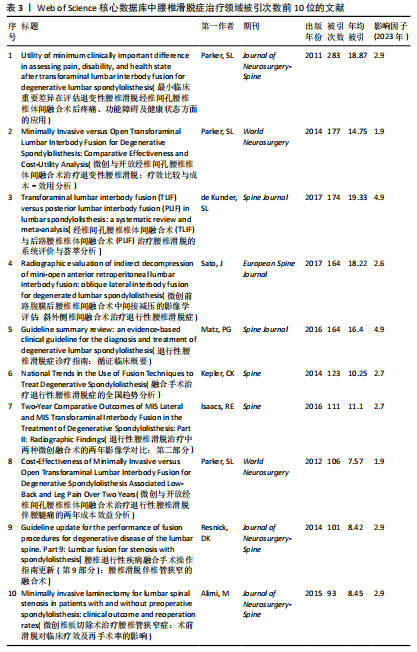
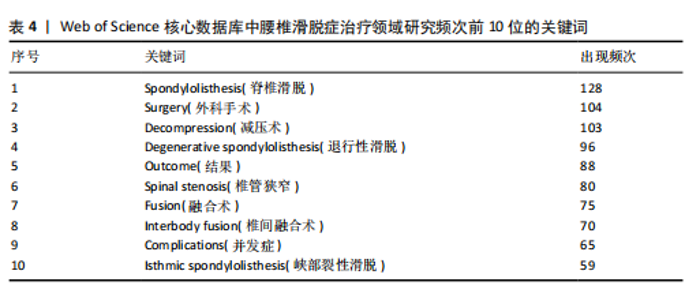
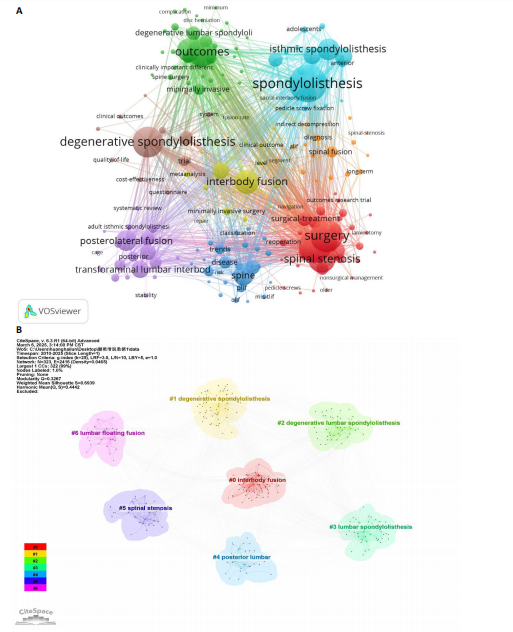
neurosurgery-spine》的被引频次高达1 118次,居于首位,该期刊作为神经外科领域的研究平台,尤其专注于脊柱相关的临床研究,因此,该期刊所刊登的研究成果,对于腰椎滑脱症的诊断、治疗及康复过程具有不可忽视的参考价值。 通过CiteSpace软件对367篇出版物进行期刊双图叠加分析,结果如图6B所示。图左侧展示了被引用论文所发表期刊的学科分布,主要集中在医学、临床医疗、神经学、运动科学以及外科学等相关领域;图右侧则呈现了施引文献所发表期刊的学科情况,大部分来自植物学、生态学、遗传学、数学、力学、心理学、教育学、健康科学以及护理学等学科的期刊。这些数据揭示了学科间的交叉引用现象,为进一步的学术研究提供了有价值的视角。 2.6 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域参考文献共被引分析 图7列出了腰椎滑脱症治疗领域前25篇最具爆发力的参考文献。表3展示了该领域引用次数最多的前10篇文献。在腰椎滑脱症治疗领域中,2018年出现的论文最具影响力。学者Bydon M、Austevoll IM、Chan AK、Koslosky E和Martin在2025年依然保持着他们的学术影响力。引用爆发力最强的是Ghogawala Z,其论文于2016年发表在《NEW ENGL J MED》上,爆发强度高达14.08。学者Parker SL在2014年于《WORLD NEUROSURGERY》发表的《Minimally Invasive versus Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Utility Analysis》排名第二,爆发强度为3.54,被引次数达到177次,平均每年被引14.75次。 2.7 腰椎滑脱症治疗领域研究关键词分析 2.7.1 关键词共现分析 通过运用VOSviewer软件对367篇学术出版物进行了深入的关键词共现分析,聚焦于腰椎滑脱症的治疗研究领域,分析涵盖了1 107个关键词,在设定阈值≥4的条件下,最终筛选出180个关键词用于可视化分析。从图8A可以看出,关键词共现网络呈现出复杂而多元的多中心结构,其中“Spondylolisthesis(脊椎滑脱)”作为核心节点,与“Surgery(外科手术)”“Fusion(融合术)”“Decompression(减压术)”等关键词紧密相连,共同构成了研究领域的主体框架。如表4所示,“Spondylolisthesis(脊椎滑脱)”以高达128次的出现频率位居首位,这充"
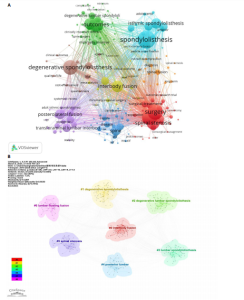
分表明该领域的研究始终以疾病本身为中心展开;与此同时,“Surgery(外科手术)”和“Decompression(减压术)”分别以104次和103次的高频出现,进一步凸显了手术干预在该治疗领域中的核心地位。另外值得关注的是,“Degenerative spondylolisthesis(退行性滑脱)”与“Isthmic spondylolisthesis(峡部裂性滑脱)”分别出现了96次和59次,这种明显的区分反映了研究对不同病因亚型的精细化关注程度。此外,“Fusion(融合术)”和“Interbody fusion(椎间融合术)”分别以75次和70次的高频出现,印证了脊柱稳定性重建技术在该领域中的重要性和关键地位。 将数据导入 Citespace 中进行关键词聚类分析(图8B),在Web of Science核心数据库中得到聚类标签分别为:#0 interbody fusion(椎间融合)、#1 Degenerative spondylolisthesis(退行性滑脱)、#2 Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis(退行性腰椎滑脱)、#3 lumbar spondylolisthesis(腰椎滑脱)、#4 posterior lumbar(腰椎后路的)、#5 spinal stenosis(椎管狭窄)、#6 lumbar floating fusion(腰椎节段性融合术)。 2.7.2 关键词突现分析 在特定时间内使用频率骤增的关键词被称为突现词,它们能够精准地反映某一研究领域的热点转变。通过运用CiteSpace软件的突现词检测功能,并结合关键词的聚类分析,深入挖掘了腰椎滑脱症治领域的前沿动态,成功绘制出突现词图谱,识别出20个关键突现词(图8C)。图片右侧的红色条块直观地展示了这些关键词在研究过程中的持续时间,2010-2025年期间爆发强度最高的关键词是Instrumentation(器械),强度为4.82,从2011持续到2015。早期热点(2010-2015):多数关键词突增始于 2010 年,如 fixation(固定)、isthmic spondylolisthesis(峡部裂性滑脱)等,集中于腰椎疾病基础治疗技术(如融合术、器械应用)的研究。近年趋势(2018-2023年):后期出"
| [1] CHAN AK, SHARMA V, ROBINSON LC, et al. Summary of Guidelines for the Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019;30(3):353-364. [2] SAREMI A, GOYAL KK, BENZEL EC, et al. Evolution of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with key radiographic features. Spine J. 2024;24(6):989-1000. [3] BHALLA A, BONO CM. Isthmic Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019;30(3):283-290. [4] MOHILE NV, KUCZMARSKI AS, LEE D, et al. Spondylolysis and Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: A Guide to Diagnosis and Management. J Am Board Fam Med. 2022;35(6):1204-1216. [5] CHUNG CC, SHIMER AL. Lumbosacral Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis. Clin Sports Med. 2021;40(3):471-490. [6] RATHBONE J, RACKHAM M, NIELSEN D, et al. A systematic review of anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF), transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), posterolateral lumbar fusion (PLF). Eur Spine J. 2023;32(6):1911-1926. [7] HAN XG, TANG GQ, HAN X, et al. Comparison of Outcomes between Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Single-Level Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(7):2093-2101. [8] WANG C, ZHANG H, ZHANG L, et al. Accuracy and deviation analysis of robot-assisted spinal implants: A retrospective overview of 105 cases and preliminary comparison to open freehand surgery in lumbar spondylolisthesis. Int J Med Robot. 