Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2525-2535.doi: 10.12307/2026.618
Previous Articles Next Articles
The relationship between gout and some lifestyles, cardiovascular disease, bone disease, and psychiatric disease
Liu Shuhong1, Xie Yuhan1, Huang Chengcheng2, Yang Zhenguo3, Li Yang3
- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabology, the Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-17Accepted:2025-06-19Online:2026-04-08Published:2025-08-29 -
Contact:Li Yang, MS, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Shuhong, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Province Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project, No. M-2023143 (to LY); Shandong Province Medicine and Health Science and Technology Project, No. 202304071638 (to YZG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Shuhong, Xie Yuhan, Huang Chengcheng, Yang Zhenguo, Li Yang. The relationship between gout and some lifestyles, cardiovascular disease, bone disease, and psychiatric disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2525-2535.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
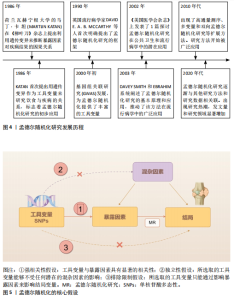
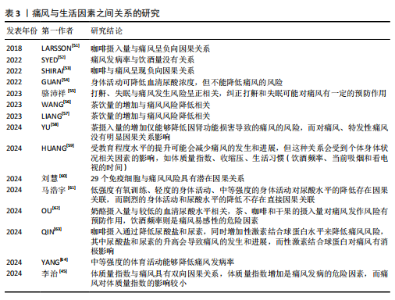
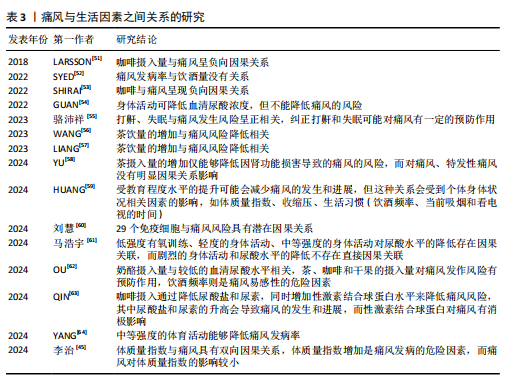
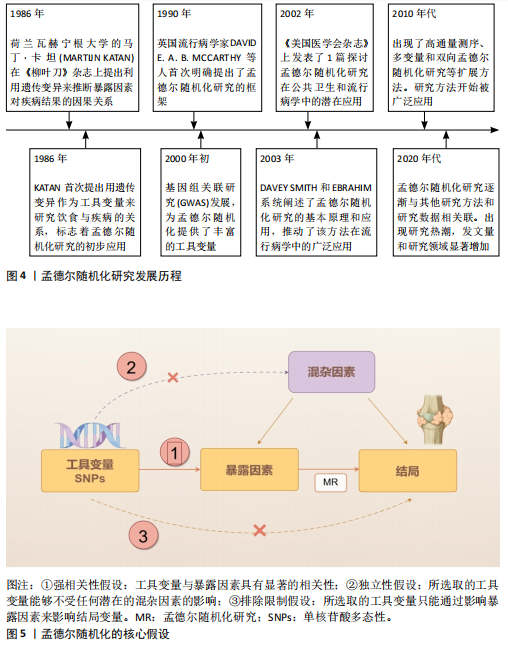
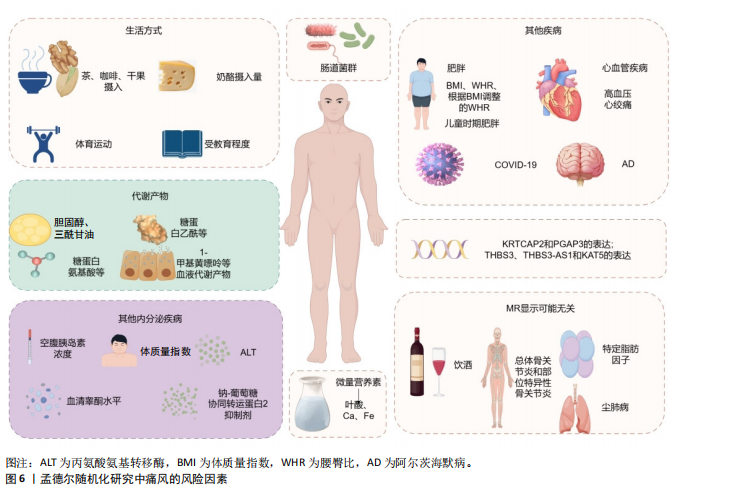
2.1 孟德尔随机化 相比于回顾性研究和随机对照试验,孟德尔随机化方兴未艾(图4)。孟德尔随机化是基于全基因组关联研究,将单核苷酸多态性作为工具变量利用自然遗传变异来模拟随机对照试验,推断可改变的暴露与疾病之间的因果关系。理论上,基因序列受疾病发展等各种其他因素影响较小,能够有效避免混杂偏倚和反向因果关系等。孟德尔随机化分析基于3个基本假设(图5):①强相关性假设:工具变量与暴露因素具有显著的相关性;②独立性假设:所选取的工具变量能够不受任何潜在的混杂因素的影响;③排除限制假设:所选取的工具变量只能通过影响暴露因素来影响结局变量。 2.2 痛风相关孟德尔随机化研究中的风险因素统计 基于痛风在不同研究领域之间的热点和关联性,将痛风的孟德尔随机化研究中的风险因素分为以下几大类进行探讨分析,汇总结果见表1-3[8-64]。 2.2.1 痛风与生活方式 OU等[62]针对一系列常见食物与痛风关系进行的孟德尔随机化研究显示:奶酪摄入量与较低的血清尿酸水平相关,茶、咖啡和干果的摄入量对痛风发作风险有预防作用,饮酒频率则是痛风易感性的危险因素;而SYED等[52]的孟德尔随机化研究发现痛风发病率与饮酒量没有关系;同样,WANG等[56]和LIANG等[57]的孟德尔随机化研究也表明茶饮量的增加与痛风风险降低相关;但YU等[58]的孟德尔随机化研究细化痛风分类后认为,茶摄入量的增加仅能够降低因肾功能损害导致的痛风的风险,而对痛风、特发性痛风没有明显因果关系的影响。 与OU等[62]提出的咖啡摄入对痛风的影响相类似,QIN等[63]对咖啡影响痛风的机制通过孟德尔随机化研究进行了深入探讨,发现咖啡摄入通过降低尿酸盐和尿素水平,同时增加性激素结合球蛋白水平来降低痛风风险,其中尿酸盐和尿素水平的升高会导致痛风的发生和进展,而性激素结合球蛋白对痛风有消极影响。SHIRAI等[53]的孟德尔随机化研究认可该观点,并细化了人种和血清尿酸水平的影响因素,发现该结果与人种无关,且在调整血清尿酸水平后该结论依旧成立。 运动可以有效降低尿酸水平[65]。YANG等[64]的孟德尔随机化研究发现,中等强度的体育活动能够降低痛风发病率;但GUAN等[54]的孟德尔随机化研究则表示身体活动可降低血清尿酸浓度,但不能降低痛风的风险。马浩宇等[61]的孟德尔随机化研究结果更为全面细致,认为低强度有氧训练、轻度的身体活动、中等强度的身体活动对尿酸水平的降低存在因果关联,"
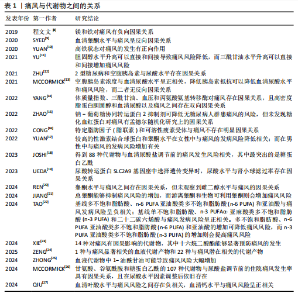
而剧烈的身体活动与尿酸水平的降低不存在直接因果关联。ZENG等[40]发现阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停与血清尿酸水平有显著因果关系,而与痛风并无任何双向因果关系。但骆沛祥等[55]的孟德尔随机化研究发现打鼾、失眠与痛风发生风险呈正相关,纠正打鼾和失眠可能对痛风有一定的预防作用。此外,HUANG等[59]的孟德尔随机化研究表明受教育程度水平的提升可能会减少痛风的发生和进展,但这种关系会受到个体身体状况相关因素的影响,如体质量指数、收缩压、生活习惯(饮酒频率、当前吸烟和看电视的时间)。 2.2.2 痛风与代谢产物 YU等[11]的孟德尔随机化研究发现胆固醇水平升高可以直接和间接导致痛风风险降低,而三酰甘油水平升高可以直接和间接增加痛风风险。 JOSHI等[18]通过前瞻性研究和孟德尔随机化研究提出,有88种代谢物与血清尿酸盐调节前的痛风发生风险相关,其中最突出的是糖蛋白乙酰;而前糖蛋白乙酰水平则与尿酸水平调整后的新发痛风和新发痛风病例中复发性痛风发作有关,且影响程度随禁食时长变化。类似的,MCCORMICK等[26]的孟德尔随机化研究发现了包括甘氨酸、谷氨酰胺和糖蛋白乙酰的107种代谢物与尿酸盐调节前的住院痛风发生率具有因果关系,且在尿酸水平因素调整后依旧存在。 