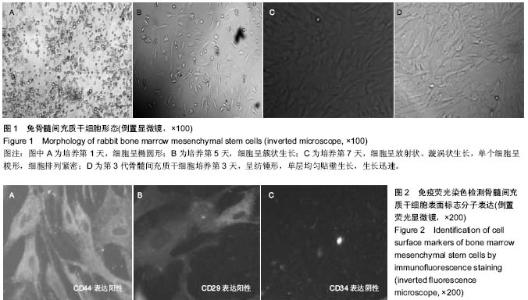
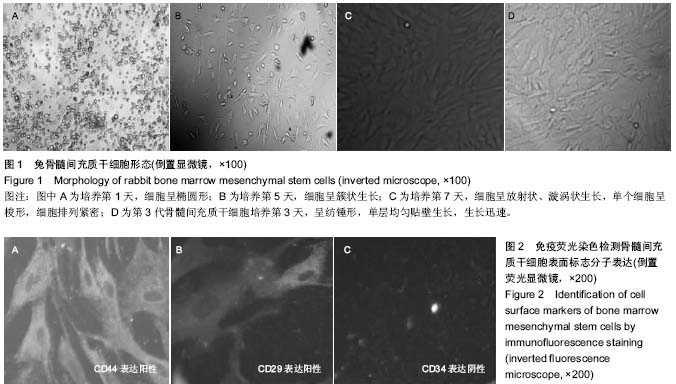
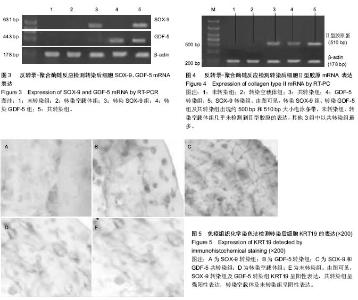
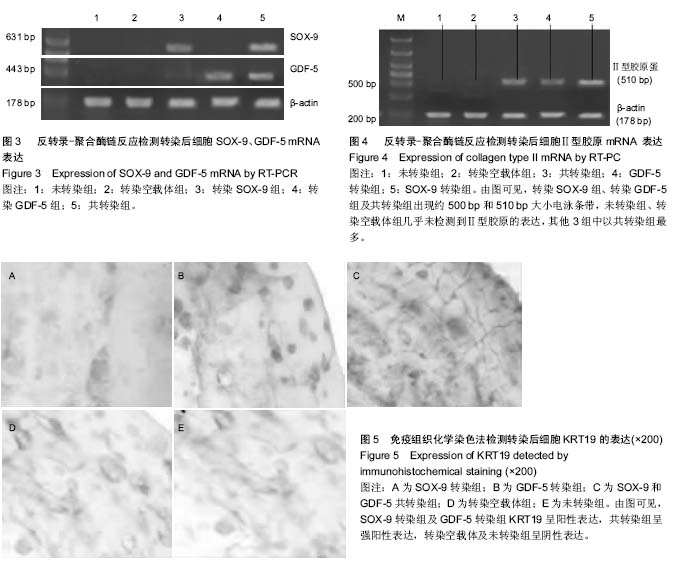
| [1] Ortiz LA, Dutreil M, Fattman C,et al.Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(26):11002-11007.
[2] Kunter U, Rong S, Djuric Z,et al.Transplanted mesenchymal stem cells accelerate glomerular healing in experimental glomerulonephritis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(8):2202-2212.
[3] Minguell JJ, Erices A. Mesenchymal stem cells and the treatment of cardiac disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006; 231(1):39-49.
[4] Lee RH, Seo MJ, Reger RL,et al. Multipotent stromal cells from human marrow home to and promote repair of pancreatic islets and renal glomeruli in diabetic NOD/scid mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(46):17438-17443.
[5] Phinney DG, Isakova I.Plasticity and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in the nervous system.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(10):1255-1265.
[6] Ryan JM, Barry F, Murphy JM,et al.Interferon-gamma does not break, but promotes the immunosuppressive capacity of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;149(2):353-363.
[7] Pang X, Yang H, Peng B. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of chronic discogenic low back pain.Pain Physician. 2014;17(4): E525-530.
[8] Yim RL, Lee JT, Bow CH,et al. A systematic review of the safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells for disc degeneration: insights and future directions for regenerative therapeutics.Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(21):2553-2567.
[9] Vadalà G, Studer RK, Sowa G, et al. Coculture of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and nucleus pulposus cells modulate gene expression profile without cell fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(8):870-876.
[10] Wuertz K, Godburn K, Iatridis JC. MSC response to pH levels found in degenerating intervertebral discs.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;379(4):824-829.
[11] Watanabe T, Sakai D, Yamamoto Y,et al. Human nucleus pulposus cells significantly enhanced biological properties in a coculture system with direct cell-to-cell contact with autologous mesenchymal stem cells.J Orthop Res. 2010; 28(5): 623-630.