2021;17(4):e2273. [9] VICKERS AJ, VERTOSICK EA, LEWITH G, et al. Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Update of an Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. J Pain. 2018;19(5):455-474. [10] GENG Y, ZHU R, MAIMAITUERXUN M. Bibliometric review of carbon neutrality with CiteSpace: evolution, trends, and framework. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022; 29(51):76668-76686. [11] BUKAR UA, SAYEED MS, RAZAK SFA, et al. A method for analyzing text using VOSviewer. MethodsX. 2023;11:102339. [12] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608. [13] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538. [14] CUI GY, HAN XG, WEI Y, et al. Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in the Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(7):1960-1968. [15] PARKER SL, MENDENHALL SK, SHAU DN, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparative effectiveness and cost-utility analysis. World neurosurgery. 2014;82(1-2):230-238. [16] CARREON LY, GLASSMAN SD, GHOGAWALA Z, et al. Modeled cost-effectiveness of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion compared with posterolateral fusion for spondylolisthesis using N(2)QOD data. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(6):916-921. [17] MATZ PG, MEAGHER RJ, LAMER T, et al. Guideline summary review: An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2016;16(3):439-448. [18] PARKER SL, ADOGWA O, PAUL AR, et al. Utility of minimum clinically important difference in assessing pain, disability, and health state after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14(5):598-604. [19] DE KUNDER SL, VAN KUIJK SMJ, RIJKERS K, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2017;17(11): 1712-1721. [20] DROSSOPOULOS PN, ONONOGBU-UCHE FC, TABARESTANI TQ, et al. Evolution of the Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF): From Open to Percutaneous to Patient-Specific. J Clin Med. 2024;13(8): 2271. [21] QIN R, LIU B, ZHOU P, et al. Minimally Invasive Versus Traditional Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of Single-Level Spondylolisthesis Grades 1 and 2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:180-189. [22] HAIK NV, BURGESS AE, TALBOT NC, et al. Robotic Systems in Spinal Surgery: A Review of Accuracy, Radiation Exposure, Hospital Readmission Rate, Cost, and Adverse Events. World Neurosurg. 2025;195:123721. [23] YANG JS, HE B, TIAN F, et al. Accuracy of Robot-Assisted Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement for Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Comparative Cohort Study. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2479-2487. [24] STURGILL D, HOW J, BLAJDA T, et al. Are the Clinical Outcomes and Cost-Effectiveness of Robot-Assisted Pedicle Screw Placement in Lumbar Fusion Surgery Superior to Computed Tomography Navigation and Freehand Fluoroscopy-Guided Techniques? A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2024;191:81-90. [25] VERMUE H, TACK P, GRYSON T, et al. Can robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty be a cost-effective procedure? A Markov decision analysis. Knee. 2021;29:345-352. [26] KIA C, ANTONACCI CL, WELLINGTON I, et al. Spinal Implant Osseointegration and the Role of 3D Printing: An Analysis and Review of the Literature. