Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5563-5571.doi: 10.12307/2025.751
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory mechanism of electroacupuncture on hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis in oligospermic rats
Zhao Zhenning1, 2, 3, Li Kaiying1, 2, 3, Yang Nan1, 2, 3, Sun Wenjing1, 2, 3, Wei Xiaoge1, 2, 3, Mu Jing1, Ma Huisheng1, 2, 3
- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Modernization of Traditional Medicine for Ethic Minorities in Ningxia, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 3Ningxia Key Laboratory of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of High-Incidence Diseases, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-06-29Accepted:2024-08-29Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-25 -
Contact:Ma Huisheng, PhD, Professor, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Modernization of Traditional Medicine for Ethic Minorities in Ningxia, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; Ningxia Key Laboratory of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of High-Incidence Diseases, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China Co-corresponding author: Mu Jing, PhD, Associate professor, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhao Zhenning, Master’s candidate, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Modernization of Traditional Medicine for Ethic Minorities in Ningxia, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; Ningxia Key Laboratory of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of High-Incidence Diseases, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Key R&D project of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2021BEG02041 (to MHS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Zhenning, , , Li Kaiying, , , Yang Nan, , , Sun Wenjing, , , Wei Xiaoge, , , Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng, , . Regulatory mechanism of electroacupuncture on hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis in oligospermic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5563-5571.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
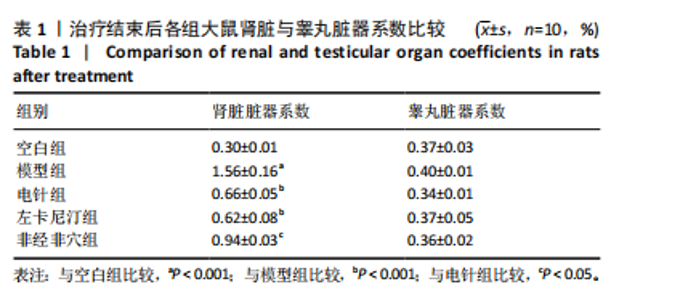
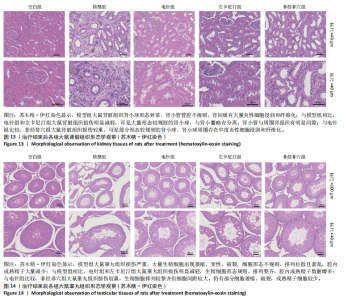
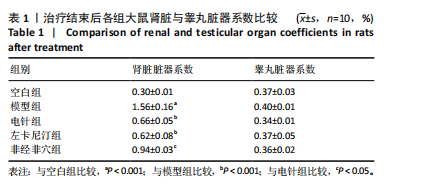
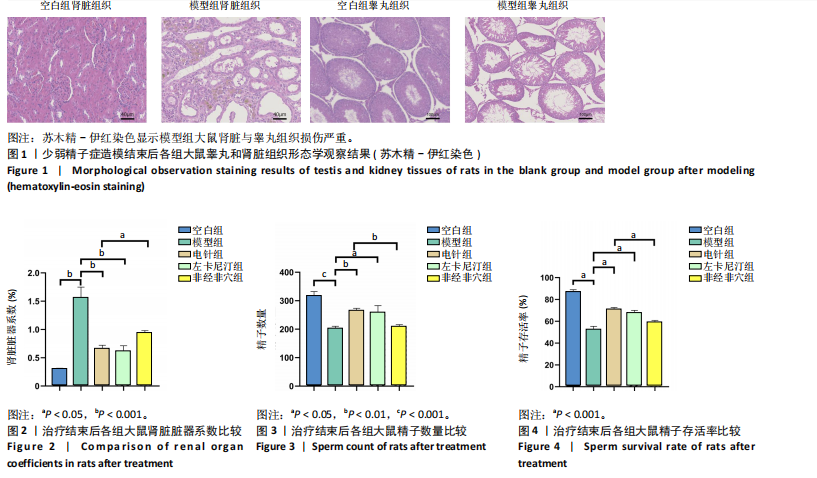
