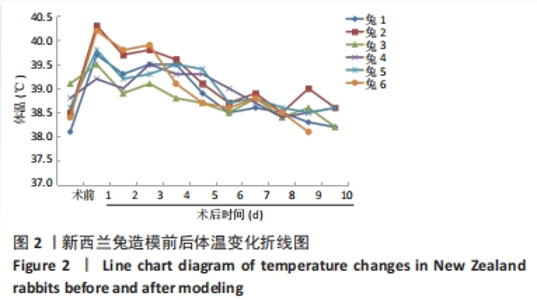
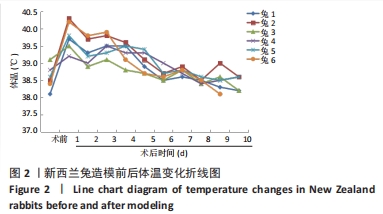
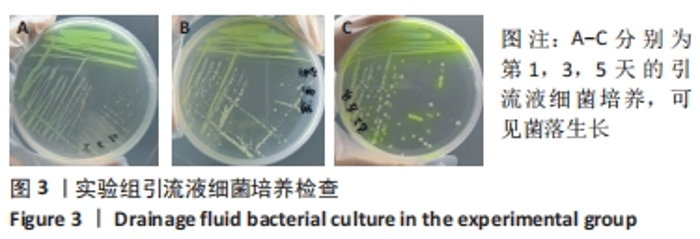
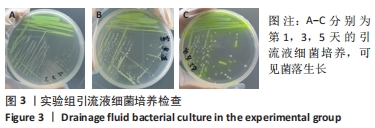
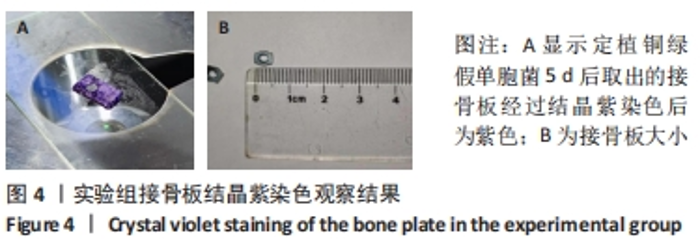
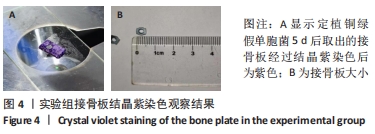
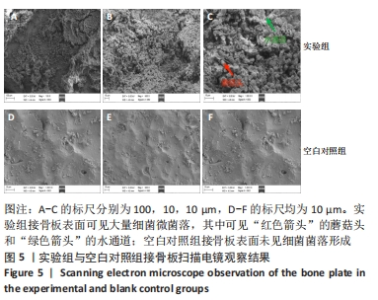
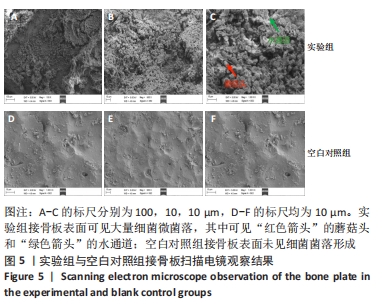
[1] ZIMMERLI W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implant-associated infection. J Intern Med. 2014;276(2):111-119.
[2] MORGENSTERN M, KUHL R, ECKARDT H, et al. Diagnostic challenges and future perspectives in fracture-related infection. Injury. 2018;Suppl 1:S83-S90.
[3] TRAMPUZ A, ZIMMERLI W. Diagnosis and treatment of infections asso-ciated wits fracture-fixation devices. Injury. 2006;suppl 2:S59-s66.
[4] MACIEJCZAK A, WOLAN-NIERODA A, WAŁASZEK M, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis in spine surgery: a comparison of single-dose and 72-hour protocols. J Hosp Infect. 2019; 103(3):303-310.
[5] DALE H, FENSTAD AM, HALLAN G, et al. Increasing risk of prosthetic joint infection after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(5):449-458.
[6] 姜楠,余斌.骨折内固定术后感染的诊治最新进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020, 22(12):1098-1104.
[7] KHATOD M, BOTTE MJ, HOYT DB, et al. Outcomes in open tibia fractures: relationship between delay in treatment and infection. J Trauma. 2003;55(5):949-954.
[8] STEWART PS, FRANKLIN MJ. Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6(3):199-210.
[9] 周鑫华,霍仁斌.保留内固定物治疗骨折内固定术后早期感染的临床观察[J].中国伤残医学,2013,21(5):3-5.
[10] 杨利斌,董玉珍,杨素敏.骨折内固定术后早期感染保留内固定物治疗效果分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2014,24(19):4844-4846.
[11] 姜楠,覃承诃,余斌.骨折内固定术后感染抗生素治疗的新进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(16):1489-1492.
[12] CLAYMAN E, BEAUCHAMP Z, TROY J. Salvage of Infected Orthopedic Hardware With Intraoperative and Postoperative Hypochlorous Acid Instillations. Eplasty. 2023;23:e1.