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(3):108. [27] LI GQ, TONG T, WANG LF. Comparative analysis of the effects of OLIF and TLIF on adjacent segments after treatment of L4 degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):203. [28] SINGHATANADGIGE W, TANGDAMRONGTHAM T, LIMTHONGKUL W, et al. Incidence and Risk Factors for Lumbar Sympathetic Chain Injury After Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Neurospine. 2024;21(3):820-832. [29] JI XK, LI J. Effect of three-volt moxibustion with helium-neon laser irradiation on quality of care in patients with lumbar radiculopathy spondylosis. World J Clin Cases. 2024; 12(15):2522-2528. [30] VARPAEI HA, FARHADI K, MOHAMMADI M, et al. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a concept analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024; 36(1):133. [31] KöHLI P, SCHöNNAGEL L, HAMBRECHT J, et al. The relationship between paraspinal muscle atrophy and degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis at the L4/5 level. Spine J. 2024;24(8):1396-1406. [32] LENG Y, TANG C, HE B, et al. Correlation between the spinopelvic type and morphological characteristics of lumbar facet joints in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2023; 38(4):425-435. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Lai Yu, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Research hotspots and frontier trends of bioactive materials in treating bone infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2132-2144. |
| [3] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [4] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [5] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [6] | Zou Rongji, Yu Fangfang, Wang Maolin, Jia Zhuopeng. Triptolide inhibits ferroptosis and improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model of cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 873-881. |
| [7] | Zhao Jingang, Liu Liping, Chen Jianwei, . Finite element analysis comparing lumbar fusion and artificial intervertebral disc replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 553-560. |
| [8] | Abudusalamu·Tuoheti, Xiao Yang, Wang Yixi, Musitapa·Mijiti, Chen Qihao, Maimaitiming·Saiyiti, Guo Hailong, Paerhati·Rexiti. Effects of three internal fixation techniques on biomechanics of adjacent segment degeneration in lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 586-595. |
| [9] | Jia Yingao, Gao Shitao, Wang Fei. Application of 3D printed titanium cage cutting model in anterior cervical vertebrae subtotal decompression and bone graft fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 604-611. |
| [10] | Wang Yalei, Wang Xuezhi, Zhou Tao, Shen Xinxin, Fang Ding, Chen Hongliang. Effect of sacroiliac joint ankylosis on outcomes of L5/S1 transforminal lumbar interbody fusion and lumbar sagittal parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 634-641. |
| [11] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [12] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [13] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [14] | Liu Tongyan, Li Yuan, Sun Wei, Yao Bing, Fang Shanshan, Zhou Lingyun. Current status and hotspot analysis of experimental research on electroacupuncture intervention for peripheral nerve regeneration: electroacupuncture parameters, acupuncture effects and molecular mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2608-2617. |
| [15] | Jiao Jingya, Zhang Yeting. Analysis of thematic evolution pathways in the field of physical activity and neurogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2653-2661. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||