[12] Yang SH, Wu CC, Shih TT,et al. In vitro study on interaction between human nucleus pulposus cells and mesenchymal stem cells through paracrine stimulation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(18):1951-1957.
[13] Mayer JE, Iatridis JC, Chan D,et al.Genetic polymorphisms associated with intervertebral disc degeneration.Spine J. 2013;13(3):299-317.
[14] Keorochana G, Johnson JS, Taghavi CE,et al.The effect of needle size inducing degeneration in the rat caudal disc: evaluation using radiograph, magnetic resonance imaging, histology, and immunohistochemistry. Spine J. 2010;10(11): 1014-1023.
[15] Martinez-Sanchez A, Murphy CL.miR-1247 functions by targeting cartilage transcription factor SOX9.J Biol Chem. 2013;288(43):30802-30814.
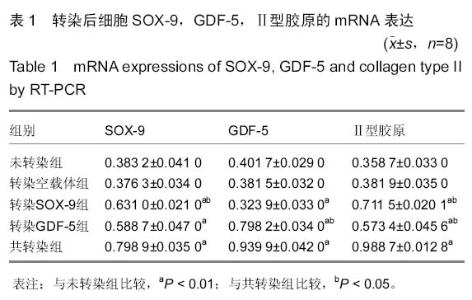
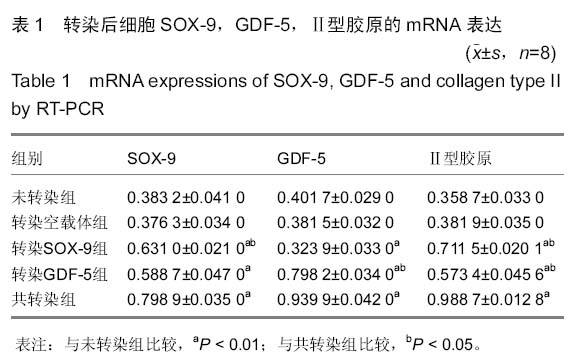
[16] 黄秀芳,原向伟.Sox9和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白在人腰椎间盘退变中的表达及意义[J].中国医药科学,2014,4(3):18-21.
[17] Gantenbein-Ritter B, Benneker LM, Alini M,et al.Differential response of human bone marrow stromal cells to either TGF-β(1) or rhGDF-5.Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6):962-971.
[18] Pelttari K, Winter A, Steck E,et al.Premature induction of hypertrophy during in vitro chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells correlates with calcification and vascular invasion after ectopic transplantation in SCID mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(10):3254-3266.
[19] Pelttari K, Steck E, Richter W.The use of mesenchymal stem cells for chondrogenesis. Injury. 2008;39 Suppl 1:S58-65.
[20] 魏强强.GDF-5联合地塞米松诱导大鼠BMSCs向类髓核样细胞分化的作用[D].南昌:南昌大学,2014:27-33.
[21] Zhang B, Yang S, Sun Z,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells induced by growth differentiation factor 5: an improved self-assembly tissue engineering method for cartilage repair.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(12):1189-1199.
[22] Weiler C, Nerlich AG, Schaaf R,et al.Immunohistochemical identification of notochordal markers in cells in the aging human lumbar intervertebral disc.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10): 1761-1770.
[23] Clouet J, Vinatier C, Merceron C,et al.The intervertebral disc: from pathophysiology to tissue engineering.Joint Bone Spine. 2009;76(6):614-618.
[24] Pelttari K, Winter A, Steck E,et al. Premature induction of hypertrophy during in vitro chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells correlates with calcification and vascular invasion after ectopic transplantation in SCID mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(10):3254-3266.
[25] 王广斌,陈洪亮,王大鹏,等.SOX-9和胰岛素样生长因子1共同转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(28):5465-5469.
[26] Gruber HE, Norton HJ, Ingram JA,et al. The SOX9 transcription factor in the human disc: decreased immunolocalization with age and disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(6):625-630.
[27] Castro-Malaspina H, Gay RE, Resnick G,et al. Characterization of human bone marrow fibroblast colony-forming cells (CFU-F) and their progeny.Blood. 1980; 56(2):289-301.
[28] Civin CI, Trischmann T, Kadan NS,et al. Highly purified CD34-positive cells reconstitute hematopoiesis.J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(8):2224-2233.
[29] Tsai MS, Lee JL, Chang YJ,et al. Isolation of human multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from second-trimester amniotic fluid using a novel two-stage culture protocol.Hum Reprod. 2004;19(6):1450-1456.
[30] Zvaifler NJ, Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Adams G,et al. Mesenchymal precursor cells in the blood of normal individuals. Arthritis Res. 2000;2(6):477-488.
[31] Yu G, Wu X, Dietrich MA, et al. Yield and characterization of subcutaneous human adipose-derived stem cells by flow cytometric and adipogenic mRNA analyzes.Cytotherapy. 2010;12(4):538-546.
|