Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (24): 3875-3881.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1297
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between miRNA and pathological development of osteoarthritis
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Online:2019-08-28Published:2019-08-28 -
Contact:Yi Zhi, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Wang Jicheng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China; Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Project of Shaanxi Province, No. 2018ZDXM-SF-054 (to YZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jicheng, Yi Zhi.
share this article
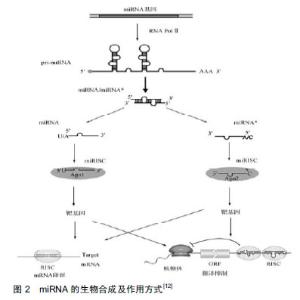
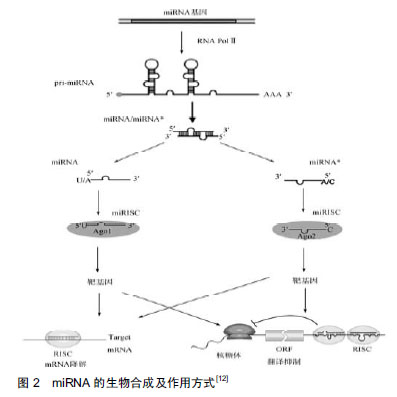
2.1 miRNA的生成及生物学作用 早在1993年,有研究者在丽新小杆线虫(C.elegans)体内发现了第1个miRNA-lin-4[9],直到2000年,Reinhart等[10]在哺乳动物体内发现了另一个具有转录后调节功能的小分子RNA:let-7。随着人们研究的不断深入,至今已发现1 000多种miRNA,每种miRNA调节多种mRNA,从而参与调控不同的生物过程[11]。 miRNA生成是一个非常复杂的生物过程,其包括胞质合成和胞核合成2个部分,并需要多种酶的参 与[12],见图2。首先,编码miRAN的基因在细胞核内经RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录形成具有特殊发夹结构[多聚腺苷酸尾巴(AAAAA)和帽子结构(7MGpppG)]的pri-miRNA,接着核酸酶Drosha(核糖核酸酶Ⅲ)将pri-miRNA进行微切割并处理成具有茎环结构、大小为70-80 nt的miRNA前体,即pre-miRNA。在Ran-GTP辅助下,细胞质转运蛋白Exportins-5将pre-miRNA从细胞核内运输到细胞胞质中,然后由核糖核酸酶Ⅲ(Dicer酶)将其剪切成为大小为19-23 nt的miRNA:miRNA*复合结构。miRNA*通常被降解[13-14],而miRNA与AGO(argonaute)蛋白结合形成成熟miRNA。成熟的miRNA与RNA诱导的沉默复合物结合发挥其生物作用,包括2种方式:①miRNA与靶mRNA完全互补时,miRNA的作用方式是降解靶mRNA[15-16];②miRNA与靶mRNA不完全互补时,miRNA与3' UTRs结合抑制靶mRNA的翻译[17-18],导致相关蛋白表达水平降低。在人体中,miRNA与靶mRNA主要是不完全互补,对基因转录后的翻译进行调控。"

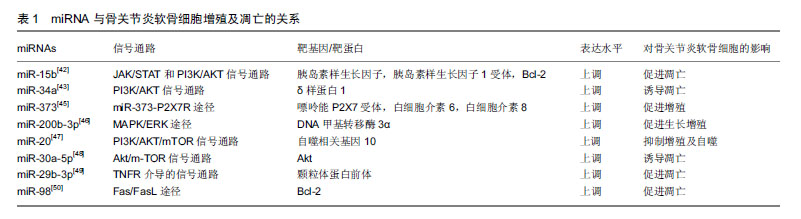
2.2 骨关节炎的病理生理 骨关节炎的发病机制尚未完全明了,其发病与年龄、肥胖、感染及创伤等多种因素相关[19]。有研究表明,软骨细胞外基质降解及软骨细胞过度凋亡导致的关节软骨退变,是骨关节炎的主要病理变 化[20]。软骨细胞是软骨组织中的主要细胞类型,其在维持骨骼、关节结构及功能方面发挥重要作用[21-22]。细胞外基质主要由Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖组成,成熟软骨细胞能够合成及分泌细胞外基质,其在维持细胞外基质合成代谢和分解代谢之间的动态平衡中发挥关键作用[23-24]。有研究表明,基质金属蛋白酶13和具有血小板反应蛋白基序的解整合素和金属蛋白酶(recombinant a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin 5,ADAMTS-5)是导致细胞外基质降解的2种主要水解酶,而基质金属蛋白酶13主要降解Ⅱ型胶原蛋白[25-28]。既往研究表明,过多的机械应激、炎症及促炎因子(白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α)参与了骨关节炎的病理过程[29-30]。由促炎因子诱导的软骨损伤过程,包括软骨细胞外基质(细胞外基质)代谢紊乱、软骨稳态破坏和基质降解酶(如基质金属蛋白酶13)的表达增强[31]。有研究报道,miRNA可通过调节炎症递质、血管内皮生长因子和神经生长因子的表达参与骨关节炎的病理过程[32]。进一步的研究表明,miRNA可能抑制或促进基质金属蛋白酶和胶原蛋白的表达,导致细胞外基质降解和软骨细胞凋亡,最终导致骨关节炎[33-34]。 2.3 miRNA在骨关节炎中的异常表达 Tew等[35]对365例骨关节炎患者和健康者软骨组织中miRNA的表达谱进行了分析,发现有16个miRNA出现了差异表达;通过对723种miRNA进行分析发现[36],7种miRNA显示出统计学意义的差异表达,在这7种人类miRNA中,1种在骨关节炎软骨细胞(hsa-miR-483-5p)中上调,6种在正常软骨细胞中上调(hsa-miR-149*,hsa-miR-582-3p,hsa-miR-1227,hsa-miR-634,hsa-miR-576-5p和hsa-miR-641);Zhang等[37]的研究发现,在骨关节炎软骨组织中包括8个上调的miRNA(miR-193b、miR-199a-3p/hsa-miR-199b-3p、miR- 455-3p、miR-210、miR-381、miR-92a、miR-320c和miR-136)及4种下调的miRNA(miR-490-5p、miR-4287、miR-BART8 *和miR-US25-1*)。Marta等[3]对19种miRNA表达的评估发现, miR-138-5p、miR-146a-5p、miR-335-5p和miR-9-5p的表达在骨关节炎中显著上调。