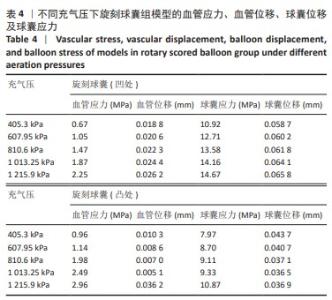
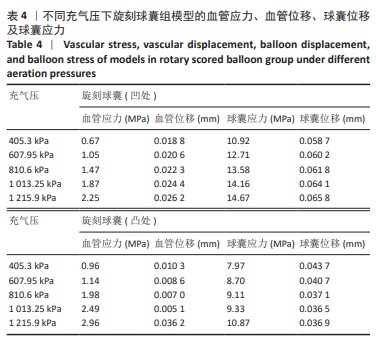
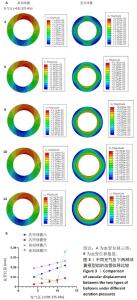
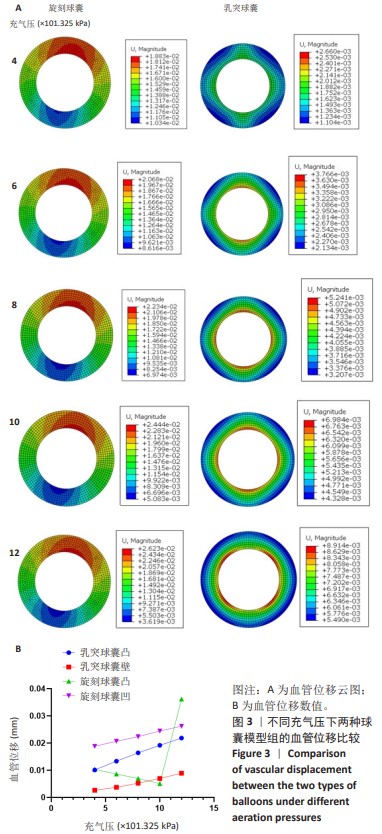
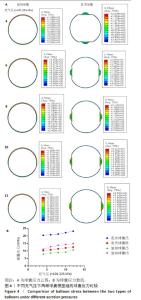
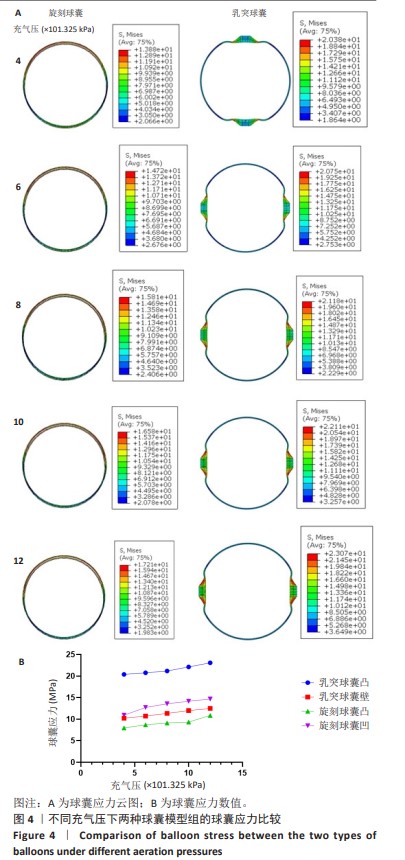
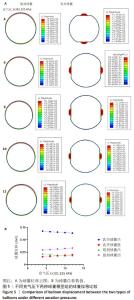
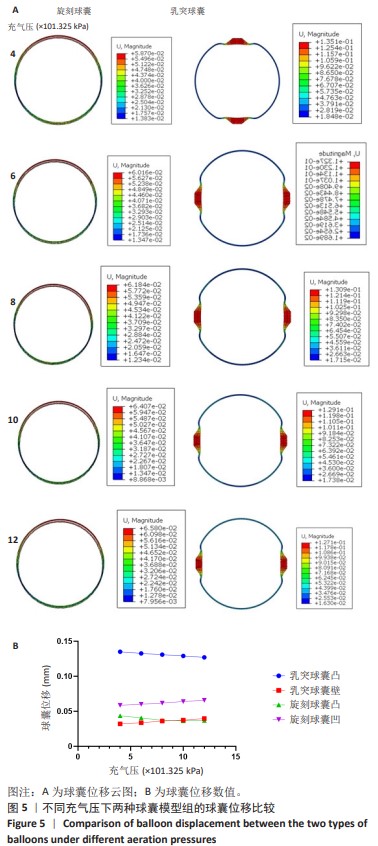
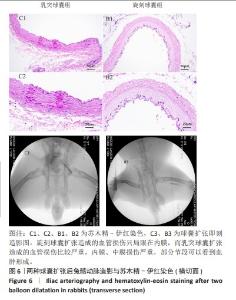
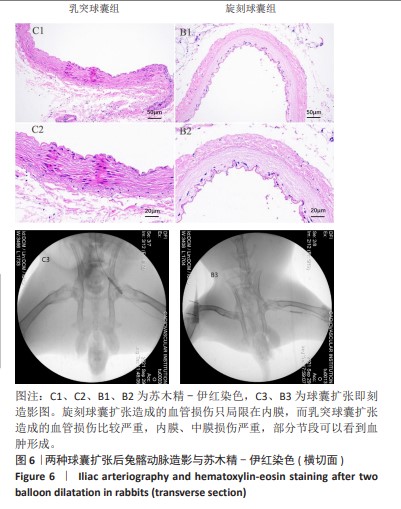
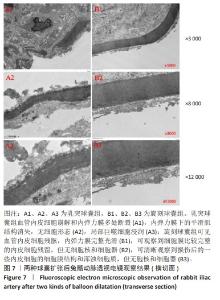
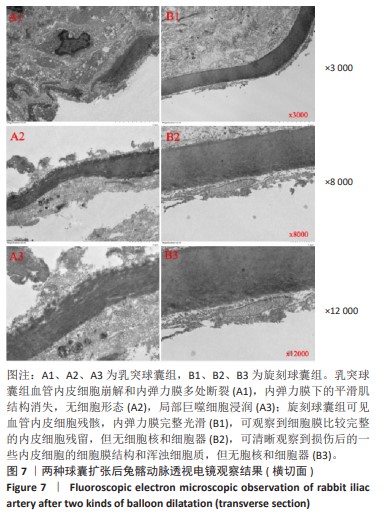
[1] CAO Z, LI J, FANG Z, et al. The factors influencing the efficiency of drug-coated balloons. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:947776.
[2] SCHELLER B, SPECK U, ROMEIKE B, et al. Contrast media as carriers for local drug delivery. Successful inhibition of neointimal proliferation in the porcine coronary stent model. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:1462-1467.
[3] BYRNE RA, JONER M, ALFONSO F, et al. Drug-coated balloon therapy in coronary and peripheral artery disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014;11:13-23.
[4] VALGIMIGLI M, PATIALIAKAS A, THURY A, et al. Zotarolimus-eluting versus bare-metal stents in uncertain drug-eluting stent candidates. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:805-815.
