Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (29): 6369-6380.doi: 10.12307/2025.715
Causal association between metabolites and sarcopenia: a big data analysis of genome-wide association studies in the European population
Chen Jiayong1, Tang Meiling2, Lu Jianqi2, Pang Yan2, Yang Shangbing1, Mao Meiling1, Luo Wenkuan1, Lu Wei1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
Chen Jiayong, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-07-08Accepted:2024-09-24Online:2025-10-18Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:Lu Jianqi, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Tang Meiling, Attending physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Chen Jiayong and Tang Meiling contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Fund), No. 82160887 (to LJQ); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, No. 2021GXNSFBA196018 (to PY); The Second Batch of Scientific Research Special Projects for the Operational Construction of the National Clinical Research Base of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. JDZX2015146 (to LJQ); National TCM Inheritance Innovation Center Project, No. 2023019-10 (to LJQ); Guangxi Qihuang Scholars Cultivation Project, No. 2024005-06-02 (to LJQ); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (General Program), No. 2021GXNSFAA220111 (to LJQ); Guangxi Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Self-financed Research Project, No. GXZYA20230065 (to PY); Guangxi High-level Key Discipline of Traditional Chinese Medicine - Cardiology of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2024016-02-02 (to LJQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei. Causal association between metabolites and sarcopenia: a big data analysis of genome-wide association studies in the European population[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6369-6380.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
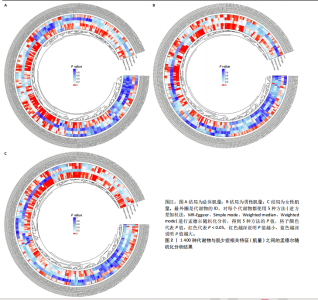
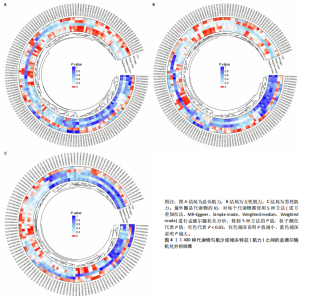
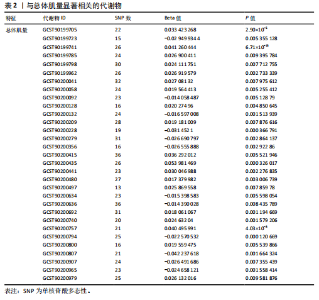
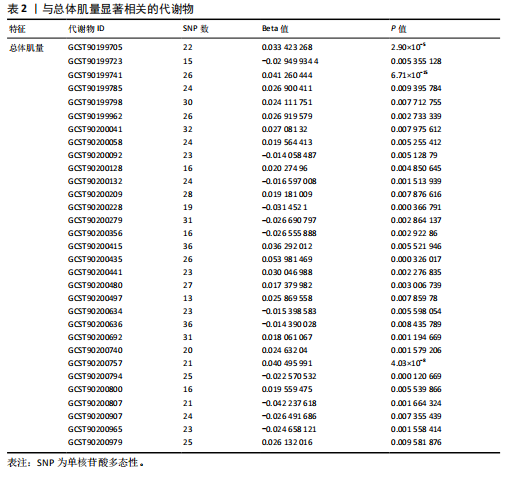
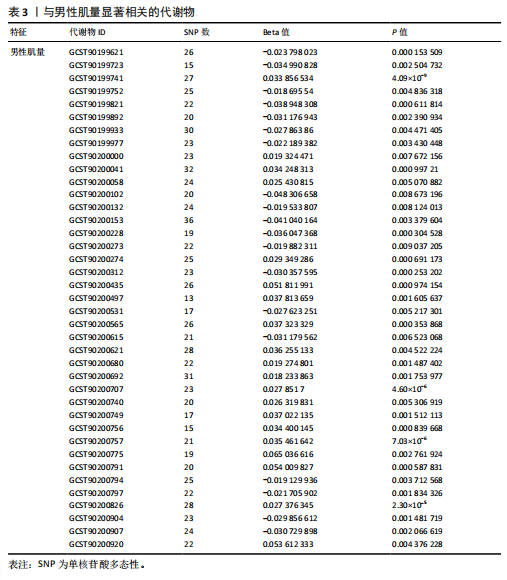
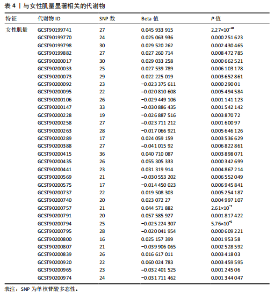
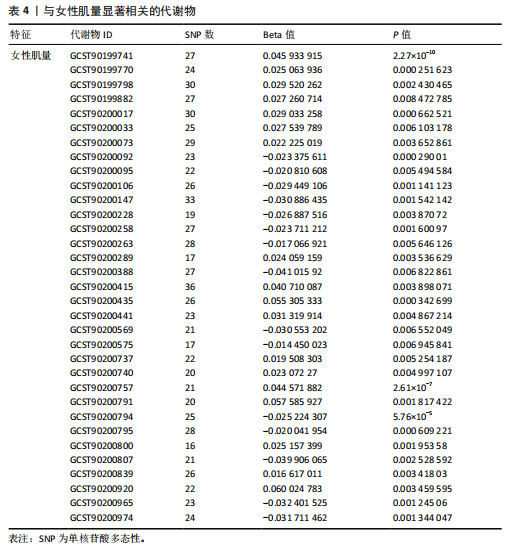
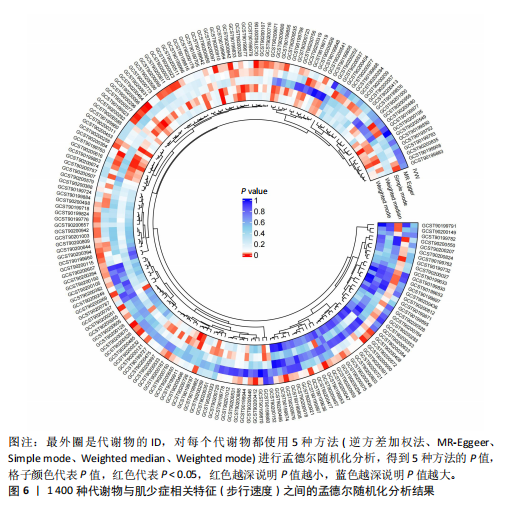
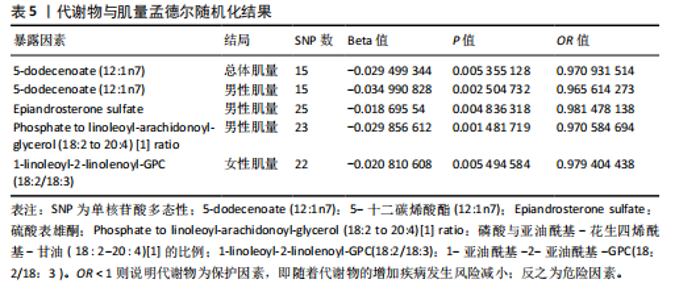
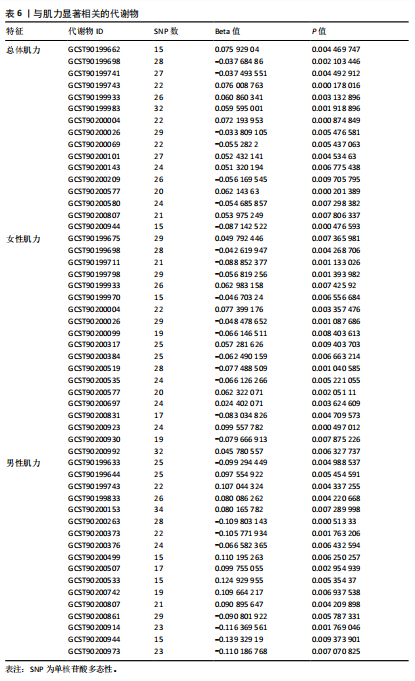
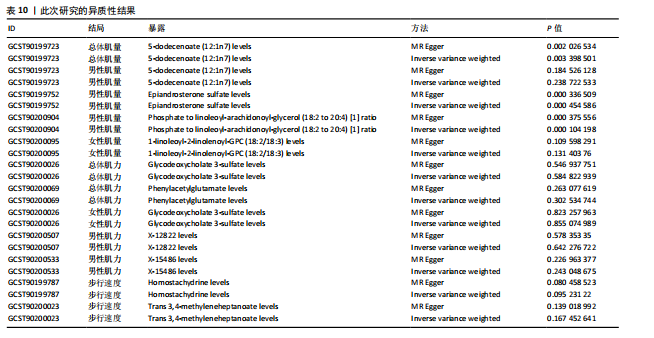
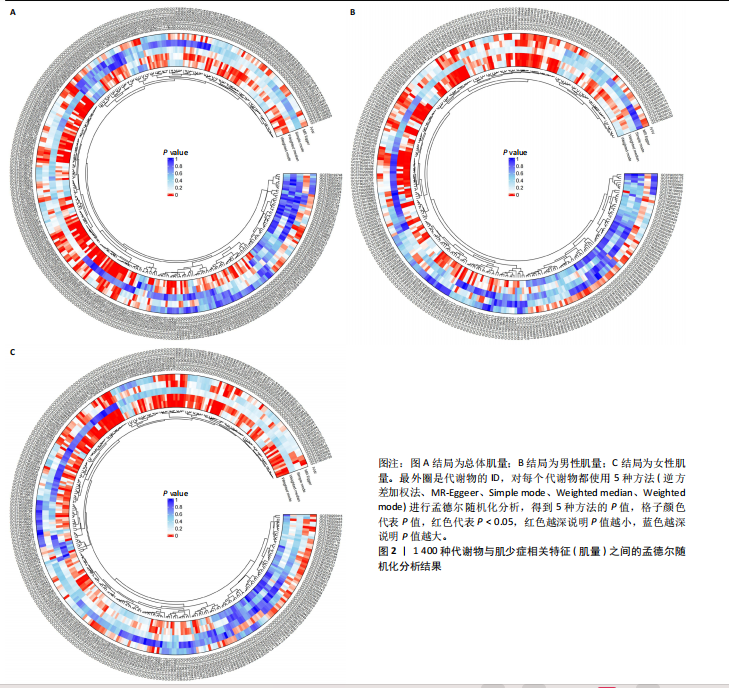
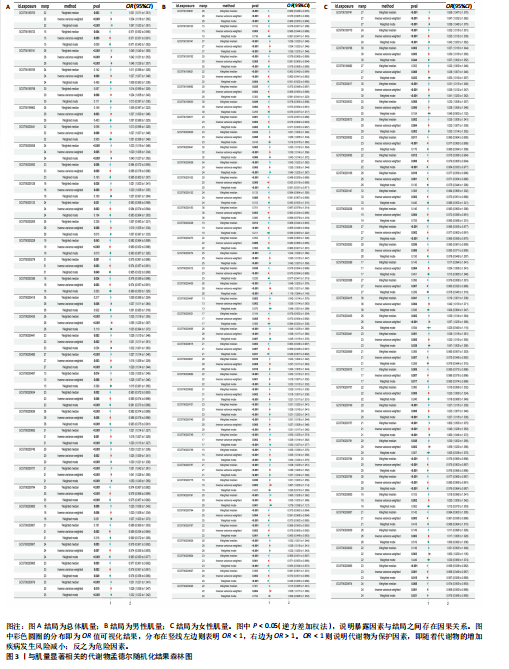
2.1 工具变量 根据研究工具变量的筛选标准对1 400种循环代谢产物进行筛选,每个代谢物得到的SNP数量从8-88个不等,得到的工具变量F值均大于10,即说明所有获得的SNPs均可进行下一步孟德尔随机化分析。 2.2 两样本孟德尔随机化分析 2.2.1 血液代谢物与肌量的孟德尔随机化分析结果 1 400种代谢物与总体肌量、男性肌量、女性肌量之间的因果关系孟德尔随机化分析结果见图2。采用IVW法对孟德尔随机化分析的结果进行过滤(P < 0.01),筛选出与总体肌量、男性肌量和女性肌量显著相关的代谢物分别有31种、39种和33种,见表2-4。森林图可以直观地评估代谢物与结局的关系,见图3。 具体来说,5-十二碳烯酸酯(12∶1n7)与总体肌量、男性肌量具有因果关系;硫酸表雄酮、磷酸与亚油酰基-花生四烯酰基-甘油(18∶2-20∶4) [1]的比例与男性肌量具有因果关系;1-亚油酰基-2-亚油酰基-GPC(18∶2/18∶3)与女性肌量有因果关系;且随着这些代谢物的增加疾病的发病风险降低。详见表 5。 2.2.2 血液代谢物与肌力的孟德尔随机化分析结果 1 400种代谢物与总体肌力、女性肌力、男性肌力之间的因果关系孟德尔随机化分析结果见图4。采用IVW法对孟德尔随机化分析的结果进行过滤(P < 0.01),筛选出与总体肌力、女性肌力和男性肌力具有显著相关的代谢物分别有16种、19种和"