Wang等[38]的研究发现,miRNA-98在骨关节炎软骨组织中表达水平升高。Zhang等[39]的研究发现,miR-21在骨关节炎软骨组织中过表达。Zhang等[40]的研究发现,miR-502-5p在骨关节炎软骨组织中显著低表达。Song等[41]的研究发现,miR-222在骨关节炎软骨组织中呈低表达。 2.4 miRNA与骨关节炎 2.4.1 miRNA与软骨细胞增殖、凋亡 Cao等[42]研究发现,miR-15b通过靶向胰岛素样生长因子和胰岛素样生长因子受体抑制软骨细胞增殖,并通过靶向Bcl-2加速软骨细胞凋亡。Zhang等[43]研究发现miR-34a在骨关节炎患者中呈过表达,miR-34a可直接抑制δ样蛋白1mRNA,导致骨关节炎软骨细胞中δ样蛋白1、总PI3K和p-AKT浓度下降,诱导细胞凋亡,在手术诱导的骨关节炎大鼠膝关节中,通过注射miR-34a拮抗剂可减弱关节软骨细胞死亡和软骨损伤。相关研究表明,抑制miR-34a表达能够解除白细胞介素1β诱导的Cyr61抑制,促进骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖[44]。Zhang等[45]发现miR-373在骨关节炎患者软骨细胞中表达下调,过表达miR-373通过抑制嘌呤能P2X7受体及炎性因子(如白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8)的表达来促进软骨细胞增殖。Wu等[46]研究发现,miR-200b-3p通过抑制DNA甲基转移酶3α的表达抑制基质金属蛋白酶的分泌,促进Ⅱ型胶原的合成,进而促进骨关节炎软骨细胞的生长和增殖。He等[47]研究发现,miR-20可通过PI3K/AKT/ mTOR信号通路靶向自噬相关基因10,抑制软骨细胞增殖和自噬。Shen等[48]发现miR-30a-5p在骨关节炎患者软骨中高表达,其可通过靶向Akt基因阻断G0/G1期软骨细胞,诱导软骨细胞凋亡;Chen等[49]研究表明,miR-29b-3p可通过靶向颗粒体蛋白前体促进软骨细胞凋亡和骨关节炎的发生,注射miR-29b-3p拮抗剂可延缓该过程。有研究表明,miR-98可能通过下调骨关节炎发病机制中Bcl-2的表达来促进软骨细胞凋亡和软骨降解[50]。miRNA与骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖及凋亡的关系,见表1。"
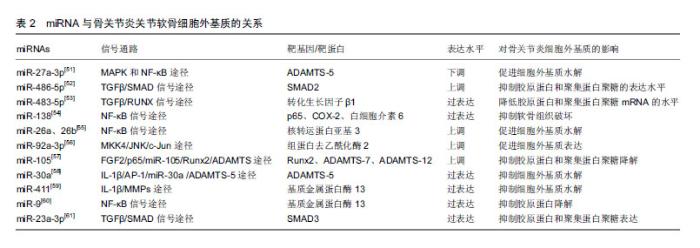
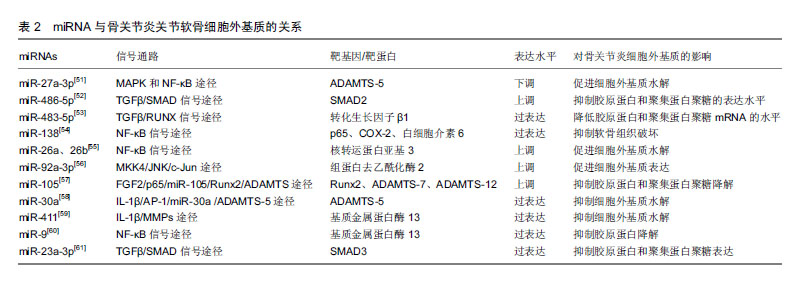
2.4.2 miRNA与关节软骨细胞外基质 已有大量文献证实,基质金属蛋白酶13与ADAMTS-5是导致细胞外基质降解的2种主要水解酶,而基质金属蛋白酶13主要降解Ⅱ型胶原蛋白[25-28]。 Li等[51]研究发现miR-27a-3p在骨关节炎患者中表达下调,白细胞介素1β可通过MAPK和NF-κB途径抑制miR-27a-3p的活性,增加ADAMTS-5的表达,进而导致细胞外基质降解,促进骨关节炎的发生。Shi等[52]发现miR-486-5p在骨关节炎患者中呈高表达,用miR-486-5p模拟物处理CHON-001人软骨细胞后,抑制了细胞的增殖和迁移,并且还抑制Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达,导致骨关节炎的发生。Xu等[53]研究发现miR-483-5p在骨关节炎患者中呈过表达,其能够降低转化生长因子β1的表达,而敲除miR-483-5p则显著提高转化生长因子β1在mRNA和蛋白水平的表达,进一步的研究发现,过表达的miR-483-5p通过下调转化生长因子β1表达显著降低胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖mRNA的水平,并增加Runx2和基质金属蛋白酶13 mRNA的水平,这些发现表明miR-483-5p对维持软骨组织具有重要作用。Wei等[54]研究发现骨关节炎软骨组织中miR-138水平显著降低,过表达miR-138能够抑制人骨关节炎软骨细胞和软骨形成SW1353细胞中p65、COX-2和白细胞介素6的蛋白质水平,延缓骨关节炎的进展。有研究发现miR-26a和miR-26b在骨关节炎患者中表达下调,用miR-26a或miR-26b抑制剂转染后,基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶13和环加氧酶2的表达水平上调,进一步研究发现,miR-26a和miR-26b的下调可能通过促进NF-κB信号传导途径参与骨关节炎的发生[55]。Mao等[56]研究发现骨关节炎软骨中miR-92a-3p表达下调,miR-92a-3p能增强聚集蛋白聚糖、软骨寡聚蛋白和胶原蛋白启动子上的H3乙酰化,并且还促进软骨基质表达。研究发现骨关节炎患者中miR-105表达下调,并且与骨关节炎患者中上调的Runx2、ADAMTS-7和ADAMTS-12表达呈负相关[57]。Ji等[58]研究发现骨关节炎软骨中miR-30a与ADAMTS-5表达呈负相关,过表达miR-30a可显著抑制ADAMTS-5的表达。Wang等[59]研究发现在骨关节炎软骨组织中,miR-411与基质金属蛋白酶13呈负相关,过表达miR-411能够显著抑制基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,延缓骨关节炎进程。Zhang等[60]发现,miR-9的表达水平在骨关节炎患者软骨组织中显著降低,在骨关节炎大鼠膝关节腔内注射miR-9拮抗剂,可显著抑制骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织中基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,降低胶原降解并增强胶原蛋白,这说明miR-9可抑制基质金属蛋白酶13的表达水平,降低其对胶原蛋白的抑制作用,延缓骨关节炎病理过程。Kang等[61]研究发现骨关节炎软骨中miR-23a-3p表达明显较高,SMAD3表达明显低于正常组织,进一步的研究发现,过表达的miR-23a-3p通过直接靶向SMAD3抑制Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达,进而促进骨关节炎进展。miRNA与关节软骨细胞外基质的关系,见表2。 