ZHONG等[25]的孟德尔随机化研究发现血液代谢物中1-油酰甘油可能导致痛风风险大幅增加。ZENG等[24]通过孟德尔随机化研究进一步证实了1种与痛风显著相关的血液代谢产物和22种与痛风潜在相关的代谢产物, 如X-11529会增加痛风风险,胡椒碱和水苏碱等其他代谢物对痛风具有保护作用;研究还进行了富集分析,表明1-甲基黄嘌呤可能通过咖啡因代谢途径参与痛风的代谢过程。XIE等[23]的孟德尔随机化研究确定了14种对痛风有因果影响的代谢物,并发现十六烷二酸酯能够显著预防痛风的发生。 TAO等[22]利用孟德尔随机化研究循环脂肪酸与痛风之间的关系,发现基线多不饱和脂肪酸、亚油酸类多不饱和脂肪酸(n-6 PUFA)和亚油酸与痛风发病风险呈负相关;基线单不饱和脂肪酸、α-亚麻酸类多不饱和脂肪酸(n-3 PUFA)和二十二碳六烯酸与痛风发病风险呈正相关。多不饱和脂肪酸、亚油酸类多不饱和脂肪酸和亚油酸的增加可降低痛风风险,而α-亚麻酸类多不饱和脂肪酸的增加则会提高痛风风险。 2.2.3 痛风与其他疾病 (1)痛风与内分泌疾病:ZHU等[12]和MCCORMICK等[13]的孟德尔随机化研究显示空腹胰岛素浓度与血清尿酸水平呈正相关,降低胰岛素抵抗可以降低血清尿酸水平和痛风风险,而二者无反向因果关系。除此之外,YANG等[14]的孟德尔随机化研究还发现体质量指数、三酰甘油、血压和丙氨酸氨基转移酶对痛风也存在因果关系,且高密度脂蛋白胆固醇和血清尿酸盐以及痛风彼此之间存在双向因果关系。 SYED等[9]的孟德尔随机化研究认为血清睾酮水平与痛风呈反向因果关系。YUAN等[17]基于性激素对多种疾病关系的研究中进一步提出性别差异,即在女性中,较高的性激素结合球蛋白和睾酮水平与痛风的发病风险降低相关,而在男性中则与痛风的发病风险增加有关。JIANG等[21]通过孟德尔随机化研究细化了睾酮在体内的状态,认为雄激素状态可能与痛风有"
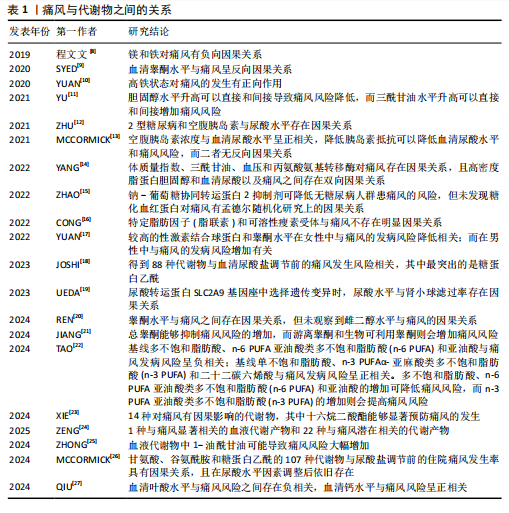
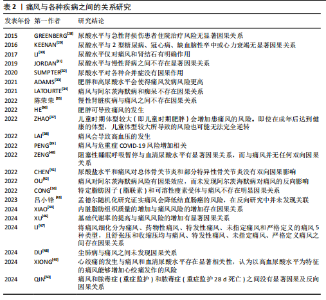
关,研究发现总睾酮能够抑制痛风风险的增加,而游离睾酮和生物可利用睾酮则会增加痛风风险。REN等[20]的孟德尔随机化研究也认可睾酮水平与痛风之间的因果关系,但未观察到雌二醇水平与痛风的因果关系。 EBSTEIN等[66]在研究中提到钠-葡萄糖协同转运蛋白2抑制剂能够降低血清尿酸水平,进而治疗痛风并降低其复发风险。ZHAO等[15]的孟德尔随机化研究结果支持钠-葡萄糖协同转运蛋白2抑制剂可降低无糖尿病人群患痛风的风险,但未发现糖化血红蛋白对痛风有孟德尔随机化研究上的因果关系。 (2)痛风与肥胖: ZHANG等[67]通过全面的全基因组交叉性状分析,提出体质量指数、腰臀比和根据体质量指数调整的腰臀比与痛风呈正相关,并在全基因组的4q22处确定了体质量指数和痛风的显著局部信号。相比于整体肥胖,XIAO等[44]的孟德尔随机化研究认为内脏脂肪组织质量的增加与痛风风险的增加存在因果关系,并提出针对内脏脂肪组织肿块的针对性干预可能有利于预防痛风。ADAMS等[33]利用孟德尔随机化研究分析发现肥胖和高尿酸水平会使得痛风发病风险更高。HE等[36]的孟德尔随机化研究也发现体质量指数的升高会导致痛风风险的增加。李治等[45]的孟德尔随机化研究认为体质量指数与痛风具有双向因果关系,体质量指数增加是痛风发病的危险因素,而痛风对体质量指数的影响较小。但CONG等[16]在针对特定脂肪因子(脂联素)和可溶性瘦素受体与痛风的孟德尔随机化研究中则表示未发现二者与痛风存在明显的因果关系。 ZHAO等[37]的孟德尔随机化研究发现,如儿童时期体型较大(即儿童时期肥胖)会增加患痛风的风险,即使在成年后达到健康的体型,儿童体型较大所导致的风险也可能无法完全逆转。值得注意的是,2型糖尿病也会导致肥胖和基础代谢率的提高。XU等[46]的孟德尔随机化研究提出基础代谢率的提高与痛风风险的增加有显著因果关系,而这种关系在控制2型糖尿病影响后依旧有显著的因果关系。 (3)痛风与心血管疾病:LAI等[38]的孟德尔随机化研究认为痛风会导致高血压的发生,但高血压对痛风没有因果影响。LI等[47]将痛风细化分为痛风、药物性痛风、特发性痛风、未指定痛风和严格定义的痛风5种类型,并发现舒张压和收缩压均与痛风、特发性痛风、未指定痛风、严格定义痛风之间存在因果关系。 与之类似的是,ZHU等[68]在随访中发现,与无高尿酸血症/痛风的个体相比,高尿酸血症患者与心血管疾病风险增加相关,其中痛风患者的风险升高甚至更高。孟德尔随机化研究发现高尿酸血症和心血管疾病之间存在显著的正相关,而痛风与心血管疾病不具备孟德尔随机化研究的因果关系,并提出除了尿酸途径外,其他与痛风相关因素对心血管疾病的发展可能有更大影响。除此之外,XIONG等[49]的孟德尔随机化研究发现心绞痛的发生与痛风和血清尿酸水平存在显著相关性,认为以高血尿酸水平为特征的痛风能够增加心绞痛发作的风险。 (4)痛风与COVID-19:在COVID-19大流行早期对英国生物库队列的分析发现[69],痛风会导致COVID-19感染风险提高1.5倍,且排除调整年龄、性别、种族等影响因素,COVID-19相关死亡的风险增加至1.7倍。基于人群的分析,痛风与COVID-19诊断风险增加相关[70];诊断为COVID-19的患者在诊断痛风后,COVID-19相关死亡的风险显著增加,且女性远高于男性。PENG等[39]的孟德尔随机化研究表明痛风与危重症COVID-19风险增加相关。 (5)痛风与骨骼疾病:痛风已成为肌肉骨骼疼痛和关节炎的主要原因[71-73],其患病率和发病率在全球范围内均有所增加[74]。血清尿酸盐水平持续升高导致尿酸单钠沉积在关节内或关节周围,形成痛风石和关节损伤[75]。LIU等[76]的Meta分析发现痛"
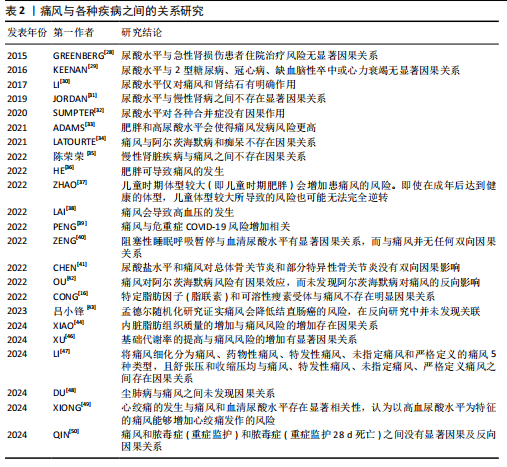

风与骨质疏松呈正相关,而与骨折的发生率没有明显关系。KWON等[77]随访研究发现痛风可能导致骨质疏松症的患病率提升,而与骨质疏松性骨折无明显关系。KIM等[78]的研究也支持上述观点。而CHEN等[41]的孟德尔随机化研究支持尿酸盐水平和痛风对总体骨关节炎和部分特异性骨关节炎没有双向因果关系。 (6)痛风与精神类疾病:研究表明,痛风患者比非痛风患者的抑郁和焦虑的发生率更高[79]。除此之外,文献检索还发现,抑郁症重要决定因素包括痛风石数量、发作频率和多关节痛风等[80]。OU等[42]的孟德尔随机化研究支持痛风对阿尔茨海默病风险的因果效应,而未发现阿尔茨海默病对痛风的反向影响。然而LATOURTE等[34]却表示孟德尔随机化分析不支持痛风与阿尔茨海默病和痴呆的因果关系。 (7)痛风与其他疾病:除外上述的各大分类,孟德尔随机化研究也发现痛风与多种其他疾病有较明显的因果关系。DU等[48]的孟德尔随机化研究认为尘肺病与痛风之间未发现因果关系。QIN等[50]将脓毒症简单分为两类,通过孟德尔随机化研究发现痛风和脓毒症(重症监护)和脓毒症(重症监护28 d死亡)之间没有显著因果及反向因果关系。