Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7679-7689.doi: 10.12307/2025.971
Previous Articles Next Articles
Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation
Gong Yuehong1, 2, Wang Mengjun3, Ren Hang3, Zheng Hui3, Sun Jiajia3, Liu Junpeng3, Zhang Fei3, Yang Jianhua1, 2, Hu Junping4
- 1Pharmaceutical Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Clinical Drug Research, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3School of Clinical Medicine, 4School of Pharmacy, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-11-04Accepted:2024-12-31Online:2025-12-18Published:2025-05-07 -
Contact:Hu Junping, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Pharmacy, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Co-corresponding author: Yang Jianhua, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Pharmaceutical Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Clinical Drug Research, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Gong Yuehong, Master, Associate chief pharmacist, Pharmaceutical Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Clinical Drug Research, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Wang Mengjun, School of Clinical Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Gong Yuehong and Wang Mengjun contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:The “Tianshan Talents” high-level medical and health personnel training plan of the Health Commission of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No.TSYC202301B095(to GYH); Xinjiang Medical University Student Innovation Training Program, No. S202310760059 (to WMJ); Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2021D01D11 (to HJP); Innovation Team Training Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, No. [2023]52 (to YJH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
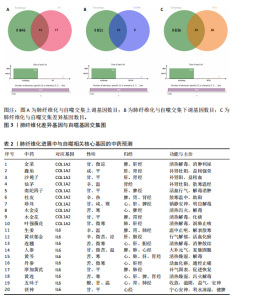
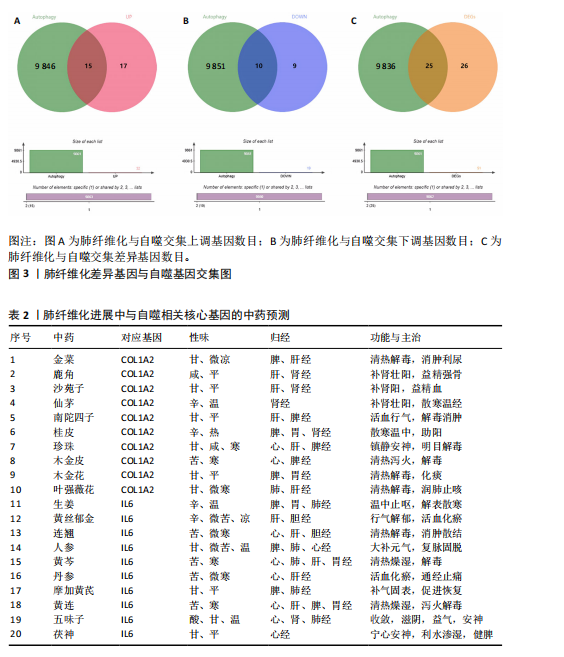
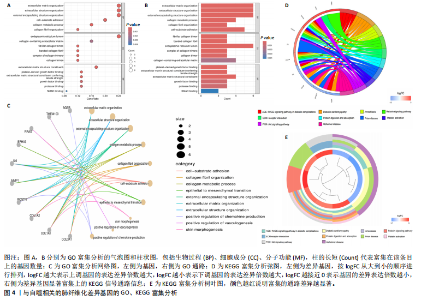
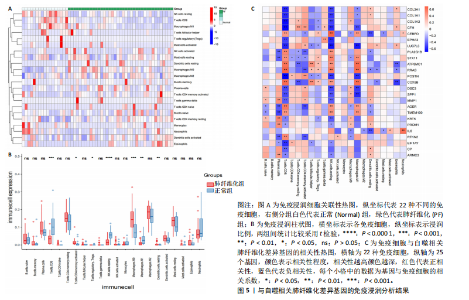
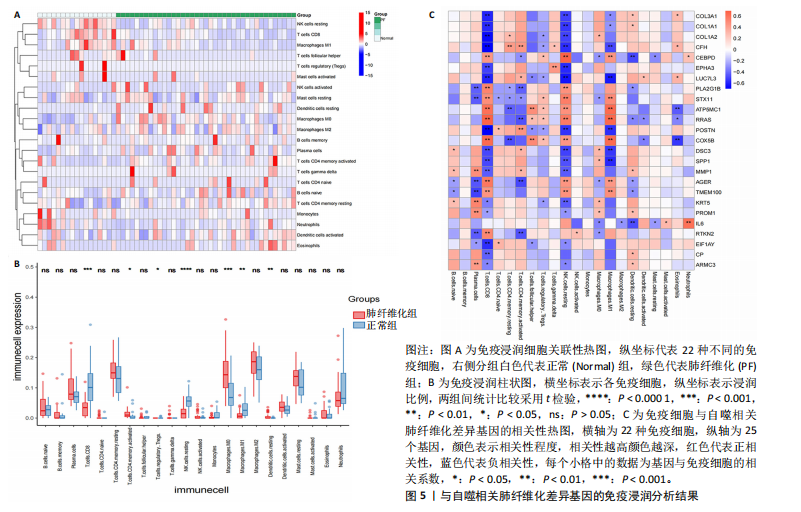
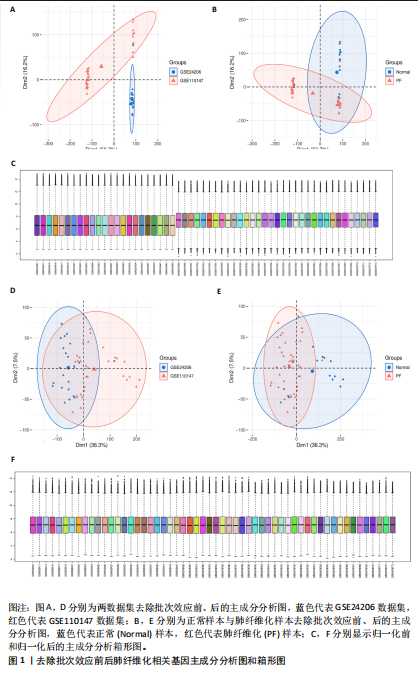
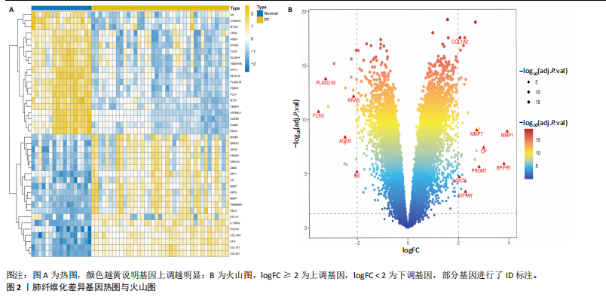
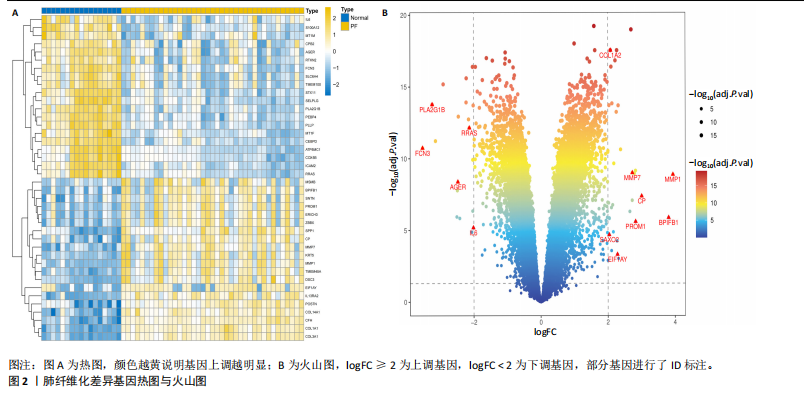
2.1 肺纤维化自噬相关基因 将肺纤维化数据集GSE24206和GSE110147进行合并,通过R软件“limma”包中的“normalize Between Arrays”函数,对两组基因表达矩阵进行常规的背景校正和分位数归一化处理,去除批次效应,见图1。 2.2 肺纤维化差异基因筛选 综合分析合并后的肺纤维化数据集后,依据筛选标准(adj.P.val < 0.05且 |logFC|> 2)鉴定出了51个差异表达基因,其中有32个上调基因,这些可能反映了肺纤维化病理过程中的适应性或激活状态;19个下调基因,这些基因可能在疾病状态下的功能受到了抑制,见图2。 2.3 肺纤维化自噬相关基因 进一步将筛选出的51个肺纤维化差异基因与GeneCards数据库中收录的9 861个已知自噬相关基因进行了交叉比对,旨在识别出既在肺纤维化中表现出显著差异,又与自噬过程紧密相关的基因。经过比对,筛选出25个交集基因,其中上调基因15个、下调基因10个,这些基因被确认为与自噬相关的肺纤维化基因,结果如图3所示。 2.4 特征基因的功能富集分析 对25个与自噬相关的肺纤维化差异基因进行GO和KEGG富集分析。GO富集分析结果显示,在生物过程方面,主要存在于细胞外基质组织、细胞外结构组织、外部包封结构组织、胶原代谢过程、胶原原纤维组织、细胞-底物黏附;分子功能方面,主要在血小板衍生生长因子结合、细胞外基质结构成分赋予拉伸强度、细胞外基质结构成分、生长因子结合、蛋白酶结合、SMAD结合中发挥作用;细胞组分方面,主要存在于纤维状胶原三聚体、带状胶原原纤维、内质网腔、胶原三聚体复合物、胶原三聚体、含胶原的细胞外基质(图4A-C)。KEGG富集分析结果显示,肺纤维化自噬差异基因主要在AGE-RAGE(高糖基化终末产物-糖基化终末产物受体)信号通路、PI3K-Akt(磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B)信号通路、松弛素信号通路、细胞外基质-受体相互作用、蛋白质消化与吸收等信号通路中(图4D,E)。 2.5 免疫浸润分析结果 采用CIBERSORT算法对合并数据集的对照组和肺纤维化组进行免疫浸润分析,探究两组之间不同免疫细胞浸润水平的差异。结果显示,正常组中CD8+ T细胞、调节性T细胞、静息NK细胞、M1巨噬细胞表达高于肺纤维化组(P < 0.05), 肺纤维化组活化记忆性CD4+ T细胞、M0巨噬细胞、静息树突状细胞表达高于正常组(P < 0.05)(图5A,B)。除IL6之外,其余24个与自噬相关的肺纤维化差异基因与CD8+ T均呈现强相关性,同时除IL6、RTKN2、CP之外,其他基因与静息NK细胞也呈现强相关性;此外,STX11、 ATP5MC1、RRAS、POSTN、COX5B、DSC3、SPP1、AGER、TMEM100、LUC7L3、CFH、CEBPD这基因与M1巨噬细胞呈现出强相关性(图5C)。 2.6 蛋白质与蛋白质相互作用网络 将与自噬相关的肺纤维化的25个基"
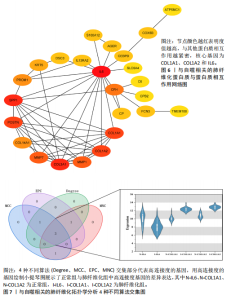
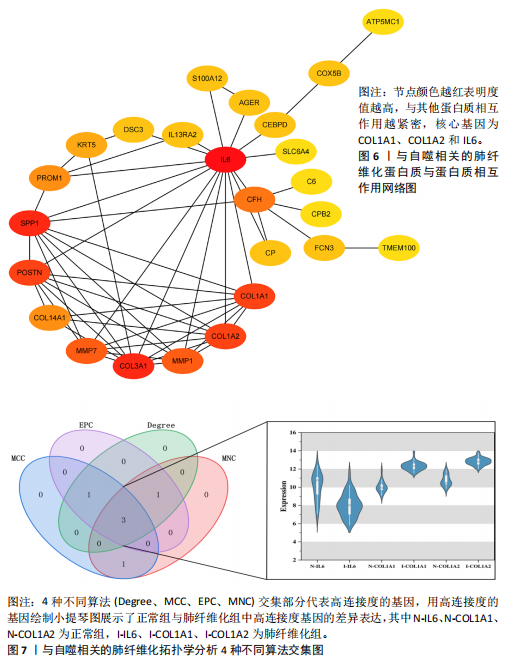