[5] CREMERS B, TONER JL, SCHWARTZ LB, et al. Inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia with a novel zotarolimus coated balloon catheter. Clin Res Cardiol. 2012;101:469-476.
[6] MARTÍNEZ-ELBAL L, RUIZ-NODAR JM, ZUECO J, et al. Direct coronary stenting versus stenting with balloon pre-dilation: immediate and follow-up results of a multicentre, prospective, randomized study. The DISCO trial. DIrect Stenting of COronary Arteries. Eur Heart J. 2002;23:633-640.
[7] ALI RM, ABDUL KADER MASK, WAN AHMAD WA, et al. Treatment of Coronary Drug-Eluting Stent Restenosis by a Sirolimus- or Paclitaxel-Coated Balloon. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:558-566.
[8] ZHENG J, CUI J, MEIYAN QING J, et al. Safety and effectiveness of combined scoring balloon and paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty for stenosis in the hemodialysis access circuit. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019;100:31-37.
[9] KUFNER S, JONER M, SCHNEIDER S, et al. Neointimal Modification With Scoring Balloon and Efficacy of Drug-Coated Balloon Therapy in Patients With Restenosis in Drug-Eluting Coronary Stents: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10:1332-1340.
[10] BONAVENTURA K, SCHWEFER M, YUSOF AKM, et al. Systematic Scoring Balloon Lesion Preparation for Drug-Coated Balloon Angioplasty in Clinical Routine: Results of the PASSWORD Observational Study. Adv Ther. 2020;37:2210-2223.
