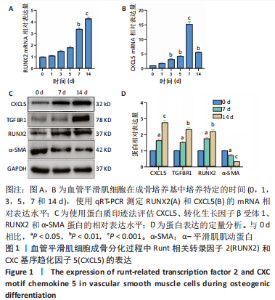
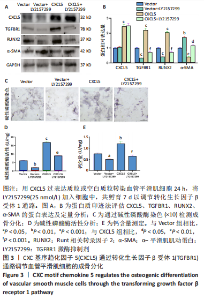
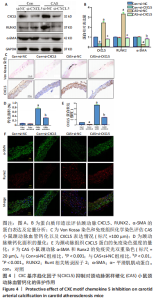
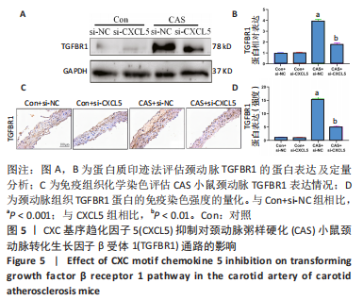
[1] 高素颖, 颜应琳, 于凯, 等. 急性缺血性脑卒中颈动脉粥样硬化的危险因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(3):327-332.
[2] SEIME T, VAN WANROOIJ M, KARLÖF E, et al. Biomechanical assessment of macro-calcification in human carotid atherosclerosis and its impact on smooth muscle cell phenotype. Cells. 2022;11(20):3279.
[3] VAN DEN BERGH G, OPDEBEECK B, D’HAESE PC, et al. The vicious cycle of arterial stiffness and arterial media calcification. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(12):1133-1146.
[4] LIN X, SHAN S K, XU F, et al. The crosstalk between endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells aggravates high phosphorus-induced arterial calcification. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):650.
[5] ZHANG W, WANG H, SUN M, et al. CXCL5/CXCR2 axis in tumor microenvironment as potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020;40(2-3):69-80.
[6] LU X, WANG Z, YE D, et al. The role of CXC chemokines in cardiovascular diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:765768.
[7] HOSSEINI A, SAHRANAVARD T, REINER Ž, et al. Effect of statins on abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022;178:106284.
[8] LEI H, HE M, HE X, et al. METTL3 induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation and migration through facilitating M1 macrophage differentiation. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(5):4376-4388.
[9] OUWENEEL AB, VERWILLIGEN RAF, VAN ECK M. Vulnerable plaque and vulnerable blood: two critical factors for spontaneous atherothrombosis in mouse models. Atherosclerosis. 2019;284:160-164.
[10] BUDOFF M, BACKLUND JC, BLUEMKE DA, et al. The association of coronary artery calcification with subsequent incidence of cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes: the DCCT/EDIC trials. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12(7 Pt 2):1341-1349.
[11] PETSOPHONSAKUL P, BURGMAIER M, WILLEMS B, et al. Nicotine promotes vascular calcification via intracellular Ca2+-mediated, Nox5-induced oxidative stress, and extracellular vesicle release in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118(9):2196-2210.
[12] HAN R, LUO J, WANG L, et al. miR-33a-5p suppresses ox-LDL-stimulated calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting METTL3. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021;21(9):737-746.
[13] HE J, ZHONG X, ZHAO L, et al. JAK2/STAT3/BMP-2 axis and NF-κB pathway are involved in erythropoietin-induced calcification in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2019;23(4):501-512.
[14] YUAN C, NI L, ZHANG C, et al. Vascular calcification: New insights into endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 2021;134:104105.
[15] WEIBERG D, THACKERAY JT, DAUM G, et al. Clinical molecular imaging of chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in atherosclerotic plaque using 68Ga-pentixafor PET: correlation with cardiovascular risk factors and calcified plaque burden. J Nucl Med. 2018;59(2):266-272.
[16] KARIMABAD MN, KOUNIS NG, HASSANSHAHI G, et al. The involvement of cxc motif chemokine ligand 10 (Cxcl10) and its related chemokines in the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and in the covid-19 vaccination: A narrative review. Vaccines. 2021;9(11):1224.
[17] YAN Y, ZHU M, MA J, et al. MEK1/2 inhibitor inhibits neointima formation by activating miR-126-3p/CXC motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12)/CXC motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):11214-11227.
[18] CHANG TT, LIAO LY, CHEN JW. Inhibition on CXCL5 reduces aortic matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression and protects against acute aortic dissection. Vascul Pharmacol. 2021;141:106926.
[19] YANG C J, TSAI S H, WANG JC, et al. Association between acute aortic dissection and the distribution of aortic calcification. PloS One. 2019; 14(7):e0219461.
[20] CHENG Y, MA X, WEI Y, et al. Potential roles and targeted therapy of the CXCLs/CXCR2 axis in cancer and inflammatory diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019;1871(2):289-312.
[21] WANG L, ZHOU J, GUO F, et al. MicroRNA-665 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting TGFBR1. Int Heart J. 2021;62(2):371-380.
[22] ZHANG J, LI R, LIU Q, et al. SB431542-loaded liposomes alleviate liver fibrosis by suppressing TGF-β signaling. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(11):4152-4162.
[23] XU Z, GAO H, ZHANG Y, et al. CCL7 and TGF-β secreted by MSCs play opposite roles in regulating CRC metastasis in a KLF5/CXCL5-dependent manner. Mol Ther. 2022;30(6):2327-2341.
[24] MOREAU JM, DHARIWALA MO, GOUIRAND V, et al. Regulatory T cells promote innate inflammation after skin barrier breach via TGF-β activation. Sci Immunol. 2021;6(62):eabg2329.
|