Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (5): 780-788.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.05.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Safety and efficacy of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for dilated cardiomyopathy: a Meta-analysis
Ai Jin-wei1, 2, 3, Liu Ying1, Liu Chu-fan1, Pei Bin1, 2, 3
- 1Evidence-Based Medicine Center, 2Department of Biotherapy, 3Department of Orthopedics, Xiangyang Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 442000, Hubei Province, China
-
Online:2017-02-18Published:2017-03-20 -
Contact:Pei Bin, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Professor, Evidence-Based Medicine Center, Xiangyang Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 442000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Ai Jin-wei, Master, Attending physician, Evidence-Based Medicine Center, Xiangyang Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 442000, Hubei Province, China Liu Ying, Master, Associate chief nurse, Evidence-Based Medicine Center, Xiangyang Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 442000, Hubei Province, China Ai Jin-wei and Liu Ying contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the General Project for Western Medicine of Hubei Province in 2015-2016, No. WJ2015MB187; the Key Teaching and Research Project of Hubei University of Medicine, No. 2015025
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ai Jin-wei, Liu Ying, Liu Chu-fan, Pei Bin. Safety and efficacy of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for dilated cardiomyopathy: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(5): 780-788.
share this article
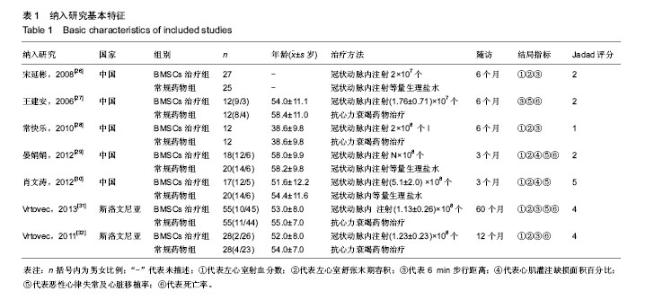
2.1 文献检索结果 各数据库初检出文献1 375篇,Note Express3.1软件排重后获文献1 217篇,经标题、摘要初筛获得可能纳入的文献119篇,再通过阅读全文复筛,最终7个RCT符合纳入标准被纳入[26-32]。其中,中文文献5篇[26-30],英文文献2篇[31-32]。 2.2 纳入文献基本特征 7个RCT共涉及扩张性心肌病患者341例,其中BMSCs治疗组169例,常规药物治疗组172例。扩张性心肌病均以症状、体征及影像学检查确诊,并符合1995年世界卫生组织/国际心脏病学协会诊断标准。各项研究均描述为两组间基线均衡,具有可比性。BMSCs治疗组干预措施为BMSCs移植加常规抗心力衰竭药物治疗,BMSCs移植均为经皮冠状动脉内注射,给细胞量介于107-108个;对照组均运用常规药物抗心力衰竭治疗,具体药物包括利尿剂、血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂、血管紧张素受体拮抗剂、β-受体拮抗剂、地高辛等,3个研究对照组设计为“假手术”——冠脉内注射生理盐水[26,29-30]。随访时间介于3-60个月。结局指标主要包括:左心室射血分数、左室舒张末期内径、6 min步行距离、心肌灌注缺损面积百分比、恶性心律失常及心脏移植率、死亡率。3个研究改良Jadad量表评分≥4分,评价为“高质量研究”[30-32],其余研究均评价为“低质量研究”,总体研究方法学质量较低。纳入研究基本特征见表1。"