2.1 造模后大鼠一般状态观察 造模结束后,非经非穴组与模型组大鼠精神萎靡,反应迟钝,毛色泛黄,饮食量少,尿量多,大便清稀不成型;电针组、左卡尼汀组大鼠较模型组精神状态好转,反应较灵敏,毛色泛黄但较光滑,饮食量恢复,尿量较模型组少且无明显异味,大便成型。 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,空白组大鼠生精小管管腔呈空腔状态,排列清晰质密,精子细胞完整且数量较多,呈现正常睾丸组织形态;与空白组比较,模型组大鼠睾丸组织生精小管管腔较小,排列松散且不规则,生精细胞结构异常,排列紊乱,出现部分坏死,见图1。苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,空白组大鼠肾脏组织肾小球形态规则,肾小管排列整齐,未见明显病理改变;模型组大鼠肾脏组织肾小球形态异常,肾小管管腔不规则,肾间质有大量炎性细胞浸润和纤维化,见图1。 2.2 实验动物数量分析 除去验证造模成功的6只大鼠,剩余50只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.3 治疗结束后各组大鼠脏器系数比较 见表1。"
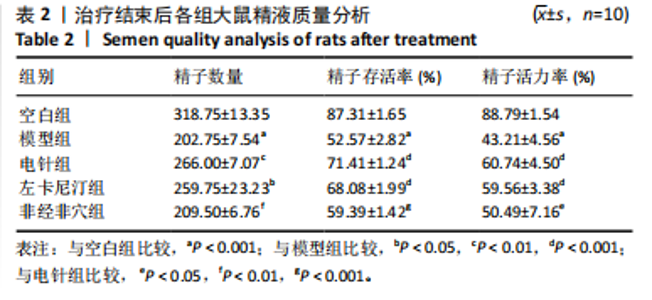
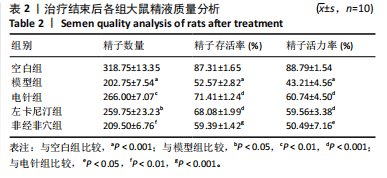
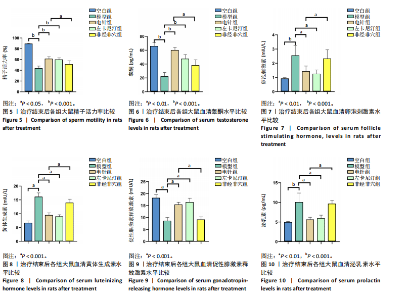
0.001),电针组、左卡尼汀组大鼠精子数量均高于模型组(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),非经非穴组大鼠精子数量低于电针组(P < 0.01),电针组大鼠精子数量与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图3。 2.4.2 精子存活率 模型组大鼠精子存活率低于空白组(P < 0.001),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠精子存活率均高于模型组(P均< 0.001),非经非穴组大鼠精子存活率低于电针组(P < 0.001),电针组大鼠精子存活率与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图4。 2.4.3 精子活力率 模型组大鼠精子活力率低于空白组(P < 0.001),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠精子活力率均高于模型组(P均< 0.001),非经非穴组大鼠精子活力率低于电针组(P < 0.05),电针组大鼠精子活力率与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图5。 2.5 治疗结束后大鼠血清性激素水平比较 见表3。"
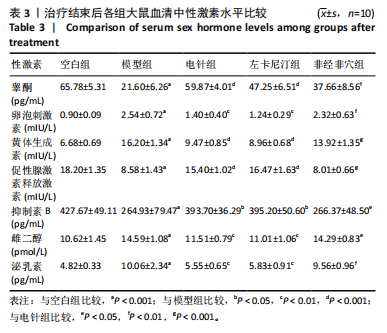
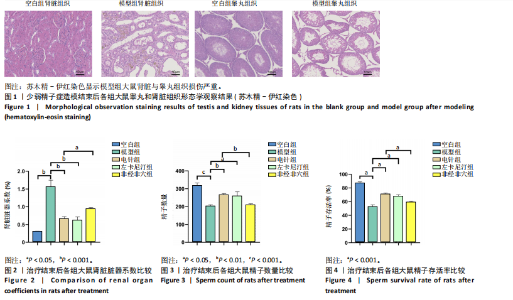
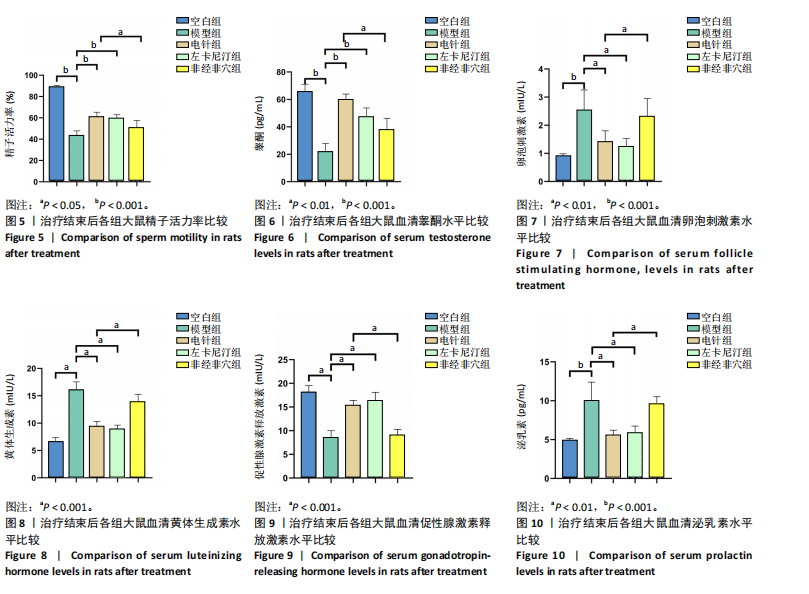
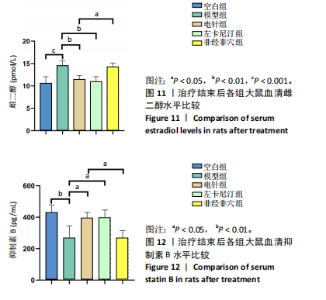
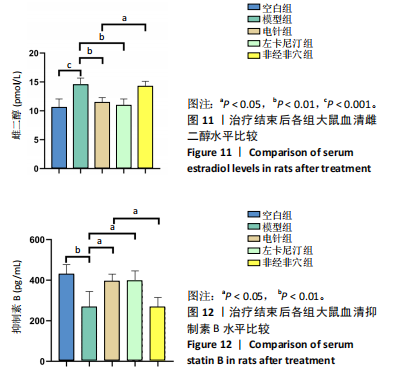
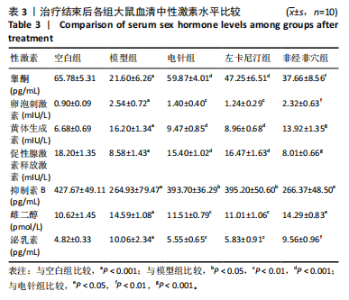
2.5.1 血清睾酮水平 模型组大鼠血清睾酮水平低于空白组(P < 0.001),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠血清睾酮水平均高于模型组(P均< 0.001),非经非穴组大鼠血清睾酮水平低于电针组(P < 0.01),电针组大鼠血清睾酮水平与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图6。 2.5.2 血清卵泡刺激素水平 模型组大鼠血清卵泡刺激素水平高于空白组(P < 0.001),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠血清卵泡刺激素水平均低于模型组(P均< 0.01),非经非穴组大鼠血清卵泡刺激素水平高于电针组(P < 0.01),电针组大鼠血清卵泡刺激素水平与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图7。 2.5.3 血清黄体生成素水平 模型组大鼠血清黄体生成素水平高于空白组(P < 0.001),与模型组对比,电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠血清黄体生成素水平均低于模型组(P均< 0.001),非经非穴组大鼠血清黄体生成素水平高于电针组(P < 0.001),电针组大鼠血清黄体生成素水平与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图8。 2.5.4 血清促性腺激素释放激素水平 模型组大鼠血清促性腺激素释放激素水平低于空白组(P < 0.001),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠血清促性腺激素释放激素水平均高于模型组(P < 0.001),非经非穴组大鼠血清促性腺激素释放激素水平低于电针组(P < 0.001),电针组大鼠血清促性腺激素释放激素水平与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图9。 2.5.5 血清泌乳素水平 模型组大鼠血清泌乳素水平高于空白组(P < 0.001),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠血清泌乳素水平均低于模型组(P均< 0.01),非经非穴组大鼠血清泌乳素水平高于电针组(P < 0.01),电针组大鼠血清泌乳素水平与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图10。 2.5.6 血清雌二醇水平 模型组大鼠血清雌二醇水平高于空白组(P < 0.001),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠血清雌二醇水平均低于模型组(P均< 0.01),非经非穴组大鼠血清雌二醇水平高于电针组(P < 0.05),电针组大鼠血清雌二醇水平与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图11。 