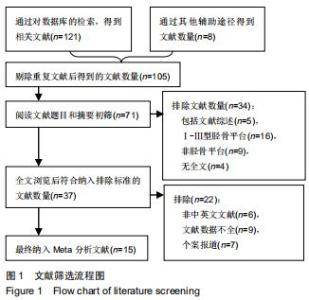
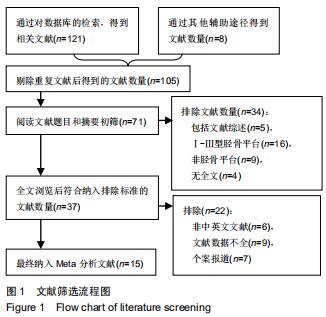
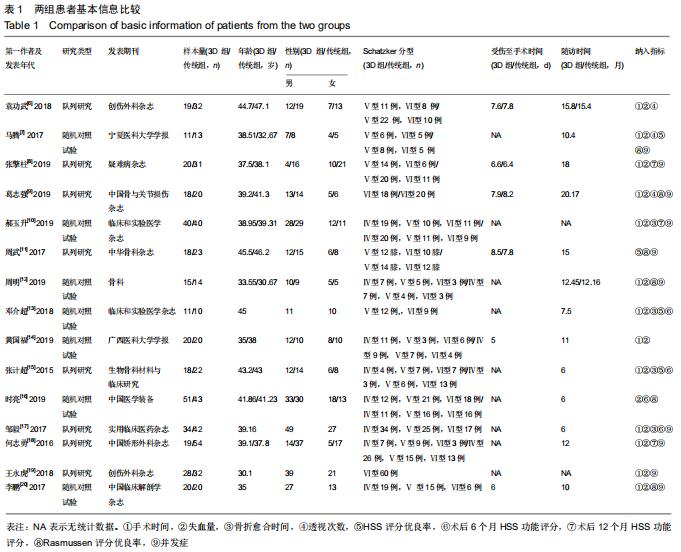
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (30): 4889-4897.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2835
Previous Articles Next Articles
A meta-analysis of efficacy and complications of 3D printing-assisted surgery for Schatzker IV-VI tibial plateau fractures
Weng Nengyuan1, Zhang Tao1, Li Kainan2, Lan Hai2, Zhang Jinli1, Fu Xuefei1, Liu Qixin1, Lin Qingyun3
- 1Department of Traumatic Knee (Part 1), Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300202, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University, Chengdu 610081, Sichuan Province, China; 3Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-26Revised:2020-01-04Accepted:2020-02-19Online:2020-10-28Published:2020-09-22 -
Contact:Zhang Tao, Master, Chief physician, Department of Traumatic Knee (Part 1), Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300202, China -
About author:Weng Nengyuan, Master candidate, Department of Traumatic Knee (Part 1), Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300202, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Plan, No. 2018YFB1307803; the Tianjin Science and Technology Plan Project, Nos. 18PTLCSY00080, and 18YFSDZC00010
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Weng Nengyuan, Zhang Tao, Li Kainan, Lan Hai, Zhang Jinli, Fu Xuefei, Liu Qixin, Lin Qingyun. A meta-analysis of efficacy and complications of 3D printing-assisted surgery for Schatzker IV-VI tibial plateau fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4889-4897.