[13] 梁金正,邵欣欣,杜少华,等.次氯酸对骨科内固定物表面细菌生物膜的清除作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(15):2367-2371.
[14] GRACIA E, LACLÉRIGA A, MONZÓN M, et al. Application of a rat osteomyelitis model to compare in vivo and in vitro the antibiotic efficacy against bacteria with high capacity to form biofilms. J Surg Res. 1998;79(2):146-153.
[15] WILLIAMS DL, HAYMOND BS, WOODBURY KL, et al. Experimental model of biofilm implant-related osteomyelitis to test combination biomaterials using biofilms as initial inocula. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(7):1888-1900.
[16] 褚立涛,郭国栋,刘刚,等.兔胫骨创伤后骨髓炎动物模型的建立[J].医学研究生学报,2012,25(11):1160-1162.
[17] 徐杨博,邓勇,魏代清,等.足踝Ⅰ类切口手术部位感染的临床分析[J].国际外科学杂志,2017,44(2):109-114.
[18] SHAO J, ZHANG H, YIN B, et al. Risk factors for surgical site infection following operative treatment of ankle fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018; 56:124-132.
[19] 芦永华,黄新玲,何文英,等.四肢骨折手术部位感染危险因素多中心调查[J].中国感染控制杂志,2016,15(6):393-396.
[20] 邝继文,杨新,肖小燕,等.开放性骨折患者发生医院感染病原学特征与危险因素分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2017,27(19):4484-4487.
[21] Lin J, LIU H, LIU P, et al. External fixators for open fractures of tibia and fibula in patients with haemophilia A. Haemophilia. 2015;21(1):e51-53.
[22] 周鸣,谈永飞,蒋建农,等.胫骨平台骨折患者术后切口感染的临床特点分析研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2015,25(23):5441-5443.
[23] 白博,桑宏勋,吴子祥,等.四肢骨折内固定术后手术部位感染危险因素[J].中国感染控制杂志,2017,16(4):334-337.
[24] SUN R, LI M, WANG X, et al. Surgical site infection following open reduction and internal fixation of a closed ankle fractures: A retrospective multicenter cohort study. Int J Surg. 2017;48:86-91.
[25] 邱双玲,陶海荣.四肢开放性骨折外固定术创口感染的危险因素分析[J].北华大学学报(自然科学版),2021,22(1):83-86.
[26] GOVAERT GAM, KUEHL R, ATKINS BL, et al. Diagnosing Fracture-Related Infection: Current Concepts and Recommendations. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(1):8-17.
[27] 陈伟,卢景宜,江文杰.PCT和CRP在骨折术后感染诊断中的临床价值研究[J].中国现代药物应用,2020,14(14):69-71.
[28] KAIM AH, GROSS T, VON SCHULTHESS GK. Imaging of chronic posttraumatic osteomyelitis. Eur Radiol. 2002;12(5):1193-1202.
[29] SANTIAGO RESTREPO C, GIMÉNEZ CR, MCCARTHY K. Imaging of osteomyelitis and musculoskeletal soft tissue infections: current concepts. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2003; 29(1):89-109.
[30] 田永刚,江毅,肖联平,等.脊柱术后感染的治疗策略[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009, 19(9):717-718.
[31] 陈小楠,申元娜,李彭宇,等.细菌生物膜的特征及抗细菌生物膜策略[J].药学学报,2018,53(12):2040-2049.
[32] OTTO M. Virulence factors of the coagulase-negative staphylococci. Front Biosci. 2004;9: 841-863.
[33] CHEN L, WEN YM. The role of bacterial biofilm in persistent infections and control strategies. Int J Oral Sci. 2011;3(2):66-73.
[34] HARRIOTT MM, NOVERR MC. Importance of Candida-bacterial polymicrobial biofilms in disease. Trends Microbiol. 2011;19(11):557-563.
[35] FIELD TR, WHITE A, ELBORN JS, et al. Effect of oxygen limitation on the in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown planktonically and as biofilms. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;24(10):677-687.
[36] CONLON BP. Staphylococcus aureus chronic and relapsing infections: Evidence of a role for persister cells: An investigation of persister cells, their formation and their role in S. aureus disease. Bioessays. 2014;36(10):991-996.
[37] HARRISON JJ, RABIEI M, TURNER RJ, et al. Metal resistance in Candida biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2006;55(3):479-491.
[38] KRÓL JE, WOJTOWICZ AJ, ROGERS LM, et al. Invasion of E. coli biofilms by antibiotic resistance plasmids. Plasmid. 2013;70(1):110-119.
[39] 蒋琪霞,李晓华.清创方法及其关键技术的研究进展[J].中华护理杂志,2009, 44(11):1045-1047.
[40] 蒋琪霞,李晓华,彭青,等.负压伤口治疗技术用于53例慢性伤口的效果评价[J].中华护理杂志,2012,47(4):293-296. |