Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (33): 5265-5272.doi: 10.12307/2021.312
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of zoledronic acid on bone mineral density and bone metabolism markers in elderly patients with osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture after hip arthroplasty: 2-year follow-up
Qiu Wei1, Lian Xingye2
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, Guangyuan Central Hospital, Guangyuan 628000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Yunnan First People’s Hospital, Kunming 650200, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-03Revised:2020-11-06Accepted:2020-12-31Online:2021-11-28Published:2021-08-02 -
Contact:Lian Xingye, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Yunnan First People’s Hospital, Kunming 650200, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Qiu Wei, Master, Attending physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Guangyuan Central Hospital, Guangyuan 628000, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qiu Wei, Lian Xingye. Effect of zoledronic acid on bone mineral density and bone metabolism markers in elderly patients with osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture after hip arthroplasty: 2-year follow-up[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5265-5272.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
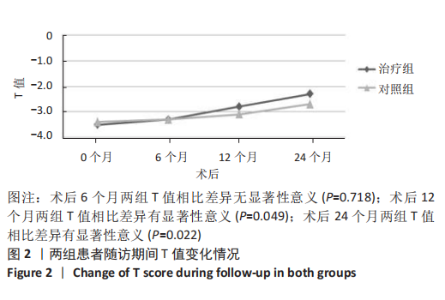
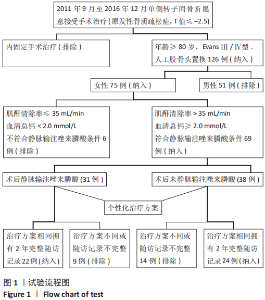
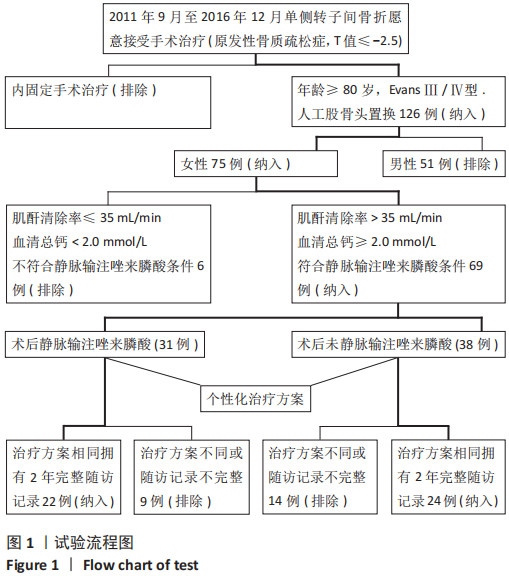
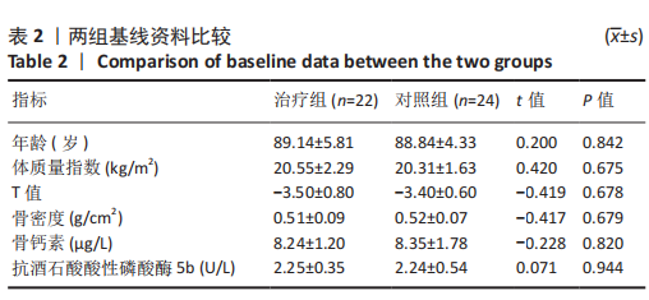
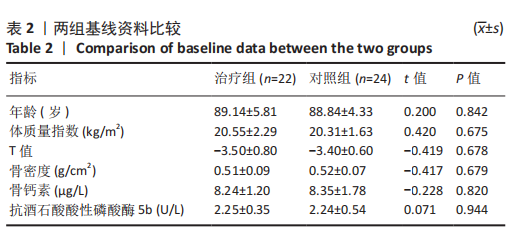
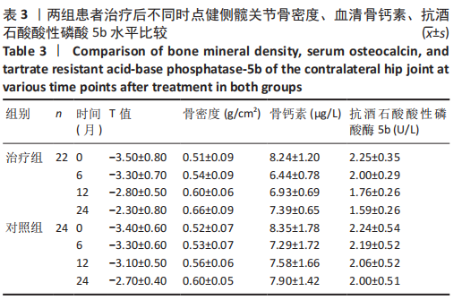
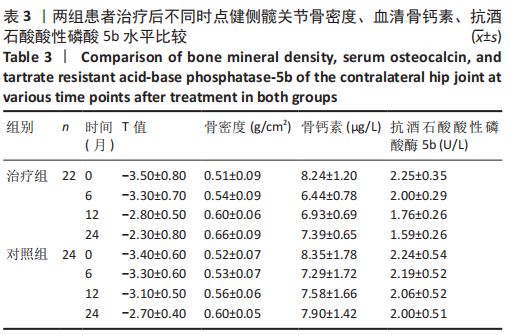
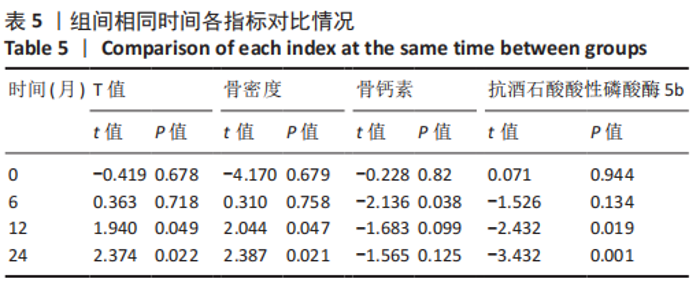
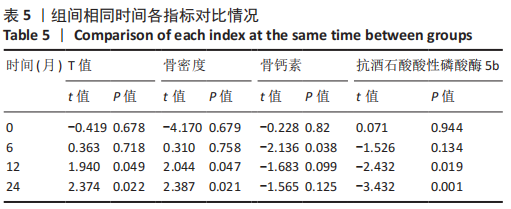
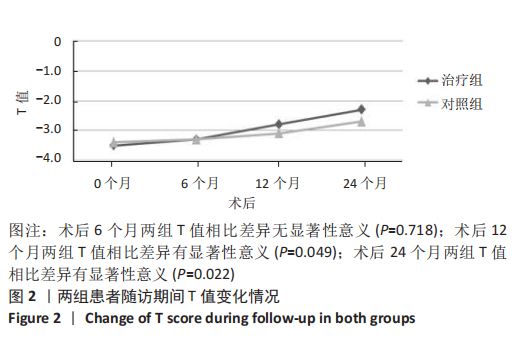
2.4.1 骨密度变化 (1) T值变化情况:见图2。 治疗组:术后6个月T值自术前-3.5±0.8上升至-3.3± 0.7,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.336);术后12个月T值变化至-2.8±0.5,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.001);术后24个月T值变化至-2.3±0.8,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后6个月与术后12个月之间差异有显著性意义(P=0.014);术后6个月与术后24个月之间差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后12个月与术后24个月之间差异有显著性意义(P=0.020)。 对照组:术后6个月T值自术前-3.4±0.6上升至-3.3± 0.6,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.675);术后12个月T值变化至-3.1±0.5,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.056);术后24个月T值变化至-2.7±0.4,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后6个月与术后12个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.086);术后6个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后12个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.011)。 相同随访时间两组T值对比:术后6个月两组T值相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.718);术后12个月两组T值相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.049);术后24个月两组T值相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.022)。 "