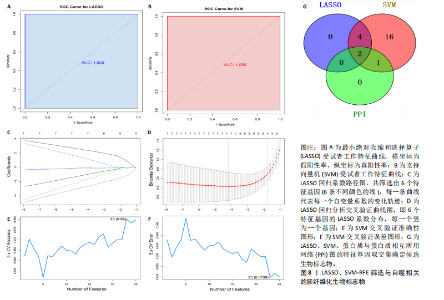
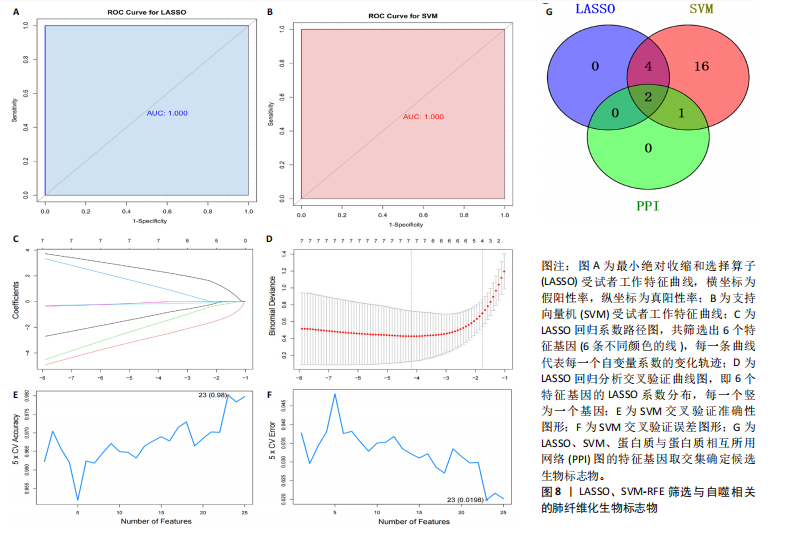
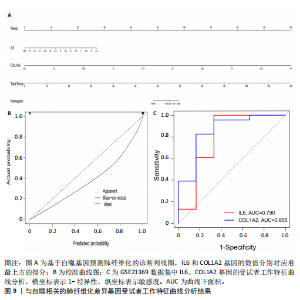
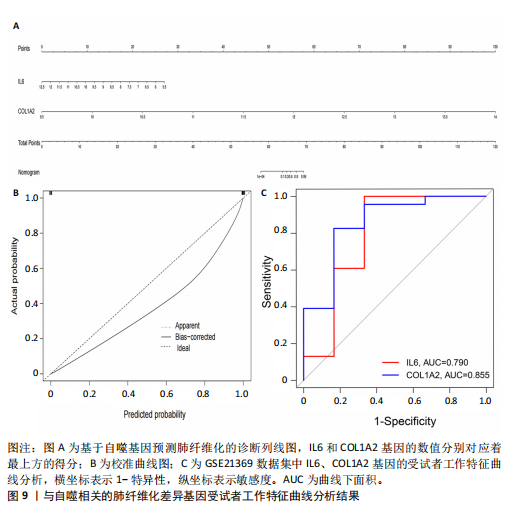
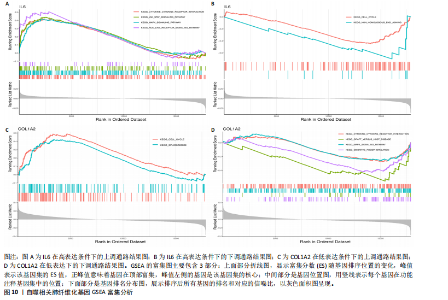
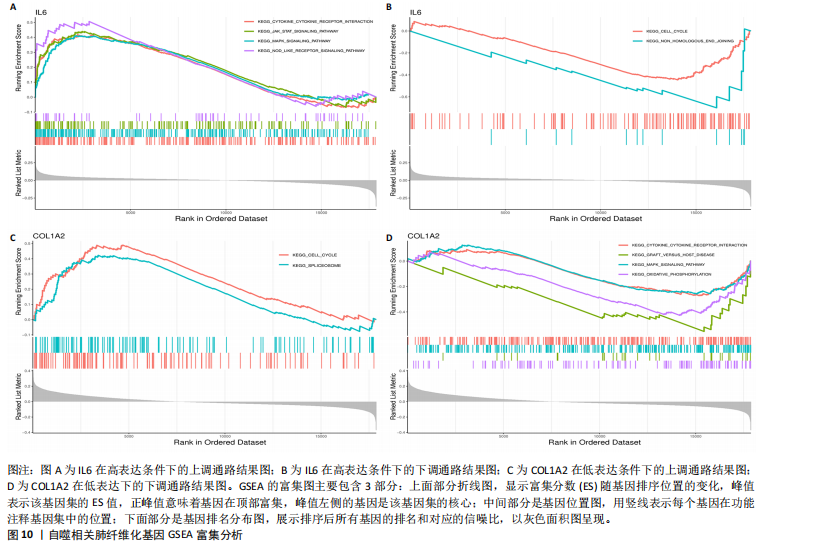
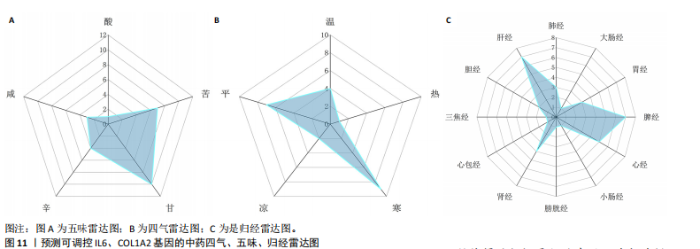
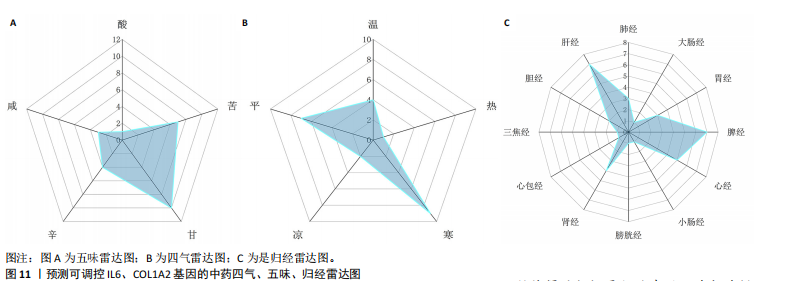
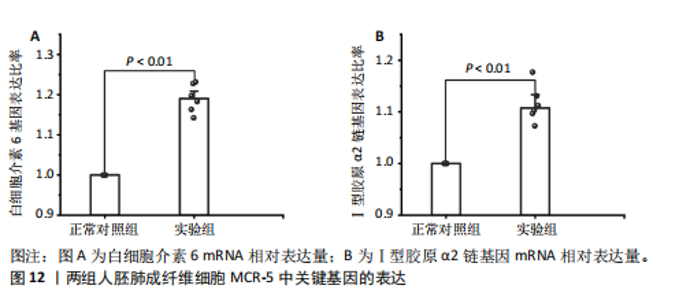
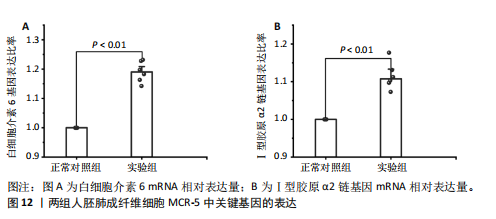
因导入STRING数据库,利用STRING数据库构建了蛋白质相互关系的蛋白质与蛋白质相互作用网络进一步识别25个基因中的核心基因,设定了合适的参数以剔除孤立节点,确保了网络的连通性。使用Cytoscape软件对网络进行了可视化处理,清晰地展示了25个节点和55条边构成的复杂网络结构(图6)。为了深入探究网络中的关键节点,进行了拓扑学分析,运用“Degree”“MCC”“EPC”和“MNC”这4种算法来评估节点的重要性。综合比较4种算法的排名结果,筛选出了节点重要性排名前5位的基因并取其交集,最终得到了3个高连接度的基因:COL1A1、COL1A2和IL6(图7)。 2.7 机器算法的选择 绘制LASSO和SVM算法的受试者工作特征曲线(图8A,B),通过对比2种算法的曲线下面积值以确定算法的准确性,最终采用LASSO和SVM两种算法用于后续分析。结果显示,LASSO算法共确定了6个候选基因,包括分别是COL3A1、COL1A2、CEBPD、EPHA3、PLA2G1B、IL6(图8C,D);SVM算法确认获得23个候选基因,包括 COL1A2、COL3A1、DSC3、ATP5MC1、CEBPD、AGER、CFHRTKN2、PLA2G1B、COX5B、PROM1、EIF1AY、RRAS、COL1A1、EPHA3、IL6、ARMC3、CP、POSTN、MMP1、TMEM100、STX11、LUC7L3(图8E,F)。将上述2种算法所得到的候选基因取交集,同时再和蛋白质与蛋白质相互作用网络中的高连接度基因取交集,共得到2个与自噬相关的肺纤维化基因(IL6和COL1A2),这2个基因被认为是参与肺纤维化进展中与自噬相关的关键基因(图8G)。 2.8 诊断基因模型的构建与验证 为了明确2个差异基因是否具有预测诊断肺纤维化的意义,基于“rms”包构建肺纤维化的诊断列线图(图9A),使用校准曲线评估该模型的预测能力,校准曲线显示真实患病风险与预测患病风险之间的差异非常小,说明列线图模型预测肺纤维化的发病较为准确(图9B)。采用外部数据集GSE21369数据集对IL6和COL1A2进行受试者工作特征分析,结果显示,在GSE21369数据集中IL6和COL1A2与空白组相比表达显著升高,2个基因中IL6和COL1A2基因的曲线下面积AUC值分别为0.790,0.855(图9C),均大于0.75,说明IL6和COL1A2这2个基因效果较为可靠,表明IL6和COL1A2可作为肺纤维化进展的自噬潜在诊断生物标志物。 2.9 GSEA富集分析 为了深入理解差异基因在不同表达水平下对各类信号通路的调控影响,研究进行了GSEA富集分析,结果显示,当COL1A2处于高表达状态时,细胞周期通路和剪接体通路呈现明显的上调趋势,而MAPK(丝裂原活化蛋白激酶)信号通路以及细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用通路则显著下调;另一方面,IL6在高表达组中则表现出对MAPK信号通路、JAK-STAT(酪氨酸激酶-信号转导及转录激活因子)信号通路以及细胞因子与细胞因子受体相互作用的显"