[11] JUJO K, SAITO K, ISHIDA I, et al. Intimal disruption affects drug-eluting cobalt-chromium stent expansion: A randomized trial comparing scoring and conventional balloon predilation. Int J Cardiol. 2016;221:23-31.
[12] FRAM DB, ARETZ TA, MIKAN JF, et al. In vivo radiofrequency thermal balloon angioplasty of porcine coronary arteries: histologic effects and safety. Am Heart J. 1993;126:969-978.
[13] KEMPIN W, KAULE S, RESKE T, et al. In vitro evaluation of paclitaxel coatings for delivery via drug-coated balloons. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;96:322-328.
[14] LEE HI, RHIM WK, KANG EY, et al. A Multilayer Functionalized Drug-Eluting Balloon for Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(5):614.
[15] KASTRATI A, DIBRA A, MEHILLI J, et al. Predictive factors of restenosis after coronary implantation of sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation. 2006;113:2293-2300.
[16] FAKHRAEI LAHIJI S, KIM Y, et al. Tissue Interlocking Dissolving Microneedles for Accurate and Efficient Transdermal Delivery of Biomolecules. Sci Rep. 2019;9:7886.
[17] KAULE S, MINRATH I, STEIN F, et al. Correlating coating characteristics with the performance of drug-coated balloons--a comparative in vitro investigation of own established hydrogel- and ionic liquid-based coating matrices. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0116080.
[18] FAENGER B, HEINRICH A, HILGER I, et al. Drug loss from Paclitaxel-Coated Balloons During Preparation, Insertion and Inflation for Angioplasty: A Laboratory Investigation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2022;45:1186-1197.
[19] FANELLI F, CANNAVALE A, GAZZETTI M, et al. Calcium burden assessment and impact on drug-eluting balloons in peripheral arterial disease. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37:898-907.
[20] HELOU B, BEL-BRUNON A, DUPONT C, et al. Patient-specific finite element simulation of peripheral artery percutaneous transluminal angioplasty to evaluate the procedure outcome without stent implantation. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2023;39:e3685.
[21] JADIDI M, RAZIAN SA, ANTTILA E, et al. Comparison of morphometric, structural, mechanical, and physiologic characteristics of human superficial femoral and popliteal arteries. Acta Biomater. 2021;121:431-443.
[22] GEITH MA, ECKMANN JD, HASPINGER DC, et al. Experimental and mathematical characterization of coronary polyamide-12 balloon catheter membranes. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0234340.
[23] BUKKA M, REDNAM PJ, SINHA M. Drug-eluting balloon: design, technology and clinical aspects. Biomed Mater. 2018;13:032001.
[24] GERVASO F, CAPELLI C, PETRINI L, et al. On the effects of different strategies in modelling balloon-expandable stenting by means of finite element method. J Biomech. 2008;41:1206-1212.
[25] HEINRICH A, ENGLER MS, GÜTTLER FV, et al. Systematic evaluation of particle loss during handling in the percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for eight different drug-coated balloons. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:17220.
[26] LI T, ZHANG Z, WANG W, et al. Simulation and Experimental Investigation of Balloon Folding and Inserting Performance for Angioplasty: A Comparison of Two Materials, Polyamide-12 and Pebax. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(6):312.
[27] MARTIN D, BOYLE F. Finite element analysis of balloon-expandable coronary stent deployment: influence of angioplasty balloon configuration. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2013;29:1161-1175.
[28] MORRIS PD, IQBAL J, CHIASTRA C, et al. Simultaneous kissing stents to treat unprotected left main stem coronary artery bifurcation disease; stent expansion, vessel injury, hemodynamics, tissue healing, restenosis, and repeat revascularization. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;92:E381-E392.
[29] MORTIER P, HOLZAPFEL GA, DE BEULE M, et al. A novel simulation strategy for stent insertion and deployment in curved coronary bifurcations: comparison of three drug-eluting stents. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38:88-99.
[30] PRENDERGAST PJ, LALLY C, DALY S, et al. Analysis of prolapse in cardiovascular stents: a constitutive equation for vascular tissue and finite-element modelling. J Biomech Eng. 2003;125:692-699.
[31] RAHINJ GB, CHAUHAN HS, SIRIVELLA ML, et al. Numerical Analysis for Non-Uniformity of Balloon-Expandable Stent Deployment Driven by Dogboning and Foreshortening. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2022;13:247-264. |