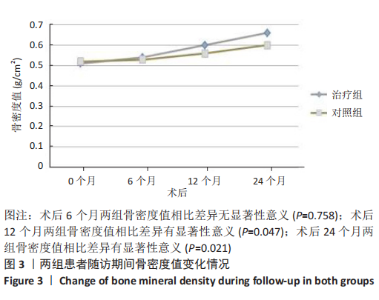
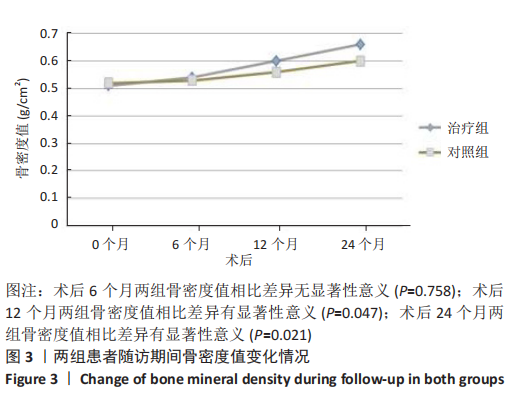
(2) 骨密度值变化情况:见图3。 治疗组:术后6个月骨密度自术前(0.51±0.09) g/cm2上升至(0.54±0.09) g/cm2,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.352);术后12个月骨密度变化至(0.60±0.06) g/cm2,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.001);术后24个月骨密度变化至(0.66±0.09) g/cm2,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.001);术后6个月与术后12个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.012);术后6个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后12个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.02)。 对照组:术后6个月骨密度自术前(0.52±0.07) g/cm2上升至(0.53±0.07) g/cm2,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.664);术后12个月骨密度变化至(0.56±0.06) g/cm2,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.052);术后24个月骨密度变化至(0.60±0.05) g/cm2,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后6个月与术后12个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.10);术后6个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后12个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.009)。 相同随访时间两组骨密度值对比:术后6个月两组骨密度值相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.758);术后12个月两组骨密度值相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.047);术后24个月两组骨密度值相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.021)。"
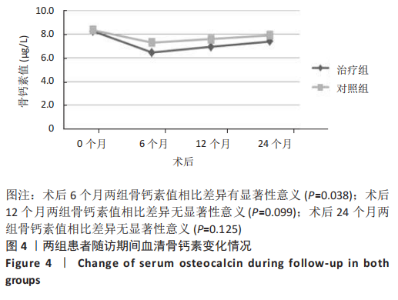
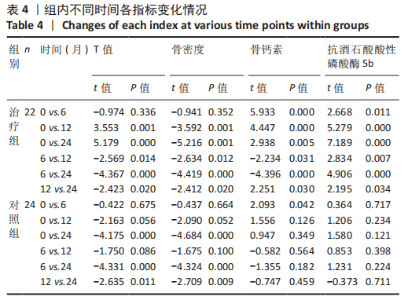
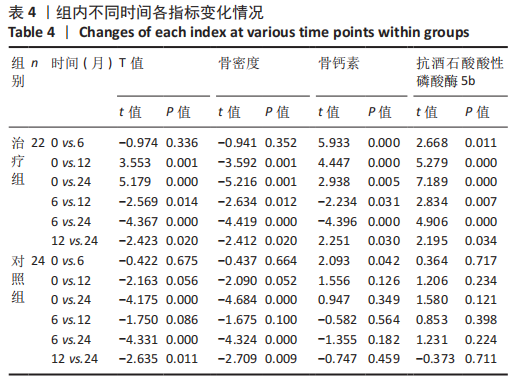
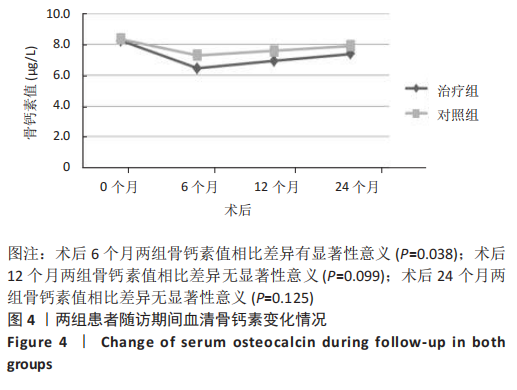
2.4.2 骨代谢标志物变化 (1)血清骨钙素变化情况:见图4。 治疗组:术后6个月骨钙素自术前(8.25±1.20) μg/L下 降至(6.44±0.78) μg/L,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后12个月骨钙素变化至(6.93±0.69) μg/L,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后24个月骨钙素变化至(7.39±0.65) μg/L,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.005);术后6个月与术后12个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.031);术后6个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后12个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.030)。 