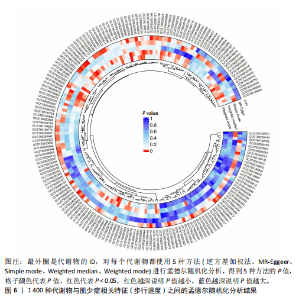
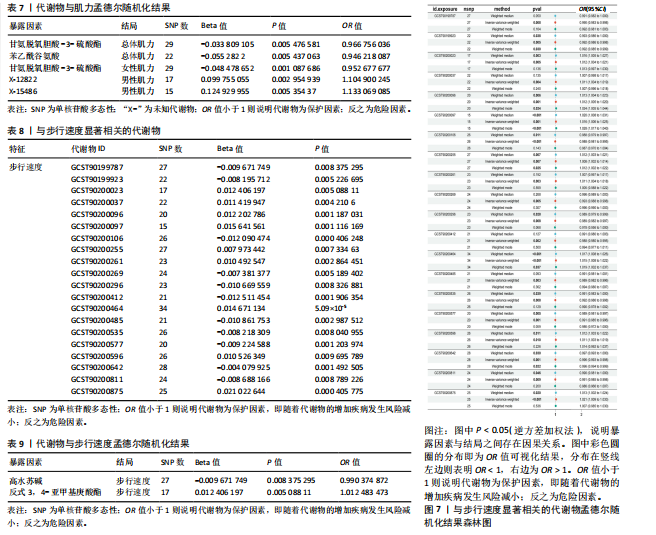
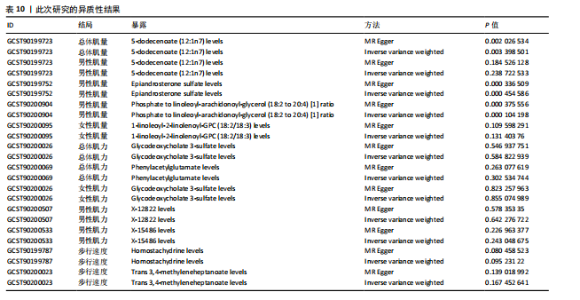
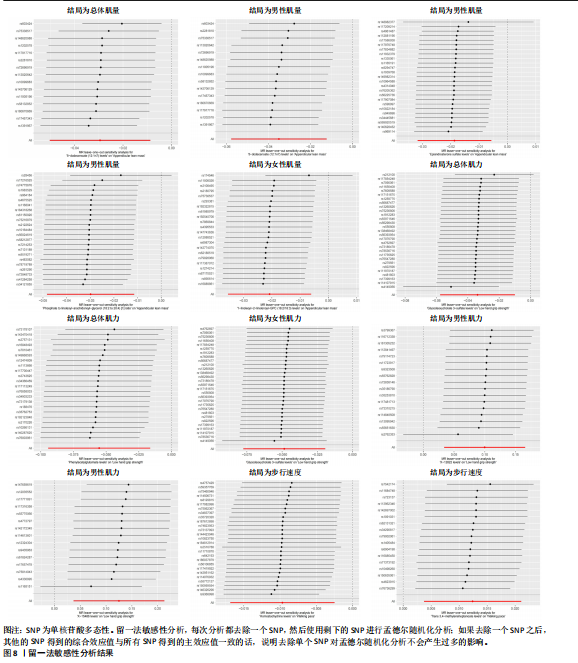
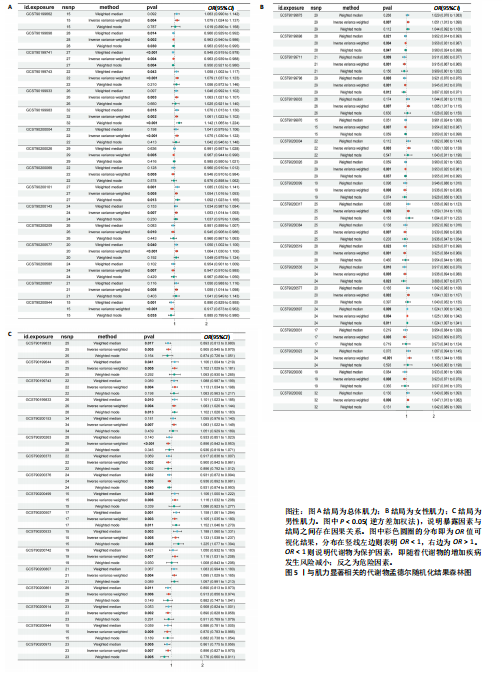
17种,见表6;其可视化结果见图5。具体地,甘氨脱氧胆酸-3-硫酸酯(Glycodeoxycholate 3-sulfate)与总体肌力、女性肌力具有因果关系,苯乙酰谷氨酸(Phenylacetylglutamate)与女性肌力有因果关系,与手握力低程度呈负相关;两种未知代谢物(X-12822和X-15486)与男性肌力低有正相关,即随着代谢物的增加,男性手握力低的程度增加,见表7。 2.2.3 血液代谢物与步行速度的孟德尔随机化分析结果 1 400种代谢物与步行速度之间的因果关系孟德尔随机化分析结果见图6。采用IVW法对孟德尔随机化分析的结果进行过滤(P < 0.01),筛选出与步行速度具有显著相关的代谢物有20种,见表 8;其森林图结果见图7。高水苏碱(Homostachydrine)与步行速度具有因果关系,随着高水苏碱的增加,疾病发病风险降低;相反的,随着反式3,4-亚甲基庚酸酯(Trans 3,4-methyleneheptanoate)的增加,发病风险增加,见表9。 2.3 对孟德尔随机化结果的多效性、异质性及敏感性分析 此文进行了敏感性分析以确保结果的可信性。通过留一法敏感性分析证实去除单个SNP对孟德尔随机化分析不会产生过多影响(图8)。来自不同的分析平台、不同的实验或者不同的人群的工具变量可能存在异质性(P < 0.05),但不影响结果的解读;异质性结果提示此次研究部分结果存在异质性,见表 10,而此次研究的研究对象均为欧洲人群,所以异质性的来源于可能是不同的分"
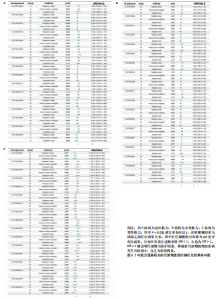
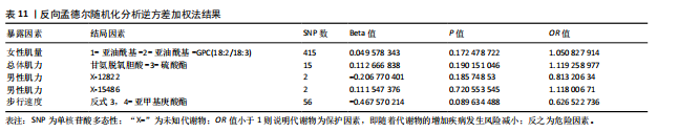
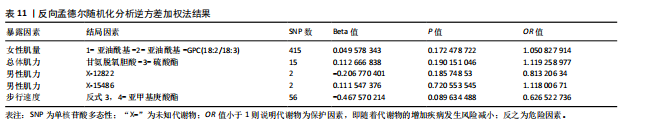
析平台和不同的实验。MR-Egger截距测试结果提示P > 0.05,说明数据结果不存在多效性。MR-PRESSO结果提示男性肌量与5-十二碳烯酸酯(12∶1n7),女性肌量与1-亚油酰基- 2-亚油酰基-GPC(18∶2/18∶3),肌力与甘氨脱氧胆酸-3-硫酸酯、苯乙酰谷氨酸和两种未知代谢物(X-12822、X-15486),以及步行速度与高水苏碱和反式3,4-亚甲基庚酸酯的所有SNP综合异常值P > 0.05,且不存在单个异常值。 2.4 反向孟德尔随机化分析 最后,将肌少症相关特征作为暴露因素,循环代谢产物作为结局,进行反向孟德尔随机化分析评估肌少症相关特征与循环代谢产物之间是否存在因果联系;余分析方法同孟德尔随机化分析。反向孟德尔随机化分析结果提示女性肌量与1-亚油酰基-2-亚油酰基-GPC(18∶2/18∶3),肌力与甘氨脱氧胆酸-3-硫酸酯和两种未知代谢物(X-12822、X-15486),以及步行速度与反式3,4-亚甲基庚酸酯不存在因果关系(P > 0.05),见表 11。"
