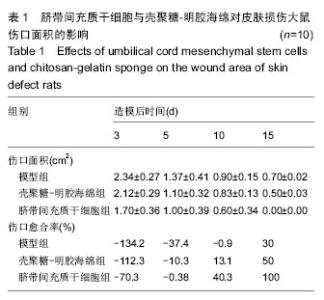
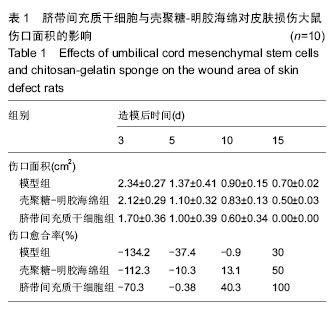
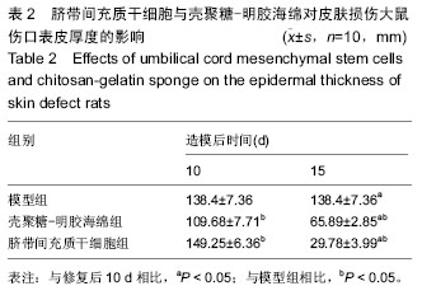
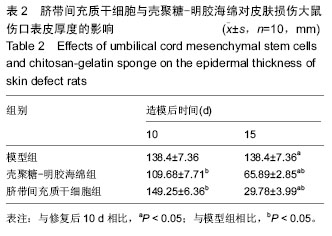
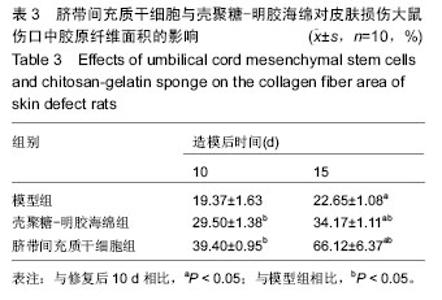
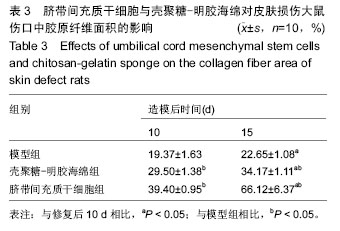
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (34): 5136-5141.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.34.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chitosan-gelatin sponge versus umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cellsfor skin wound healing
Fang Shao-xia, Guo Fen
- Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Tongji Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2016-06-01Online:2016-08-19Published:2016-08-19 -
Contact:Fang Shao-xia, Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Tongji Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Fang Shao-xia, Nurse, Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Tongji Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Shao-xia, Guo Fen. Chitosan-gelatin sponge versus umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cellsfor skin wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(34): 5136-5141.
share this article
| [1] Wu Y, Huang S, Enhe J, et al. Insights into bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells safety for cutaneous repair and regeneration. Int Wound J. 2012; 9(6):586-594.
[2] Falanga V. Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1736-1743.
[3] Shaw TJ, Martin P. Wound repair at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2009;122(Pt 18):3209-3213.
[4] Tario JD Jr, Muirhead KA, Pan D, et al. Tracking immune cell proliferation and cytotoxic potential using flow cytometry. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;699:119-164.
[5] Brissett AE, Hom DB. The effects of tissue sealants, platelet gels, and growth factors on wound healing. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;11(4): 245-250.
[6] Efron PA, Moldawer LL. Cytokines and wound healing: the role of cytokine and anticytokine therapy in the repair response. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2004;25(2): 149-160.
[7] Alemdaro?lu C, De?im Z, Celebi N, et al. An investigation on burn wound healing in rats with chitosan gel formulation containing epidermal growth factor. Burns. 2006;32(3):319-327.
[8] Alsarra IA. Chitosan topical gel formulation in the management of burn wounds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2009;45(1):16-21.
[9] Hocking AM, Gibran NS. Mesenchymal stem cells: paracrine signaling and differentiation during cutaneous wound repair. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(14): 2213-2219.
[10] Wu Y, Chen L, Scott PG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2007;25(10):2648-2659.
[11] Goldman R. Growth factors and chronic wound healing: past, present, and future. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2004; 17(1):24-35.
[12] Akela A, Nandi SK, Banerjee D, et al. Evaluation of autologous bone marrow in wound healing in animal model: a possible application of autologous stem cells. Int Wound J. 2012;9(5):505-516.
[13] Chen M, Przyborowski M, Berthiaume F. Stem cells for skin tissue engineering and wound healing. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2009;37(4-5):399-421.