share this article
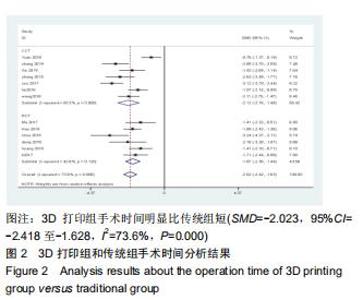
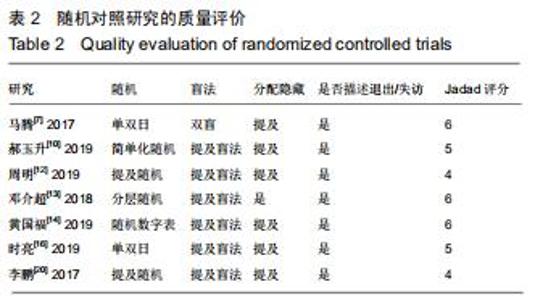
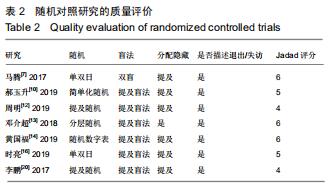
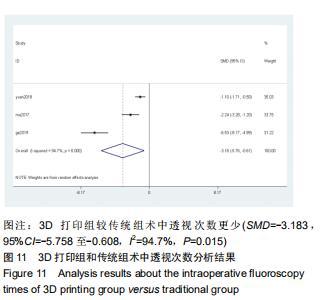
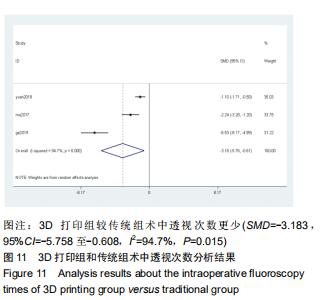
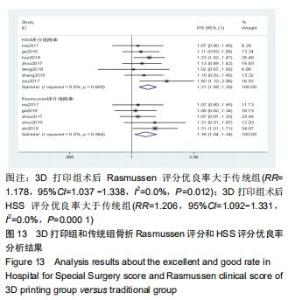
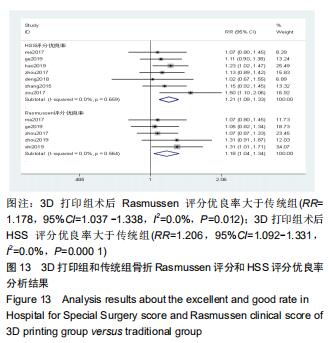
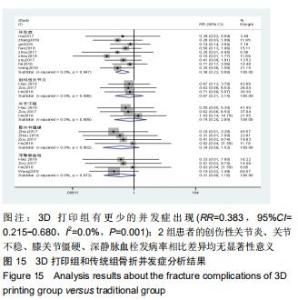
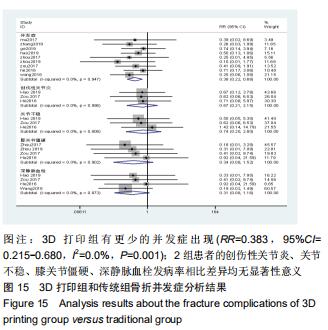
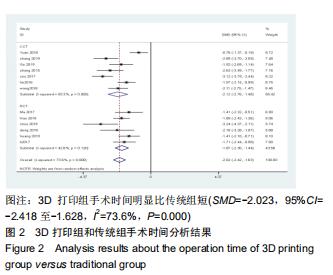
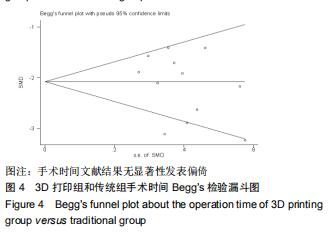
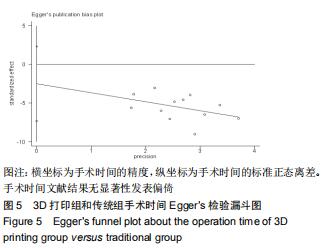
2.2.1 手术时间 共有13篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折手术的手术时间进行描述[6-10,12-15,17-20]。 各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-2.023,95%CI=-2.418至-1.628,I2=73.6%,P=0.000),6篇随机对照试验显示,3D打印组手术时间明显比传统组短(SMD=-1.869,95%CI=-2.300至-1.437,I2=42.8%,P=0.000),同时在病例对照研究里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-2.122,95%CI=-2.760至-1.484,I2= 83.3%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除袁功武等[6]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至67.9%和42.8%,总体异质性下降至61.9%。Begg’s检验漏斗图和Egger’s检验漏斗图均显示无明显发表偏倚,文章结论较稳健(P > 0.05)。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印组患者的手术时间短于传统组,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-2.080,95%CI=-2.291至-1.869,I2=61.9%,P=0.000),详见图2-5。 "

2.2.1 手术时间 共有13篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折手术的手术时间进行描述[6-10,12-15,17-20]。 各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-2.023,95%CI=-2.418至-1.628,I2=73.6%,P=0.000),6篇随机对照试验显示,3D打印组手术时间明显比传统组短(SMD=-1.869,95%CI=-2.300至-1.437,I2=42.8%,P=0.000),同时在病例对照研究里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-2.122,95%CI=-2.760至-1.484,I2= 83.3%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除袁功武等[6]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至67.9%和42.8%,总体异质性下降至61.9%。Begg’s检验漏斗图和Egger’s检验漏斗图均显示无明显发表偏倚,文章结论较稳健(P > 0.05)。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印组患者的手术时间短于传统组,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-2.080,95%CI=-2.291至-1.869,I2=61.9%,P=0.000),详见图2-5。 "

