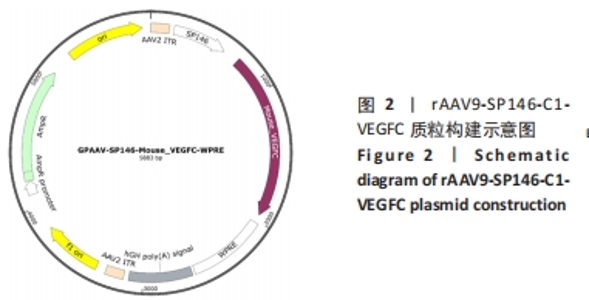
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (26): 4202-4208.doi: 10.12307/2024.392
Previous Articles Next Articles
Macrophage-specific promoter SP146-C1 enhances vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in atherosclerotic mice
Li Sijin, Feng Xiaoteng, Wang Yiru, Liu Ping
- Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
-
Received:2023-05-26Accepted:2023-07-04Online:2024-09-18Published:2023-10-07 -
Contact:Liu Ping, Professor, Chief physician, Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China -
About author:Li Sijin, MD candidate, Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82074200 and 81873117 (both to LP); National Natural Science Foundation of China for the Youth, No. 82204849 (to WYR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Sijin, Feng Xiaoteng, Wang Yiru, Liu Ping. Macrophage-specific promoter SP146-C1 enhances vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in atherosclerotic mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4202-4208.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
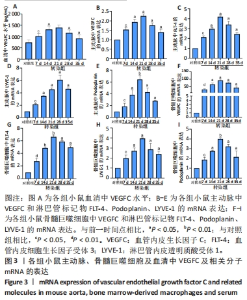
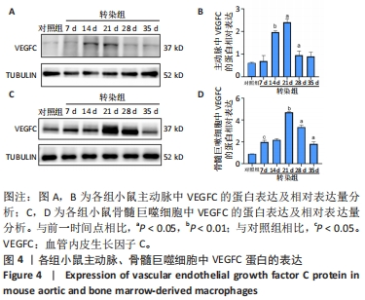
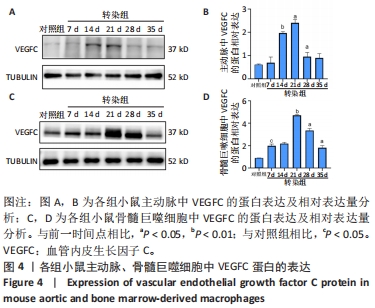
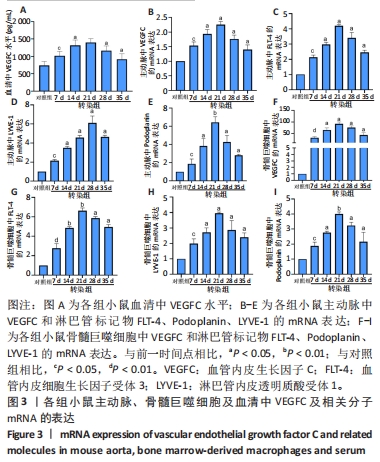
2.3 小鼠血清中VEGFC水平 与对照组相比,转染7 d组小鼠血清VEGFC水平增加(P < 0.05)。转染rAAV9-SP146-C1-VEGFC的各组小鼠血清VEGFC水平差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),且随着时间推移而增多,在28 d时开始减少,除21 d与14 d比较无差异外,其余时间点与前一个时间点相比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3A。 2.4 主动脉及骨髓巨噬细胞中VEGFC及相关分子的mRNA表达 与对照组相比,转染7 d组的小鼠主动脉及骨髓巨噬细胞中VEGFC、FLT-4、Podoplanin、LYVE-1的mRNA表达量增高;转染rAAV9-SP146-C1-VEGFC的各组小鼠主动脉及骨髓巨噬细胞中VEGFC、FLT-4、Podoplanin、LYVE-1的mRNA表达差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),且随着转染时间推移而增加,其中LYVE-1的mRNA在28 d时表达量最高,35 d时下降(P < 0.05),其余均在21 d时表达最高,28 d后逐渐减少(P < 0.05),见图3B-I。"
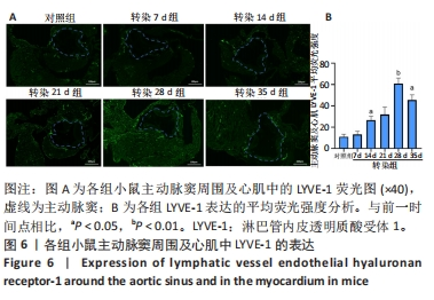
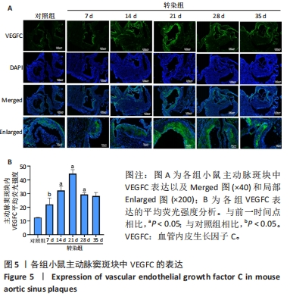
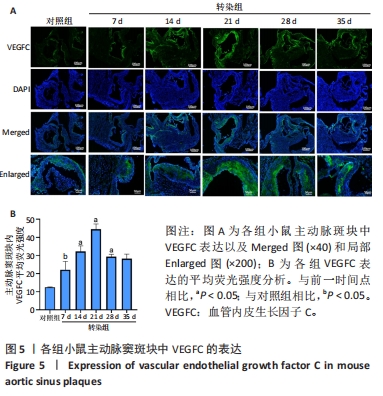
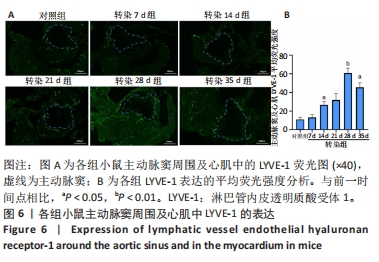
2.6 主动脉窦和心肌中VEGFC及淋巴管标志物LYVE-1的免疫荧光表达 免疫荧光检测结果显示,VEGFC主要在主动脉斑块中表达,LYVE-1主要在主动脉窦外膜周围及心肌中表达。与对照组相比,转染7 d组小鼠主动脉窦斑块的VEGFC表达增高(P < 0.05);转染rAAV9-SP146-C1-VEGFC的各组小鼠主动脉窦斑块的VEGFC表达差异有显著性意义,且随着转染时间延长而增多,在21 d时表达量最高,21 d后随着时间延长逐渐减少(P < 0.05),28 d组与35 d组比较差异无显著性意义,见图5;与对照组相比,转染7 d组小鼠主动脉窦周围及心肌的LYVE-1平均荧光强度差异无显著性意义;转染rAAV9-SP146-C1-VEGFC的各组小鼠主动脉窦周围及心肌的LYVE-1平均荧光强度相比差异有显著性意义,且随着转染时间延长而增高,在28 d时表达量最高,35 d组较28 d组减少(P < 0.05),而14 d组与21 d组比较差异无显著性意义,见图6。"
| [1] LIBBY P. The biology of atherosclerosis comes full circle: lessons for conquering cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18(10):683-684. [2] DROSOS I, PAVLAKI M, ORTEGA CARRILLO MDP, et al. Increased Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphangiogenic Growth Factor Expression in Perivascular Adipose Tissue of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7):1000. [3] MIYAZAKI T, MIYAZAKI A. Hypercholesterolemia and Lymphatic Defects: The Chicken or the Egg? Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:701229. [4] D’AMORE PA, ALCAIDE P. Macrophage efferocytosis with VEGFC and lymphangiogenesis: rescuing the broken heart. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132(9):e158703. [5] BOZOGLU T, LEE S, ZIEGLER T, et al. Endothelial Retargeting of AAV9 In Vivo. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(7):e2103867. [6] 谢佳,杨毅宁,马依彤,等.重组9型腺相关病毒载体转染动脉粥样硬化模型小鼠主动脉:最佳在体表达时间点的确定[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(5):733-738. [7] KANG WS, KWON JS, KIM HB, et al. A macrophage-specific synthetic promoter for therapeutic application of adiponectin. Gene Ther. 2014; 21(4):353-362. [8] ENGELEN SE, ROBINSON AJB, ZURKE YX, et al. Therapeutic strategies targeting inflammation and immunity in atherosclerosis: how to proceed? Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(8):522-542. [9] HONG CG, FLORIDA E, LI H, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein associates with cardiovascular disease by a vicious cycle of atherosclerosis and inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;9:1023651. [10] TANG C, DENG L, LUO Q, et al. Identification of oxidative stress-related genes and potential mechanisms in atherosclerosis. Front Genet. 2023;13:998954. [11] LIBBY P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021; 592(7855):524-533. [12] RAN S, MONTGOMERY KE. Macrophage-mediated lymphangiogenesis: the emerging role of macrophages as lymphatic endothelial progenitors. Cancers (Basel). 2012;4(3):618-657. [13] MIYAZAKI T, TAKETOMI Y, HIGASHI T, et al. Hypercholesterolemic Dysregulation of Calpain in Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Interferes With Regulatory T-Cell Stability and Trafficking. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023;43(2):e66-e82. [14] MORONI F, AMMIRATI E, NORATA GD, et al. The Role of Monocytes and Macrophages in Human Atherosclerosis, Plaque Neoangiogenesis, and Atherothrombosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:7434376. [15] ORECCHIONI M, KOBIYAMA K, WINKELS H, et al. Olfactory receptor 2 in vascular macrophages drives atherosclerosis by NLRP3-dependent IL-1 production. Science. 2022;375(6577):214-221. [16] FENG X, DU M, LI S, et al. Hydroxysafflor yellow A regulates lymphangiogenesis and inflammation via the inhibition of PI3K on regulating AKT/mTOR and NF-κB pathway in macrophages to reduce atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Phytomedicine. 2023;112:154684. [17] HATADA I, MORITA S, HORII T. CRISPR/Cas9. Methods Mol Biol. 2023; 2637:41-47. [18] EL MARJOU F, JOUHANNEAU C, KRNDIJA D. Targeted Transgenic Mice Using CRISPR /Cas9 Technology. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2214:125-141. [19] LIU B, JING Z, ZHANG X, et al. Large-scale multiplexed mosaic CRISPR perturbation in the whole organism. Cell. 2022;185(16):3008-3024. [20] WEN JH, LI DY, LIANG S, et al. Is LysM-Cre a good candidate Cre for knocking out Atg5 gene in mice? Front Immunol. 