Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (46): 6986-6992.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.46.020
Exercise-induced myocardial stunning: fantasy or reality?
Li Shun-chang1, 2
- 1School of Sports Science of Xichang University, Xichang 615022, Sichuan Province, China; 2Sport Science College of Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2016-08-16Online:2016-11-11Published:2016-11-11 -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of General Administration of Sport of China, No. 10B038; the Natural Science Foundation of Xichang University, No. XA1205; the Grant from China Scholarship Council, No. 201405620017
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Shun-chang. Exercise-induced myocardial stunning: fantasy or reality?[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(46): 6986-6992.
share this article
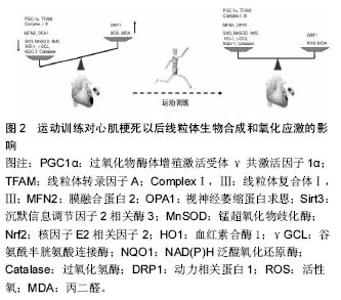
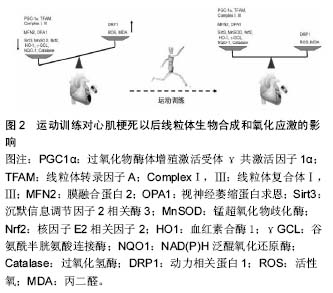
2.1 心肌顿抑 心肌顿抑(myocardial stunning, MS)又称缺血后心肌功能障碍,是指心肌短暂缺血尚未造成心肌坏死,但再灌注恢复正常的血流后其机械功能障碍却需数小时、数天或数周才能完全恢复的现象[3]。 1975年,Heyndrickx等[4]研究发现清醒的犬在经历了短时间冠状动脉闭塞并恢复再灌注后,其心肌功能障碍仍持续存在一段时间,第一次描述了缺血后心肌功能障碍现象。1982年,Braunwald等[5]正式地将这一现象定义为心肌顿抑。心肌顿抑现象最初在动物实验中发现,曾一度被认为仅存在与实验过程中,经过多年研究,其临床意义已被广泛接受。 心肌顿抑不是一个单一体,而是众多的实验研究和临床状态所得到的综合症状。心肌顿抑目前多采用Bolli的分类方法。即心肌顿抑可分为继发于冠状动脉血流减少局部缺血的心肌顿抑、继发于冠状动脉血流减少全心缺血的心肌顿抑和继发于需氧量增加的心肌顿抑。临床常见的情况有冠状动脉成形术引起的心肌顿抑、不稳定型心绞痛引起的心肌顿抑、急性心肌梗死再灌注治疗引起的心肌顿抑、心脏手术后的心肌顿抑、神经源性的心肌顿抑、心脏复律后的心肌顿抑和运动诱发的心肌顿抑[6]。 2.2 运动与心肌顿抑关系的研究现状 目前关于心肌顿抑与运动关系的研究主要集中在运动训练对心肌顿抑潜在的保护性作用上(图2)[7-14]。尽管大多数文献报道运动训练对心肌顿抑心肌收缩功能的恢复有积极的作用,但也有学者在研究运动训练对缺血再灌注损伤保护作用时失败[15]。这些结果的冲突可能是由于所采用的实验方案(如:缺血持续时间、整体或局域性缺血等)不同所致,也可能是由于运动训练的方案不同所致。特别要提出的是,Libonati 等[15]研究了2种不同的运动训练方案对20 min缺血损伤的影响,结果发现:低强度的耐力训练对收缩功能障碍的恢复没有任何影响。即提示运动训练在诱导心肌顿抑收缩功能改善方面所起的潜在性保护作用与运动训练的强度有关。"
| [1] OKeefe JH PH, Lavie CJ, et al. Potential adverse cardiovascular effects from excessive endurance exercise. Mayo Clinic proceedings.2012;87(6): 587-595. [2] 李顺昌,段意梅,苏全生.力竭性跑台运动致大鼠心肌顿抑现象研究[J].体育科学. 2012,32(8):49-54. [3] Maranta F, Tondi L, Agricola E, et al.Ivabradine reduces myocardial stunning in patients with exercise-inducible ischaemia. Basic research in cardiology.2015;110(6):55. [4] Heyndrickx GR, Millard RW, McRitchie RJ, et al.Regional myocardial functional and electrophysiolonical alterations after brief coronary artery occlusion in concious dogs.J Clin Invest.1975;56(4):978-985. [5] Braunwald E, Kloner RA. The stunned myocardium_ prolonged, postischemic ventricular dysfunction. Circulation.1982;66(6):1146-1149. [6] 颜姝,韦星,冯大明.心肌顿抑的防治机制新进展.[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2013,21(12):1149-1152. [7] Lalonde F, Poirier P, Sylvestre MP, et al. Exercise-induced ischemic preconditioning detected by sequential exercise stress tests: a meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol.2015;22(1):100-112. [8] Lalonde F, Poirier P, Arvisais D, et al. Exercise-induced ischemic preconditioning and the potential application to cardiac rehabilitation: a systematic review.J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2015; 35(2): 93-102. [9] Quindry JC, Hamilton KL.Exercise and cardiac preconditioning against ischemia reperfusion injury. Current cardiology reviews.2013;9(3):220-229. [10] Marongiu E, Crisafulli A. Cardioprotection acquired through exercise: the role of ischemic preconditioning. Current cardiology reviews.2014;10(4):336-348. [11] Rahimi M, Shekarforoush S, Asgari AR, et al. The effect of high intensity interval training on cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in wistar rats. EXCLI journal.2015;14:237-246. [12] 王凯.蛋白激酶C对晚期运动预处理心肌保护效应中缝隙连接蛋白43表达的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2015, 34(11):1079-1084. [13] 张城林,张艳,吴立玲,等. 运动训练对心肌梗死后心脏的保护作用[J]. 生理科学进展,2015,46(2):137-142. [14] 贾绍辉,刘君,寇现娟,等. 运动诱导的细胞自噬对小鼠心肌的保护作用[J]. 武汉体育学院学报,2014,48(10): 53-56. [15] Libonati JR, Gaughan JP, Hefner CA, et al. Reduced ischemia and reperfusion injury following exercise training. Med Sci Sports Exerc.1997;29(4):509-516. [16] Powers SK,Demirel HA,Vincent HK,et al.Exercise training improves myocardial tolerance to in vivo ischemia-reperfusion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275(5 Pt 2):R1468-1477. [17] Powers SK, Sollanek KJ, Wiggs MP, et al. Exercise-induced improvements in myocardial antioxidant capacity: the antioxidant players and cardioprotection. Free radical research.2014;48(1): 43-51. [18] Rigg RA, Healy LD, Nowak MS, et al. Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) regulates platelet integrin activation, granule secretion and aggregation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(7):C568-75 [19] Snoeckx LH, Cornelussen RN, Van Nieuwenhoven FA, et al. Heat shock proteins and cardiovascular pathophysiology.Physiol Rev.2001;81(4):1461-1497. [20] Meissner A, Luss I, Rolf N, et al. The early response genes c-jun and HSP-70 are induced in regional cardiac stunning in conscious mammals. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000 Apr;119(4 Pt1):820-825. [21] Melling CW, Thorp DB, Milne KJ, et al. Myocardial Hsp70 phosphorylation and PKC-mediated cardioprotection following exercise. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2009;14(2):141-150. [22] Liu J, Han Q, Peng T, et al.The oncogene c-Jun impedes somatic cell reprogramming. Nature cell biology.2015;17(7):856-867. [23] Saltin b, Stenberg J.Circulatory response to prolonged severe exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1964;19:833-838. [24] Homans DC SublettE, Dai XZ, et al. Persistence of regional left ventricular dysfunction after exercise-induced myocardial ischemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 ;77(1):66-73. [25] Vatner SF HL. Coronary vascular mechanisms involved in decompensation from hypertrophy to heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22(4 Suppl A):34A-40A. [26] 李新建,张钢林,刑少东,等.超速驱动诱发大鼠离体心脏心肌顿抑的研究[J]. 成都体育学院学报,2010,36(4):73-77. [27] 陶小平,苏全生,邹斌,等. 运动诱发大鼠在体心脏心肌顿抑现象的研究[J]. 成都体育学院学报,2011,37(8):83-87. [28] 李顺昌,段意梅,苏全生.力竭性跑台运动致大鼠心肌顿抑现象研究[J].体育科学. 2012,32(8):49-54. [29] Oxborough D, Birch K, Shave R, et al. "Exercise-induced cardiac fatigue"--a review of the echocardiographic literature. Echocardiography. 2010; 27(9):1130-1140. [30] Shave R, Oxborough D. Exercise-Induced Cardiac Injury: Evidence From Novel Imaging Techniques and Highly Sensitive Cardiac Troponin Assays.Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. 2012;54(5):407-415. [31] La Gerche A. Can intense endurance exercise cause myocardial damage and fibrosis?. Curr Sports Med Rep.2013;12(2):63-69. [32] La Gerche A, Heidbuchel H.Exercise-Induced Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Cardiac Electrophysiology Clinics.2013;5(1):97-105. [33] Guasch E, Benito B, Qi X, et al. Atrial fibrillation promotion by endurance exercise: demonstration and mechanistic exploration in an animal model.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(1):68-77. [34] Douglas PS, O'Toole ML, Hiller WD, et al. Cardiac fatigue after prolonged exercise. Circulation. 1987; 76(6):1206-1213. [35] Middleton N, Shave R, George K, et al. Left ventricular function immediately following prolonged exercise: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38(4): 681-687. [36] Vanoverschelde JL, Younis LT, Melin JA, et al. Prolonged exercise induced left ventricular dysfunction in healthy subjects.J Appl Physiol.1985; 70(3): 1356-1363. [37] McGavock J HM, Warburton D, et al.Left ventricular systolic performance during prolonged strenuous exercise in femal triathletes. Dyn Med.2003;2(1):1-8. [38] Middleton N SR, George K, et al. Left ventricular function immediately following prolonged exercise: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38(4):681-687. [39] HG P. Marathon run: cardiovascular adaptation and cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(44):3091-3098. [40] Patil HR, O'Keefe JH, Lavie CJ, et al.cardiovascular damage resulting from chronic excessive endurance exercise.Mo Med.2012;109(4):312-321. [41] Oxborough D SR, Warburton D, et al. Dilatation and dysfunction of the right ventricle immediately after ultraendurance exercise: exploratory insights from conventional two-dimensional and speckle tracking echocardiography. Circulation Cardiovascular imaging. 2011;4(3):253-263. [42] La Gerche A, Burns AT, Mooney DJ,et al. Exercise-induced right ventricular dysfunction and structural remodelling in endurance athletes. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(8):998-1006. [43] Elliott AD LGA. The right ventricle following prolonged endurance exercise: are we overlooking the more important side of the heart? A meta-analysis.Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(11):724-729. [44] Redpath CJ, Backx PH. Atrial fibrillation and the athletic heart. Curr Opin Cardiol.2015;30(1):17-23. [45] O'Keefe JH, Patil HR, Lavie CJ, et al.Potential adverse cardiovascular effects from excessive endurance exercise. Mayo Clin Proc.2012;87(6):587-595. [46] Wilhelm M, Roten L, Tanner H,et al. Atrial remodeling, autonomic tone, and lifetime training hours in nonelite athletes. Am J Cardiol.2011;108(4):580-585. [47] Grimsmo J, Grundvold I, Maehlum S, et al.High prevalence of atrial fibrillation in long-term endurance cross-country skiers: echocardiographic findings and possible predictors--a 28-30 years follow-up study. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil.2010;17(1):100-105. [48] Trivax JE, Franklin BA, Goldstein JA, et al. Acute cardiac effects of marathon running. J Appl Physiol (1985).2010;108(5):1148-1153. [49] La Gerche A, Burns AT, Mooney DJ, et al. Exercise-induced right ventricular dysfunction and structural remodelling in endurance athletes.Eur Heart J.2012;33(8):998-1006. [50] Wilson M, O'Hanlon R, Prasad S, et al. Diverse patterns of myocardial fibrosis in lifelong, veteran endurance athletes. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;110(6):1622-1626. |
| [1] | Zhang Yuantong. Body composition and bone mineral density of juvenile basketball players versus ordinary middle school students: data from a middle school [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 341-347. |
| [2] | Lan Qingshi. Participation degree and control ability of human latissimus dorsi, trapezius, triceps, musculus and deltoid during cross support of hand ring: analysis on contribution rate of major muscle group [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 361-366. |
| [3] | Kong Lingyao, Li Tao, Zeng Xinglin, Li Jian, Xiong Yan. Synovial chondromatosis: how to improve the diagnosis accuracy and clearance rate of tumor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4570-4575. |
| [4] | Yu Hong, Liu Yan. Strength of knee flexor and extensor in football athletes after vibration training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2327-2331. |
| [5] | Zhu Yaojia1, Huo Hongfeng1, 2. Balance ability and foot type characteristics during different postures of standing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2345-2349. |
| [6] | Li Xintong1, Pan Weimin2, Qin Huasheng1, Qu Lei1, Zhang Hengyin1, Zhu Xinrui1. Blood flow restriction training: a new method for accelerating musculoskeletal rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2415-2420. |
| [7] | Wang Minjia1, Qi Ziyi2, Zhu Weihua1, Sun Junzhi1. Mechanism and clinical research advance of muscle atrophy: thinking based on the 65th Annual Meeting of American College of Sports Medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2421-2426. |
| [8] | Yuan Yiwen, Gui Zhu, Zhang Hongchao. Changes in muscle injury and pulse wave velocity after exercise with compression leg cuffs in college students without fitness habits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(11): 1687-1692. |
| [9] | Xie Hao-dong1, 2, Luo Jiong1, 2. Stiffness of the lower extremities during landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(8): 1306-1312. |
| [10] | Wang Zhao-feng1, Gong Ming-ming2, Chen Jia-qun2, Mo Wei-bin3. Effects of Glycyrrhiza Flavone on the pathological changes of quadriceps and expression of fatty acid translocase/CD36 in training rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 529-534. |
| [11] | Ma Tao, Li Jian, Jin Jia-peng . Effects of different sports events on bone mineral density in the recent decade: a bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 631-634. |
| [12] | Lei Bingkai1, 2, Sun Junzhi1, Zhao Xiaoqin3, Ding Haili1, Liu Yong2, Wang Ruiyuan2, Li Junping2. Role of Omi/Beclin-1 signaling pathway in the eccentric exercise-induced skeletal muscle autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5791-5796. |
| [13] | Wang Dandan, Zhang Lei, Wu Xueping . Physical activity of people with intellectual disability measured by motion sensor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5889-5896. |
| [14] | Chen Zhen-yong. Correlation of bone mineral density with sports ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4452-4456. |
| [15] | Li Lin, Yu Liang. Biological role of myonectin and its correlation with exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4566-4573. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||