Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (30): 4788-4794.doi: 10.12307/2024.630
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of positioning and non-positioning cervical rotatory manipulation on tensile mechanical properties of internal carotid artery with different degrees of atherosclerosis
Zhang Shaoqun, Zheng Chuanjiang, Liu Jiafu, Jiang Shunwan
- Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Fourth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518033, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-05-30Accepted:2023-08-01Online:2024-10-28Published:2023-12-25 -
Contact:Jiang Shunwan, Master, Chief physician, Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Fourth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518033, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Shaoqun, MD, Attending physician, Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Fourth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518033, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Provincial Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Regional Joint Youth Fund Project, No. 2020A1515111191 (to ZSQ); Basic Research Project of Shenzhen Science and Technology Plan, No. JCYJ20210324111613037 (to ZSQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Shaoqun, Zheng Chuanjiang, Liu Jiafu, Jiang Shunwan. Effect of positioning and non-positioning cervical rotatory manipulation on tensile mechanical properties of internal carotid artery with different degrees of atherosclerosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4788-4794.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
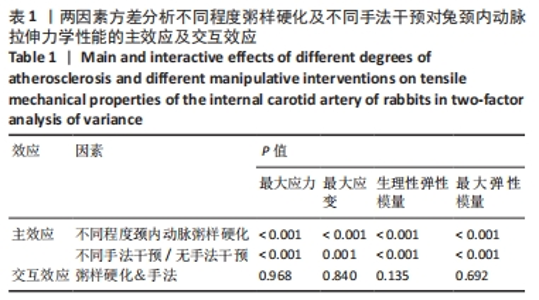
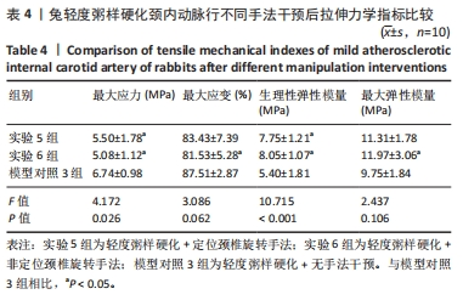
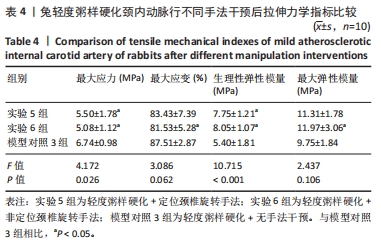
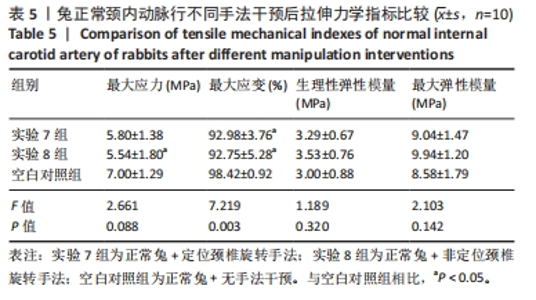
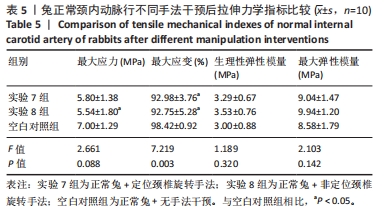
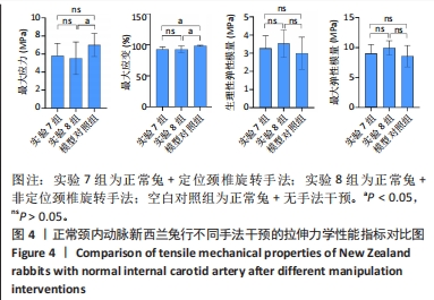
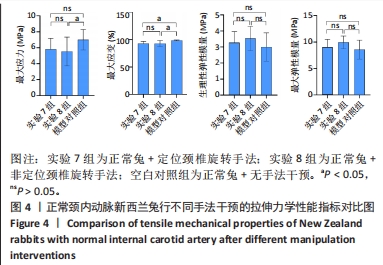
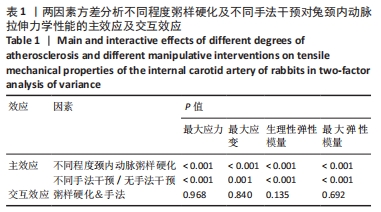
2.1 实验动物数量分析 在整个实验过程中,最终造模成功的重度粥样硬化新西兰兔有3只因中途死亡而脱落,中度粥样硬化新西兰兔有1只因中途死亡而脱落,轻度粥样硬化及正常新西兰兔均无脱落,脱落的新西兰兔没有明显创伤、瘫痪或感染的迹象,考虑为正常死亡。重度粥样硬化新西兰兔随机分为实验1组、实验2组及模型对照1组,每组各9只,其颈内动脉狭窄率分别为(85.87±2.91)%、(86.47±5.86)%和(86.80±3.82)%,且差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);中度粥样硬化新西兰兔随机分为实验3组、实验4组及模型对照2组,样本量分别为10,9,10只,其颈内动脉狭窄率分别为(60.07±4.86)%、(62.79±2.43)%和(59.89±5.84)%,且差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);轻度粥样硬化新西兰兔随机分为实验5组、实验6组及模型对照3组,每组各10只,其颈内动脉狭窄率分别为(41.71±4.54)%、(40.83±3.93)%和(38.13±4.37)%,且差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);正常新西兰兔随机分为实验7组、实验8组及空白对照组,每组各10只。 2.2 两因素方差分析结果 如表1所示,两因素方差分析结果显示,不同程度粥样硬化及不同颈椎旋转手法均对颈内动脉拉伸力学指标(最大应力、最大应变、生理性弹性模量及最大弹性模量)的影响具有主效应(P < 0.01),但二者对颈内动脉拉伸力学指标不具有交互效应。"