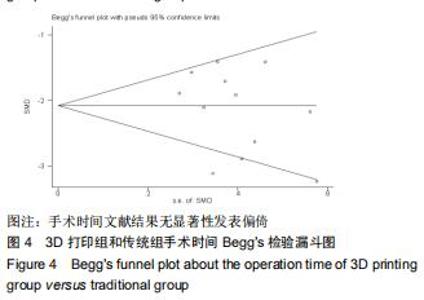
2.2.1 手术时间 共有13篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折手术的手术时间进行描述[6-10,12-15,17-20]。 各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-2.023,95%CI=-2.418至-1.628,I2=73.6%,P=0.000),6篇随机对照试验显示,3D打印组手术时间明显比传统组短(SMD=-1.869,95%CI=-2.300至-1.437,I2=42.8%,P=0.000),同时在病例对照研究里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-2.122,95%CI=-2.760至-1.484,I2= 83.3%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除袁功武等[6]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至67.9%和42.8%,总体异质性下降至61.9%。Begg’s检验漏斗图和Egger’s检验漏斗图均显示无明显发表偏倚,文章结论较稳健(P > 0.05)。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印组患者的手术时间短于传统组,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-2.080,95%CI=-2.291至-1.869,I2=61.9%,P=0.000),详见图2-5。 "
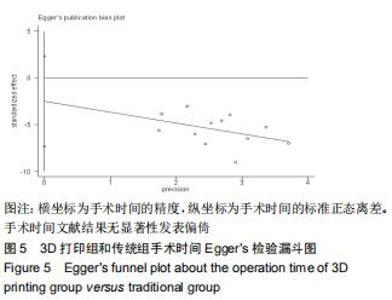
2.2.1 手术时间 共有13篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折手术的手术时间进行描述[6-10,12-15,17-20]。 各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-2.023,95%CI=-2.418至-1.628,I2=73.6%,P=0.000),6篇随机对照试验显示,3D打印组手术时间明显比传统组短(SMD=-1.869,95%CI=-2.300至-1.437,I2=42.8%,P=0.000),同时在病例对照研究里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-2.122,95%CI=-2.760至-1.484,I2= 83.3%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除袁功武等[6]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至67.9%和42.8%,总体异质性下降至61.9%。Begg’s检验漏斗图和Egger’s检验漏斗图均显示无明显发表偏倚,文章结论较稳健(P > 0.05)。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印组患者的手术时间短于传统组,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-2.080,95%CI=-2.291至-1.869,I2=61.9%,P=0.000),详见图2-5。 "
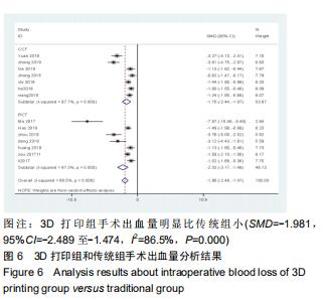
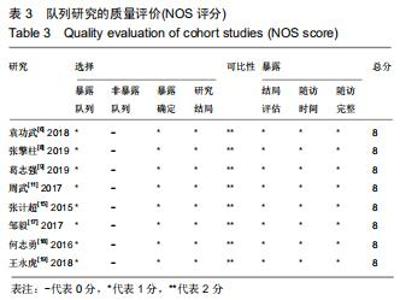
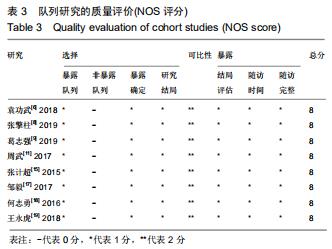
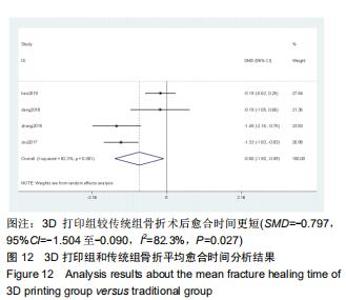
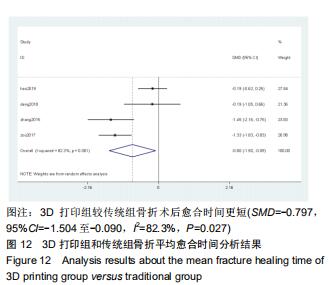
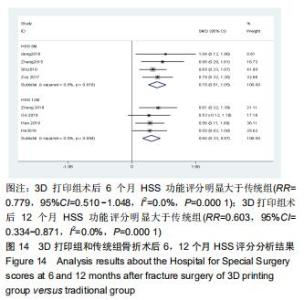
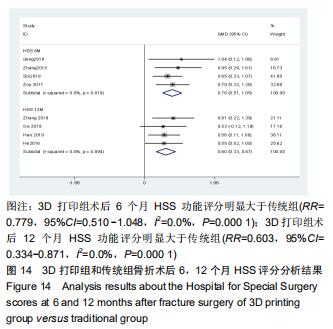