| [1] ZHU JQ, TIAN YY, CHAN KL, et al. Modified Qing-Zao-Jiu-Fei decoction attenuated pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in rats via modulating Nrf2/NF-κB and MAPKs pathways. Chin Med. 2024;19(1):10. [2] ZUO WL, ROSTAMI MR, LEBLANC M, et al. Dysregulation of club cell biology in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0237529. [3] DENG Z, FEAR MW, SUK CHOI Y, et al. The extracellular matrix and mechanotransduction in pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;126:105802. [4] RAGHU G, REMY-JARDIN M, RICHELDI L, et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(9):e18-e47. [5] MAHER TM, BENDSTRUP E, DRON L, et al. Global incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2021;22(1):197. [6] ZENG Q, JIANG D. Global trends of interstitial lung diseases from 1990 to 2019: an age-period-cohort study based on the Global Burden of Disease study 2019, and projections until 2030. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1141372. [7] SPAGNOLO P, BALESTRO E, ALIBERTI S, et al. Pulmonary fibrosis secondary to COVID-19: a call to arms. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(8):750-752. [8] COTTIN V, SCHMIDT A, CATELLA L, et al. Burden of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Progression: A 5-Year Longitudinal Follow-Up Study. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0166462. [9] PODOLANCZUK AJ, THOMSON CC, REMY-JARDIN M, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: state of the art for 2023. Eur Respir J. 2023;61(4):2200957. [10] JESSEN H, HOYER N, PRIOR TS, et al. Longitudinal serological assessment of type VI collagen turnover is related to progression in a real-world cohort of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm Med. 2021;21(1):382. [11] KINOSHITA T, GOTO T. Molecular Mechanisms of