2.4.3 miRNA与软骨细胞炎症 Ding等[62]研究发现miR-93具有抑制炎症作用,使用脂多糖诱导软骨细胞损伤后,miR-93表达显著升高,主要抑制促炎细胞因子(包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6)的表达来减弱炎症反应;进一步的研究发现,Toll样受体4是miR-93在软骨细胞中的直接靶标,miR-93通过Toll样受体4介导的NF-κB信号通路参与骨关节炎的炎症反应,miR-93拮抗剂可促进炎症的发生。Wang等[63]研究发现,miR-142-3p表达在骨关节炎小鼠关节软骨组织中显著降低,过表达miR-142-3p可显著抑制NF-κB和促炎细胞因子的产生,包括白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α;高迁移率族蛋白1是骨关节炎的重要炎症递质,进一步的研究发现,miR-142-3p可通过抑制高迁移率族蛋白1介导的NF-κB信号通路,抑制骨关节炎中炎症细胞及炎症因子的表达。Tardif等[64]发现miR-140在骨关节炎软骨细胞中低表达,过表达miR-140可显著抑制炎症反应。Yang等[65]研究发现miR-365可促进骨关节炎关节软骨炎症因子的表达,诱导骨关节炎的发生及发展。 2.4.4 miRNA与关节疼痛 绝大部分骨关节炎患者会出现关节疼痛,关节疼痛既是骨关节炎的主要临床症状,也是导致患者关节活动障碍的原因之一。周围疼痛感受器与中枢感觉系统之间的信号传导可导致疼痛。Wang等[66]研究发现,miR-146a参与了骨关节炎关节疼痛,其通过对白细胞介素1受体相关激酶1和肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6进行调控,改变上述细胞因子的表达,进而影响神经细胞的分化与疼痛发生。既往研究发现,过表达miR-199a-3P可使骨关节炎动物模型中炎症因子表达上调,诱发疼痛效应,异常表达的miR-146a和miR-183能够加剧膝关节疼痛,miR-558在骨关节炎软骨组织中低表达,转染miR-558模拟物能抑制炎症因子的表达并减轻疼痛[67]。 2.4.5 miRNA与骨关节炎早期诊断 Soyocak等[34]研究发现骨关节炎患者血清中的miR-146a和miR-155表达明显高于健康对照组,且随骨关节炎的进程增加,因此miR-146a和miR-155可作为骨关节炎的辅助诊断标志物,骨关节炎病程越长其表达越高。既往研究发现let-7e在骨关节炎患者血清中低表达,其可作为诊断骨关节炎的标志物。同样有研究报道miR-4284和miR-1282可作为诊断骨关节炎的标志物[67]。 2.4.6 miRNA与骨关节炎治疗 Cui等[68]研究发现,miR-634可通过靶向PIK3R1基因调节PI3K/Akt/S6和PI3K/Akt/mTOR/S6轴来抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞的存活和基质合成,miR-634抑制剂可逆转该过程。Si等[69]发现在骨关节炎大鼠模型关节腔内注射miR-140,能够调节大鼠的细胞外基质稳态,延缓骨关节炎进展,miR-14可能是一种新型潜在治疗靶点。Baek等[70]研究发现miR-449a在骨关节炎中表达上调,在骨关节炎动物模型关节腔内注射锁核酸-抗-miR-449a能够增加软骨再生,Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖表达水平升高,延缓了骨关节炎进展。 "
| [1]Tarucuy RL,Lynch SA.Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoarthritis.Orthop Surg.2013;40(4):821-836. [2]Fransen M,McConnell S,Harmer AR,et al.Exercise for osteoarthritis of the knee: A Cochrane systematic review.Br J Sports Med.2015;49(24):1554-1557.[3]Kopańska M,Szala D,Czech J,et al.MiRNA expression in the cartilage of patients with osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):51.[4]Aigner T,Söder S,Gebhard PM,et al. Mechanisms of Disease: role of chondrocytes in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis- structure, chaos and senescence. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3(7):391-399.[5]Le LT,Swingler TE,Clark IM.Review: the role of microRNAs in osteoarthritis and chondrogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65(8):1963-1974.[6]Beyer C,Zampetaki A,Lin NY,et al.Signature of circulating microRNAs in osteoarthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(3): e18.[7]Cannell IG,Kong YW,Bushell M.How do microRNAs regulate gene expression?Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:1224-1231.[8]Ha M,Kim VN.Regulation of microRNA biogenesis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2014;15(8):509-524.[9]Lee RC,Feinbaum RL,Ambros V.The C.elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14.Cell.1993;75(5):843-854.