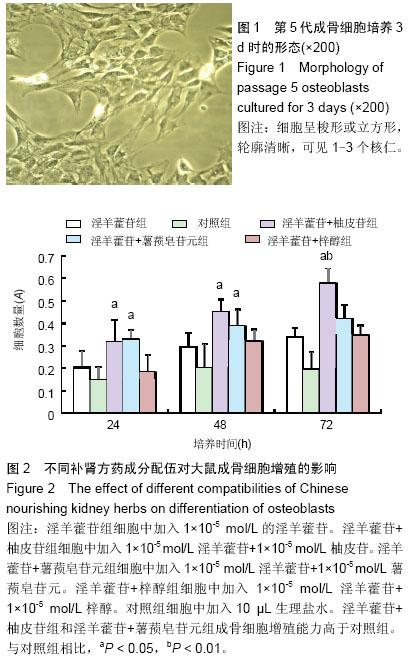
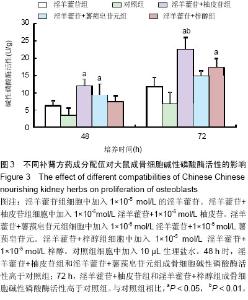
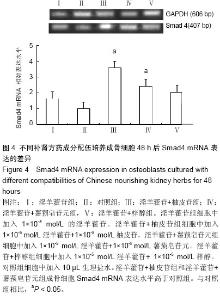
| [1] 李恩,薛延,王洪复,等.骨质疏松鉴别诊断与治疗[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:1-12.
[2] Zhao XL, Feng YX, Peng Y. Prevention and treatment of osteoporosis with Chinese herbal medicines. Chin Herb Med. 2012;4(4):265-270.
[3] 胡军,张华,牟青.骨质疏松症的流行病学趋势与防治进展[J].临床荟萃,2011,26(8):729-731.
[4] 王鸥,邢小平.老年性骨质疏松症发病机制及药物治疗进展[J].中国实用内科杂志,2012,31(8):584-586.
[5] 郭世绂,罗先正,邱贵兴.骨质疏松基础与临床[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社,2001:10-11.
[6] 靳慧,葛娅娜,张成仁,等.成骨细胞中基因表达的调控[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2011,20(5):499-502.
[7] 程浩,张延芳,许巍.新生大鼠成骨细胞原代培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(41):7199-7204.
[8] Dumas A, Le Drévo MA, Moreau MF, et al. Isolation of osteoprogenitors from murine bone marrow by selection of CD11b negative cells. Cytotechnology. 2008;58(3):163-171.
[9] 陈述祥,康乐.中药促成骨细胞增殖和分化的机制与作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(7):1299-1302.
[10] 贾英民,武密山,李恩.补肾方剂对成骨细胞体外培养干预的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20(31):4035-4037.
[11] 陶丽,范方田,刘玉萍,等.中药及其组分配伍的整合作用研究实践与进展[J].中国药理学通报,2013,29(2):153-155.
[12] 司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M].西安:世界图书出版社, 1996: 111-116.
[13] 李娟,申广浩,程光,等.组织块法培养SD大鼠的成骨细胞及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,17(46):8571-8574.
[14] 易东升,林琳,高峰.大鼠乳鼠成骨细胞建立及其生物学活性的研究[J].大连医科大学学报,2014,36(5):430-434.
[15] 辛欣,詹文红,王建华.植物雌激素对大鼠成骨细胞TGF-β信号转导蛋白Smad4表达的影响[J].天然产物研究与开发,2010,22(4): 575-577.
[16] 朱慧锋,王维佳,王珠美.骨碎补总黄酮对骨质疏松大鼠Smad1 Smad5基因表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2010;28(1): 200-204.
[17] 雪原,王沛,齐清会,等.淫羊藿甙对成骨细胞Smad4 mRNA作用的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(2):119-123.
[18] 王洪复.骨细胞图谱与骨细胞体外培养技术[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2001:1-18.
[19] 金明柱,郑洪新.骨痿与骨质疏松症[J].辽宁中医杂志,2007,34(3): 286-287.
[20] 刘继平,程玥.中药促进成骨细胞功能和ALP活性影响研究的意义[J].陕西中医学院学报,2010,33(1):7-8.
[21] 杨帆,邓兆智,韩云,等.中药治疗骨质疏松症的用药规律探析[J].广东药学院学报,2003,19(1):70-71.
[22] 李烨,童杰,周衍晶,等.补肾壮骨中药抗骨质疏松有效成分及其药理作用研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(6):1038-1043.