Pulmonary Fibrogenesis and Its Progression to Lung Cancer: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6):1461. [12] SCHÄFER SC, FUNKE-CHAMBOUR M, BEREZOWSKA S. [Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-epidemiology, causes, and clinical course]. Pathologe. 2020;41(1):46-51. [13] GUENTHER A, KRAUSS E, TELLO S, et al. The European IPF registry (eurIPFreg): baseline characteristics and survival of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2018;19(1):141. [14] JEGAL Y, PARK JS, KIM SY, et al. Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Management, and Outcomes of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Korea: Analysis of the Korea IPF Cohort (KICO) Registry. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2022;85(2):185-194. [15] Lu JL, Yu CX, Song LJ. Programmed cell death in hepatic fibrosis: current and perspectives. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):449. [16] WEN JH, LI DY, LIANG S, et al. Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization, chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:946832. [17] ZHAN L, LI J, WEI B. Autophagy in endometriosis: Friend or foe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(1):60-63. [18] WANG K, ZHANG T, LEI Y, et al. Identification of ANXA2 (annexin A2) as a specific bleomycin target to induce pulmonary fibrosis by impeding TFEB-mediated autophagic flux. Autophagy. 2018;14(2): 269-282. [19] ZMIJEWSKI JW, THANNICKAL VJ. Autophagy in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Predisposition of the Aging Lung to Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023;68(1):3-4. [20] ARAYA J, KOJIMA J, TAKASAKA N, et al. Insufficient autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013;304(1):L56-69. [21] CABRERA S, MACIEL M, HERRERA I, et al. Essential role for the ATG4B protease and autophagy in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Autophagy. 