[10]Reinhart BJ,Slack FJ,Basson M.The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature.2000;403(6772):901-906.[11]Farh KK,Grimson A,Jan C,et al.The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science.2005;310(5755):1817-1821.[12]马圣运,白玉,韩凝,等.miRNA生物合成及其功能研究的新发现[J].遗传,2012,34(4):5-10.[13]Carthew RW,Sontheimer EJ.Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs.Cell.2009;136(4):642-655.[14]Zeng Y,Cullen BR.Structural requirements for premicroRNA binding and nuclear export by Exportin 5.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(16):4776-4785.[15]Rhoades MW,Reinhart BJ,Lim LP,et al.Prediction of plant microRNA targets.Cell. 2002;110(4):513-520.[16]Chen X.MicroRNA biogenesis and function in plants.FEBS Lett.2005;579(26):5923-5931.[17]Smalheiser NR,Torvik VI.Complications in mammalian microRNA target prediction. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342: 115-127.[18]Lewis BP,Shih IH,Jones-Rhoades MW,et al.Prediction of Mammalian MicroRNA Targets.Cell.2003; 115(7):787-798.[19]Yang M,Jiang L,Wang Q,et al.Traditional Chinese medicine for knee osteoarthritis: An overview of systematic review.Plos One.2017;12(12):e0189884.[20]van der Kraan PM,van den Berg WB.Chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis: role in initiation and progression of cartilage degeneration? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(3):223-232. [21]Nielsen FK,Egund N,Jørgensen A,et al.Risk factors for joint replacement in knee osteoarthritis; a 15-year follow-up study.BMC MusculoskeletDisord.2017;18(1):510.[22]Duarte N,Rodrigues AM,Branco JDC,et al.Health and Lifestyles Factors Associated With Osteoarthritis among Older Adults in Portugal. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017; 4:192.[23]Yan S,Wang M,Zhao J,et al.MicroRNA-34a affects chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation by targeting the SIRT1/p53 signaling pathway during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Med.2016;38(1):201209.[24]Goldring MB.Update on the biology of the chondrocyte and new approaches to treating cartilage diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol.2006;20(5):1003-1025.[25]Fosang AJ,Last K,Knäuper V,et al.Degradation of cartilage aggrecan by collagenase-3 (MMP-13).FEBS Lett. 1996; 380(1-2):17-20.[26]Goldring MB,Marcu KB.Cartilage homeostasis in health and rheumatic diseases.Arthritis ResTher.2009;11(3):224.[27]Mitchell PG,Magna HA,Reeves LM,et al.Cloning, expression, and type II collagenolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase-13 from human osteoarthritic cartilage.Clin Invest.1996;97(3):761-768.[28]Wang M,Sampson ER,Jin H,et al.MMP13 is a critical target gene during the progression of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther.2013;15(1):R5.