对照组:术后6个月骨钙素自术前(8.35±1.78) μg/L下 降至(7.29±1.72) μg/L,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.042);术后12个月骨钙素变化至(7.58±1.66) μg/L,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.126);术后24个月骨钙素变化至(7.90±1.42) μg/L,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.349);术后6个月与术后12个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.564);术后6个月与术后24个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.182);术后12个月与术后24个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.459)。 相同随访时间两组骨钙素值对比:术后6个月两组骨钙素值相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.038);术后12个月两组骨钙素值相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.099);术后24个月两组骨钙素值相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.125)。"

(2)血清TRACP-5b变化情况:见图5。 治疗组:术后6个月TRACP-5b自术前(2.25±0.35) U/L下 降至(2.00±0.29) U/L,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.011);术后12个月TRACP-5b变化至(1.76±0.26) U/L, 与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后24个月TRACP-5b变化至(1.59±0.26) U/L,与治疗前相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后6个月与术后12个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.007);术后6个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.000);术后12个月与术后24个月之间的差异有显著性意义(P=0.034)。 对照组:术后6个月TRACP-5b自术前(2.24±0.54) U/L 下降至(2.19±0.52) U/L,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.717);术后12个月TRACP-5b变化至(2.06±0.52) U/L,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.234);术后24个月TRACP-5b变化至(2.01±0.51) U/L,与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.121);术后6个月与术后12个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.398);术后6个月与术后24个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.224);术后12个月与术后24个月之间的差异无显著性意义(P=0.711)。 "

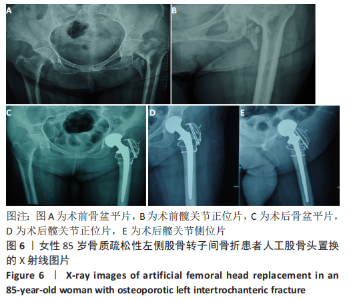
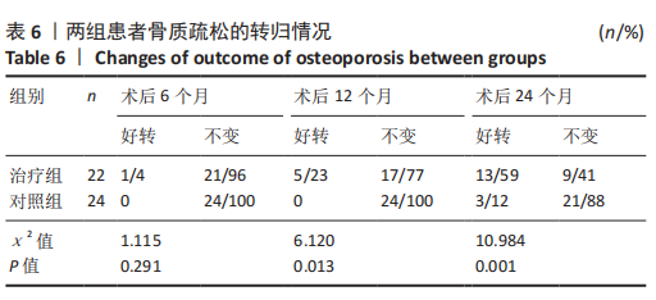
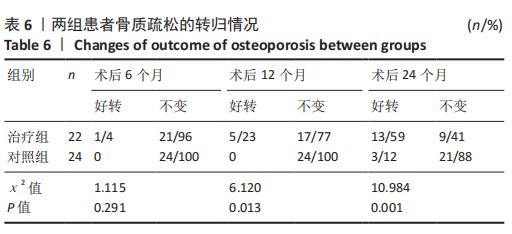
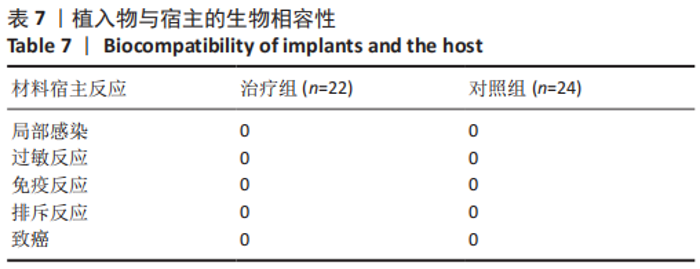
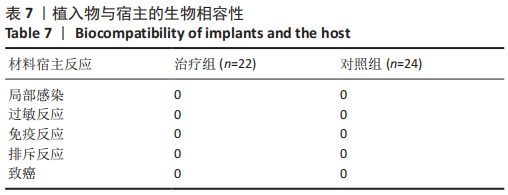
治疗组治疗6个月有1例患者骨密度自骨质疏松转变为骨含量减少,好转率为4%;治疗12个月共有5例患者骨密度自骨质疏松转变为骨含量减少,好转率为23%;治疗24个月后共有13例患者骨密度自骨质疏松转变为骨含量减少,好转率为59%。 对照组治疗6个月未见患者的骨密度自骨质疏松转变为骨含量减少,好转率为0;治疗12个月也未见患者骨密度自骨质疏松转变为骨含量减少,好转率亦为0;治疗24个月后共有3例患者骨密度自骨质疏松转变为骨含量减少,好转率为12%。 两组之间的变化在6个月时相比差异无显著性意义,12,24个月两组相比差异均有显著性意义。2年后未见患者的骨密度转变为正常,变化仅由骨质疏松转变为骨含量减少。 2.6 典型病例 女性患者,85岁,因摔伤致左髋部疼痛、活动受限4 d于2013-12-10入住云南省第一人民医院骨科。入院完善相关检查排除手术禁忌,与患者本人及家属充分沟通后行左侧人工股骨头置换,术后第5天下地行走。术后第3天给静脉输注唑来膦酸抗骨质疏松治疗,术后1年及2年2次静脉输注唑来膦酸,期间患者规律服用骨化三醇及钙剂。相关图片见图6。 "