2.2.2 手术出血量 共有14篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的手术出血量进行描述[6-10,12-20]。各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-1.981,95%CI=-2.489至-1.474,I2=86.5%,P=0.000),7篇随机对照试验显示3D打印组手术出血量明显比传统组小(SMD=-2.326,95%CI=-3.166至-1.486,I2=87.3%,P=0.000),同时在临床对照试验里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-1.753,95%CI=-2.436至-1.069,I2= 87.7%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除张擎柱等[8]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至79.0%和87.3%,总体异质性下降至83.6%。进行Begg’s检验显示无发表偏倚存在(P=0.127),而Egger’s检验则显示存在发表偏倚(P=0.002),再进行剪补法后显示无文章增补结论,剪补法前后文献变量估值均为0.576,文章结论较稳健。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印手术组患者的手术出血量较传统组患者减少,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-1.804,95%CI=-2.276至-1.333,I2=83.6%,P=0.0001) ,详见图6-10。 "
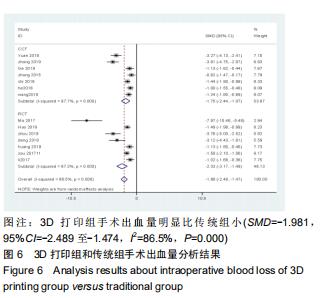
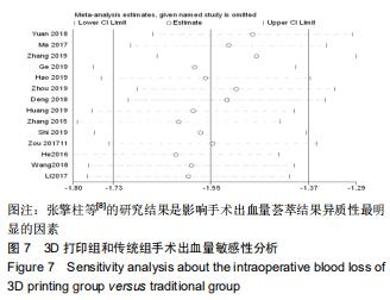
2.2.2 手术出血量 共有14篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的手术出血量进行描述[6-10,12-20]。各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-1.981,95%CI=-2.489至-1.474,I2=86.5%,P=0.000),7篇随机对照试验显示3D打印组手术出血量明显比传统组小(SMD=-2.326,95%CI=-3.166至-1.486,I2=87.3%,P=0.000),同时在临床对照试验里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-1.753,95%CI=-2.436至-1.069,I2= 87.7%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除张擎柱等[8]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至79.0%和87.3%,总体异质性下降至83.6%。进行Begg’s检验显示无发表偏倚存在(P=0.127),而Egger’s检验则显示存在发表偏倚(P=0.002),再进行剪补法后显示无文章增补结论,剪补法前后文献变量估值均为0.576,文章结论较稳健。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印手术组患者的手术出血量较传统组患者减少,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-1.804,95%CI=-2.276至-1.333,I2=83.6%,P=0.0001) ,详见图6-10。"
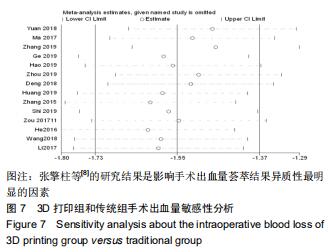
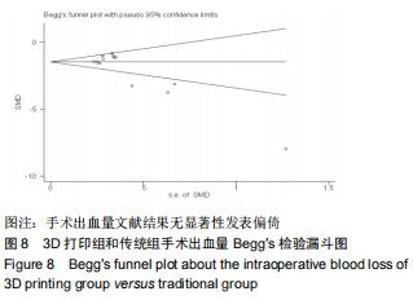
2.2.2 手术出血量 共有14篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的手术出血量进行描述[6-10,12-20]。各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-1.981,95%CI=-2.489至-1.474,I2=86.5%,P=0.000),7篇随机对照试验显示3D打印组手术出血量明显比传统组小(SMD=-2.326,95%CI=-3.166至-1.486,I2=87.3%,P=0.000),同时在临床对照试验里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-1.753,95%CI=-2.436至-1.069,I2= 87.7%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除张擎柱等[8]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至79.0%和87.3%,总体异质性下降至83.6%。