Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 1092-1097.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.07.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Morphological characteristics of hips in children with developmental dislocation of the hip: three-dimensional reconstruction of computed tomography scan
Hao Yun1, He Jin-peng2
- 1Department of Radiology, 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Tongji Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
-
Revised:2016-11-04Online:2017-03-08Published:2017-04-11 -
Contact:He Jin-peng, M.D., Department of Pediatric Surgery, Tongji Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Hao Yun, Master, Physician, Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hao Yun, He Jin-peng. Morphological characteristics of hips in children with developmental dislocation of the hip: three-dimensional reconstruction of computed tomography scan[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1092-1097.
share this article

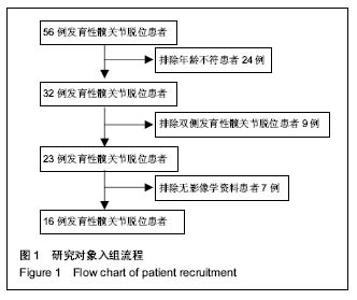
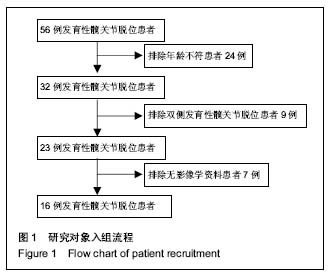
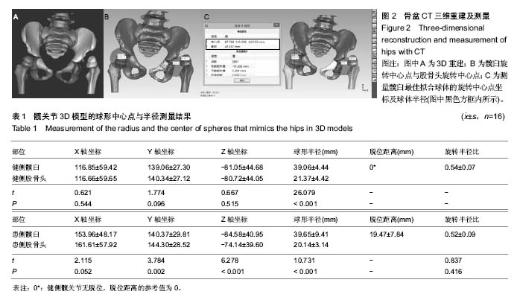
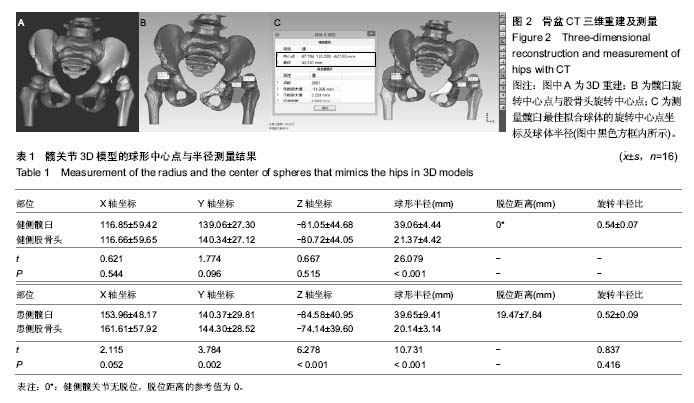
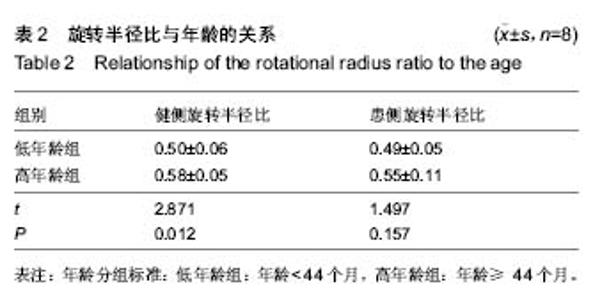
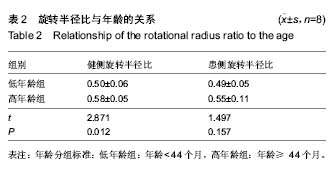
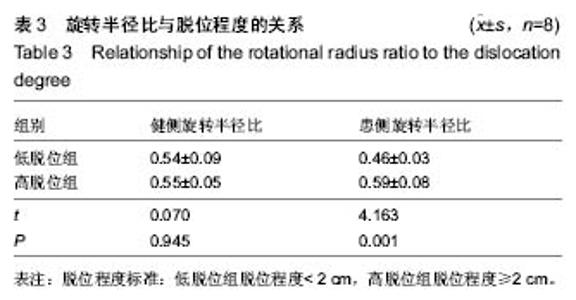
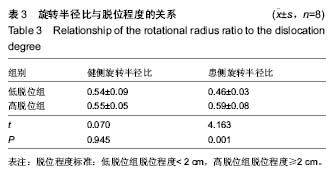
健侧髋臼最佳拟合球体X轴、Y轴和Z轴坐标值平均为116.85±59.42、139.06±27.30和-81.05±44.68,健侧髋臼的最佳拟合球体半径为(39.06±4.44)mm;健侧股骨头最佳拟合球体X轴、Y轴和Z轴坐标值平均为116.66±59.65、140.34±27.12和-80.72±44.05,与髋臼三维坐标值进行配对t 检验,差异无显著性意义(P均 > 0.05),健侧股骨头的最佳拟合球体半径为(21.37±4.42) mm,结果见表1。 患侧髋臼最佳拟合球体X轴、Y轴和Z轴坐标值平均为153.96±48.17、140.37±29.81和-84.58±40.95,患侧髋臼的最佳拟合球体半径为(39.65±9.41) mm;患侧股骨头最佳拟合球体X轴、Y轴和Z轴坐标值平均为161.61±57.92、144.30±28.52和-74.14±39.60,患侧股骨头的最佳拟合球体半径为(20.14±3.14) mm;与髋臼三维坐标值进行配对t检验,差异有显著性意义(PX > 0.05,PY < 0.05,PZ < 0.05),结果见表1。 上述结果符合实际中髋关节的空间位置关系。再根据三维坐标系中距离公式1计算患侧髋关节脱位距离;患侧髋关节三维脱位距离平均(19.47±7.84) mm。根据公式2计算髋关节的旋转半径比,健侧髋关节旋转半径比平均为0.54±0.07,患侧髋关节旋转半径比平均为0.52±0.09,进行配对t 检验,差异无显著性意义(P均 > 0.05)。"

| [1] Cooper AP, Doddabasappa SN, Mulpuri K. Evidence-based management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(3):341-354.[2] Thomas SR, Wedge JH, Salter RB. Outcome at forty-five years after open reduction and innominate osteotomy for late-presenting developmental dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(11):2341-2350.[3] Graf R. The diagnosis of congenital hip-joint dislocation by the ultrasonic Combound treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1980;97(2):117-133.[4] Harcke HT. Screening newborns for developmental dysplasia of the hip: the role of sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162(2):395-397.[5] Omero?lu H. Use of ultrasonography in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(2):105-113.[6] Vedantam R, Bell MJ. Dynamic ultrasound assessment for monitoring of treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15(6):725-728.[7] Sink EL, Ricciardi BF, Torre KD, et al. Selective ultrasound screening is inadequate to identify patients who present with symptomatic adult acetabular dysplasia. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(6):451-455.[8] White KK, Sucato DJ, Agrawal S, et al. Ultrasonographic findings in hips with a positive Ortolani sign and their relationship to Pavlik harness failure. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(1):113-120.