[29]Loeser RF,Collins JA,Diekman BO.Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2016;12(7):412-20.[30]Mobasheri A,Rayman MP,Gualillo O,et al.The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2017;13(5):302-311.[31]Kapoor M,Martel-Pelletier J,Lajeunesse D,et al.Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2011;7(1):33-42.[32]Tao L,Zeng Y,Wang J,et al.Differential microRNA expression in aristolochic acid-induced upper urothelial tract cancers ex vivo.Mol Med Rep.2015;12(5):6533-6546.[33]Zhen Y, Xinghui Z, Chao W, et al. Several microRNAs could predict survival in patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer. Sci Rep.2017;7:45195.[34]Soyocak A,Kurt H,Ozgen M,et al.miRNA-146a, miRNA-155 and JNK expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells according to grade of knee osteoarthritis.Gene. 2017; 627:207-211.[35]Tew SR,Mcdermott BT, Fentem RB,et al.Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of Messenger RNA Decay in Normal and Osteoarthritic Human Articular Chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheumatol.2015;66(11):3052-3061.[36]Silvia DP,Claudia C,Emma ML,et al.Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal and osteoarthritic human chondrocytes.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13(1): 144.[37]Zhang Z,Kang Y,Zhang Z,et al.Expression of microRNAs during chondrogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2012;20(12):1638-1646.[38]Wang GL,Wu YB,Liu JT,et al.Upregulation of miR-98 inhibits apoptosis in cartilage cells in osteoarthriti.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers.2016;20(11):645-653.[39]Zhang Y,Jie J,Yang S,et al.MicroRNA-21 controls the development of osteoarthritis by targeting GDF-5 in chondrocytes.Exp Mol Med.2014;46(2):e79.[40]Zhang G,Sun Y,Wang Y,et al.MiR-502-5p inhibits IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury by targeting TRAF2.Cell Immunol.2016;302:50-57.[41]Song J,Jin EH,Kim D,et al. MicroRNA-222 regulates MMP-13 via targeting HDAC-4 during osteoarthritis pathogenesis.Bba Clinical.2015;3(1):79-89.[42]Cao P,Feng Y,Deng M,et al.MiR-15b is a key regulator of proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes from patients with condylar hyperplasia by targeting IGF1, IGF1R and BCL2. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2018.pii: S1063-4584(18)31481-X.[43]Zhang W,Hsu P,Zhong B,et al.MiR-34a Enhances Chondrocyte Apoptosis, Senescence and Facilitates Development of Osteoarthritis by Targeting DLL1 and Regulating PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 48(3):1304-1316. [44]Yang B,Ni J,Long H,et al.IL-1β-induced miR-34a up-regulation inhibits Cyr61 to modulate osteoarthritis chondrocyte proliferation through ADAMTS-4.J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119(10):7959-7970. [45]Zhang W,Zhong B,Zhang C,et al.miR-373 regulates inflammatory cytokine-mediated chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis by targeting the P2X7 receptor.FEBS Open Bio. 2018;8(3):325-331.