进行Begg’s检验显示无发表偏倚存在(P=0.127),而Egger’s检验则显示存在发表偏倚(P=0.002),再进行剪补法后显示无文章增补结论,剪补法前后文献变量估值均为0.576,文章结论较稳健。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印手术组患者的手术出血量较传统组患者减少,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-1.804,95%CI=-2.276至-1.333,I2=83.6%,P=0.0001) ,详见图6-10。"
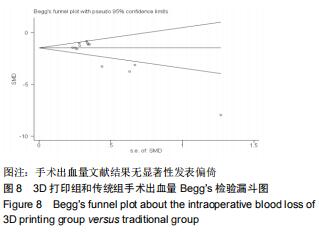
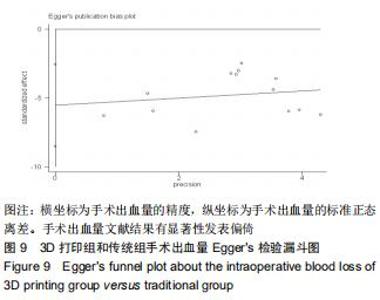
2.2.2 手术出血量 共有14篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的手术出血量进行描述[6-10,12-20]。各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-1.981,95%CI=-2.489至-1.474,I2=86.5%,P=0.000),7篇随机对照试验显示3D打印组手术出血量明显比传统组小(SMD=-2.326,95%CI=-3.166至-1.486,I2=87.3%,P=0.000),同时在临床对照试验里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-1.753,95%CI=-2.436至-1.069,I2= 87.7%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除张擎柱等[8]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至79.0%和87.3%,总体异质性下降至83.6%。进行Begg’s检验显示无发表偏倚存在(P=0.127),而Egger’s检验则显示存在发表偏倚(P=0.002),再进行剪补法后显示无文章增补结论,剪补法前后文献变量估值均为0.576,文章结论较稳健。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印手术组患者的手术出血量较传统组患者减少,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-1.804,95%CI=-2.276至-1.333,I2=83.6%,P=0.0001) ,详见图6-10。"
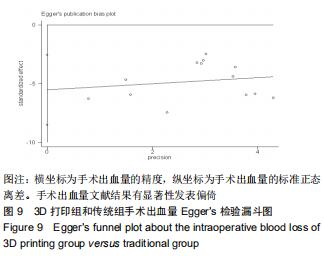
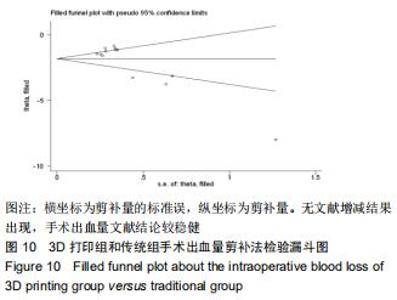
2.2.2 手术出血量 共有14篇文献对传统组和3D打印组行SchatzkerⅣ-Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的手术出血量进行描述[6-10,12-20]。各研究结果间具有明显统计学异质性(SMD=-1.981,95%CI=-2.489至-1.474,I2=86.5%,P=0.000),7篇随机对照试验显示3D打印组手术出血量明显比传统组小(SMD=-2.326,95%CI=-3.166至-1.486,I2=87.3%,P=0.000),同时在临床对照试验里发现更高的异质性(SMD=-1.753,95%CI=-2.436至-1.069,I2= 87.7%,P=0.000);敏感性分析发现去除张擎柱等[8]的文章以后,队列研究和随机对照试验亚组异质性分别降至79.0%和87.3%,总体异质性下降至83.6%。进行Begg’s检验显示无发表偏倚存在(P=0.127),而Egger’s检验则显示存在发表偏倚(P=0.002),再进行剪补法后显示无文章增补结论,剪补法前后文献变量估值均为0.576,文章结论较稳健。在除外临床异质性因素后采用随机效应模型进行统计学分析,结果显示3D打印手术组患者的手术出血量较传统组患者减少,其差异有显著性意义(SMD=-1.804,95%CI=-2.276至-1.333,I2=83.6%,P=0.0001) ,详见图6-10。"
|
[1] 张英泽.胫骨平台骨折微创治疗策略与进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017, 19(10):829-32.