| [1] SHA T, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Genetic Variants, Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels, and Sarcopenia: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(8):e2331558. [2] PETERMANN-ROCHA F, BALNTZI V, GRAY SR, et al. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):86-99. [3] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAEYENS JP, BAUER JM, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412-423. [4] 江强,于洁,耿子翔,等.两种肌少症小鼠模型的功能表型、肌肉质量及力量特点比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(14):2922-2929. [5] SHIN HE, WON CW, KIM M. Metabolomic profiles to explore biomarkers of severe sarcopenia in older men: A pilot study. Exp Gerontol. 2022;167:111924. [6] TAN Y, LIU X, YANG Y, et al. Metabolomics analysis reveals serum biomarkers in patients with diabetic sarcopenia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1119782. [7] VANDERWEELE TJ, TCHETGEN TCHETGEN EJ, CORNELIS M, et al. Methodological challenges in mendelian randomization. Epidemiology. 2014; 25(3):427-435. [8] BOWDEN J, HOLMES MV. Meta-analysis and Mendelian andomization: A review. Res Synthesis Methods. 2019;10(4):486-496. [9] BIRNEY E. Mendelian randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4):a041302. [10] SEKULA P, DEL GRECO MF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253-3265. [11] SHA T, WANG N, WEI J, et al. Genetically Predicted Levels of Serum Metabolites and Risk of Sarcopenia: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023;15(18):3964. [12] GOLDSBOROUGH E 3RD, OSUJI N, BLAHA MJ. Assessment of Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A 2022 Update. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2022;51(3):483-509. [13] PETERMANN-ROCHA F, HO FK, WELSH P, et al. Physical capability markers used to define sarcopenia and their association with cardiovascular and respiratory outcomes and all-cause mortality: A prospective study from UK Biobank. Maturitas. 2020;138:69-75. [14] CHEN Y, LU T, PETTERSSON-KYMMER U, et al. Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases. Nat Genet. 2023;55(1):44-53. [15] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31. [16] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665. [17] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389. [18] DAMLUJI AA, ALFARAIDHY M, ALHAJRI N, et al. Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation. 2023;147(20):1534-1553. [19] CHEN B, WANG C, LI W. Serum albumin levels and risk of atrial fibrillation: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024;11:1385223. [20] DAI N, DENG Y, WANG B. Association between human blood metabolome and the risk of hypertension. BMC Genom Data. 2023;24(1):79. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [6] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [7] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [8] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [9] | Wang Wanchun, , Yi Jun, Yan Zhangren, Yang Yue, Dong Degang, Li Yumei. 717 Jiedu Decoction remodels homeostasis of extracellular matrix and promotes repair of local injured tissues in rats after Agkistrodon halys bite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6457-6465. |
| [10] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| [11] | Zhang Bochun, Li Wei, Li Guangzheng, Ding Haoqin, Li Gang, Liang Xuezhen, . Association between neuroimaging changes and osteonecrosis: a large sample analysis from UK Biobank and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6574-6582. |
| [12] | Xu Zhi, Chen Yundong, Sun Yujie, Gong Xiaonan, Li Yuwan. Data of spinal osteosarcoma patients in United States based on SEER database: construction and validation of a prediction model for treatment outcomes and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6583-6590. |
| [13] | Luo Weidong, Pu Bin, Gu Peng, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiaohui, Chen Fuhong. Mendelian randomization study on the association between telomere length and 10 common musculoskeletal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 654-660. |
| [14] | Jiang Siqi, Huang Huanhuan, Yu Xinyu, Peng Ying, Zhou Wei, Zhao Qinghua. Meta-analysis of dose-effect of exercise on improving muscle health in community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6295-6304. |
| [15] | Chen Tianxin, , Zhang Zhilong, Zhang Shuai, Gao Yun, Zhu Yuqi, Yang Shengping. Causal relationship between immune cells and bone metabolic diseases: a Mendelian randomization analysis of European populations in international databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6326-6332. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||