Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (1): 71-76.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.01.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Adipose mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of traumatic brain injury
Zhu Jun-qing, Hong Jun, Cui Jian-zhong, Wang Kai-jie
- Tangshan Gongren Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2017-01-08Published:2017-03-15 -
About author:Zhu Jun-qing, Associate chief physician, Tangshan Gongren Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Jun-qing, Hong Jun, Cui Jian-zhong, Wang Kai-jie. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of traumatic brain injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(1): 71-76.
share this article
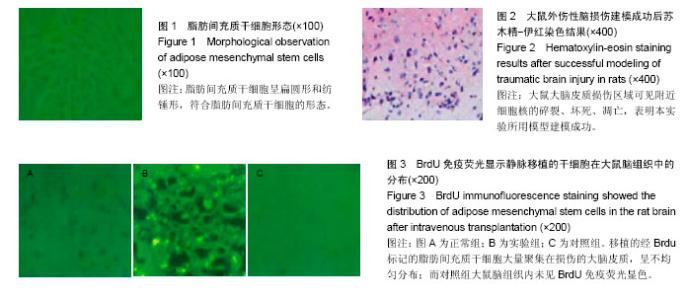
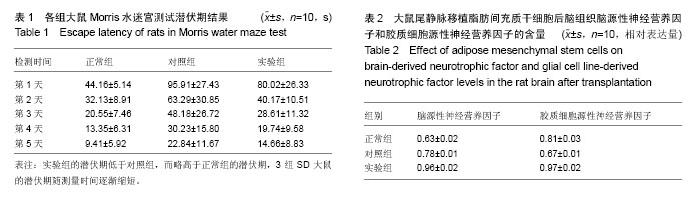
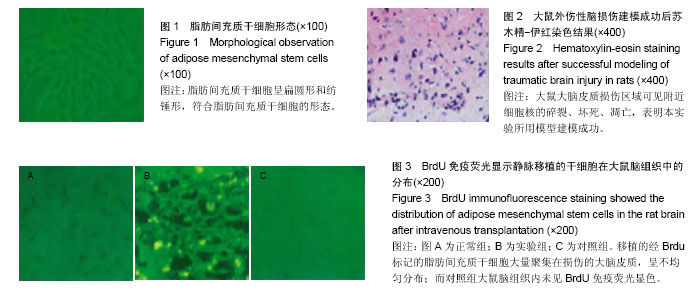
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验中所用到的50只SD大鼠全部进入结果分析,无脱失。 2.2 体外培养的脂肪间充质干细胞检测结果 在体外培养的SD大鼠腹腔肠系脂肪间充质干细胞经流式细胞仪检测,所分离出的细胞培养整合达90%左右时,脂肪间充质干细胞呈扁圆形和纺锤形,符合脂肪间充质干细胞的形态,具有较好的自我更新能力(图1)。 2.3 SD大鼠外伤性脑损伤建模结果 实验采用脑冷冻伤制作大鼠外伤性脑损伤模型。各组SD大鼠脑冷冻伤建模后没有出现死亡现象,对大鼠的活动没有显著影响,可以正常进行Morris水迷宫测试。苏木精-伊红染色检测显示,建模后的大鼠大脑皮质损伤区域出现局限性损伤,各大鼠脑损伤区域基本一致,可见附近细胞核的碎裂、坏死、凋亡,表明本实验所用模型建模成功(图2)。 2.4 各组大鼠Morris水迷宫测试结果 各组大鼠测量的第1,2,3,4,5天的平均潜伏期,采用单个重复测量因素的方差分析,5次重复测量的数据间存在高度的相关性。脂肪干细胞移植后Morris水迷宫测试潜伏期第1,2,3,4,5天后,实验组与对照组比,实验组SD大鼠平均逃避潜伏期迅速下降,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而同时实验组大鼠逃避潜伏期越来越接近于正常组大鼠,结果见表1。各组潜伏期指标总体而言不同,可以看出,实验组的潜伏期低于对照组,而略高于正常组的潜伏期,3组SD大鼠的潜伏期随测量时间逐渐缩短。 2.5 干细胞在大鼠脑损伤区域中的分布 BrdU标记的第4代脂肪间充质干细胞经SD大鼠尾静脉移植后,免疫组织化学后置于倒置显微镜观察在大鼠脑细胞内的分布结果显示,移植的经Brdu标记的脂肪间充质干细胞大量聚集在损伤的大脑皮质,呈不均匀分布。而对照组大鼠脑组织内未见BrdU免疫荧光显色。说明脂肪间充质干细胞经大鼠尾静脉移植后能通过大鼠血脑屏障迁移至外伤性损伤的大鼠的受损区域,进一步在大脑组织中分散(图3)。 2.6 大鼠脑组织中脑源性神经营养因子和胶质细胞源性神经营养因子含量检测结果 与对照组比,实验组经脂肪干细胞静脉移植后SD大鼠脑源性神经营养因子、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子的含量明显高于对照组(P < 0.05)。而与正常组SD大鼠比较,对照组大鼠脑源性神经营养因子含量升高,而皮质周围的胶质细胞源性神经营养因子含量却明显下降(表2)。单向方差分析显示,各组SD大鼠脑组织损伤部位或附近的脑源性神经营养因子与胶质细胞源性神经营养因子的相对表达量有明显的差异性,同时组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] Abu-Abeeleh M, Bani Ismail ZA, Alzaben KR,et al. A preliminary study of the use of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells for the treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in a rat model. Comp Clin Pathol.2010; 19(1):1-4.[2] Hess DC,Borlongan CV.Stem cells and neurological diseases. Cell Prolif.2008;41Suppl 1:94-114.[3] Chen Z,Palmer TD.Cellular repair of CNS disorders: an immunological perspcetive.Hum Mol Genet.2008;17(Rl): R84-R92.[4] Longhi L,Zanier ER,Royo N,et al.Stem cell transplantation as a therapeutic strategy for traumatic brain injury.Transpl immunol. 2005;15(2):143-148.[5] Bjorklund LM,Sanchez-Pernaute R,Chung S,et al.Embryonic cells develop into functional dopaminergic neurons after transplantation in a parkinson rat model.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2002;99(4):2344-2349.[6] Gregory CA,Gunn WG,Peister A,et al.An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: comparison with cetylpyridiniurn chloride extraction.Ana lBiochem.2004;329(1):77-84.[7] Hayashi O,Katsube Y,HiroseM,et al.Comparison of osteogenic ability of rat mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow,periosteum,and adipose tissue.Caleif Tissue Int. 2008;82 (3): 238-247.[8] Planat-Benard V,Silvestre JS,Cousin B,et al.Plasticity of human adipose lineage cells toward endothelial cells: Physiological and therapeutic perspectives. Cireulation. 