[9] White KK, Sucato DJ, Agrawal S, et al. Ultrasonographic findings in hips with a positive Ortolani sign and their relationship to Pavlik harness failure. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(1):113-120.[10] Chin MS, Betz BW, Halanski MA. Comparison of hip reduction using magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography in hip dysplasia. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(5):525-529.[11] Kotlarsky P, Haber R, Bialik V, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: What has changed in the last 20 years. World J Orthop. 2015;6(11):886-901.[12] Schwend RM, Shaw BA, Segal LS. Evaluation and treatment of developmental hip dysplasia in the newborn and infant. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2014;61(6):1095-1107.[13] Bin K, Laville JM, Salmeron F. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in neonates: evolution of acetabular dysplasia after hip stabilization by brief Pavlik harness treatment. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(4):357-361.[14] Jia J, Li L, Zhang L, et al. Can excessive lateral rotation of the ischium result in increased acetabular anteversion? A 3D-CT quantitative analysis of acetabular anteversion in children with unilateral developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(8):864-869.[15] Kothari A, Grammatopoulos G, Hopewell S, et al. How Does Bony Surgery Affect Results of Anterior Open Reduction in Walking-age Children With Developmental Hip Dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(5):1199-1208.[16] Sankar WN, Neubuerger CO, Moseley CF. Femoral head sphericity in untreated developmental dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30(6):558-561.[17] 何金鹏,郝运,王小林,等.数字化模板联合骨性参数测量辅助髋关节假体型号选择的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015, 29(6): 688-692.[18] Stanton RP, Capecci R. Computed tomography for early evaluation of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992;12(6):727-730.[19] Mandel DM, Loder RT, Hensinger RN. The predictive value of computed tomography in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998;18(6):794-798.[20] Argenson JN, Ryembault E, Flecher X, et al. Three-dimensional anatomy of the hip in osteoarthritis after developmental dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(9): 1192-1196.[21] 郝运,何金鹏.计算机辅助膝关节内外翻畸形个体化矫形[J].CT 理论与应用研究,2016,25(4): 393-401. [22] Zhao X, Yan YB, Cao PC, et al. Surgical results of developmental dysplasia of the hip in older children based on using three-dimensional computed tomography. J Surg Res. 2014;189(2):268-273.[23] Franceschi JP, Sbihi A,Computer Assisted Orthopedic Surgery-France (CAOS-France). 3D templating and patient-specific cutting guides (Knee-Plan) in total knee arthroplasty: postoperative CT-based assessment of implant positioning. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6 Suppl): S281-286.[24] Chin KR, Mills MV, Seale J, et al. Ideal starting point and trajectory for C2 pedicle screw placement: a 3D computed tomography analysis using perioperative measurements. Spine J. 2014;14(4):615-618.[25] Fukunishi S, Okahisa S, Fukui T, et al. Significance of preoperative 3D-CT angiography for localization of the femoral artery in complicated THA. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(3): 457-464.