[46]Wu J,Tao Y,Shang A,et al.Effect of the interaction between MiR-200b-3p and DNMT3A on cartilage cells of osteoarthritispatients.J Cell Mol Med.2017;21(10):2308-2316.[47]He W,Cheng Y.Inhibition of miR-20 promotes proliferation and autophagy in articular chondrocytes by PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother.2018;97:607-615.[48]Shen PF,Qu YX,Wang B,et al.miR-30a-5p promotes the apoptosis of chondrocytes in patients with osteoarthritis by targeting protein kinase B.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017; 97(39):3079-3084.[49]Chen L,Li Q,Wang J,et al. MiR-29b-3p promotes chondrocyte apoptosis and facilitates the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by targeting PGRN.J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(12): 3347-3359.[50]Wang J,Chen L,Jin S,et al. MiR-98 promotes chondrocyte apoptosis by decreasing Bcl-2 expression in a rat model of osteoarthritis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016; 48(10):923-929.[51]Li X,He P,Li Z,et al.Interleukin 1β mediated suppression of microRNA 27a 3p activity in human cartilage via MAPK and NF κB pathways: A potential mechanism of osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Mol Med Rep.2018;18(1):541-549.[52]Shi J,Guo K,Su S,et al.miR 486 5p is upregulated in osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte proliferation and migration by suppressing SMAD2.Mol Med Rep. 2018; 18(1):502-508. [53]Xu R,Li J,Wei B,et al.MicroRNA-483-5p Modulates the Expression of Cartilage-Related Genes in Human Chondrocytes through Down-Regulating TGF-β1 Expression.Tohoku J Exp Med.2017;243(1):41-48.[54]Wei ZJ,Liu J,Qin J.miR-138 suppressed the progression of osteoarthritis mainly through targeting p65.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2017;21(9):2177-2184.[55]Yin X,Wang JQ,Yan SY.Reduced miR 26a and miR 26b expression contributes to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis via the promotion of p65 translocation.Mol Med Rep. 2017; 15(2):551-558. [56]Mao G,Zhang Z,Huang Z, et al. MicroRNA-92a-3p regulates the expression of cartilage-specific genes by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2 in chondrogenesis and degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2017;25(4):521-532.[57]Ji Q,Xu X, Xu Y,et al. miR-105/Runx2 axis mediates FGF2-induced ADAMTS expression in osteoarthritis cartilage. J Mol Med.2016;94(6):681-694. [58]Ji Q,Xu X,Zhang Q,et al.The IL-1β/AP-1/miR-30a/ADAMTS-5 axis regulates cartilage matrix degradation in human osteoarthritis.J Mol Med.2016;94(7):771-785.