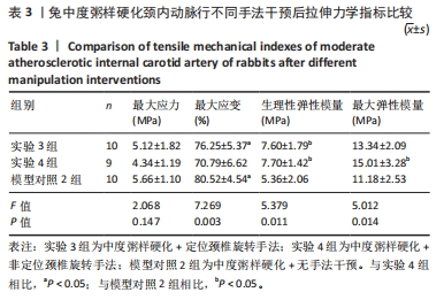
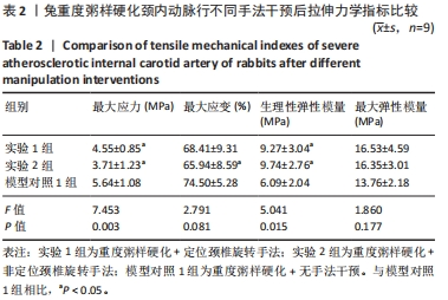
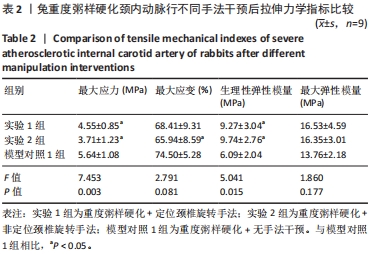
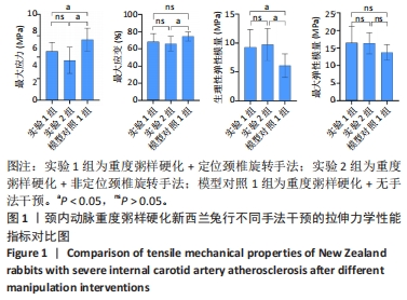
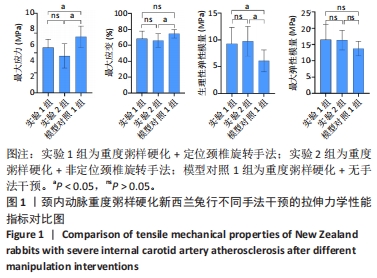
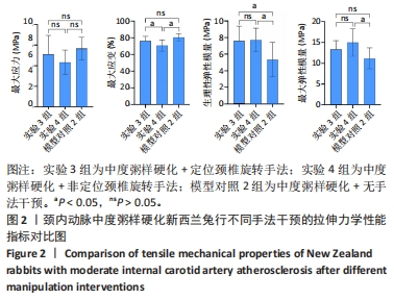
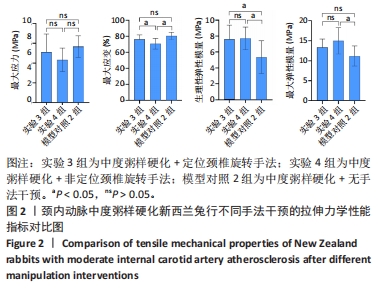
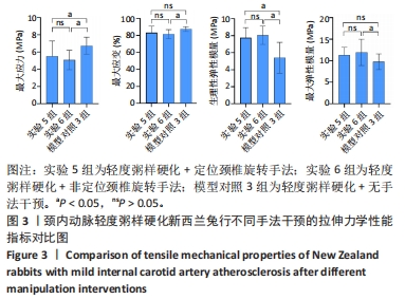
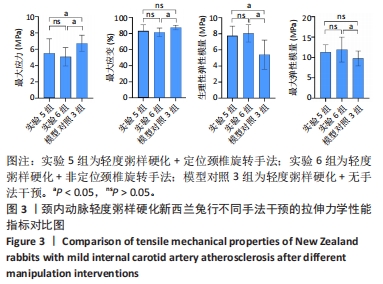
2.3.2 中度粥样硬化颈内动脉行不同手法干预后拉伸力学性能的差异 如表3及图2所示:①3组间的最大应变、生理性弹性模量及最大弹性模量差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②实验4组的最大应变分别小于实验3组及模型对照2组(P < 0.05),实验4组较模型对照组的最大应变下降12.08%,而实验3组和模型对照2组的最大应变无显著性差异(P > 0.05);③实验3组和实验4组的生理性弹性模量均大于模型对照2组(P < 0.05),其中实验3组的生理性弹性模量较模型对照2组升高29.47%,而实验4组升高30.39%;④实验4组的最大弹性模量较模型对照2组升高27.20%(P < 0.05),而实验3组和模型对照2组的最大弹性模量无显著性差异(P > 0.05);⑤除最大应变外,实验3组和实验4组颈内动脉的其余拉伸力学指标均无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。 "

| [1] 黄学成,叶林强,江晓兵,等.不同体位下颈椎旋转手法对颈椎间盘位移和内在应力的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(12): 1470-1475. [2] 钟仲,周红海,徐毅高,等. 颈椎定点旋转手法研究进展[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2021,42(3):419-420+422. [3] HAYNES M. Risk of vertebrobasilar stroke and chiropractic care: results of a population based case control and case-crossover study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36:92. [4] CASSIDY JD, BOYLE E, COTE P, et al. Risk of carotid stroke after chiropractic care: a population based case cross over study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26(4):842-850. [5] DEBUHR NB, TRAGER RJ, TAO C. An Adult Patient With Acute Ischemic Stroke and Carotid Stenosis Presenting to a Chiropractor: A Case Report. Cureus. 2023;15:e37209. [6] CHEN Y, MOFATTEH M, NGUYEN TN, et al. Carotid Artery Dissection and Ischemic Stroke Following Cervical Chiropractic Manipulation: Two Case Reports. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2022;56:303-307. [7] ZHANG S, QI J, ZHANG L, et al. Cervical Rotatory Manipulation Decreases Uniaxial Tensile Properties of Rabbit Atherosclerotic Internal Carotid Artery. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017: 5189356. [8] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导性意见[R]. 2006-09-30. [9] MENG L, LV B, ZHANG S, et al. In vivo optical coherence tomography of experimental thrombosis in a rabbit carotid model. Heart. 2008;94(6): 777-780. [10] 陶丽.彩色多普勒超声和CT血管造影对颈动脉狭窄患者颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的诊断价值[J].中外医学研究,2023,21(4):72-75. [11] 李义凯. 推拿学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2012:97. [12] XIONG J, WANG SM, ZHOU W, et al. Measurement and analysis of ultimate mechanical properties, stress-strain curve fit, and elastic modulus formula of human abdominal aortic aneurysm and nonaneurysmal abdominal aorta. J Vasc Surg. 2008;48(1):189-195. [13] KHANAFER K, DUPREY A, ZAINAL M, et al. Determination of the elastic modulus of ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm at different ranges of pressure using uniaxial tensile testing. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142(3): 682-686. [14] MILNOR WR. Hemodynamics. 2nd. Baltimore: Williams &Wilkins, 1989. [15] KARIMI A, NAVIDBAKHSH M. Measurement of the uniaxial mechanical properties of rat skin using different stress-strain definitions. Skin Res Technol. 2015;21(2):149-157. [16] DUPREY A, KHANAFER K, SCHLICHT M, et al. In vitro characterisation of physiological and maximum elastic modulus of ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms using uniaxial tensile testing. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;39(6):700-707. [17] KWAN TW, WONG SS, HONG Y, et al. Epidemiology of Diabetes and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Among Asian American Adults: Implications, Management, and Future Directions: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2023;148(1):74-94. [18] PIERI K, TRICHIA E, NEVILLE MJ, et al. Polygenic risk in Type III hyperlipidaemia and risk of cardiovascular disease: An epidemiological study in UK Biobank and Oxford Biobank. Int J Cardiol. 2023;373:72-78. [19] XING L, LI R, ZHANG S, et al. High Burden of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Rural Northeast China: A Population-Based Study. Front Neurol. 2021;12:597992. [20] 潘雯, 邢立莹, 张立敏, 等. 无心血管风险因素中老年人群颈动脉粥样硬化及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2021, 29(3):183-186. [21] 丁晓明, 张旖文, 张鑫. 颈动脉粥样硬化性重度狭窄患者血管超声评估参数与缺血性脑卒中的相关性[J]. 心脑血管病防治,2023, 23(3):41-43. [22] 李晓霞, 张丽杨, 林静. 短暂性脑缺血发作患者早期卒中与颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的关系[J]. 山东医药,2015,55(12):43-44. [23] MOHAMMADI T, HOOSHANGINEZHAD Z, MOHAMMADI B, et al. The association of stroke risk factors with the future thickness of carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Neurol Res. 2023;45(9):818-826. [24] 袁钰, 蒋涛, 陈辉. 推拿干预颈动脉粥样硬化动物模型安全性的系统评价和Meta分析[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报,2023,42(4):49-55. [25] 祁冀,张少群,张磊,等. 颈椎旋转手法对兔颈动脉重度粥样硬化斑块稳定性的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(7):2776-2780. [26] 王辉昊,王宽,邓真,等. 定位与非定位颈椎旋转手法应力作用比较:三维有限元分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2019,34(S1):55. [27] LABROPOULOS N, ZARGE J, MANSOUR MA, et al. Compensatory arterial enlargement is a common pathobiologic response in early atherosclerosis. Am J Surg. 1998;176(2):140-143. [28] RASTEGARI K, MOKHTARI-DIZAJI M, HARIRCHIAN MH, et al. Biomechanical changes of the common carotid artery and internal jugular vein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Ultrasonography. 