陈荣荣等[35]的孟德尔随机化研究认为慢性肾脏疾病与痛风之间不存在因果关系。吕小锋等[43]在孟德尔随机化研究中发现痛风会降低结直肠癌的风险,而在反向研究中并未发现二者之间的关联。刘慧等[60]的孟德尔随机化研究发现29个免疫细胞与痛风风险具有潜在因果关系。 2.2.4 痛风与肠道菌群 WANG等[81]的孟德尔随机化研究发现肠道微生物群与痛风和血清尿酸水平之间存在双向因果关系,认为特定肠道微生物群分类丰度在血清尿酸水平和痛风的发展中起着重要作用,痛风和血清尿酸水平会影响肠道微生物群的组成。LOU等[82]的孟德尔随机化研究种发现了196种细菌性状与痛风风险之间可能有潜在因果关系,并确定Coprococcus 3属和痛风风险存在正相关性,但在反向孟德尔随机化分析中未发现这些细菌属与痛风之间的因果关系。 TANG等[83]的孟德尔随机化研究则未发现痛风与肠道菌群的显著双向因果关系,但提出Rikenellaceae对痛风可能有轻微的保护作用,Ruminococcaceae UCG_011的存在可能与痛风风险的增加有关。 2.2.5 痛风与微量营养素 临床试验发现,利用叶酸配合依那普利治疗可以降低高血压患者的尿酸水平[84],而尿酸正是导致痛风的主要物质;横断面调查研究发现,痛风患者头发中B、Fe、I和Mo水平较对照组高[85],Cr、V、Al、As和Pb含量较对照组高,Mg和Zn水平降低,且男性患者比女性表现更严重。QIU等[27]的孟德尔随机化研究了特定的10种微量营养素与痛风的关系,研究结果显示血清叶酸水平与痛风风险之间存在负相关,血清钙水平与痛风风险呈正相关。YUAN等[10]的孟德尔随机化研究显示高铁状态对痛风的发生有正向作用。程文文等[8]的孟德尔随机化研究同样发现镁和铁对痛风有负向因果关系。 2.2.6 痛风与基因表达 大规模流行病学研究和实验小鼠模型表明,克隆性造血疾病可促进痛风的发生[86],其中表观遗传调节因子TET2和DNMT3A是克隆性造血最常见的突变基因,并认为痛风的发病可能与这两个突变基因有关。研究人员在临床试验中发现,痛风患者有7个DNA甲基化位点[87],这些位点映射到PGGT1B、UBAP1、RAPTOR、INSIG1、ANGPTL2、CNTN5和JNK1这7个基因上,推测其可能与痛风的发生有密切关系。WANG等[88]通过孟德尔随机化研究分析了来自血液和肾脏组织相关基因位点与痛风的关系,发现KRTCAP2和PGAP3的表达增加可以导致痛风风险的增加,而THBS3、THBS3-AS1 和KAT5的表达增加则会导致痛风的风险降低,且在肾组织中未观察到与痛风显著关联的基因。"
| [1] MIKULS TR. Gout. N Engl J Med. 2022; 387(20):1877-1887. [2] REIS C, VIANA QUEIROZ M. Prevalence of self-reported rheumatic diseases in a Portuguese population. Acta Reumatol Port. 2014;39(1):54-59. [3] WILSON L, SASEEN JJ. Gouty Arthritis: A Review of Acute Management and Prevention. Pharmacotherapy. 2016;36(8): 906-922. [4] SCHUMACHER HR JR. The pathogenesis of gout. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008;75 Suppl 5:S2-4. [5] KIM YS, KIM Y, PARK G, et al. Genetic analysis of ABCG2 and SLC2A9 gene polymorphisms in gouty arthritis in a Korean population. Korean J Intern Med. 2015;30(6):913-920. [6] WAN GHAZALI WS, WAN ZAINUDIN WMKB, YAHYA NK, et al. Older age and diclofenac are associated with increased risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in gout patients. PeerJ. 2021;9:e11468. [7] YARRARAPU SNS, GOYAL A, VENKATA VS, et al. Comprehensive review of statin-intolerance and the practical application of Bempedoic Acid. J Cardiol. 2024;84(1):22-29. [8] 程文文,朱强,张红雨.矿物质营养与慢性病风险:孟德尔随机化研究[C]//2019中国化学会第十五届全国计算(机)化学学术会议论文集,2019:309. [9] SYED AAS, HE L, SHI Y. The Potential Effect of Aberrant Testosterone Levels on Common Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(7):721. [10] YUAN S, LARSSON S. Causal associations of iron status with gout and rheumatoid arthritis, but not with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Nutr. 2020;39(10):3119-3124. [11] YU X, WANG T, HUANG S, et al. Evaluation of the causal effects of blood lipid levels on gout with summary level GWAS data: two-sample Mendelian randomization and mediation analysis. J Hum Genet. 