2004; 109(5):656-663.[9] Zuk PA,Zhu M,Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng.2001;7(2):211-228.[10] Safford KM,Safford SD,Gimble JM,et al.Characterization of neuronal/glial differentiation of murine adipose-derived adult stromal cells.Exp Neurol.2004;187(2):319-328.[11] Dhar S,Yoon ES,Kachgal S,et al.Long-term maintenance of neuronally differentiated human adipose tissue-derived stem cells.Tissue Eng.2007;13(11):2625-2632.[12] Safford KM,Hieok KC,Saflbrd SD,et al.Neurogenic differentiation of murine and human adipose-derived stromal cells.Bioehem Biophys Res Commun.2002;294(2): 371-379.[13] Casteilla L,Planat-Benard V,Cousin B,et al.Plasticity of adipose tissue:a promising therapeutic avenue in the treatment of cardiovascular and blood diseases?.Aich Mal Coeur Vaiss.2005;98(9):922-926.[14] Oedayrajsingh-Vanna MJ,Van HS,KniPPenberg M,et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell yield and growth charaeteristics are affected by the tissue-harvesting procedure. CytotheraPy.2006;8(2):166-177.[15] Hombach-Klonisch S,Panigrahi S,Rashedi I,et al.Adult stem cells and their trans differentiation potential-perspeetives and therapeutic applications.J Mol Med.2008.[16] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[17] Grasso G,Sfacteria A,Meli F,et al.Neuroprotection by erythropoietin administration after experimental traumatic brain injury.Brain Res.2007;1182:99-105.[18] Bhang SH,Lee YE,Cho SW,et al.Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes bone marrow stromal cell transplantation-mediated neural regeneration in traurnatic brain injury.Biochem BioPhys Res Commun.2007;359(l):40-45.[19] Gotherstrom C,Ringden O,Tammik C.et al.Immunologic ProPerties of human fetal mesenchmal stem cells.Am J Obstet Gyneeol.2004;190:239-245.[20] Booekvar JA,Sehouten J,Royo N,et al.Experimental traumatic brain injury modulates the survival,migration,and terminal phenotype of transplanted epidermal growth factor receptor- aetivated neural stem cells. Neurosurgery. 2005;56(1): 163-171,171.[21] Chen X,Katakowski M,Li Y,et al.Human bone marrow stromal cell cultures conditioned by traurnatic brain tissue extracts: growth factor produetion.J Neurosci Res.2002; 69(5): 687-691.[22] Harting MT,Baumgartner JE,Worth LL,et al.Cel ltherapies for traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Focus.2008;24(3-4):E18.[23] Jiang Y,Jahagirdar BN,Reinhardt RL,et al.Plurpotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.[24] Kogler G,Sensken S,Airey JA,et al.A new human somatic stem cell from placental cord blood with intrinsic Pluripotent differentiation potential.J ExP Med.2004;200(2):123-135.[25] Zvaifler NJ,Marinova-Mutafchieva L,Adams G,et al. Mesenchymal precursor cells in the blood of normal individuals. Arthritis Res.2000;2(6):477-488.[26] Jiang Y,Vaessen B,Lenvik T,et al.MultiPotent progenitor cells can be isolated from postuatal murine bone marrow,musele, and brain. ExP Hematol.2002;30(8):896-904.[27] Pittenger MF,Mackay AM,Beck SC,et al.Multilineage Potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Seienee. 1999; 254(5411):143-247.[28] Kamishina H,Farese JP,Storm JA,et al.The frequency,growth kinetics,and osteogenice/ adiPogenic differeniiation pro Perties of canine bone marrow stromal cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(10):472- 479.