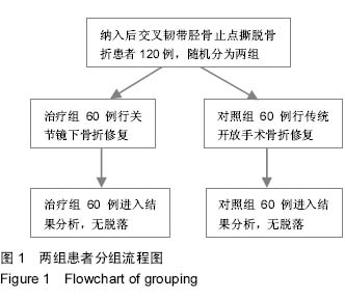
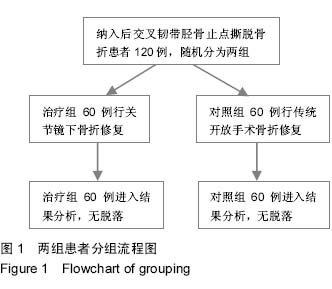
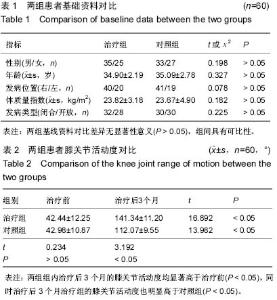
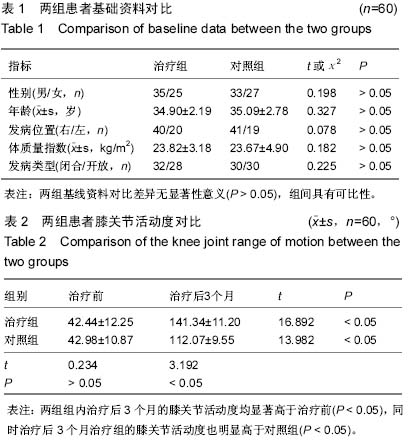
| [1] Bovid KM, Salata MJ, Vander Have KL, et al. Arthroscopic posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a skeletally immature patient: a new technique with case report. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(4):563-570.
[2] 高彦平,伍中庆,苏培基,等.前交叉韧带胫骨棘止点撕脱骨折不同内固定方式的疗效分析及其临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2006,14(2):90-92.
[3] 刘世峰,崔文波,廖志峰,等.后内侧入路手术治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].中国伤残医学,2014,9(2):98-99.
[4] 唐金兵,湛梅圣,张彬.关节镜下治疗后交叉韧带断裂12例体会[J].内蒙古中医药,2014,33(4):34-35.
[5] 郭林,杨柳.膝关节前交叉韧带的发育与结构生理[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(18):188-189.
[6] Mao YT, Dong QR, Wang Y. Ganglion cysts of the cruciate ligaments: a series of 31 cases and review of the literature. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13(3):137.
[7] 曹建刚,张宇,田峥巍,等.关节镜下松解治疗全膝置换术后僵硬的疗效分析[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(1):70-71.
[8] 刘玉杰,敖英芳,陈世益,等.膝关节韧带损伤修复与重建[M].北京:人民出版社, 2008:127-128.
[9] 李智尧,张磊,刘劲松,等.关节镜下胫骨端RigidFix、股骨端IntraFix固定技术重建后交叉韧带[J].中国微创外科杂志, 2014, 20(1):7-11.
[10] 范钦波,范继峰.关节镜下先进人工韧带加强系统和四股自体半腱肌腱重建前交叉韧带的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(6):676-679.
[11] 黄令坚,尤瑞金,黄钿锋,等.关节镜下钢丝闩套可吸收钉内固定治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2007,9(30): 298-299.
[12] 许文杰,沈为栋,张铁洪,等. 早期关节镜下钢丝穿套治疗胫骨髁间嵴骨折20例体会[J].中国内镜杂志,2007,13(8):857-858.
[13] Wang L, Song KD, Wang H, et al. Desmoid tumor of posterior cruciate ligament of the knee: a case report. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14(3):69-72.
[14] 姜荣锋,闫继强,吴昊,等.胫骨嵌入技术治疗膝关节后交叉韧带损伤的疗效观察[J].中日友好医院学报,2014,28(2):113-115.
[15] 卢启贵,王平,黄东红,等.关节镜辅助钢丝固定治疗胫骨髁间棘撕脱骨折[J].中国实用医刊, 2008,35(14):11-12.