2021;66(5):465-473. [12] ZHU J, SUN L, YANG J, et al. Genetic Predisposition to Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Levels Is Positively Associated With Serum Urate Levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(7):e2547-e2556. [13] MCCORMICK N, O’CONNOR MJ, YOKOSE C, et al. Assessing the Causal Relationships Between Insulin Resistance and Hyperuricemia and Gout Using Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(11):2096-2104. [14] YANG Y, XIAN W, WU D, et al. The role of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic factors in gout: A Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:917056. [15] ZHAO SS, RAJASUNDARAM S, KARHUNEN V, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 inhibition and gout: Mendelian randomisation study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;56:152058. [16] CONG R, ZHANG X, SONG Z, et al. Assessing the Causal Effects of Adipokines on Uric Acid and Gout: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2022;14(5):1091. [17] YUAN S, WANG L, SUN J, et al. Genetically predicted sex hormone levels and health outcomes: phenome-wide Mendelian randomization investigation. Int J Epidemiol. 2022;51(6):1931-1942. [18] JOSHI AD, MCCORMICK N, YOKOSE C, et al. Prediagnostic Glycoprotein Acetyl Levels and Incident and Recurrent Flare Risk Accounting for Serum Urate Levels: A Population-Based, Prospective Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75(9):1648-1657. [19] UEDA M, FUKUI K, KAMATANI N, et al. GLUT9 as a potential drug target for chronic kidney disease: Drug target validation by a Mendelian randomization study. J Hum Genet. 2023;68(10):699-704. [20] REN Y, JIANG Y, PENG H, et al. Causal association between several gender-driven factors and gout: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024; 27(3):e15111. [21] JIANG Y, LIU S, LIU G, et al. Association between sex hormones and gout: An analysis of the UK Biobank cohort. Steroids. 2024;207:109422. [22] TAO HW, LIU ZY, JIANG W, et al. Lower plasma linoleic acids as a risk factor for gout: an integrated analysis of population-based cohort and genetic data. Food Funct. 2024;15(14):7567-7576. [23] XIE Y, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. Assessing the causal association between human blood metabolites and the risk of gout. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024;54(3):e14129. [24] ZENG H, LAI J, LIU Z, et al. Specific blood metabolite associations with Gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2025;79(1):24-32. [25] ZHONG Y, YANG C, ZHANG B, et al. Causal impact of human blood metabolites and metabolic pathways on serum uric acid and gout: a mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024; 15:1378645. [26] MCCORMICK N, JOSHI AD, YOKOSE C, et al. Prediagnostic Amino Acid Metabolites and Risk of Gout, Accounting for Serum Urate: Prospective Cohort Study and Mendelian Randomization. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024;76(12):1666-1674. [27] QIU Y, LI C, HUANG Y, et al. Exploring the causal associations of micronutrients on urate levels and the risk of gout: A Mendelian randomization study. Clin Nutr. 2024;43(4):1001-1012. [28] GREENBERG KI, MCADAMS-DEMARCO MA, KÖTTGEN A, et al. Plasma Urate and Risk of a Hospital Stay with AKI: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(5):776-783. [29] KEENAN T, ZHAO W, RASHEED A, et al. Causal Assessment of Serum Urate Levels in Cardiometabolic Diseases Through a Mendelian Randomization Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(4):407-416. [30] LI X, MENG X, TIMOFEEVA M, et al. Serum uric acid levels and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of evidence from observational studies, randomised controlled trials, and Mendelian randomisation studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j2376. [31] JORDAN DM, CHOI HK, VERBANCK M, et al. No causal effects of serum urate levels on the risk of chronic kidney disease: A Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2019;16(1):e1002725. [32] SUMPTER NA, SAAG KG, REYNOLDS RJ, et al. Comorbidities in gout and hyperuricemia: causality or epiphenomena? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020;32(2):126-133. [33] ADAMS CD, BOUTWELL BB. Using multiple Mendelian randomization approaches and genetic correlations to understand obesity, urate, and gout. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):17799. [34] LATOURTE A, DUMURGIER J, PAQUET C, et al. Hyperuricemia, Gout, and the Brain-an Update. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(12):82. [35] 陈荣荣,季世昌,宋飞超,等.基于孟德尔随机化方法分析尿酸与慢性肾脏病的因果关系[J].现代预防医学,2022, 49(22):4039-4044. [36] HE C, ZHANG M, LI J, et al. Novel insights into the consequences of obesity: a phenotype-wide Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Hum Genet. 2022;30(5):540-546. [37] ZHAO SS, BOWES J, BARTON A, et al. Separating the effects of childhood and adult body size on inflammatory arthritis: a Mendelian randomisation study. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002321. [38] LAI B, YU HP, CHANG YJ, et al. Assessing the causal relationships between gout and hypertension: a bidirectional Mendelian randomisation study with coarsened exposures. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):243. [39] PENG H, WU X, XIONG S, et al. Gout and susceptibility and severity of COVID-19: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. J Infect. 2022;85(3):e59-e61. [40] ZENG Z, JIN T, NI J, et al. Assessing the causal associations of obstructive sleep apnea with serum uric acid levels and gout: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;57:152095. [41] CHEN D, XU H, SUN L, et al. Assessing causality between osteoarthritis with urate levels and gout: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(4):551-558. [42] OU YN, ZHAO B, FU Y, et al. The Association of Serum Uric Acid Level, Gout, and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;89(3):1063-1073. [43] 吕小锋,刘姗姗,陈雄,等.痛风与结直肠癌的因果关系:双向两样本孟德尔随机化研究[J].现代预防医学,2023,50(17): 3257-3264. [44] XIAO W, WANG Q, LIU Y, et al. Association of visceral adipose tissue with gout: Observational and Mendelian randomization analyses. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024;137(19):2351-2357. [45] 李治,陈锋,闫乾,等.