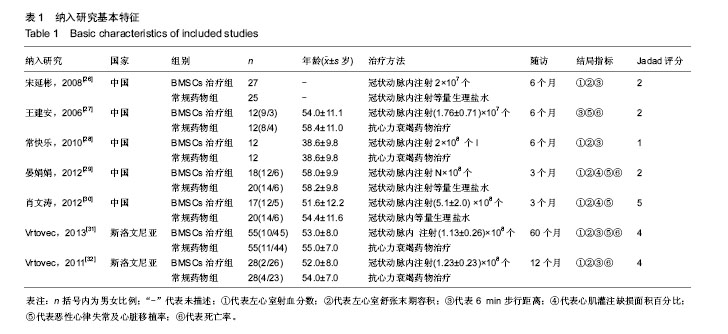
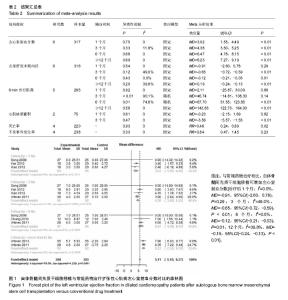
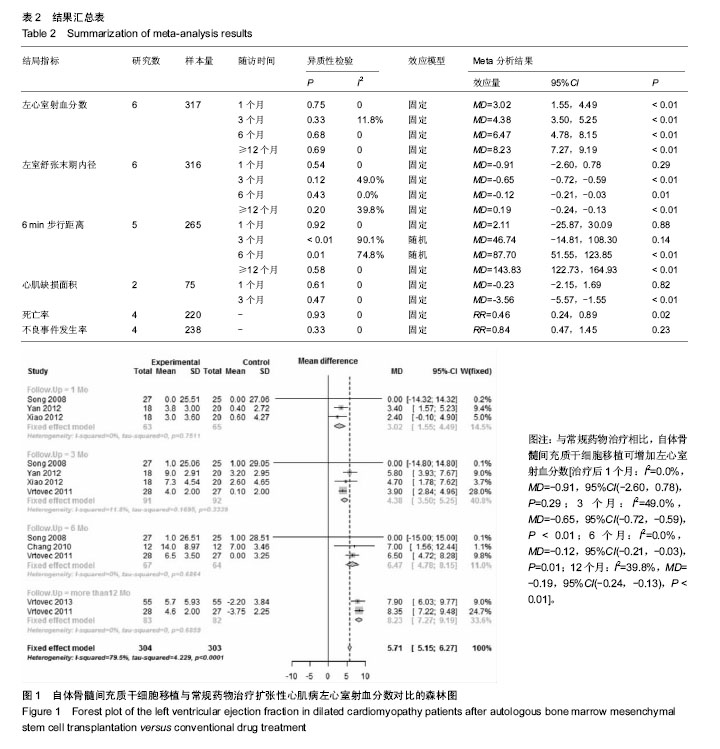
2.3 Meta分析结果 Meta分析结果汇总,见表2。 2.3.1 左心室射血分数 6个研究报告了左心室射血分数结局指标[26,28-32],合计样本量317例,BMSCs治疗组158例,常规药物治疗组159例。Meta分析结果显示:与常规药物治疗组比较,BMSCs治疗组可增加左心室射血分数[治疗后1个月:I2=0,MD=3.02,95%CI(1.55,4.49),P < 0.01;3个月:I2=0,MD=4.38,95%CI(3.50,5.25),P < 0.01;6个月:I2=0,MD=6.47,95%CI(4.78,8.15),P < 0.01;12个月:I2=0,MD=8.23,95%CI(7.27,9.19),P < 0.01],见图1。"
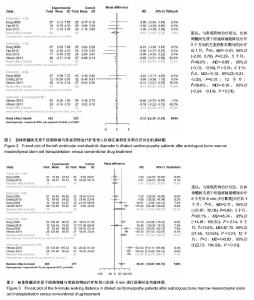
2.3.2 左室舒张末期内径 6个研究报告了左室舒张末期内径结局指标[26,28-32],合计样本量316例,BMSCs治疗组157例,常规药物治疗组159例。Meta分析结果显示:对于减小左室舒张末期内径,BMSCs与常规药物在治疗后1个月时疗效比较差异无统计学意义,但在3个月后比较差异均有显著性意义[治疗后1个月:I2=0,MD=-0.91, 95%CI(-2.60,0.78),P=0.29;3个月:I2=49.0%,MD=-0.65,95%CI(-0.72,-0.59),P < 0.01;6个月:I2=0,MD=-0.12,95%CI(-0.21,-0.03),P=0.01;12个月:I2=39.8%,MD=-0.19,95%CI(-0.24,-0.13),P < 0.01],见图2。 2.3.3 6 min步行距离 5个研究报告了两种治疗措施治疗前后6 min步行距离差异[26-28,31-32],合计样本量265例,BMSCs治疗组134例,常规药物治疗组131例。Meta分析结果显示:两组治疗1个月和3个月6 min步行距离比较差异无显著性意义,治疗6,12个月后比较差异有显著性意义[治疗后1个月:I2=0,MD=2.11,95%CI(-25.87,30.09),P=0.88;3个月:I2=90.1%,MD=46.74,95%CI(-14.81,108.30),P < 0.14;6个月:I2=74.8%,MD=87.70,95%CI(51.55,123.85),P < 0.01;12个月:I2=0, MD,95%CI(122.73,164.93),P < 0.01],见图3。=143.83 在治疗后3,6个月各研究结果异质性较大,3个月时Vrtovec等[32]和常快乐等[28]对异质性影响较明显,分别予以排除进行敏感性分析。发现排除后异质性明显降低且结果性质未发生变化[治疗后3个月:I2=20.2%,MD=15.17,95%CI(-9.62,39.97),P=0.14;6个月:I2=29.8%,MD=108.60,95%CI(93.46,123.74),P < 0.01]。"
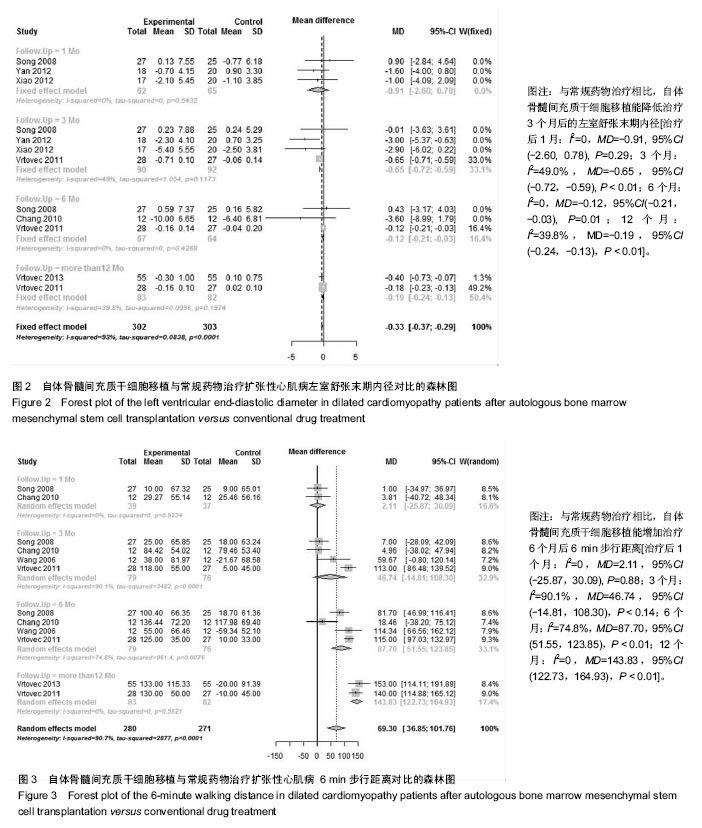
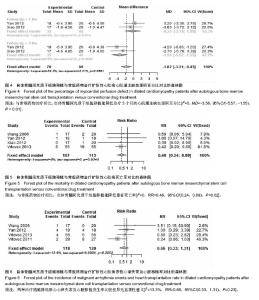
2.3.4 心肌灌注缺损面积百分比 2个研究报告了治疗前后心肌灌注缺损面积百分比变化情况[26,30],合计样本量75例,BMSCs治疗组35例,常规药物治疗组40例。Meta分析结果显示:两组治疗后1个月心肌灌注缺损面积百分比比较差异无显著性意义[I2=0,MD=-0.23,95%CI(-2.15,1.69),P=0.82],治疗3个月比较差异有显著性意义[I2=0,MD=-3.56,95%CI(-5.57,-1.55),P < 0.01],见图4。 2.3.5 死亡率 4个研究报随访过程中两组死亡率情况[27,29-31],合计样本量220例,BMSCs治疗组107例,常规药物治疗组123例。Meta分析结果显示:与常规药物治疗相比,自体BMSCs移植能降低患者死亡率[I2=0,RR=0.46,95%CI(0.24,0.89),P=0.02],见图5。 2.3.6 恶性心律失常、心脏移植发生率 4个研究报告了治疗及随访过程中恶性心律失常及心脏移植发生率[27,29,31-32],合计样本量238例,BMSCs治疗组118例,常规药物治疗组120例。Meta分析结果显示:两种治疗措施降低恶心心律失常及心脏移植发生率比较差异无显著性意义[I2=13.3%,RR=0.66,95%CI(0.33,1.31),P=0.23],见图6。"
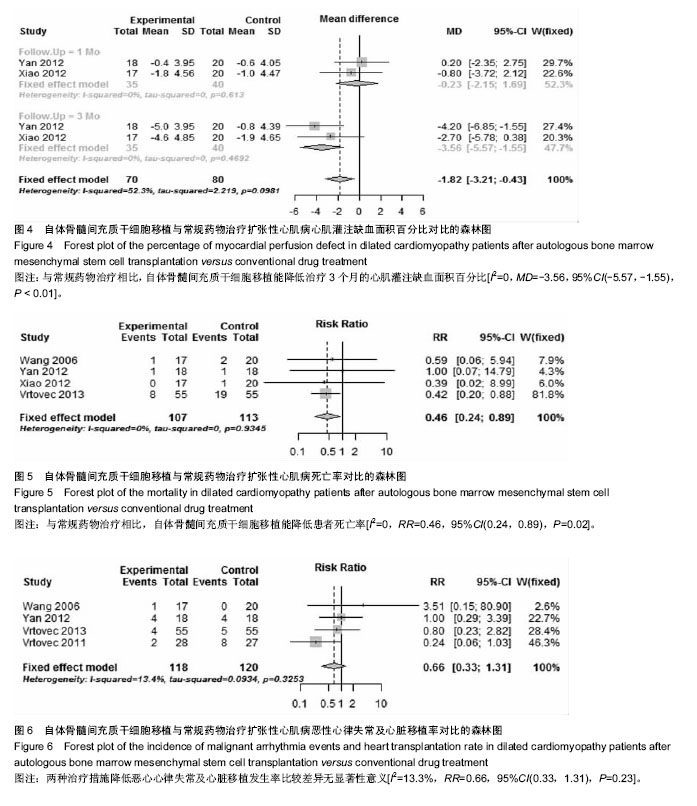