2015;11(4):670-684. [22] SHERAFATIAN M. Tree-based machine learning algorithms identified minimal set of miRNA biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis and molecular subtyping. Gene. 2018;677:111-118. [23] HU S, GU S, WANG S, et al. Robust Prediction of Prognosis and Immunotherapy Response for Bladder Cancer through Machine Learning Algorithm. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(6):1073. [24] 王远敏,罗敏,苏穆,等.山柰酚对博来霉素诱导小鼠肺纤维化、MRC-5细胞胶原蛋白生成的影响[J]. 中成药,2023, 45(10):3425-3428. [25] HERBERTS MB, TEAGUE TT, THAO V, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the United States: time to diagnosis and treatment. BMC Pulm Med. 2023;23(1):281. [26] MIGNEAULT F, HÉBERT MJ. Autophagy, tissue repair, and fibrosis: a delicate balance. Matrix Biol. 2021;100-101:182-196. [27] MARGARITOPOULOS GA, TSITOURA E, TZANAKIS N, et al. Self-eating: friend or foe? The emerging role of autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:420497. [28] MI S, LI Z, YANG HZ, et al. Blocking IL-17A promotes the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via TGF-beta1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Immunol. 2011;187(6):3003-3014. [29] 李鹏,牛璐,赵国静,等.基于自噬探究补肺活血胶囊对博来霉素诱发小鼠肺纤维化的抑制作用[J].中成药,2024,46(4): 1337-1342. [30] TANAKA T, NARAZAKI M, KISHIMOTO T. Immunotherapeutic implications of IL-6 blockade for cytokine storm. Immunotherapy. 2016;8:959-970. [31] PAN X, CHEN X, REN Q, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics identifies Col1a1 and Col1a2 as hub genes in obesity-induced cardiac fibrosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;618:30-37. [32] 王信光,薄存香,潘志峰.IL-6家族细胞因子在肺纤维化中的作用[J].中国工业医学杂志,2024,37(3):263-266. [33] PAPIRIS SA, TOMOS IP, KARAKATSANI A, et al. High levels of IL-6 and IL-8 characterize early-on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis acute exacerbations. Cytokine. 2018;102:168-172. [34] WANG Y, SANG X, SHAO R, et al. Xuanfei Baidu Decoction protects against macrophages induced inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022; 283:114701. [35] PULIVENDALA G, BALE S, GODUGU C. Honokiol: A polyphenol neolignan ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad signaling, matrix proteins and IL-6/CD44/STAT3 axis both in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;391: 114913. [36] 陈乾,付琦,王天明,等.胃癌中COL1A2表达及其与免疫细胞浸润关系的研究[J].医学理论与实践, 2023,36(12):1997-2000. [37] 姚鸿飞.血清尿酸可通过抑制单核-巨噬细胞COL1A2和ITGA5表达减缓肺纤维化的形成[D].百色:右江民族医学院,2024. [38] SONG C, LIU X, TAN W, et al. Fluorofenidone attenuates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting the IL-11/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Shock. 2022;58(2):137-146. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [3] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [4] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [5] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [6] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [7] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [9] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [10] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [11] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [12] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [13] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [14] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [15] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||