| [1] YUAN BJ, ABDEL MP, CROSS WW, et al. Hip Arthroplasty After Surgical Treatment of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(11):3438-3444. [2] JU JB, ZHANG PX, JIANG BG. Hip Replacement as Alternative to Intramedullary Nail in Elderly Patients with Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2019; 11(5):745-754. [3] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年)[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011,4(1): 2-17. [4] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则)[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015, 8(5):371-374. [5] 徐青青,许兵. 唑来膦酸联合髋关节置换治疗绝经后骨质疏松性股骨颈骨折临床效果分析[J]. 中华内分泌外科杂志,2020,14(4): 327-332. [6] 孟增东,连星烨,刘伟,等.人工髋关节置换术治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(8):759-760. [7] 张晨,李永宁,宋国瑞,等.快速康复外科理念中不放置引流管对人工全膝关节置换术后康复的影响[J].中国临床研究,2020,33(5): 619-622. [8] 陈德才,廖二元,徐苓,等. 骨代谢生化标志物临床应用指南[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2015,8(4):283-293. [9] LIU L, SUN Y, WANG L, et al. Total hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fracture fixation failure. Eur J Med Res. 2019;24(1):39. [10] BRÖMME D, PANWAR P, TURAN S. et al. osteoporosis trials, pycnodysostosis and mouse deficiency models: Commonalities and differences. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016;11(5):457-472. [11] SMITH A, DENEHY K, ONG KL, et al. Total hip arthroplasty following failed intertrochanteric hip fracture fixation treated with a cephalomedullary nail. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(6_Supple_B):91-96. [12] ZENG X, ZHAN K, ZHANG L, et al. Conversion to total hip arthroplasty after failed proximal femoral nail antirotations or dynamic hip screw fixations for stable intertrochanteric femur fractures: a retrospective study with a minimum follow-up of 3 years. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):38. [13] LEE YK, KIM JT, ALKITAINI AA, et al. Conversion Hip Arthroplasty in Failed Fixation of Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Propensity Score Matching Study. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(5):1593-1598. [14] 原小兵,马玉伟.唑来膦酸对骨质疏松症患者骨代谢和骨转换指标的影响[J]. 中国合理用药探索,2019,16(3):82-84. [15] ZHOU W, LIU Y, GUO X, et al. Effects of zoledronic acid on bone mineral density around prostheses and bone metabolism markers after primary total hip arthroplasty in females with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(8):1581-1589. [16] MORI Y, KASAI H, OSE A, et al. Modeling and simulation of bone mineral density in Japanese osteoporosis patients treated with zoledronic acid using tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b, a bone resorption marker. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(5):1155-1163. [17] EIKEN P, VESTERGAARD P. Treatment of osteoporosis after alendronate or risedronate. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(1):1-12. [18] MOON NH, SHIN WC, KIM JS, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty following failed internal fixation for femoral neck and intertrochanteric fractures: A comparative study with 3-13 years’ follow-up of 96 consecutive patients. Injury. 2019;50(3):713-719. [19] WANG C. Efficacy and Safety of Zoledronic Acid for Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Ther. 2017;24(5):e544-e552. [20] GAO J, GAO C, LI H, et al. Effect of zoledronic acid on reducing femoral bone mineral density loss following total hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis from randomized controlled trails. Int J Surg. 2017;47: 116-126. [21] ZHU K, ZHANG J, ZHANG C, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of zoledronic acid combined with calcitriol in elderly patients receiving total hip arthroplasty or hemiarthroplasty for osteoporotic femoral neck fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2021;32(3):559-564. [22] FU GT, LIN LJ, SHENG PY, et al. Efficiency of Zoledronic Acid in Inhibiting Accelerated Periprosthetic Bone Loss After Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty in Osteoporotic Patients: A Prospective, Cohort Study. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(4):653-663. [23] FRIEDL G, RADL R, STIHSEN C, et al. The effect of a single infusion of zoledronic acid on early implant migration in total hip arthroplasty. A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(2):274-281. [24] TANTAVISUT S, TANAVALEE A, THANAKIT V, et al. Spontaneous acetabular periprosthetic fracture in a patient continuously having zoledronic acid. Clin Orthop Surg. 2014;6(3):358-360. [25] HUANG TW, WANG CJ, SHIH HN, et al. Bone turnover and periprosthetic bone loss after cementless total hip arthroplasty can be restored by zoledronic acid: a prospective, randomized, open-label, controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):209. [26] SCOTT DF, WOLTZ JN, SMITH RR. Effect of zoledronic acid on reducing femoral bone mineral density loss following total hip arthroplasty: preliminary results of a prospective randomized trial. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(4):671-675. [27] JAKOBSEN T, KOLD S, SHIGUETOMI-MEDINA J, et al. Topical zoledronic acid decreases micromotion induced bone resorption in a sheep arthroplasty model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):441. [28] QASEEM A, FORCIEA MA, MCLEAN RM, et al. Treatment of Low Bone Density or Osteoporosis to Prevent Fractures in Men and Women: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(11):818-839. (责任编辑:GD,ZN,ZH) |