[26] Shang C, Liu T, Xie H, et al. Spatial changes of the peri-acetabular pelvic in developmental dysplasia of the hip---a combined 3-dimentional computed tomography (3D-CT) study in patients and experimental study in rats.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(12):4983-4989.[27] Jia J, Li L, Zhang L, et al. Can excessive lateral rotation of the ischium result in increased acetabular anteversion? A 3D-CT quantitative analysis of acetabular anteversion in children with unilateral developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(8):864-869.[28] Li X, Viceconti M, Cohen MC, et al. Developing CT based computational models of pediatric femurs. J Biomech. 2015; 48(10):2034-2040.[29] Chan HH, Siewerdsen JH, Vescan A, et al. 3D Rapid Prototyping for Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery: Applications in Image-Guidance, Surgical Simulation and Patient-Specific Modeling. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136370.[30] 何金鹏. 3D重建与 3D打印技术在恶性骨与软组织肿瘤治疗中的应用研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2014:1-120.[31] Liu XZ, Shu DL, Ran W, et al. Digital surgical templates for managing high-energy zygomaticomaxillary complex injuries associated with orbital volume change: a quantitative assessment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(10):1712-1723. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [3] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [4] | Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe. Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [5] | Pan Baoshun, Fang Zhen, Gao Mingjie, Fang Guiming, Chen Jinshui. Design for posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation system with fusion cage based on imaging data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1372-1376. |
| [6] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [7] | Lu Pan, Zhang Chunlin, Wang Yongkui, Yan Xu, Dong Chao, Yue Yisen, Li Long, Zhu Andi. Volume changes of cervical herniated discs after open-door laminoplasty and conservative treatment as assessed by three-dimensional volume method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1395-1401. |
| [8] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [10] | Xu Kuishuai, Zhang Liang, Chen Jinli, Ren Zhongkai, Zhao Xia, Li Tianyu, Yu Tengbo. Effect of force line changes on lower limb joints after medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 821-826. |
| [11] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [12] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [13] | Ma Chao, Wang Fei, Liu Xiaomin, Wang Ziyun, Xu Kui, Yang Wendong, Feng Wei. Quantification of the objective index of lumbar disc herniation with body surface topography map: three-dimensional angulation of the elastically fixed turning point of the lower back curve [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 924-928. |
| [14] | Yi Xinrong, Jia Fuquan, He Xin, Zhang Shaojie, Ren Xiaoyan, Li Zhijun. Establishment of cervical bone age equation for male adolescents aged 8-16 years old in Hohhot based on thin-slice CT [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 954-958. |
| [15] | Wang Shaoling, Wang Yanxue, Zheng Yaochao, Yu Shaojun, Ma Chao, Wu Shaoling. Feasibility of ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection in rabbit hip joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 657-662. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||