| [1] Sanbe A.Dilated cardiomyopathy: a disease of the myocardium. Biol Pharm Bull.2013;36(1):18-22.[2] Lakdawala NK,Winterfield JR,Funke BH.Dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(1): 228-237.[3] 蒋超鹏,刘强.扩张型心肌病的病因学研究进展[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2012,36(9):1051-1053.[4] 梁华生,张黔桓,陈泗林.扩张型心肌病致病基因的研究进展[J].国际心血管病杂志,2016,43(1):22-24.[5] Biesbroek PS,Beek AM,Germans T,et al.Diagnosis of myocarditis: Current state and future perspectives.Int J Cardiol.2015;191:211-219.[6] Sliwa K,Mayosi BM.Recent advances in the epidemiology, pathogenesis and prognosis of acute heart failure and cardiomyopathy in Africa.Heart.2013;99(18):1317-1322.[7] Spinarova L,Spinar J.Pharmacotherapy of dilated cardiomyopathy.Curr Pharm Des.2015; 21(4):449-458.[8] Kawai C,Matsumori A.Dilated cardiomyopathy update: infectious-immune theory revisited. Heart Fail Rev.2013; 18(6):703-714.[9] Selem SM,Kaushal S,Hare JM.Stem cell therapy for pediatric dilated cardiomyopathy.Curr Cardiol Rep.2013;15(6):369-388.[10] Vrtovec B,Poglajen G,Haddad F.Stem cell therapy in patients with heart failure. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J.2013; 9(1):6-10.[11] Mendez-Ferrer S,Scadden DT,Sanchez-Aguilera A.Bone marrow stem cells: current and emerging concepts.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2015;1335:32-44.[12] Duke CM,Taylor HS.Stem cells and the reproductive system: historical perspective and future directions. Maturitas. 2013; 76(3):284-289.[13] Ali-Hassan-Sayegh S,Mirhosseini SJ,Lotfaliani MR,et al. Transplantation of bone marrow stem cells during cardiac surgery.Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann.2015;23(3):363-374.[14] Sampson S,Botto-Van BA,Aufiero D.Autologous bone marrow concentrate: review and application of a novel intra-articular orthobiologic for cartilage disease.Phys Sportsmed. 2013; 41(3):7-18.[15] Perin EC,Borow KM,Silva GV,et al.A phase II dose-escalation study of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells in patients with Ischemic or Nonischemic Heart Failure.Circ Res. 2015; 117(6):576-584.[16] Golpanian S,El-Khorazaty J,Mendizabal A,et al.Effect of aging on human mesenchymal stem cell therapy in ischemic cardiomyopathy patients.J Am Coll Cardiol.2015; 65(2): 125-132.[17] Jimenez-Quevedo P,Gonzalez-Ferrer JJ,Sabate M,et al. Selected CD133(+) progenitor cells to promote angiogenesis in patients with refractory angina: final results of the PROGENITOR randomized trial.Circ Res.2014;115(11): 950-960.