基于两样本双向孟德尔随机化法分析体质指数与痛风的因果关系[J].广西医学,2024,46(8):1152-1159. [46] XU C, LI K, WANG F. Basal metabolic rate is associated with increased risk of gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(2):837-838. [47] LI Y, XIE Y, LI J, et al. Diastolic and systolic blood pressure and gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1367621. [48] DU YJ, LU ZW, LI KD, et al. No causal association between pneumoconiosis and three inflammatory immune diseases: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1373044. [49] XIONG J, SUN Y, HUANG H, et al. The Causal Relationship between Angina Pectoris and Gout Based on Two Sample Mendelian Randomization. Pain Res Manag. 2024;2024:4564596. [50] QIN Y, YANG X, NING Z. Causal roles of serum uric acid levels and gout in sepsis: a mendelian randomization study. Shock. 2024;62(1):44-50. [51] LARSSON SC, CARLSTRÖM M. Coffee consumption and gout: a Mendelian randomisation study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018; 77(10):1544-1546. [52] SYED AAS, FAHIRA A, YANG Q, et al. The Relationship between Alcohol Consumption and Gout: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(4):557. [53] SHIRAI Y, NAKAYAMA A, KAWAMURA Y, et al. Coffee Consumption Reduces Gout Risk Independently of Serum Uric Acid Levels: Mendelian Randomization Analyses Across Ancestry Populations. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022;4(6):534-539. [54] GUAN Y, WEI J, MENG L, et al. Genetically predicted physical activity is associated with lower serum urate concentrations. Genes Genomics. 2022;44(7):843-853. [55] 骆沛洋,陈伟伟,刘彬,等.基于两样本孟德尔随机化方法探讨睡眠与痛风的关联[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2023, 47(8):932-937+943. [56] WANG Q, LIU YN, ZHANG H, et al. Causal Association Between Tea Consumption and Gout: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Curr Med Sci. 2023;43(5):947-954. [57] LIANG X, CAI J, FAN Y. Causal association between tea intake and risk for gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Genet. 2023;14:1220931. [58] YU Y, YANG X, HU G, et al. Effect of tea intake on genetic predisposition to gout and uric acid: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024; 14:1290731. [59] HUANG X, CHEN X, LIU Q, et al. The relationship between education attainment and gout, and the mediating role of modifiable risk factors: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Public Health. 2024;11:1269426. [60] 刘慧,朱瑜琪,赵英君,等.免疫细胞与炎性关节病风险的因果关系:一项孟德尔随机化研究[J].医学研究杂志,2024,53(8): 102-106+114. [61] 马浩宇,史冬博.不同强度的身体活动与血清尿酸含量的关联研究:样本孟德尔随机化分析[J].湖北体育科技,2024, 43(4): 55-60+105. [62] OU G, WU J, WANG S, et al. Dietary Factors and Risk of Gout: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Foods. 2024;13(8):1269. [63] QIN T, CHU Y, YAO Y, et al. Coffee intake reduced gout risk by decreasing urate and urea while increasing SHBG levels in plasma: a mediation Mendelian randomization study. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(5):1735-1743. [64] YANG T, BI S, ZHANG X, et al. The Impact of Different Intensities of Physical Activity on Serum Urate and Gout: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Metabolites. 2024; 14(1):66. [65] 吴昱苇,朱江,郑兵,等.运动调控尿酸的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(34):5552-5557. [66] EBSTEIN E, OTTAVIANI S. Managing Gout in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Drugs Aging. 2024;41(8):653-663. [67] ZHANG L, ZHANG W, XIAO C, et al. Using human genetics to understand the epidemiological association between obesity, serum urate, and gout. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(10):3280-3290. [68] ZHU J, ZENG Y, ZHANG H, et al. The Association of Hyperuricemia and Gout With the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Cohort and Mendelian Randomization Study in UK Biobank. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;8:817150. [69] TOPLESS RK, PHIPPS-GREEN A, LEASK M, et al. Gout, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and the Risk of Death Related to Coronavirus Disease 2019: An Analysis of the UK Biobank. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021;3(5):333-340. [70] NISSEN CB, HENDRICKS O, SCHREIBER K. Women with gout and COVID-19-an unfortunate combination? Lancet Rheumatol. 2022;4(4):e233-e234. [71] ELFISHAWI MM, ZLEIK N, KVRGIC Z, et al. The Rising Incidence of Gout and the Increasing Burden of Comorbidities: A Population-based Study over 20 Years. J Rheumatol. 2018;45(4):574-579. [72] 林泽玉,徐林.痛风致骨破坏机制的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(8):1295-1300. [73] 邵子晨,李华南,顾兵,等.痛风过程中微小RNA、长链非编码RNA和环状RNA介导降尿酸、抗炎及调控骨代谢的协同调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(5):765-771. [74] PEREZ-RUIZ F, CASTILLO E, CHINCHILLA SP, et al. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of gout. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2014; 40(2):193-206. [75] REIJNIERSE M, SCHWABL C, KLAUSER A. Imaging of Crystal Disorders:: Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease, Calcium Hydroxyapatite Crystal Deposition Disease and Gout Pathophysiology, Imaging, and Diagnosis. Radiol Clin North Am. 2022;60(4):641-656. [76] LIU Y, FENG J, JI P, et al. Association between gout and the risk of osteoporosis and fractures: a meta-analysis. Z Rheumatol. 2024;83(Suppl 1):191-199. [77] KWON MJ, PARK JY, KIM SG, et al. Potential Association of Osteoporosis and Not Osteoporotic Fractures in Patients with Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study. Nutrients. 2022;15(1):134. [78] KIM JH, KIM SR, KANG G, et al. Gout as a risk factor for osteoporosis: A Korean population-based study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(45):e31524. [79] HOWREN A, SAYRE EC, CHOI HK, et al. Onset of depression and anxiety among patients with gout after diagnosis: a population-based incident cohort study. BMC Rheumatol. 2022;6(1):56. [80] HOWREN A, BOWIE D, CHOI HK, et al. Epidemiology of Depression and Anxiety in Gout: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. J Rheumatol. 