[59]Wang G,Zhang Y,Zhao X,et al. MicroRNA-411 inhibited matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression in human chondrocytes.AmJ Trans Res.2015;7(10):2000-2006.[60]Zhang H,Song B,Pan Z.Downregulation of microRNA-9 increases matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression levels and facilitates osteoarthritis onset.Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3): 3708-3714. [61]Kang L,Yang C,Song Y, et al. MicroRNA-23a-3p promotes the development of osteoarthritis by directly targeting SMAD3 in chondrocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478(1): 467-473.[62]Ding Y,Wang L,Zhao Q,et al.MicroRNA 93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis by targeting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2019;43:779-790.[63]Wang X,Guo Y,Wang C,et al.MicroRNA-142-3p Inhibits Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Inflammation in Osteoarthritis by Targeting HMGB1.Inflammation.2016;39(5):1-11.[64]Tardif G,Pelletier JP,Fahmi H,et al.NFAT3 and TGF-β/SMAD3 regulate the expression of miR-140 in osteoarthritis.Arth Res Ther.2013;15(6):R197.[65]Yang X,Guan Y,Tian S, et al.Mechanical and IL-1β Responsive miR-365 Contributes to Osteoarthritis Development by Targeting Histone Deacetylase 4.Int J Mol Sci.2016;17(4):436.[66]Wang JH,Shih KS,Wu YW,et al.Histone deacetylase inhibitors increase microRNA-146a expression and enhance negative regulation of interleukin-1β signaling in osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; 21(12):1987-1996.[67]顾宗欣,王五洲.微小RNA对骨关节炎发生发展影响的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(12):1102-1105.[68]Cui X,Wang S,Cai H,et al. Overexpression of microRNA-634 suppresses survival and matrix synthesis of human osteoarthritis chondrocytes by targeting PIK3R1.Sci Rep. 2016;6:23117.[69]Si HB,Zeng Y,Liu SY,et al.Intra-articular injection of microRNA-140 (miRNA-140) alleviates osteoarthritis (OA) progression by modulating extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(10): 1698-1707.[70]Baek D,Lee KM,Park KW,et al.Inhibition of miR-449a Promotes Cartilage Regeneration and Prevents Progression of Osteoarthritis in In Vivo Rat Models.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;13:322-333. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [5] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [6] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [7] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [8] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [9] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [10] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [11] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [12] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [13] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [14] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [15] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||