[2] TRIKHA V, GABA S, AGRAWAL P, et al. CT based management of high energy tibial plateau fractures: A retrospective review of 53 cases. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(1):201-208.
[3] KOKKALIS ZT, ILIOPOULOS ID, PANTAZIS C, et al. What's new in the management of complex tibial plateau fractures? Injury. 2016;47(6): 1162-1169.
[4] WANG H, NEWMAN S, WANG J, et al. Corrective Osteotomies for Complex Intra-Articular Tibial Plateau Malunions using Three-Dimensional Virtual Planning and Novel Patient-Specific Guides. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(7):642-648.
[5] BIZZOTTO N, TAMI I, SANTUCCI A, et al. 3D Printed replica of articular fractures for surgical planning and patient consent: a two years multi-centric experience. 3D Print Med. 2015;2(1):2.
[6] 袁功武,聂宇,刘曦明,等. 3D打印技术辅助治疗与传统手术方法治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的对比研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2018,20(5):324-328.
[7] 马腾,魏代好,秦悦,等.常规影像学结合3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折治疗中的应用[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2017,39(12):1452-1454,1506.
[8] 张擎柱,万乾,张义,等. 3D打印技术辅助后内侧倒"L"形切口三间隙显露联合前外侧入路治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2019, 18(2):170-174.
[9] 葛志强,杨振环,崔书伟,等. 3D打印技术辅助下内固定治疗SchatzkerⅥ型胫骨平台骨折疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(8):855-857.
[10] 郝玉升,刘巍,王臣,等. 3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折临床诊治中的应用[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2019,18(1):108-111.
[11] 周武,曹发奇,刘国辉,等. 3D打印技术辅助手术对复杂胫骨平台骨折治疗的价值[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(17):1100-1105.
[12] 周明,丁文斌,刘全,等. 3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折手术中的应用研究[J].骨科,2019,10(1):31-36.
[13] 邓介超,丛云海,朱治国,等. 3D打印在治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折制定术前计划中的应用价值[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2018,17(21):2336-2339.
[14] 黄国福,苏福锦,何忠,等. 3D打印技术结合数字化设计辅助手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折20例临床分析[J].广西医科大学学报, 2019,36(10): 1660-1664.
[15] 张计超,宁宇,王向前,等. 3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2015,12(6):26-28.
[16] 时亮,段亮,董向辉,等.3D打印联合数字化设计在复杂胫骨平台骨折内固定治疗中的应用[J].中国医学装备,2019,16(10):10-13.
[17] 邹毅,叶茂,何玲莉,等. 3D打印用于胫骨平台骨折辅助治疗的临床效果分析[J].实用临床医药杂志, 2017,21(11):138-140.
[18] 何志勇,张擎柱,林影影,等.传统手术与应用3D打印技术后手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(8):682-686.
[19] 王永虎,史福东,谢伟. 3D打印技术在SchatzkerⅥ型胫骨平台骨折钢板内固定中的作用研究[J].创伤外科杂志, 2018,20(12):926-929.
[20] 李鹏,彭文标,李鉴轶,等.数字化设计结合3D打印技术辅助手术治疗复杂型胫骨平台骨折[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2017,35(2):151-155.
[21] JADAD AR, MOORE RA, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12.
[22] KRAUSE M, MULLER G, FROSCH KH. Extended medial and extended lateral approach for tibial plateau fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2019;31(2):127-142.
[23] TARNG YW, LIN KC. A combined prone and supine approaches for complex three column tibial plateau fracture with posterolateral articular injury. Injury. 2019;50(10):1756-1763.
[24] RAZA A, KUMAR S, KUMAR D, et al. Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures: Primary Fixation Using the Ilizarov External Fixator. A Two-year Study at Civil Hospital Karachi, Pakistan. Cureus. 2019; 11(8):e5375.
[25] CHANG H, ZHENG Z, YU Y, et al. The use of bidirectional rapid reductor in minimally invasive treatment of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: preliminary radiographic and clinical results. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):419.