| [1] | An Yang, Liao Yinan, Xie Chengxin, Li Qinglong, Huang Ge, Jin Xin, Yin Dong. Mechanism of Inulae flos in the treatment of osteoporosis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [3] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [4] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [7] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [8] | Qin Qian, Yang Yang, Chen Jingfeng, Wang Shoujun, Ding Suying. Cut-off point of visceral fat area: predicting low bone mass in women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5577-5581. |
| [9] | An Yang, Liao Yinan, Xie Chengxin, Li Qinglong, Huang Ge, Jin Xin, Yin Dong. Mechanism of Inulae flos in the treatment of osteoporosis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5662-5669. |
| [10] | Yang Jiujie, Wang Tao, Li Zhi, Yang Lifeng, Tian Ye, Bi Zheng, Zeng Yaling. Cervical spondylosis with osteoporosis treated by the new pedicle fixation system through the anterior cervical approach with three-dimensional printing technology: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5249-5253. |
| [11] | Lin Ruohui, Chen Sainan, Ye Yunjin, Chen Juan, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang. Protective mechanism of Gushukang granule in a rat osteoporosis model based on TMT proteomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5141-5147. |
| [12] |
Li Yinglian, Chang Qiong.
Changes in serum tumor necrosis factor alpha, transforming growth factor beta 1, and interleukin-6 levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease combined with osteoporosis#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5085-5090.
|
| [13] | Zhang Fucai, Zheng Feng, Wang Furong, Chen Gang . Effects of paeonol on forkhead box O3a/Wnt signal pathway and vertebral bone mineral density in ovariectomized osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5091-5096. |
| [14] | Qin Yichuan, Zhao Bin, Yuan Jie, Xu Chaojian, Lü Jie Hao Jiaqi Wang Yongfeng. Effects of internal fixation types and osteoporosis on oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(30): 4767-4773. |
| [15] | Guo Haiwei, Xie Jiahao, Lin Yanping, Wang Yufeng, Yang Qingqi. Effects and safety of fenestrated and conventional pedicle screw combined with cement-augmentation in osteoporotic vertebral fixation: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(30): 4891-4899. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||