[18] Vrtovec B,Poglajen G,Lezaic L,et al.Comparison of Transendocardial and Intracoronary CD34+ Cell Transplantation in Patients With Nonischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy.Circulation. 2013;128(11, suppl_1):S42-S49.[19] Lezaic L,Socan A,Poglajen G,et al.Intracoronary Transplantation of CD34+ Cells Is Associated With Improved Myocardial Perfusion in Patients With Nonischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy.J Card Fail.2015;21(2):145-152.[20] Mushtaq M,Difede D,Golpanian S,et al.Rationale and design of the percutaneous stem cell injection delivery effects on neomyogenesis in dilated cardiomyopathy (The POSEIDON- DCM Study).J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2014; 7(9):769-780.[21] Martino H,Oliveira P,Souza F,et al.A safety and feasibility study of cell therapy in dilated cardiomyopathy.Braz J Med Biol Res.2010;43(10):989-995.[22] 邢冬梅,朱明军,吴泰相,等.干细胞移植治疗扩张型心肌病疗效和安全性的系统评价[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2012,32(3): 321-325.[23] 杨柳,唐其柱,郭毅.骨髓干细胞移植治疗扩张性心肌病疗效及安全性的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2015,15(2):194-200.[24] Moher D,Liberati A,Tetzlaff J,et al.Reprint--preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement.Phys Ther.2009;89(9):873-880.[25] 曾宪涛,包翠萍,曹世义,等.Meta分析系列之三:随机对照试验的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(3):183-185.[26] 宋延彬,高峰.经冠脉移植自体骨髓干细胞治疗扩张型心肌病的安全性及疗效[J].心血管康复医学杂志,2008,17(4):348-350.[27] 王建安,谢小洁,何红,等.骨髓间质干细胞移植治疗原发性扩张型心肌病的疗效与安全性[J].中华心血管病杂志,2006,34(2): 107-110.[28] 常快乐,于军,张守信,等.经冠脉自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗扩张型心肌病的临床研究[J].西北国防医学杂志,2010,31(5):351-353.[29] 晏娟娟,高传玉,高永举,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗扩张型心肌病的临床观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2012,26(6): 544-546.[30] 肖文涛,高丽君,高传玉,等.不同类型骨髓干细胞移植治疗扩张型心肌病的疗效对比[J].中华心血管病杂志,2012,40(7):575-578.[31] Vrtovec B,Poglajen G,Lezaic L,et al.Effects of intracoronary CD34+ stem cell transplantation in nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy patients: 5-year follow-up.Circ Res. 2013; 112(1):165-173. [32] Vrtovec B,Poglajen G,Sever M,et al.Effects of intracoronary CD34+ stem cell transplantation in nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy patients: 5-year follow-up.J Card Fail. 2011; 17(4):272-281.