2.5.7 血清抑制素B水平 模型组大鼠血清抑制素B水平低于空白组(P < 0.01),电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠血清抑制素B水平均高于模型组(P均< 0.05),非经非穴组大鼠血清抑制素B水平低于电针组(P < 0.05),电针组鼠与左卡尼汀组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图12。 2.6 治疗结束后大鼠肾脏组织形态观察结果 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,空白组大鼠肾脏组织肾小球形态规则,肾小管排列整齐,未见明显病理改变;模型组大鼠肾脏组织肾小球形态异常,肾小管管腔不规则,肾间质有大量炎性细胞浸润和纤维化;与模型组相比,电针组和左卡尼汀组大鼠肾脏组织损伤明显减轻,可见大量形态较规则的肾小球,与肾小囊略有分离,肾小管与周围肾组织有明显间隙;与电针组比较,非经非穴组大鼠肾脏组织损伤较重,可见部分形态较规则的肾小球,肾小球周围存在中度炎性细胞浸润和纤维化,见图13。 2.7 治疗结束后大鼠睾丸组织形态学观察结果 见图14。 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,空白组大鼠睾丸组织结构完整,形态正常,生精细胞和生精小管排列规则,腔"
| [1] 申玉行,陈广辉,王广建,等.基于“肾藏精”理论运用补肾填精法治疗少弱精子症的研究进展[J].中国性科学,2020,29(4):118-121. [2] 孙自学,陈央娣,陈建设,等.益肾通络方治疗肾虚络阻型少弱精子症不育疗效观察[J].中华中医药学刊,2024,42(8):1-6. [3] SHARMA A, JAYASENA CN, DHILLO WS. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis: Pathophysiology of Hypogonadism. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2022;51(1):29-45. [4] YANG Y, ZUO Z, YANG Z, et al. Nickel chloride induces spermatogenesis disorder by testicular damage and hypothalamic-pituitary-testis axis disruption in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;225:112718. [5] 黄念文,李海松,王彬,等.基于“肾主生殖”理论探讨少弱精子症的病机及龟鹿育麟汤组方思路[J].天津中医药大学学报,2024,43(3):285-288. [6] 李威,叶佰盛,黄振,等.从“天癸竭,地道不通”谈绝经后骨质疏松症研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2024,44(5):623-626. [7] 朱善意,高越颖,陈爽,等.颐和春口服液对肾阳虚大鼠睾丸功能的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2010,21(2):133-136. [8] 柳强龙,李玉来,杨月,等.针药联合治疗少弱精症[J].亚太传统医药,2022, 18(8):136-139. [9] 马亮.基于“肾藏精”理论针刺治疗肾虚精亏型少弱精症的临床研究[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2023. [10] ADACHI Y, SASAGAWA I, TATENO T, et al. Influence of adenine-induced chronic renal failure on testicular function in the rat. Andrologia. 1998;30(2):115-118. [11] 罗芳芳,林木南,黄冬娥,等.电针疏密波、电针断续波、电针连续波在瘀血阻滞型膝骨关节炎中的应用对比[J].中国医药导报,2022,19(15):136-139. [12] 陈赟,韩紫阳,孙志兴,等.基于全国名老中医徐福松教授“内肾外肾”理论浅析男性生殖 [J].中华男科学杂志,2024,30(2):163-166. [13] 马东岳,王安民,杨九天,等.基于“脑-心-肾-精室”轴理论探讨早泄的生物学基础[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(10):203-209. [14] 吴霞,程华初,谭金曲,等.基于频数统计方法的“中极穴”主治病症的古代文献研究[J].中国医药导报,2021,18(13):104-107,111. [15] 罗诗雨,徐福.《针灸大成》关元穴应用规律探析[J].浙江中医杂志,2023, 58(1):41-42. [16] MBIYDZENYUY NE, QULU LA. Stress, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, and aggression. Metab Brain Dis. 2024;39(8): 1613-1636. [17] 马晓杰,杨大鹏,陈少宇,等.性激素受体在双峰驼正常睾丸及隐睾的分布[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2024,39(2):27-35. [18] 吕银娟,龚健,萧闵.下丘脑Kiss1系统在产前应激诱导男性后代生殖功能异常中的潜在作用[J].