2023; 42(1):100-110. [29] BOESEN ME, SINGH D, MENON BK, et al. A systematic literature review of the effect of carotid atherosclerosis on local vessel stiffness and elasticity. Atherosclerosis. 2015;243(1):211-222. [30] MULVIHILL JJ, CUNNANE EM, MCHUGH SM, et al. Mechanical, biological and structural characterization of in vitro ruptured human carotid plaque tissue. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(11):9027-9035. [31] WALSH MT, CUNNANE EM, MULVIHILL JJ, et al. Uniaxial tensile testing approaches for characterisation of atherosclerotic plaques. J Biomech. 2014;47(4):793-804. [32] WANG X, SHEN Y, SHANG M, et al. Endothelial mechanobiology in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;undefined:37163659. [33] 于波,孙长江,权铁刚,等. 动脉粥样硬化模型动物脑血管的拉伸力学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24):4445-4448. [34] ZAINA C, GRANT R, JOHNSON C, et al. The effect of cervical rotation on blood flow in the contralateral vertebral artery. Man Ther. 2003;8(2): 103-109. [35] SILLA A, FOGACCI F, PUNZO A, et al. Treatment with PCSK9 Inhibitor Evolocumab Improves Vascular Oxidative Stress and Arterial Stiffness in Hypercholesterolemic Patients with High Cardiovascular Risk. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(3):36978827. [36] HODES RJ, LAKATTA EG, MCNEIL CT. Another modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease? Some evidence points to arterial stiffness. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1995;43(5):581-582. [37] BOUTOUYRIE P, TROPEANO AI, ASMAR R, et al. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of primary coronary events in hypertensive patients: a longitudinal study. Hypertension. 2002;39(1):10-15. [38] SHIMOYAMA T, GAJ S, NAKAMURA K, et al. Quantitative CTA vascular calcification, atherosclerosis burden, and stroke mechanism in patients with ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2023;449:120667. [39] 刘肖瑜,余伟波.不同旋转手法治疗椎动脉型颈椎病临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志,2014,30(4):315-316. |
| [1] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [2] | Liang Jiyao, Zhou Honghai, Wei Guikang, Su Shaoting, Chen Longhao, He Xinyu, Liu Liangpu. Quantification of in vivo biomechanics and analysis of influencing factors in cervical spine fixed-point rotation manipulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 486-492. |
| [3] | Li Qingyin, Li Linhua, Zhang Chunle, Fu Ping. Endothelial progenitor cell and mesenchymal stem cell therapy for vascular stent-associated diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4091-4101. |
| [4] | Song Mingxiao, Chen Junshunzi, Wang Ningwei, Cai Huan, Feng Hong. Role of prohibitin 2 in mitophagy pathway against atherosclerosis in rats undergoing endurance training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2294-2300. |