[29] Baksh D,Yao R,Tuan RS.Comparison of Proliferative and multilineage differentiation Potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from ulnbilical cord and bone marrow. Stem Cells.2007;25(6):1384-1392.[30] Yamaguehi S,Kuroda S,Kobayashi H,et al.The effects of neuronal induction on gene expression profile in bone marrow stromal cells(BMSC)-a preliminary Study using mieroarray analysis. Brain Res.2006;1087(l):15-27.[31] LewinGR,Barde YA.Physiology of the neurotrophins.Annu Rev Neurosci.1996;19:289-317.[32] Bowling H, Bhattacharya A, Klann E,et al.Deconstructing brain-derived neurotrophic factor actions in adult brain circuits to bridge an existing informational gap in neuro-cell biology. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(3): 363-367.[33] Lv XM,Liu Y,Wu F,et al.Human umbilical cord blood-derived stem cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor protect injured optic nerve: viscoelasticity characterization. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(4): 652-656.[34] Yamada K,Nabeshima T.Brain-derived neurotrophic factor/TrkB signaling in memory Processes.J Pharmacol Sci.2003;91(4):267-270.[35] Saarelainen T,Pussinen R,KoPonen E,et al.Transgenic mice overexpressing truneated trkB neurotrophin receptors in neurons have impaired long-term spatial memory but normal hippocampal LTP.Synapse.2000;38(l):102-104.[36] Saarelainen T,Lukkarinen JA,KoPonen S,et al.Transgenic mice overexpressing truncated trkB neurotrophin receptors in neurons show inereased susceptibility to cortical injury after focal cerebral ischemia.Mol Cell Neurosci.2000;16(2):87-96.[37] Lin LF,Doherty DH,Lile JD,et al.GDNF:a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic faetor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science.1993;260(5111):1130-1132.[38] 闫中杰.人羊膜及脐带来源间充质干细胞对创伤性脑损伤治疗潜力的生物学特性比较[D].南方医科大学,2013.[39] 李东飞.静脉移植脂肪间充质干细胞治疗大鼠创伤性脑损伤[D].南方医科大学,2010.[40] Cheng Q,diLiberto V,Caniglia G,et al.Time-eourse of GDNF and its receptor expression after brain injury in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 2008;439(l):24-29.[41] Fujimoto T,Nakamura T,Ikeda T,et al.Potent protective effects of melatonin on experimental spinal cord injury.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2000;25(7):769-775.[42] Saavedra A,BaltaZar G,Duarte EP.Driving GDNF expression: the green and the red traffic lights.Prog Neurobiol.2008; 86(3): 186-215. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [5] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [6] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [7] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng . Effects of aerobic and resistance exercises on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nuclear factor-kappa B and inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle of type II diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 669-675. |
| [11] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [12] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [13] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| [14] | Fan Danyang, Fu Runze, Mi Jiajing, Liu Chunyan. Expression and role of cannabinoid receptors during bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 283-288. |
| [15] | Zhou Hongbo, Yu Zhengwen, Liu Jianguo. Molecular mechanism of bone regeneration promoted by medical metal implant materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1588-1596. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||