[14] Luo G, Cheng W, He W, et al. Promotion of cutaneous wound healing by local application of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood. Wound Repair Regen. 2010;18(5):506-513.
[15] Amado LC, Saliaris AP, Schuleri KH, et al. Cardiac repair with intramyocardial injection of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(32):11474-11479.
[16] Li Y, Chen J, Zhang CL, et al. Gliosis and brain remodeling after treatment of stroke in rats with marrow stromal cells. Glia. 2005;49(3):407-417.
[17] Caplan AI, Dennis JE. Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(5): 1076-1084.
[18] Sasaki M, Abe R, Fujita Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells are recruited into wounded skin and contribute to wound repair by transdifferentiation into multiple skin cell type. J Immunol. 2008;180(4):2581-2587.
[19] Seifert AW, Monaghan JR, Voss SR, et al. Skin regeneration in adult axolotls: a blueprint for scar-free healing in vertebrates. PLoS One. 2012; 7(4):e32875.
[20] Qi Y, Jiang D, Sindrilaru A, et al. TSG-6 released from intradermally injected mesenchymal stem cells accelerates wound healing and reduces tissue fibrosis in murine full-thickness skin wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(2):526-537.
[21] Mohd Zohdi R, Abu Bakar Zakaria Z, Yusof N, et al. Gelam (Melaleuca spp.) Honey-Based Hydrogel as Burn Wound Dressing. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:843025.
[22] Hengartner NE, Fiedler J, Schrezenmeier H, et al. Crucial role of IL1beta and C3a in the in vitro-response of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to inflammatory mediators of polytrauma. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116772.
[23] Zhao J, Hu L, Gong N, et al. The effects of macrophage-stimulating protein on the migration, proliferation, and collagen synthesis of skin fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(5-6): 982-991.
[24] Louis KS, Siegel AC. Cell viability analysis using trypan blue: manual and automated methods. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;740:7-12.
[25] Hsu SH, Hsieh PS. Self-assembled adult adipose-derived stem cell spheroids combined with biomaterials promote wound healing in a rat skin repair model. Wound Repair Regen. 2015;23(1):57-64.
[26] Fu X, Fang L, Li X, et al. Enhanced wound-healing quality with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells autografting after skin injury. Wound Repair Regen. 2006;14(3):325-335.
[27] Sunay O, Can G, Cakir Z, et al. Autologous rabbit adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of bone injuries with distraction osteogenesis. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(6):690-702.
[28] Veronesi F, Maglio M, Tschon M, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering: state-of-the-art in in vivo studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(7):2448-2466.
[29] Salem SA, Hwie AN, Saim A, et al. Human adipose tissue derived stem cells as a source of smooth muscle cells in the regeneration of muscular layer of urinary bladder wall. Malays J Med Sci. 2013;20(4): 80-87.
[30] Jeong HH, Piao S, Ha JN, et al. Combined therapeutic effect of udenafil and adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC)/brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-membrane system in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Urology. 2013;81(5):1108.e7-14.
[31] Langer R, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260(5110):920-926.
[32] Jang CH, Cho YB, Choi CH, et al. Effect of umbilical cord serum coated 3D PCL/alginate scaffold for mastoid obliteration. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;78(7):1061-1065.
[33] Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009;326(5957):1216-1219.
[34] Lutolf MP. Integration column: artificial ECM: expanding the cell biology toolbox in 3D. Integr Biol (Camb). 2009;1(3):235-241.
[35] Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 24): 4195-4200.
[36] Lu H, Hoshiba T, Kawazoe N, et al. Cultured cell-derived extracellular matrix scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2011;32(36):9658-9666.
[37] Choi KH, Choi BH, Park SR, et al. The chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on an extracellular matrix scaffold derived from porcine chondrocytes. Biomaterials. 2010;31(20):5355-5365.
[38] Wang Y, Kim UJ, Blasioli DJ, et al. In vitro cartilage tissue engineering with 3D porous aqueous-derived silk scaffolds and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26(34):7082-7094. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Xu Xiaoming, Chen Yan, Song Qian, Yuan Lu, Gu Jiaming, Zhang Lijuan, Geng Jie, Dong Jian. Human placenta derived mesenchymal stem cell gel promotes the healing of radiation skin damage in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3976-3980. |
| [14] | Zhang Degang, Liu Dong, Li Peng, Wang Zhaolin, Zhang Kai, Zhang Xinjun. Short-term follow-up of elastic intramedullary nail and plate in the treatment of displaced middle clavicle type B fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3860-3864. |
| [15] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||