2022;13:964496. [21] KARKKAINEN MJ, HAIKO P, SAINIO K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C is required for sprouting of the first lymphatic vessels from embryonic veins. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(1):74-80. [22] JÄSCHKE N, BÜNING H. Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Design-Moving the Adeno-Associated Virus to a Bioengineered Therapeutic Nanoparticle. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2022;36(4):667-685. [23] CHEN X, HE Y, TIAN Y, et al. Different Serotypes of Adeno-Associated Virus Vector- and Lentivirus-Mediated Tropism in Choroid Plexus by Intracerebroventricular Delivery. Hum Gene Ther. 2020;31(7-8):440-447. [24] ZHANG H, LI T, SUN Y, et al. Perfecting Targeting in CRISPR. Annu Rev Genet. 2021;55:453-477. [25] IQBAL AJ, MCNEILL E, KAPELLOS TS, et al. Human CD68 promoter GFP transgenic mice allow analysis of monocyte to macrophage differentiation in vivo. Blood. 2014;124(15):e33-44. [26] LI AC, GUIDEZ FR, COLLIER JG, et al. The macrosialin promoter directs high levels of transcriptional activity in macrophages dependent on combinatorial interactions between PU.1 and c-Jun. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(9):5389-5399. [27] HORVAI A, PALINSKI W, WU H, et al. Scavenger receptor A gene regulatory elements target gene expression to macrophages and to foam cells of atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92(12):5391-5395. [28] HE W, QIANG M, MA W, et al. Development of a synthetic promoter for macrophage gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2006;17(9):949-959. [29] LEVIN MC, LIDBERG U, JIRHOLT P, et al. Evaluation of macrophage-specific promoters using lentiviral delivery in mice. Gene Ther. 2012; 19(11):1041-1047. [30] PETROVA TV, KOH GY. Biological functions of lymphatic vessels. Science. 2020;369(6500):eaax4063. [31] KAIPAINEN A, KORHONEN J, MUSTONEN T, et al. Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 gene becomes restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(8): 3566-3570. [32] LAWRANCE W, BANERJI S, DAY AJ, et al. Binding of Hyaluronan to the Native Lymphatic Vessel Endothelial Receptor LYVE-1 Is Critically Dependent on Receptor Clustering and Hyaluronan Organization. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(15):8014-8030. [33] MARUYAMA Y, MARUYAMA K, KATO Y, et al. The effect of podoplanin inhibition on lymphangiogenesis under pathological conditions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(8):4813-4822. [34] MAN JJ, BECKMAN JA, JAFFE IZ. Sex as a Biological Variable in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2020;126(9):1297-1319. |