[23] 贾英民,武密山,李恩.Smads蛋白介导的TGF-β超家族信号转导的研究进展[J].疑难病杂志,2008,7(3):185-188.
[24] 杨晓.Smad4 介导转化生长因子β信号调节骨骼发育和稳态维持的功能[J].生命科学,2008,20(2):165-169.
[25] Blobe GC, Schiemann WP, Lodish HF. Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342(18):1350-1358.
[26] Miyazono K, Kusanagi K, Inoue H. Divergence and convergence of TGF-beta/BMP signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2001;187(3):265-276.
[27] 刘素彩,孔德娟,赵京山,等.淫羊藿甙对大鼠成骨细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2001,7(8):28-30.
[28] 成魁,葛宝丰,甄平等.口服淫羊藿苷可提高大鼠的峰值骨密度和骨质量[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(2):120-124.
[29] Ma HP, Ming LG, Ge BF, et al. Icariin is more potent than genistein in promoting osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(3):916-923.
[30] 马小妮,葛宝丰,陈克明,等.淫羊藿苷调节成骨细胞骨形成和破骨细胞骨吸收的机制[J].中国医学科学院学报, 2013,35(4): 432-438.
[31] 武丽南,陆榕,谷元,等.梓醇在大鼠体内的药代动力学和生物利用度研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2012,17(2):126-130.
[32] 武密山,赵素芝,李恩,等.地黄活性成分梓醇对小鼠成骨细胞MC3T3-E1增殖、分化和矿化的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2010, 26(4):509-513.
[33] 曹亚军,陈虹,杨光,等.薯蓣皂苷对亚急性衰老小鼠的抗氧化作用研究[J].中药药理与临床,2008,24(3):19-20.
[34] 张春芳,吴珊,彭金咏,等.薯蓣皂苷通过上调Lrp5、β-catenin 表达促进成骨细胞MC3T3-E1增殖、分化[J].中国药理学通报, 2013,29(9):1255-1260.
[35] 翟远坤,牛银波,潘亚磊,等.柚皮苷对体外培养乳鼠颅骨成骨细胞增殖和分化成熟的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2012,38(1):105-111.
[36] 丁佩惠,唐琪,陈莉丽.柚皮苷对小鼠成骨细胞MC3T3-E1增殖、分化和矿化的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2009,34(13):1712-1716.
[37] 李念虎,徐展望.柚皮苷促进成骨细胞分化并有效改善卵巢切除所致的骨质疏松[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(8):777-781.
[38] Pivodova V, Frankova J, Ulrichova J. Osteoblast and gingival fibroblast markers in dental implant studies. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2011;155(2): 109-116.
[39] Orimo H. The mechanism of mineralization and the role of alkaline phosphatase in health and disease. J Nippon Med Sch. 2010;77(1):4-12.
[40] Hessle L, Johnson KA, Anderson HC, et al. Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase and plasma cell membrane glycoprotein-1 are central antagonistic regulators of bone mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(14): 9445-9449.
[41] Orimo H, Shimada T. The role of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase in the phosphate-induced activation of alkaline phosphatase and mineralization in SaOS-2 human osteoblast-like cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008;315(1-2):51-60.
[42] Narisawa S, Wennberg C, Millán JL. Abnormal vitamin B6 metabolism in alkaline phosphatase knock-out mice causes multiple abnormalities, but not the impaired bone mineralization. J Pathol. 2001;193(1):125-133.
[43] Harmey D, Hessle L, Narisawa S, et al. Concerted regulation of inorganic pyrophosphate and osteopontin by akp2, enpp1, and ank: an integrated model of the pathogenesis of mineralization disorders. Am J Pathol. 2004;164(4):1199- 1209.
[44] Addison WN, Azari F, Sørensen ES, et al. Pyrophosphate inhibits mineralization of osteoblast cultures by binding to mineral, up-regulating osteopontin, and inhibiting alkaline phosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(21):15872- 15883.
[45] Macrae VE, Davey MG, McTeir L, et al. Inhibition of PHOSPHO1 activity results in impaired skeletal mineralization during limb development of the chick. Bone. 2010;46(4):1146- 1155.
[46] Liu J, Nam HK1, Campbell C1, et al. Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase deficiency causes abnormal craniofacial bone development in the Alpl(-/-) mouse model of infantile hypophosphatasia. Bone. 2014;67:81-94.
[47] adav MC, Simão AM, Narisawa S, et al. Loss of skeletal mineralization by the simultaneous ablation of PHOSPHO1 and alkaline phosphatase function: a unified model of the mechanisms of initiation of skeletal calcification. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(2):286-297. |