[26] MITEV K, ZAFIROSKI G, MLADENOVSKI S, et al. Arthroscopic Reduction and Percutaneous Osteosynthesis of Tibial Plateau Fractures. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019;7(5):779-781.
[27] WU WY, XU WG, WAN CY, et al. Preoperative Plan with 3D Printing in Internal and External Fixation for Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(4):560-568.
[28] KIM HJ, PARK J, PARK KH, et al. Evaluation of Accuracy of a Three-Dimensional Printed Model in Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(9):841-846.
[29] YANG L, SHANG X. W, FAN J. N, et al. Application of 3D Printing in the Surgical Planning of Trimalleolar Fracture and Doctor-Patient Communication. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2482086.
[30] WEIDERT S, ANDRESS S, SUERO E, et al. 3D printing in orthopedic and trauma surgery education and training : Possibilities and fields of application. Unfallchirurg. 2019;122(6):444-451.
[31] SHI J, LV W, WANG Y, et al. Three dimensional patient-specific printed cutting guides for closing-wedge distal femoral osteotomy. Int Orthop. 2019;43(3):619-624.
[32] LOU Y, CAI L, WANG C, et al. Comparison of traditional surgery and surgery assisted by three dimensional printing technology in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Int Orthop. 2017;41(9):1875-1880.
[33] FOO GL, KWEK EB. Are Three-Dimensional Printed Models Useful for Preoperative Planning of Tibial Plafond Fractures?. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(4):723-729.
[34] GIANNETTI S, BIZZOTTO N, STANCATI A, et al. Minimally invasive fixation in tibial plateau fractures using an pre-operative and intra-operative real size 3D printing. Injury. 2017;48(3):784-788.
[35] SCHRODER E. SOUZA BG, LEITE TA, SILVA TABD, et al. Comparative Study of Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Fracture of the Tibial Plateau Operated with Locked or Conventional Plates. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2019;54(1):37-44.
[36] SONG Z, WANG Q, MA T, et al. Failure analysis of primary surgery and therapeutic strategy of revision surgery for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):110.
[37] NIE W, GU F, WANG Z, et al. Preliminary application of three-dimension printing technology in surgical management of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2019;50(2):476-483.
[38] KALMET PHS, VAN HORN YY, SANDULEANU S, et al. Patient-reported quality of life and pain after permissive weight bearing in surgically treated trauma patients with tibial plateau fractures: a retrospective cohort study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(4): 483-488.
[39] EVANGELOPOULOS D, CHALIKIAS S, MICHALOS M, et al. Medium-Term Results after Surgical Treatment of High-Energy Tibial Plateau Fractures. J Knee Surg. 2019.
[40] KUGELMAN D, QATU A, HAGLIN J, et al. Complications and unplanned outcomes following operative treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2017;48(10):2221-2229.
[41] RUFFOLO MR, GETTYS FK, MONTIJO HE, et al. Complications of high-energy bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with dual plating through 2 incisions. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(2):85-90.
[42] GONZALEZ LJ, LOTT A, KONDA S, et al. The Hyperextension Tibial Plateau Fracture Pattern: A Predictor of Poor Outcome. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(11):e369-e74.
[43] GIORDANO V, DO AMARAL NP, KOCH HA, et al. Outcome evaluation of staged treatment for bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2017; 48 Suppl 4:S34-S40.
[44] LU M, WANG J, TANG F, et al. A three-dimensional printed porous implant combined with bone grafting following curettage of a subchondral giant cell tumour of the proximal tibia: a case report. BMC Surg. 2019;19(1):29.
[45] HUANG H, HSIEH MF, ZHANG G, et al. Improved accuracy of 3D-printed navigational template during complicated tibial plateau fracture surgery. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2015;38(1):109-117.
[46] HORAS K, HOFFMANN R, FAULENBACH M, et al. Advances in the pre-operative planning of revision trauma surgery using 3D printing technology. J Orthop Trauma. 2019.
[47] SARAGAGLIA D, RUBENS-DUVAL B, PAILHE R. Intra- and extra-articular proximal tibia malunion. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019.
[48] YANG P, DU D, ZHOU Z, et al. 3D printing-assisted osteotomy treatment for the malunion of lateral tibial plateau fracture. Injury. 2016; 47(12):2816-2821. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [8] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [9] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [10] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [11] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [12] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [13] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [14] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||