2021;48(1):129-137. [81] WANG M, FAN J, HUANG Z, et al. Causal Relationship between Gut Microbiota and Gout: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4260. [82] LOU Y, LIU B, JIANG Z, et al. Assessing the causal relationships of gut microbial genera with hyperuricemia and gout using two-sample Mendelian randomization. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2024;34(4):1028-1035. [83] TANG C, LI L, JIN X, et al. Investigating the Impact of Gut Microbiota on Gout Through Mendelian Randomization. Orthop Res Rev. 2024;16:125-136. [84] QIN X, LI Y, HE M, et al. Folic acid therapy reduces serum uric acid in hypertensive patients: a substudy of the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial (CSPPT). Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;105(4):882-889. [85] SKALNY AV, KOROBEINIKOVA TV, SOTNIKOVA TI, et al. Estimation of Hair Toxic and Essential Trace Element and Mineral Profiles of Patients with Chronic Gout. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025;203(3):1351-1361. [86] BELIZAIRE R, WONG WJ, ROBINETTE ML, et al. Clonal haematopoiesis and dysregulation of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23(9):595-610. [87] TSENG CC, WONG MC, LIAO WT, et al. Systemic Investigation of Promoter-wide Methylome and Genome Variations in Gout. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4702. [88] WANG Y, CHEN J, YAO H, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis identified potential genes pleiotropically associated with gout. Front Genet. 2024;15:1426860. |
| [1] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [2] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [3] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [4] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [5] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [6] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [7] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [8] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [9] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [10] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [11] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [12] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| [13] | Jiang Kai, Rong Yifa, Jia Haifeng, Li Hanzheng, Lu Bowen, Liang Xuezhen, Li Gang. Relationship between inflammatory factors and rheumatoid arthritis: a large-sample analysis based on the FinnGen R10 database and genome-wide association studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2629-2640. |
| [14] | Tian Meng, Lou Tianwei, Zhang Yongchen, Jia Hongling . Cathepsin F as a potential serum biomarker for stroke risk prediction: GWAS database data analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2662-2670. |
| [15] | Du Yanli, , Wang Yi, , Wang Zhenyu, Wang Xuanhui, , Li Xinye, , Xiong Xifeng, Miao Haixiong, . The role of p53 in musculoskeletal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2503-2514. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||