中国现代医学杂志,2024,34(10):54-59. [19] 马琳,李学智,姚太万,等.不同针灸疗法对老年雄性大鼠下丘脑-睾丸中生殖激素调控系统相关基因表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2019,44(3):200-204,219. [20] GROSSMANN M, WITTERT GA. Dysregulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis due to Energy Deficit. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(12): e4861-e4871. [21] SMITH BK, WARD M. The Role of Testosterone Therapy in Men’s Health. Nurs Clin North Am. 2023;58(4):525-539. [22] ODUWOLE OO, HUHTANIEMI IT, MISRAHI M. The Roles of Luteinizing Hormone, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone and Testosterone in Spermatogenesis and Folliculogenesis Revisited. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(23):12735. [23] 袁茜,徐晓英,董云华.血清生物标记物在非梗阻性和梗阻性无精子症鉴别诊断中的应用[J].临床医学进展,2023,13(6):10369-10375. [24] 曾勇,宋明哲,赵明,等.性激素负反馈作用在男性不育诊疗中的应用[J].生殖医学杂志,2017,26(8):743-748. [25] WANG CN, SANG MM, GONG SN, et al. Two resveratrol analogs, pinosylvin and 4,4’-dihydroxystilbene, improve oligoasthenospermia in a mouse model by attenuating oxidative stress via the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Bioorg Chem. 2020; 104:104295. [26] GÖKALP ÖZKORKMAZ E, ÖZDEMIR BAŞARAN S, AFŞIN M, et al. Comparison of testosterone, FSH, LH and E2 hormone levels in infertility suspected males with COVID-19 infection. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(43):e35256. [27] JIAO W, SUN J, ZHANG X, et al. Improvement of Qilin pills on male reproductive function in tripterygium glycoside-induced oligoasthenospermia in rats. Andrologia. 2021;53(4):e13923. [28] SPAGGIARI G, COSTANTINO F, GRANATA ARM, et al. Prolactin and spermatogenesis: new lights on the interplay between prolactin and sperm parameters. Endocrine. 2023;81(2):330-339. [29] LIU Y, WANG G, ZHANG F, et al. Correlation between serum levels of reproductive hormones and testicular spermatogenic function in men with azoospermia. Andrologia. 2022;54(10):e14546. [30] TERASAWA E. Neuroestradiol in regulation of GnRH release. Horm Behav. 2018; 104:138-145. [31] RUSSELL N, GROSSMANN M. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Estradiol as a male hormone. Eur J Endocrinol. 2019;181(1):R23-R43. [32] LEAVY M, TROTTMANN M, LIEDL B, et al. Effects of Elevated β-Estradiol Levels on the Functional Morphology of the Testis - New Insights. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39931. [33] ANDREONE L, AMBAO V, PELLIZZARI EH, et al. Role of FSH glycan structure in the regulation of Sertoli cell inhibin production. Reproduction. 