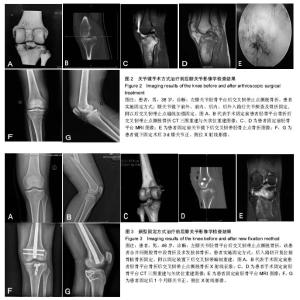
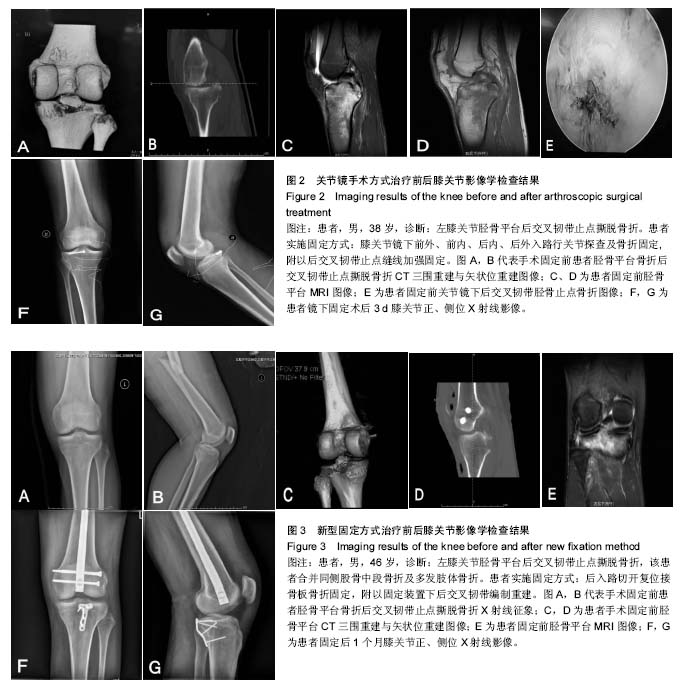
| [1] Ambra LF, Franciozi CE, Werneck LG, et al. Posteromedial versus direct posterior approach for posterior cruciate ligament reinsertion. Orthopedics. 2016;39(5):e1024-e1027. [2] Zehir S, Elmal? N, ?ahin E, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction via tibial inlay technique in multiligament knee injuries. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(6):579-585. [3] Chen LB, Wang H, Tie K, et al. Arthroscopic fixation of an avulsion fracture of the tibia involving the posterior cruciate ligament: a modified technique in a series of 22 cases. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97-B(9):1220-1225. [4] Muhm M, Winkler H. The posterocentral approach to the posterior tibial plateau. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2015;27(1):80-93. [5] Jia KJ, Guan JJ, Yang CL, et al. Cannulated screw fixation through posteromedial approach screw for the treatment of tibial avulsion fracture of the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(9):727-729. [6] Li Q, Song K, Sun Y, et al. Severe cartilage damage from a broken absorbable screw head after fixation of an avulsion fracture of the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(43):e5180.[7] Mamatkerimulla, Xu Gang, Wang X, et al. Clinical observation of one-stage arthroscopic reconstruction and strict immobilization for treatment of knee dislocation. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;30(4):412-415. [8] Espejo-Baena A, López-Arévalo R, Urbano V, et al. Arthroscopic repair of the posterior cruciate ligament: two techniques. Arthroscopy. 2000;16(6):656-660.[9] Choi NH, Kim SJ. Arthroscopic reduction and fixation of bony avulsion of the posterior cruciate ligament of the tibia. Arthroscopy. 1997;13(6):759-762.[10] Buckley SL, Sturm PF, Tosi LL, et al. Ligamentous instability of the knee in children sustaining fractures of the femur: a prospective study with knee examination under anesthesia. J Pediatr Orthop. 1996;16(2):206-209.[11] Barton TM, Torg JS, Das M. Posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. A review of the literature. Sports Med. 1984;1(6):419-430. [12] Wu Y, Li Y, Chen B. Effect of posterior cruciate ligament retaining or not on knee-joint proprioception. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27:851-854.[13] Bischoff MJ, van Raaij TM, Reininga IH, van Raay JJ. Patellar resurfacing in posterior cruciate ligament retaining total knee arthroplasty (PATRES): design of a randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:358. [14] Song EK, Park HW, Ahn YS, Seon JK. Transtibial versus tibial inlay techniques for posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: long-term follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(12):2964-2971. [15] Risberg MA, Holm I, Steen H, Beynnon BD. Sensitivity to changes over time for the IKDC form, the Lysholm score, and the Cincinnati knee score. A prospective study of 120 ACL reconstructed patients with a 2-year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1999;7(3):152-159.[16] Knop C, Oeser M, Bastian L, et al. Development and validation of the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) Spine Score. Unfallchirurg. 2011;104:488-497.[17] 左金增,史福东,刘仕杰,等.关节镜下前交叉韧带断裂合并ramp损伤手术的临床研究[J].中国临床研究,2015,28(9):1167-1169.[18] 胡联英,贾其余,曹溢,等.涉及前后交叉韧带胫骨止点骨折的治疗研究[J].重庆医学,2017,46(20):2802-2805.[19] Chen SY, Chen CY, chang SS, et al. Arthroscopic suture fixation fou avulsion fractures in the tibialattachment of the posterior cruciate ligament. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(10):1454-1463.[20] Frosch KH, Balcarek P, Walde T, et al. A new posterolateral approach without fibula osteotomy for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(8):515-520.[21] Nicandri GT,Klineberg EO,Wahl CJ,et al. Treatment of posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fractures through a modified open posterior approach: operative technique and 12-to48-month outcomes. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(5):317-324. |