| [1] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [2] | Zeng Fanzhuo, Li Yuxin, Sun Jiachen, Gu Xinyang, Wen Shan, Tian He, Mei Xifan. Efficient strategies for microglia replacement in spinal cord injury models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [3] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [4] | Zhang Jie, Xiao Tianjiao, Li Li, Kang Jiabing, Zhan Jifan, Wei Yan, Tian Ai. Interleukin-4 regulates macrophage polarization and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3960-3966. |
| [5] | Zhao Guangjian, Liu Danan, Zhou Bo, Wang Yao. Action mechanism by which fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 inhibits macrophage pyroptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 4005-4012. |
| [6] | Ge Ruiyang, Ni Can, Yang Kun, Yan Fuhua. The role of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis and treatment of periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3246-3251. |
| [7] | Wang Zengshun, Suonan Angxiu, Liu Limin, Zhou Jingyuan. Role and mechanism of miR-155/leptin receptor/adenosine phosphate-dependent protein kinase axis in tuberculin-induced osteoclast formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3190-3195. |
| [8] | Qi Ming, Wang Lei, Zhang Zhen. CXCL5 participates in carotid plaque formation by inducing vascular calcification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 186-192. |
| [9] | Meng Zhicheng, Qiao Weiping, Zhao Yang, Liu Hongfei, Li Kaijie, Ma Bo. Effects of immune cells and related cytokines in the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 280-287. |
| [10] | Yang Quan, He Huiyu, Wang Sifan, Lyu Shangyi, Zhou Qiqi, Han Xiangzhen. Overexpression of miR-378a promotes macrophage M2 polarization and inhibits M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2036-2041. |
| [11] | Dong Hongfei, Huang Xi, Li Xianhui, Zhang Yanbiao, Wang Xuyang, Wang Bing, Sun Hongyu. Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in promoting acute skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2047-2053. |
| [12] | Zhang Chenhui, Fu Tingting, Wu Yanglin, Zhang Qin, Liu Ang, Yang Huilin, Lin Jun. Melatonin alleviates CoCrMo particle-induced osteolysis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1484-1489. |
| [13] | Deng Jing, Li Tinghua, Zhu Hai, Yang Xiao, Cao Jun, Zhu Xiangdong. Various arginine configurations-modified chitosan hydrogels promote skin wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1497-1504. |
| [14] | Bei Ying, Li Wenjing, Li Meiyun, Su Meng, Zhang Jin, Huang Yu, Zhu Yanzhao, Li Jiali, Wu Yan. Prussian blue nanoparticles promote wound healing of diabetic skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1526-1532. |
| [15] | Yu Dehao, Ning Fengting, Du Yilang, Wang Yeyuan, Bai Bing. Regulatory effects of micro-arc oxidation on anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of metal implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1613-1619. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||