2017;154(5):711-721. [34] NEGRI F, BOERI L, CILIO S, et al. The Importance of Discordant Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Inhibin B Levels in Primary Infertile Men: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Study. World J Mens Health. 2024.doi: 10.5534/wjmh.230298. [35] LIU L, HUANG W, LUO K, et al. Relationship between semen parameters, serum InhB, and INSL-3 levels, and the degree of varicocele. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024; 79:100339. [36] LI J, HU T, WANG Y, et al. Development a nomogram to predict fertilisation rate of infertile males with borderline semen by using semen parameters combined with AMH and INHB. Andrologia. 2021;53(9):e14182. [37] YANG Q, SU S, LUO N, CAO G. Adenine-induced animal model of chronic kidney disease: current applications and future perspectives. Ren Fail. 2024;46(1): 2336128. [38] BARATI E, NIKZAD H, KARIMIAN M. Oxidative stress and male infertility: current knowledge of pathophysiology and role of antioxidant therapy in disease management. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(1):93-113. [39] HASSANIN HM, KAMAL AA, ISMAIL OI. Resveratrol ameliorates atrazine-induced caspase-dependent apoptosis and fibrosis in the testis of adult albino rats. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):17743. [40] ADACHI Y, SASAGAWA I, NAKADA T. Reproductive insufficiency in the male rat with adenine-induced chronic renal failure. Urol Int. 1993;51(4):228-230. [41] MATEUS FG, MOREIRA S, MARTINS AD, et al. L-Carnitine and Male Fertility: Is Supplementation Beneficial? J Clin Med. 2023;12(18):5796. [42] MA L, SUN Y. COMPARISON OF L-CARNITINE VS. Coq10 and Vitamin E for idiopathic male infertility: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(13):4698-4704. |
| [1] | Wang Ziheng, Wu Shuang. Oxidative stress-related genes and molecular mechanisms after spinal cord injury: data analysis and verification based on GEO database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6893-6904. |
| [2] | Wang Wanchun, , Yi Jun, Yan Zhangren, Yang Yue, Dong Degang, Li Yumei. 717 Jiedu Decoction remodels homeostasis of extracellular matrix and promotes repair of local injured tissues in rats after Agkistrodon halys bite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6457-6465. |
| [3] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| [4] | Xu Zhi, Chen Yundong, Sun Yujie, Gong Xiaonan, Li Yuwan. Data of spinal osteosarcoma patients in United States based on SEER database: construction and validation of a prediction model for treatment outcomes and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6583-6590. |
