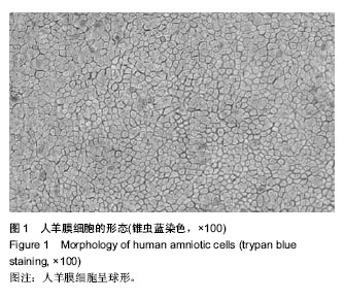
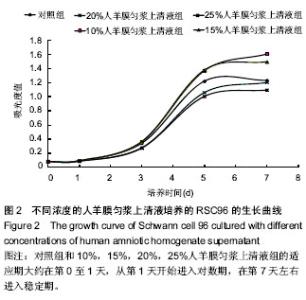
| [1] 汪琴.烧伤所致周围神经损伤[J].现代康复,2000,4(12):1785- 1787.
[2] 孙晓宇.雪旺细胞对于周围神经再生的功能与作用[J].内蒙古民族大学学报:自然科学版,2010,25(1):105-107.
[3] 郑灿镔,朱庆棠,刘小林,等.富血小板血浆对大鼠许旺细胞生物学行为的影响[J].中华显微外科杂志,2013,36(2):137-143.
[4] 蔡源源.血管内皮生长因子的调控及其作用研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2011,7(1):51-54.
[5] 杜婵,姜保国.许旺细胞增殖和分化过程中的信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(3):563-566.
[6] Krikorian D, Manthorpe M, Varon S. Purified mouse Schwann cells: mitogenic effects of fetal calf serum and fibroblast growth factor. Dev Neurosci. 1982;5(1):77-91.
[7] 高髻云,张伟.羊膜匀浆液对兔小梁切除术后滤过泡及TGFβ1、CTGF表达的影响[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2008,46(2): 163-166.
[8] 唐敏.人羊膜匀浆提取液对培养的兔角膜成纤维细胞增殖及TGF-β1mRNA表达的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2007.
[9] 郭礼和.人羊膜细胞临床前研究:治疗非神经系统的损伤性疾病研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2011,33(7):830-834.
[10] 杨雅岚,席兴华,唐罗生,等.人羊膜匀浆上清液对兔角膜上皮细胞中bFGF表达的影响[J].国际眼科杂志,2012,12(9):1639-1643.
[11] 李世洋,王一.羊膜对培养的人视网膜色素上皮细胞增殖影响的实验研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2003,25(5):407-409.
[12] 杨文贤,刘亮,朱富军,等.液氮快速冻存法保存人羊膜抗冻剂筛选研究[J].华南国防医学杂志,2013,27(4):229-233.
[13] 杨文贤,朱富军,詹球,等.锥虫蓝直接染色法鉴定人羊膜细胞活力方案研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2013,29(3):312-314.
[14] 朱富军,杨文贤,童亚林,等.新鲜人羊膜微粒与自体微粒皮混合移植对创面愈合的实验研究[J].华南国防医学杂志,2013,27(5): 294-298.
[15] Steed DL, Trumpower C, Duffy D, et al. Amnion-derived cellular cytokine solution: a physiological combination of cytokines for wound healing. Eplasty. 2008;8:e18.
[16] Payne WG, Wachtel TL, Smith CA, et al. Effect of amnion-derived cellular cytokine solution on healing of experimental partial-thickness burns. World J Surg. 2010; 34(7):1663-1668.
[17] 赵婧.羊膜移植治疗眼化学烧伤及热烧伤的临床观察[D].长春:吉林大学,2012.
[18] Silini A, Parolini O, Huppertz B, et al. Soluble factors of amnion-derived cells in treatment of inflammatory and fibrotic pathologies. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(1):6-14.
[19] 童亚林.一种复合抗冻液及其应用和使用该抗冻液保存人羊膜的方法:中国,CN201210250809.0[P].2012-11-07.
[20] Larry R. Squire. 神经科学百科全书⑧科爱传播•精编百科大系:神经胶质细胞[M].北京:科学出版社,2010.
[21] Koizumi NJ, Inatomi TJ, Sotozono CJ, et al. Growth factor mRNA and protein in preserved human amniotic membrane. Curr Eye Res. 2000;20(3):173-177.
[22] 窦肇华,张远强,郭顺根,等.免疫细胞学与疾病[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2004. |