[16] 段鑫,杨勇,肖国庆,等.关节镜下修复重建膝关节脱位合并多发韧带损伤的疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(6): 673-675.
[17] Li L, Tian W. Displaced avulsion fractures of the posterior cruciate ligament: Treated by stellate steel plate fixation. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(2):171-175.
[18] Lan J, Wang JW, Zhang KY. [Treatment of tibial avulsion fracture at the insertion of the posterior cruciate ligament through a minimally posteromedial transverse incision in the hip knee flexion]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(1): 48-51.
[19] Li W, Ji WF, Ma ZC. [Observation of clinical effects of surgery for trailing edge fracture of tibial plateau medial condyle and posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(5):422-424.
[20] Gwinner C, Kopf S, Hoburg A, et al. Arthroscopic Treatment of Acute Tibial Avulsion Fracture of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament Using the TightRope Fixation Device. Arthrosc Tech. 2014;3(3):e377-382.
[21] Singla R, Devgan A, Gogna P, et al. Fixation of delayed union or non-union posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2014;22(1):70-74.
[22] Jia KJ, Guan JJ, Yang CL, et al. [Cannulated screw fixation through posteromedial approach screw for the treatment of tibial avulsion fracture of the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013; 26(9):727-729.
[23] Ouyang ZS, Li Q, Li J. [Absorbable screw fixation for the treatment of tibial avulsion fracture of the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament through posterior middle mini incision of knee joint]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(9): 720-723.
[24] Peltola EK, Lindahl J, Koskinen SK. The reverse Segond fracture: not associated with knee dislocation and rarely with posterior cruciate ligament tear. Emerg Radiol. 2014;21(3): 245-249.
[25] Feucht MJ, Salzmann GM, Pestka JM, et al. Simultaneous avulsion fracture of the posterior medial and posterior lateral meniscus root: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(4):509-514.
[26] Liu J, Deng B, Huang G, et al. [Arthroscopically assisted treatment of acute tibial insertion avulsion fracture of posterior cruciate ligament via posteromedial incision]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(5):591-593.
[27] Muhm M, Schneider P, Ruffing T, et al. [Posterocentral approach to the posterior tibial plateau. Reconstruction of tibial plateau fractures and avulsions of the posterior cruciate ligament].Unfallchirurg. 2014;117(9):813-821.
[28] White EA, Patel DB, Matcuk GR, et al. Cruciate ligament avulsion fractures: anatomy, biomechanics, injury patterns, and approach to management.Emerg Radiol. 2013;20(5): 429-440.
[29] Al-Ahaideb A. Posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture in children: a case report with long-term follow-up and comprehensive literature review. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 2:S257-260.
[30] Zhang X, Cai G, Xu J, et al. A minimally invasive postero-medial approach with suture anchors for isolated tibial avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament. Knee. 2013;20(2):96-99.
[31] Chen CW, Chen L, Pan ZE, et al. [Open reduction and internal fixation via a posterior approach for posterior fractures of tibial plateau].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7): 561-565.
[32] Chen SY, Cheng CY, Chang SS, et al.Arthroscopic suture fixation for avulsion fractures in the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament.Arthroscopy. 2012;28(10):1454- 1463.
[33] Chan AP, Liu KL, Ng BK. Occult posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture in a paediatric patient: easily missed diagnosis.Hong Kong Med J. 2012;18(1):73-75.
[34] Chen W, Tang D, Kang L, et al. Effects of microendoscopy-assisted reduction and screw fixation through a single mini-incision on posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fracture.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(4): 429-435.
[35] Wajsfisz A, Makridis KG, Van Den Steene JY, et al. Fixation of posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture with the use of a suspensory fixation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20(5):996-999.
[36] Ogawa H, Sumi H, Shimizu K.Posterior cruciate ligament mediated avulsion fracture of the lateral tibial condyle: a case report.J Orthop Surg Res. 2010;5:67. |