| [5] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei. Causal association between metabolites and sarcopenia: a big data analysis of genome-wide association studies in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6369-6380. |
| [6] | Tao Chenyue, Chen Shuai, Wang Liping, Meng Defang, Zhou Dongjie, Zhou Luojing. Expression of Rab27A in ovarian tissue of polycystic ovary syndrome model mice treated with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5289-5295. |
| [7] | Yang Jun, Yin Peng, Zheng Zhonghua. Mechanism of stachydrine-induced autophagy in improving atherosclerosis in high-fat-fed mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5140-5147. |
| [8] | Deng Yiran, Wang Xianliang, Li Dandan. Meta-analysis of exercise intervention on cardiopulmonary function in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5203-5211. |
| [9] | Wu Diyou, Huang Jiajun, Tao Guangyi, Zhao Yu, Huang Junqing, Yang Bin, Xue Yun. Pueraria lobata decoction intervenes in neuroinflammatory response and apoptosis in rats with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4249-4257. |
| [10] | Wang Shijie, Wen Dengtai, Sun Guoqi, Wang Jingfeng, Gao Yinghui. The role of Timeless/Period gene mediated multiple pathways in circadian rhythm [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4305-4315. |
| [11] | Zhang Shuo, Cui Yinglin, Zhou Panpan, Li Yile, Wang Lei, Zou Qianqian. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress-autophagy in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4325-4332. |
| [12] | Shi Peili, Lin Sen, Zhao Wenteng, Peng Yali, Hu Yazhe. Effects of pressor stimulation at different times on rat skeletal muscle morphology and tumor necrosis factor alpha and nuclear factor kappaB [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3588-3595. |
| [13] | Xie Yanli, Wei Siang, Zhang Guodong. Effects of treadmill exercise on metabolism and chronic neuroinflammation in type 1 diabetes mice of different sexes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5577-5583. |
| [14] | Ma Hailong, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin, Sun Jun. Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 is involved in the occurrence and development of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head in a rabbit model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5167-5172. |
| [15] | Cai Zhiguo, Du Shasha, Yang Kun, Zhao Na, Liu Qi. Lipopolysaccharides mediate autophagy of mouse insulinoma βtc6 cells in high glucose state [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3127-3132. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||