[33] Martino H,Brofman P,Greco O,et al.Multicentre, randomized, double-blind trial of intracoronary autologous mononuclear bone marrow cell injection in non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy (the dilated cardiomyopathy arm of the MiHeart study). Eur Heart J.2015;36(42):2898-2904.[34] 曾宪涛,田国祥,张超,等.Meta分析系列之十五:Meta分析的进展与思考[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2013,12(6):561-563.[35] Bilgimol JC,Ragupathi S,Vengadassalapathy L,et al.Stem cells: An eventual treatment option for heart diseases.World J Stem Cells.2015;7(8):1118-1126.[36] Dong X,Zhu F,Liu Q,et al.Transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects myocardium by regulating 14-3-3 protein in a rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy.Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2014;7(7):3714-3723.[37] Yu Q,Li Q,Na R,et al.Impact of repeated intravenous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells infusion on myocardial collagen network remodeling in a rat model of doxorubicin- induced dilated cardiomyopathy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2014; 387(1-2):279-285.[38] Selem SM,Kaushal S,Hare JM.Stem cell therapy for pediatric dilated cardiomyopathy.Curr Cardiol Rep.2013;15(6): 369-388.[39] Chin S,Poey AC,Wong C,et al.Intramyocardial and intracoronary autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment in chronic severe dilated cardiomyopathy. Cytotherapy.2011;13(7):814-821.[40] Seth S,Bhargava B,Narang R,et al.The ABCD (Autologous Bone Marrow Cells in Dilated Cardiomyopathy) trial a long-term follow-up study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(15): 1643-1644. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [3] | Wu Min, Zhang Yeting, Wang Lu, Wang Junwei, Jin Yu, Shan Jixin, Bai Bingyi, Yuan Qiongjia. Effect of concurrent training sequences on body composition and hormone response: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1305-1312. |
| [4] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [6] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [7] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [8] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [10] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [13] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [14] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [15] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||