| [5] | Cao Zheng, Zheng Xiaoxin, Jiang Xuejun. Finite element analysis of safety and efficacy of a novel scored balloon for coronary arteries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2083-2090. |
| [6] | Li Sijin, Feng Xiaoteng, Wang Yiru, Liu Ping. Macrophage-specific promoter SP146-C1 enhances vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in atherosclerotic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4202-4208. |
| [7] | Huang Dong, Ge Jin, Liu Guangluan, Guo Zonglei, Wang Yehua. Anatomical risk factors for tibial insertion avulsion fracture of anterior cruciate ligament based on MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3890-3896. |
| [8] | Qi Ming, Wang Lei, Zhang Zhen. CXCL5 participates in carotid plaque formation by inducing vascular calcification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 186-192. |
| [9] | Deng Rui, Huang Keming, Luo Jian, Chen Gong, Feng Jian, Huang Weiyi, Wei Gang. Effect of heme oxygenase-1-mediated atorvastatin on macrophage polarization and cholesterol accumulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 62-67. |
| [10] | Zhao Quanwei, Li Hui, Liu Danan, Gong Caiwei, Chen Long. Dapagliflozin attenuates endothelial cell pyroptosis and dysfunction induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 80-85. |
| [11] | Han Weiyu, Chen Yuanxing, Huang Youyang, Liu Weiwei, Zhao Yongchao, Zhao Ranzun. Regulation of cardiovascular diseases by histone deacetylation modification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5707-5713. |
| [12] | Wang Shurui, Zhang Yilei, Jiao Weijie, Liu Zhihua, Zhang Kuiming, Cui Yinglin. Effects of Yiqi Tongmai Fang on serum amino acid metabolism of atherosclerotic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4441-4447. |
| [13] | Ou Hangjun, Zhao Guangjian, Pan Yujia, Gong Caiwei, Zhao Quanwei, Liu Danan. Construction of a lentiviral vector overexpressing fibronectin type III domain containing 5 to inhibit apoptosis of endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 216-222. |
| [14] | Su Jingyang, Zhang Yaojie, Cao Bin, Hao Xuewei, Li Xiao, Han Yongtai. Analysis of collapse and related factors in the treatment of ARCO I-II non-traumatic necrosis of femoral head with porous tantalum rod [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2400-2404. |
| [15] | Wei Gang, Gao Shangyuan, Zhang Ying, Huang Weiyi. Immunostimulation combined with liquid nitrogen freezing to construct a rat model of atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5656-5661. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||